Year 10 Physics - Obey the Law
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
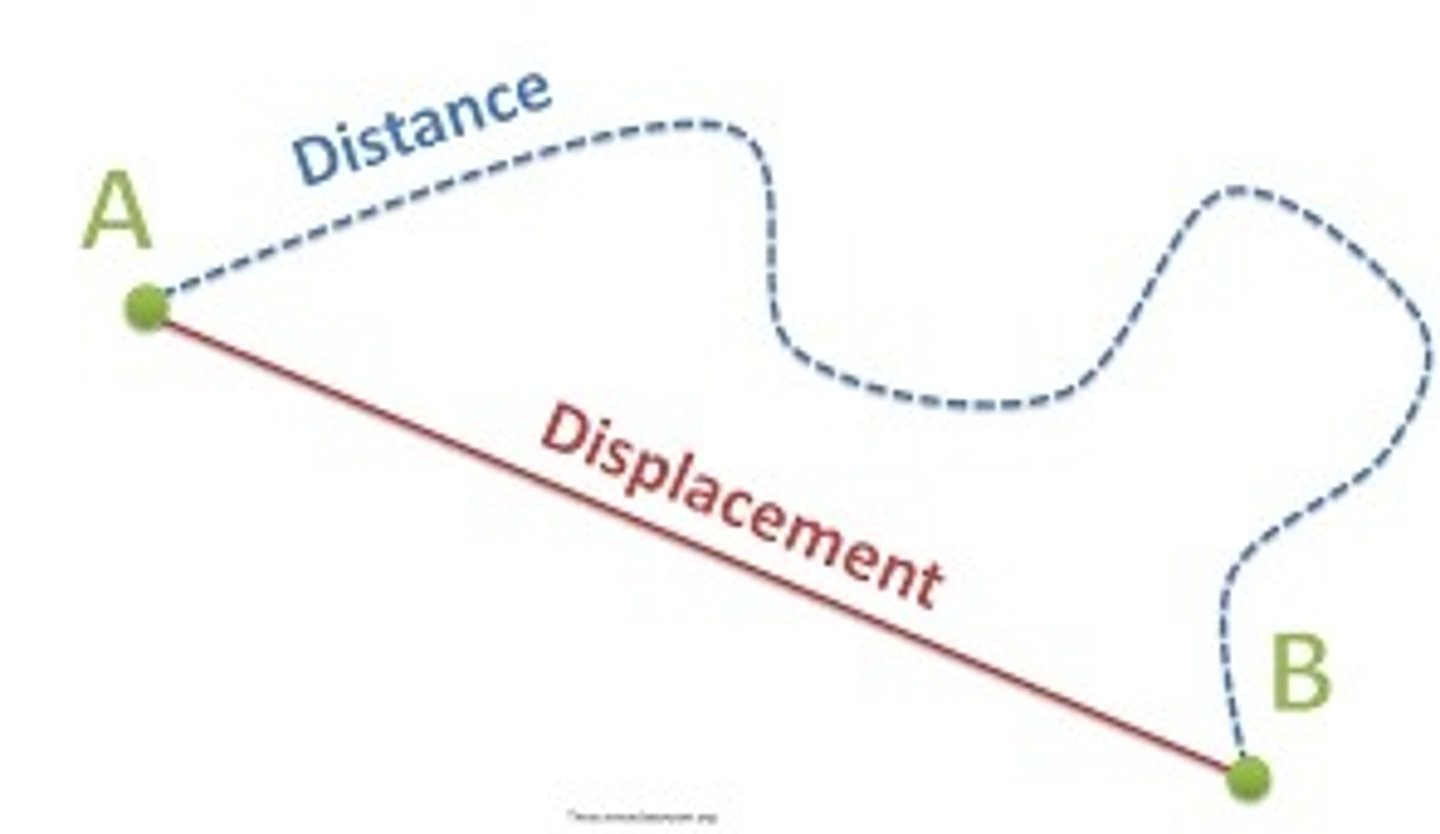
Distance
- Scalar quantity
- The length of a path travelled between two points (A to B).
- Units: metres
Displacement
- Vector
- Change in position (A to B)
- Distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point.
