Part 3: Neurons and Synapses
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Ramon y Cajal
who established the Neuron Doctrine
Neuron Doctrine
what states that the brain is made of many small cells
100
there are almost _______ billion neurons in the human brain
membrane, nucleus, and specialized organelles
neurons, like other cells, have these three parts
dendrites, soma, axon, and axon terminals
the four important regions of neurons
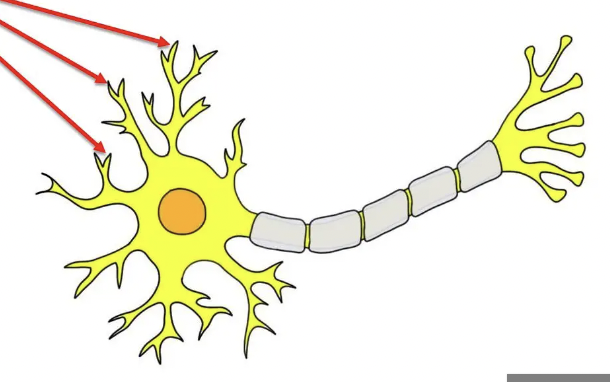
dendrites
branching projections that collect information in neuron
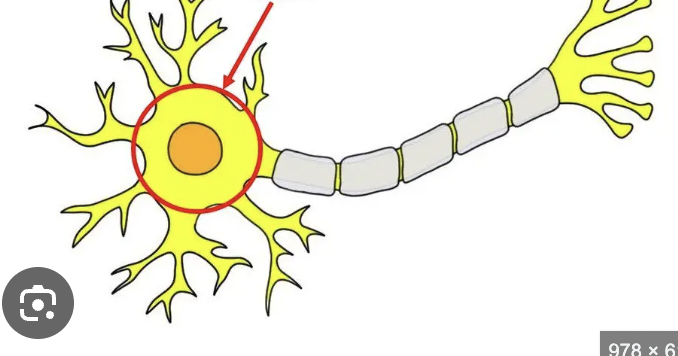
soma (cell body)
contains the nucleus and integrates information
axon
conducts the neural signal in neuron. transmit electrical impulses to other neurons, muscles, and glands
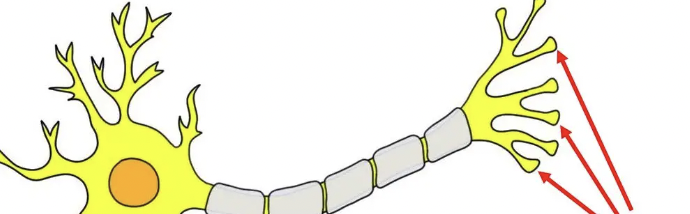
axon terminals
small swellings that release signals to other neurons (outputs info)
synapses
neurotransmitters (chemical signals) cross small gaps, known as ________
neurotransmitters
___________ are released by the presynaptic cell to affect the postsynaptic cell
500
there are about _______ trillion synapses in the adult brain
sensory neurons
these neurons carry information to the brain
function
different types of neurons can be classified by their ___________
motor neurons
these neurons carry information from the brain to the muscles
interneurons
these neurons convey signals around the nervous system
glial cells
these cells speed up neuronal signaling, regulate extracellular chemicals, and enable neurons to modify connections
oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
these two things wrap myelin around axons to speed up signals
astrocytes
these regulate extracellular chemicals and local blood flow
microglia
what provides immune system functions for the CNS
receptors
specialized proteins in the cell membrane
postsynaptic
neurotransmitters interact with receptors to affect the ____________ cell
ionotropic receptors
these receptors allow ions to flow across the membrane, changing the charge of the cell membrane
metabotropic receptors
these receptors relay information into the cell using a series of proteins
receptors
neurotransmitters only bind to _________ briefly and then are removed
degradation
when the neurotransmitter is broken apart
diffusion
when the neurotransmitter moves down the concentration gradient and out of the synapse
reuptake
when the neurotransmitter is transported back into the original cell
voltage difference
at rest, there is a _______ _______ between the inside and the outside of the cell
negative; -70
the inside of the cell is normally more _______ than the outside (about ______ mV)
excitatory postsynaptic potentials
________ _________ _________ move the membrane voltage closer to 0
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
_________ __________ ________ move the voltage further from 0. they are small and fast
action potentials
_______ _______ are all or none
soma; membrane voltage
the ________ receives 100s or 1000s of PSPs at the time - EPSPs and IPSPs combine to affect the ______ _______
depolarize
EPSPs sum together to _____________ the cell
depolarization
when the voltage moves closer to 0
action potential
if the membrane voltage reaches threshold (approx -60 mV), an ________ _______ is generated
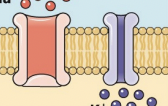
Na+; K+
How an action potential travels part 1: at rest, there are more ______ ions outside of the cell and more _______ ions inside the cell
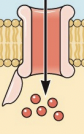
Na+; chemical; electrical
How an action potential travels part 2: threshold, voltage-gated ______ channels open, allowing the ions to flow in, down the ________ concentration and _________ gradients
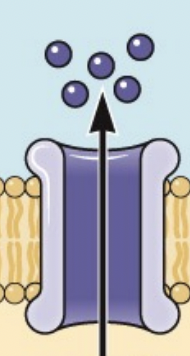
K+; repolarize
How an action potential travels part 3: voltage-gated ______ channels open, and the ions flow out to _______ the cell
Na+; depolarize
How an action potential travels part 4: current formed by the _______ ions flow down the neuron to ___________ the next part
refractory period
How an action potential travels part 5: a _______ _______ follows the action potential, when voltage gated Na+ ion channels are less likely to open
calcium; chloride
How an action potential travels part 6: ________ and ________ ions also contribute to the action potential
myelination
this makes action potentials travel faster
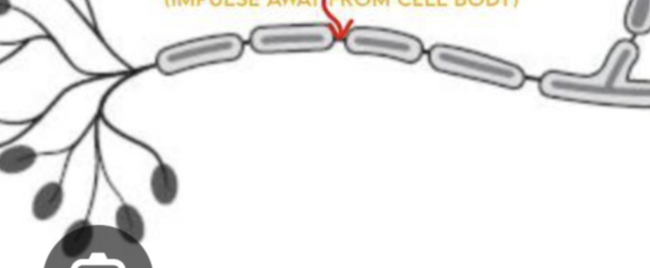
nodes of Ranvier
myelin is interrupted by _______ ___ _______, where the action potential is regenerated
transmission
action potentials jump from node to node which speed up ________
decreases
myelination ________ the amount of energy used by the neuron
communication
when myelin is damaged, ____________ in brain is critically compromised
voltage-gated
action potentials cause _____ ______ calcium channels to open in the axon terminals
calcium ions
_______ ______ cause vesicles with neurotransmitters to bind to the presynaptic neuron
synapse
when neurotransmitters are released, they cross the _______