- Units: metres and compass direction
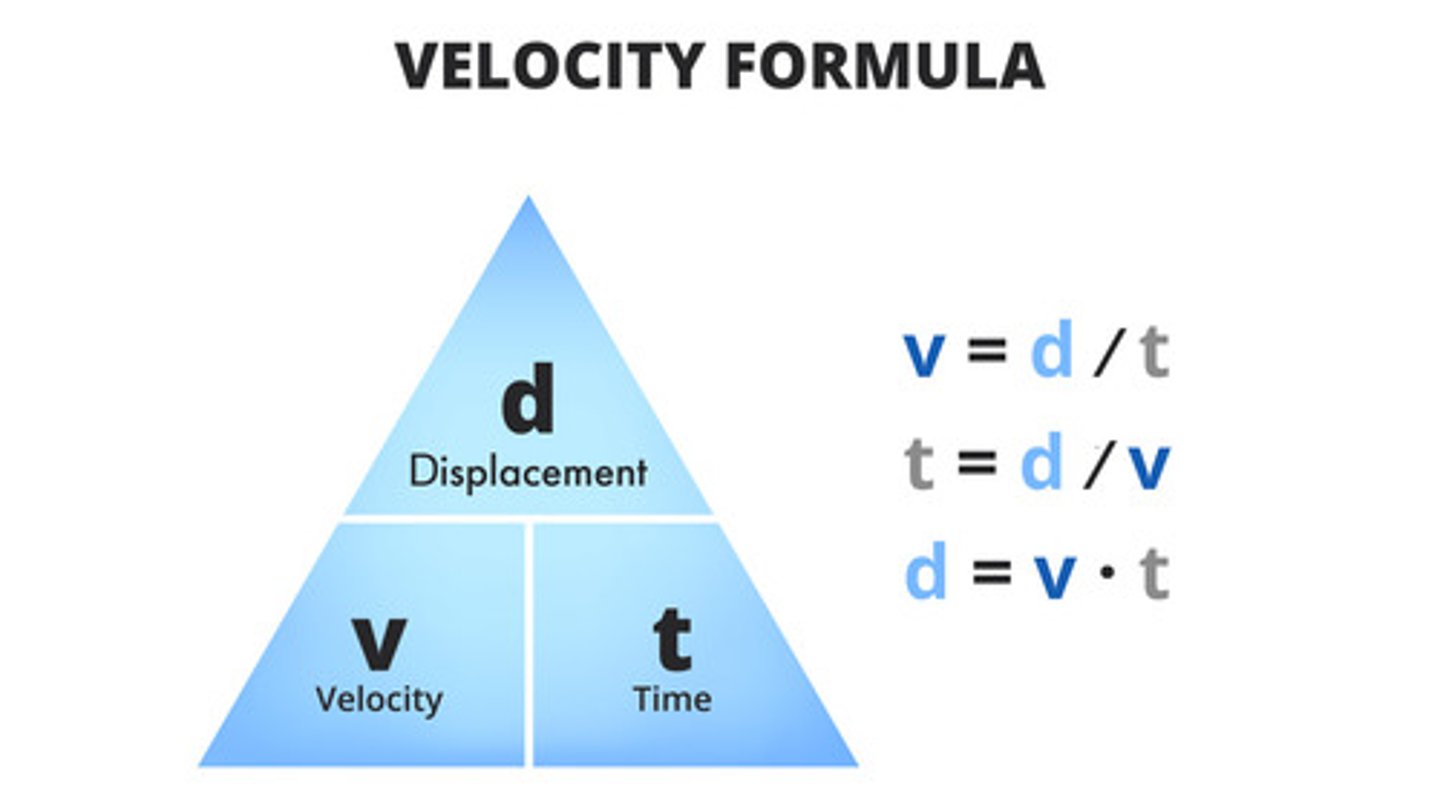
speed
- Scalar quantity
- How fast something moves.
- Distance travelled over time
- Units: metres per second (m/s), or km/h.
Velocity
- Vector
- speed and direction
- Units: metres per second (m/s).
For example: 10 m/s South.
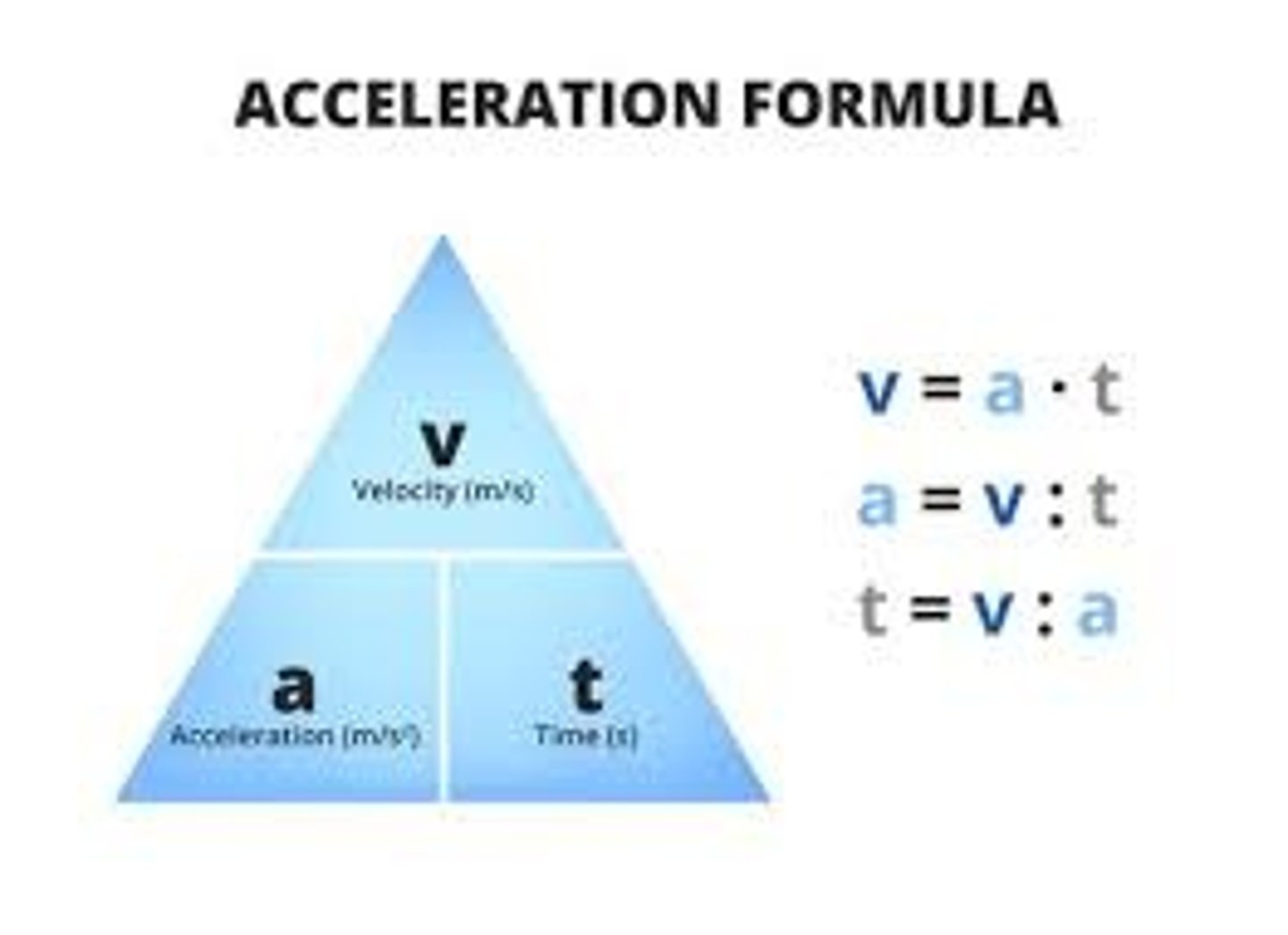
Acceleration
- Vector
- Change in velocity over time.
- Units: metres per second squared and direction (m.s^-2).
Vector
- magnitude and a direction.
- Displacement
- Velocity
- Acceleration
- Force.
Scalar quantity
- magnitude only (how big something is)
- Distance
- Speed
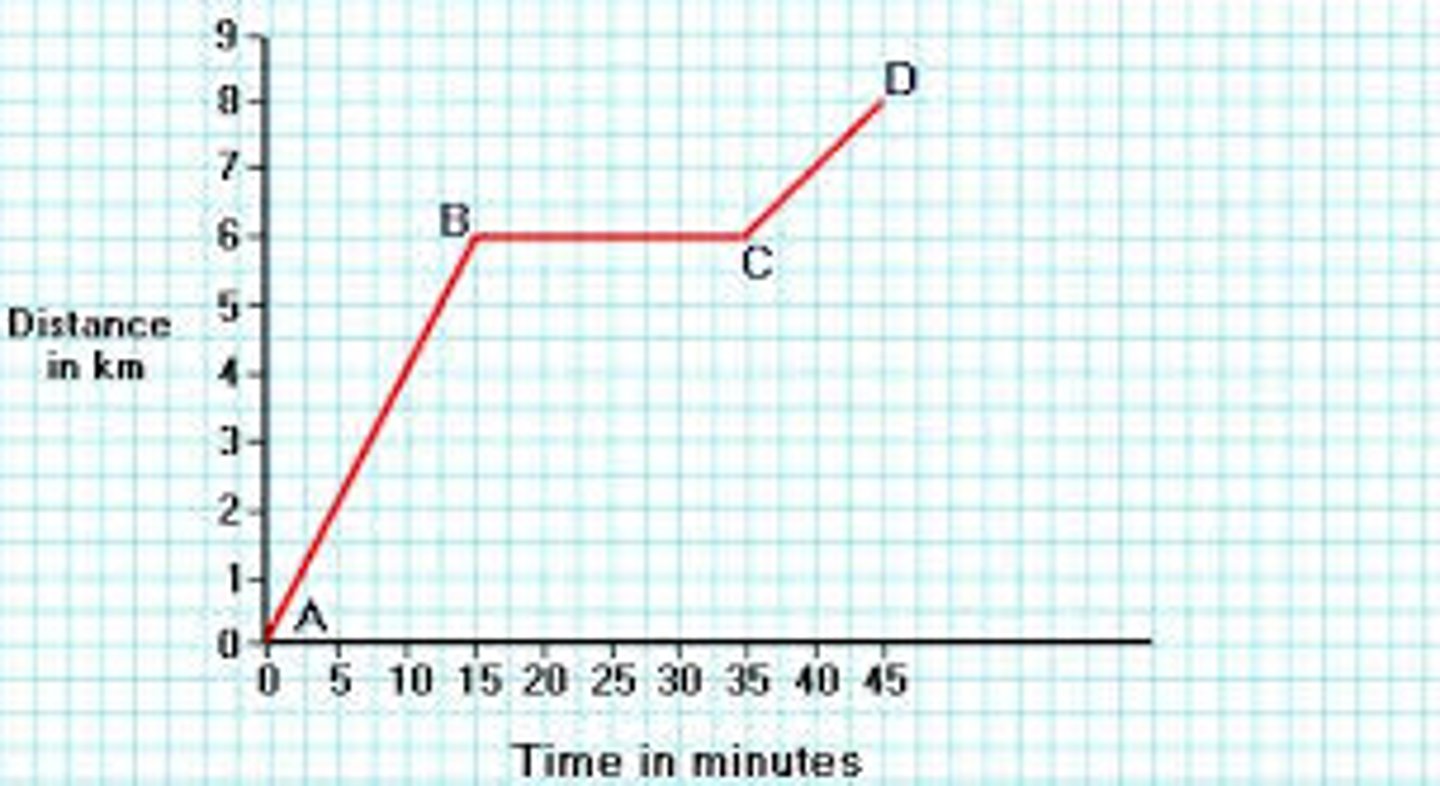
Motion graph
- A way of showing the movement of an object during a period of time
X-axis: Time
Y-axis: Distance
Trend: Speed
- the greater the slope the greater the speed
- no slope = stationary
Force
- A push or pull exerted on an object.
- Measured in Newtons (N).

Newton's three laws of motion
1. The Law of inertia
2. F=ma
3. Action ~ Reaction pairs
First Law of Motion
Law of Inertia
- the velocity of an object does not change unless the object is acted upon by an external force

Second Law of Motion
Force = mass x acceleration (F=Ma)
- An object acted on by an unbalanced force will accelerate in the direction of the force with an acceleration equal to the force divided by the object's mass (a=F/m)

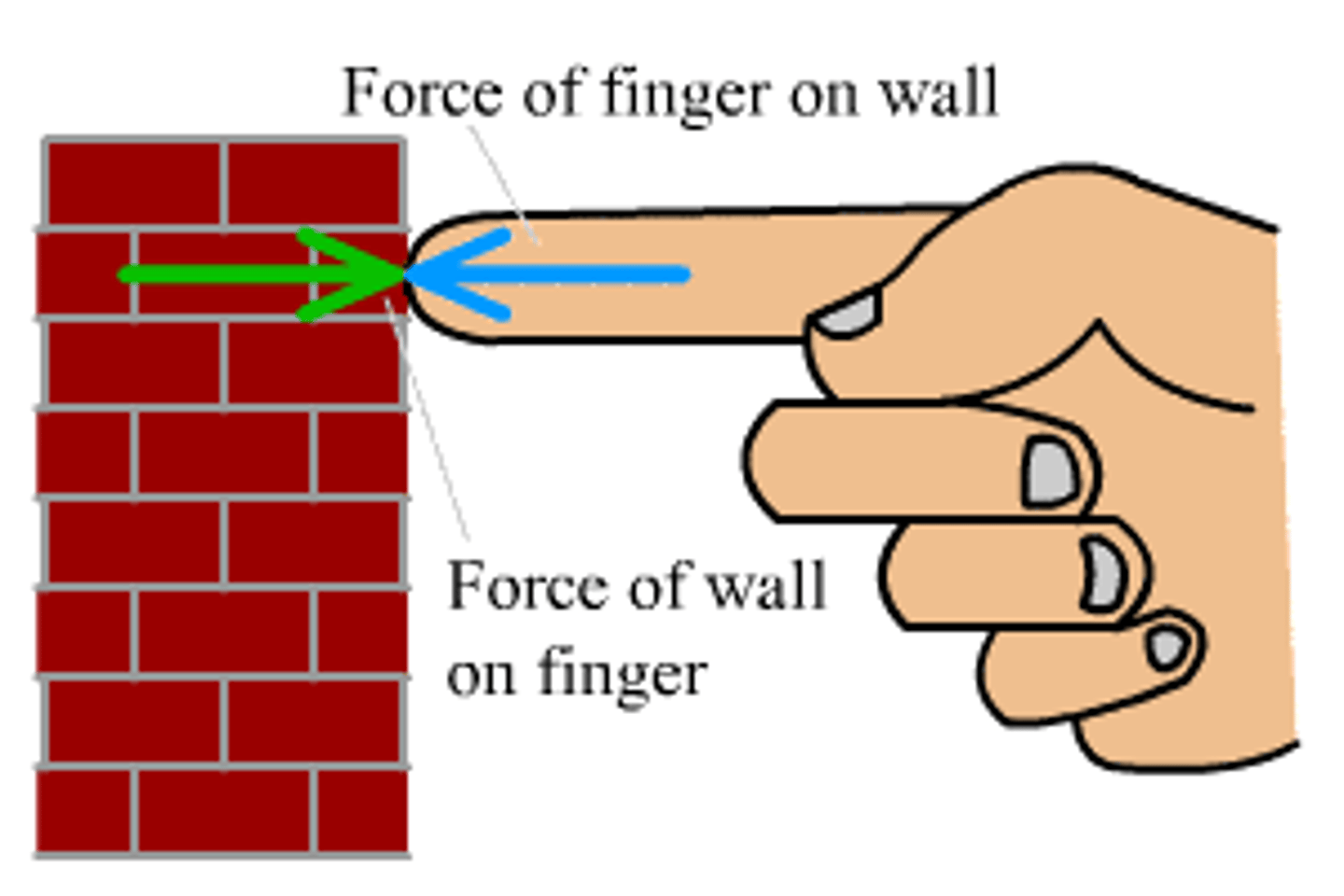
Third Law of Motion
Action ~ Reaction pair
- For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Air resistance
A force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air
Acceleration due to gravity
9.8 m.s^-2
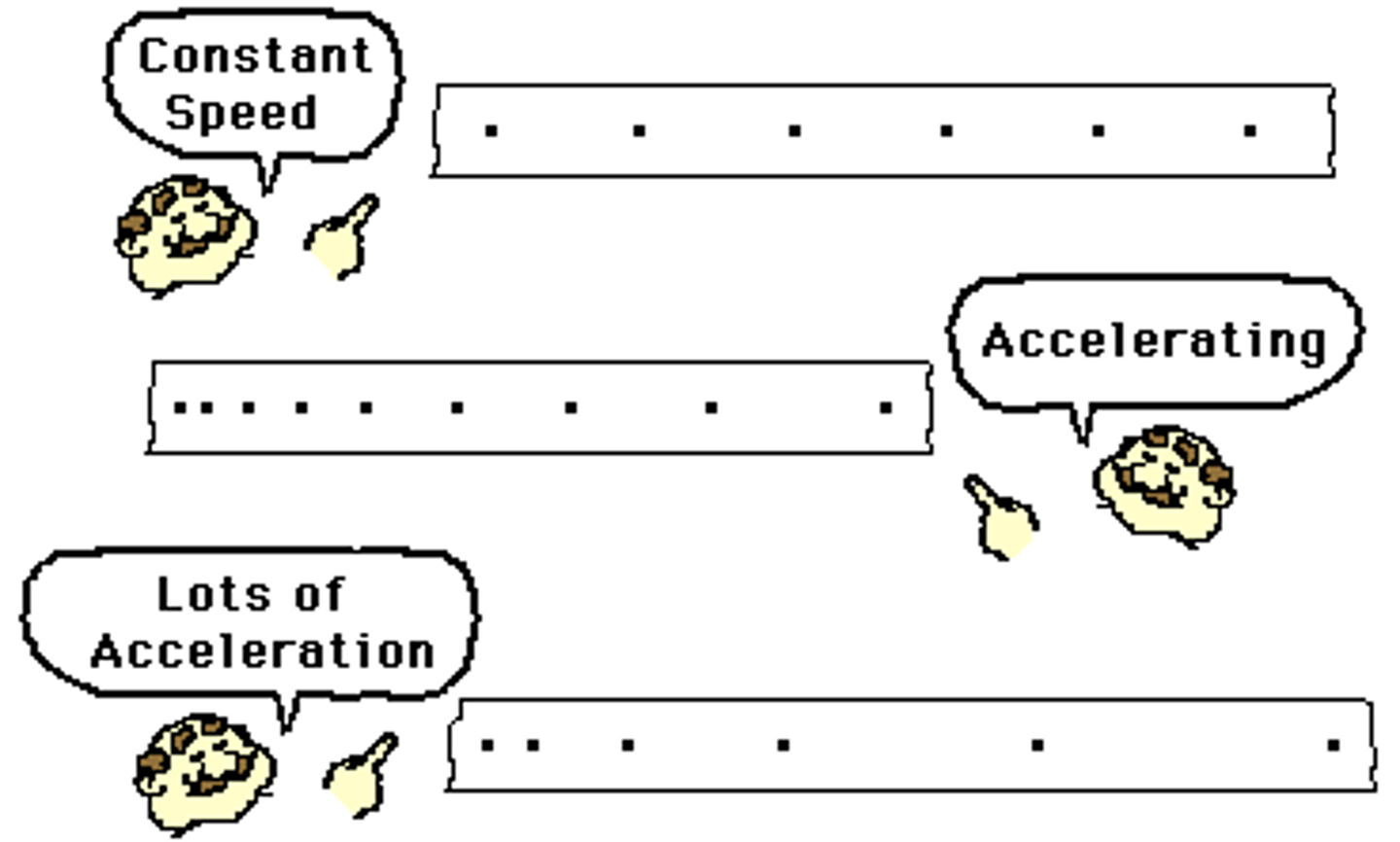
ticker timer
A device used to show movement, that makes dots on paper at a rate of 50 dots per second (50Hz)
Mass
How much matter there is.
An object’s mass is the same regardless of where in the universe you take it to.
Units: kilograms (kg).

Describe an everyday example of Newton's 1st Law (Inertia).
Students standing on a bus: If the bus suddenly accelerates forward, the student tends to fall backward due to their body's inertia. This is because the student, initially at rest, wants to remain at rest as the bus moves forward. Conversely, when the bus suddenly brakes, the student leans forward, as their body's inertia causes them to resist the bus's deceleration, wanting to maintain their forward motion.

Describe an everyday example of Newton's 2nd Law (F=ma)
An everyday example of Newton's second law of motion, F=ma, involving a student carrying a bag, can be seen when the student accelerates or decelerates while carrying a bag.
If the bag is heavy, requiring more force to accelerate, the student must exert greater force to achieve the same acceleration. Conversely, when the student stops walking, they must exert a force in the opposite direction to decelerate the bag.

Describe an everyday example of Newton's 3rd Law (Action~Reaction)
An everyday example of Newton's third law of motion is demonstrated when a student pushes bench weights.
When the student pushes against the weights, they exert a force on the weights. According to Newton's third law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, the weights exert an equal and opposite force back on the student.
This means that as the student pushes the weights upward, the weights push downward with an equal force. This downward force from the weights is what provides resistance to the student's upward motion, making the exercise challenging.

Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion

Convert 1 kilometer to metres
1 x 1000
= 1000 m
Convert 1 hour to seconds
1 x 3600
= 3600 s
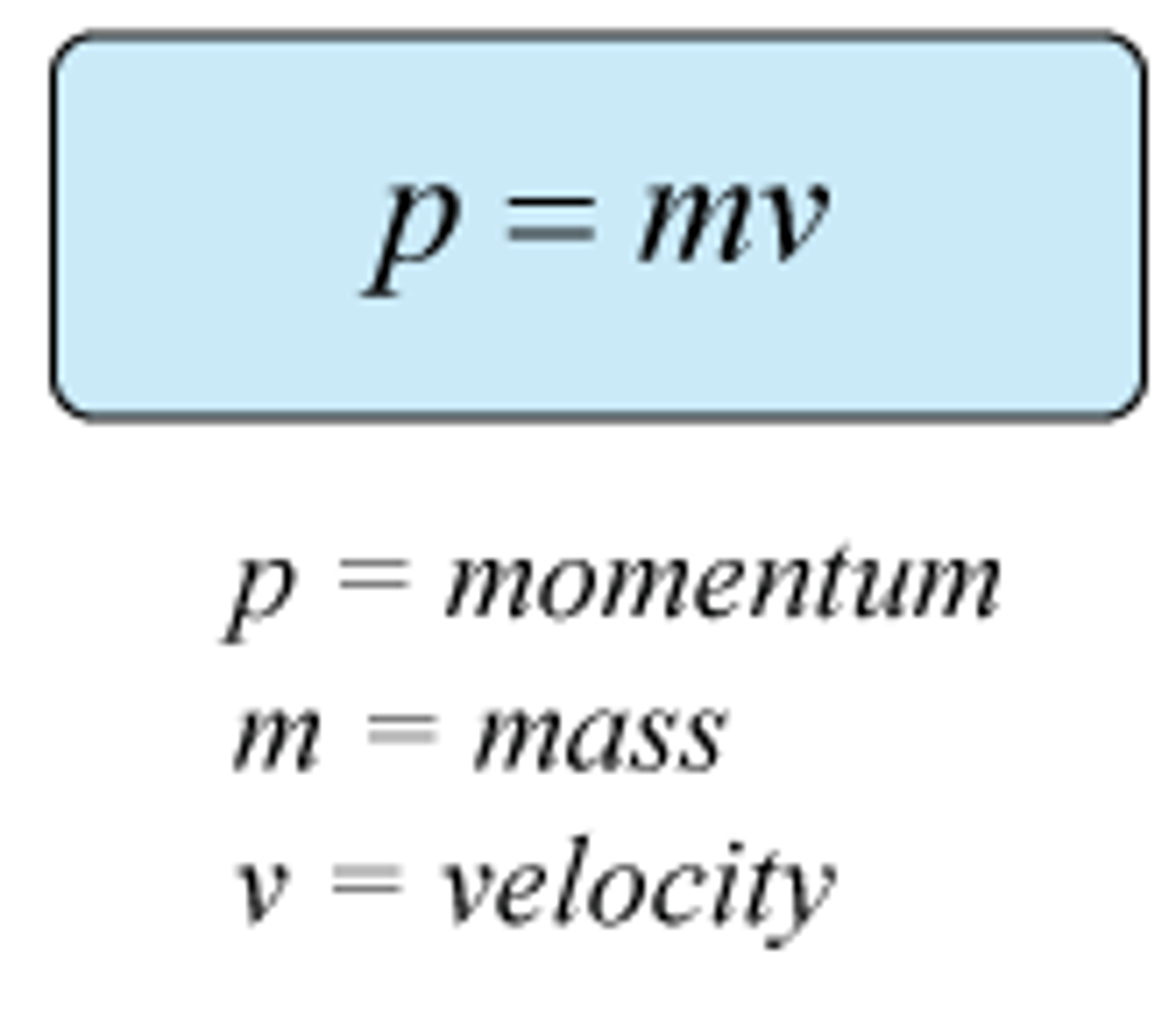
Momentum
mass x velocity
Friction
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact

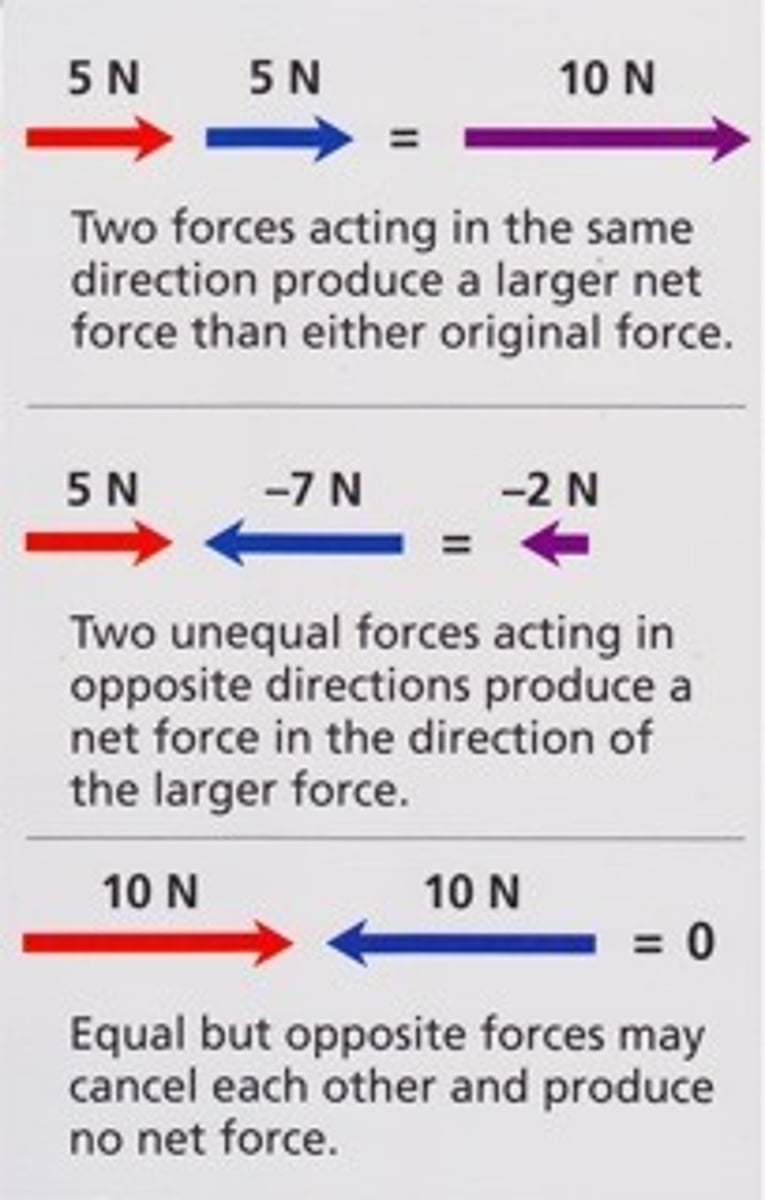
Net force
The combination of all forces acting on an object.
What force would be needed to give a 3 kg mass an acceleration of 4 m.s^-2 to the east?
12 N East
Calculate the acceleration of a 2 kg toy car if a force of 10 N South was applied to it.
5 m.s^-2 South
What mass would be given an acceleration of magnitude 2 m.s^-2, when a 12 N force was applied to it?
6 kg
What force would be needed to give a 9.0 kg mass an acceleration of 2 m.s^-2 west?
18 N
What is the acceleration of a vehicle that changes velocity from 20 m/s to 30 m/s in 10 seconds?
1 m.s^-2
What is the deceleration of a vehicle that changes velocity from 12 m/s to 8 m/s south in 2 seconds?
- 2 m.s^-2
A car is travelling at a velocity of 30 m/s west and decelerates at rate of -10 m.s^-2. How long does it take for the vehicle to come to a complete stop?
3 seconds
A car is travelling at a velocity of 25 m/s east and starts to accelerate at a rate of 5 m.s^-2. What is their velocity after 10 seconds?
75 m/s east
Two groups of students have a tug of war at the school carnival. Group 1 pull with a force of 250N east. Group 2 pull with a force of 300N west. What was the net force?
50 N west
A student walks to school along a path 1200 m in length. If they leave home at 8:00am and arrive at 8:20am, what was their speed?
Distance = 1200m
Time = 20 min
= 1200 s
Speed = distance / time
= 1200 / 1200
= 1 m/s
A car travels from home to the shops along a path 2 km in length. If travel at 50 km/hr, how long with the journey take?
Distance = 2 km
Speed = 50 km/hr
Time = distance / speed
= 2 / 50
= 0.04 hours
A student walks along a straight path of 1500m west. It takes the student 10 minutes. What was the students velocity?
Displacement = 1500m west
Time = 10 min
= 600 s
Velocity = displacement / time
= 1500 / 600
= 2.5 m/s west
Distinguish distance and displacement.
Distance is a scalar quantity the describes the length of a path travelled. Displacement is a vector that describes the length and direction between two points.
Explain Newton's first law of Inertia
Motion requires an unbalanced force to act upon an object. An an object will therefore remain at rest or remain in motion, unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force.
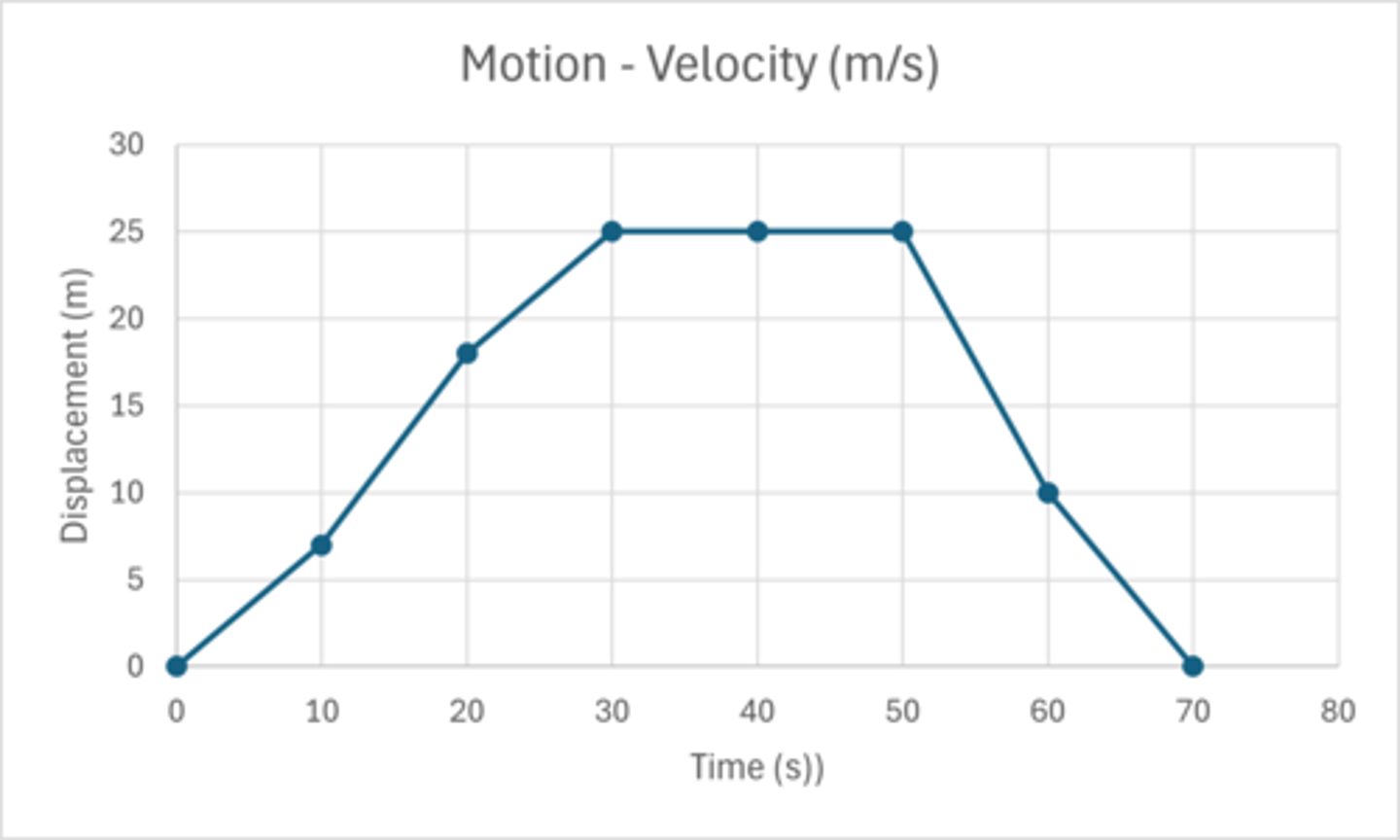
A student is a the library, studying for their science test. They get up from their desk, retrieve a book off a shelf, east of the desk, and then return to their desk. Create a motion graph and determine the velocity of their return to the desk.
Time (s) Displacement (m)
0 0
10 7
20 18
30 25
40 25
50 25
60 10
70 0
Displacement = 25 m west
Time = 20 s
Velocity = Displacement / Time
= 25 /20
= 1.25 m/s west
How do you find the speed of an object in motion?
Distance (m) divided by time (s).
Units: m/s
How do you find the acceleration of an object in motion?
Change in velocity divided by time.
Units: m/s/s
Tripping on a crack in the footpath whilst running is an example of which of Newton's three laws?
No. 1 - The Law of Inertia
Needing extra force to run with a heavy backpack is an example of which motion law?
No 2. - Force = mass x acceleration
A rocket launching is an example of which motion law?
No 3 - Action~Reaction pair
What is the scientific unit for distance?
metre (m)
What is the scientific unit for time?
second (s)
What is the scientific unit for force?
Newton (N)
Heavier trucks require more breaking force to slow down. This is an example of Newton's ____ law.
No. 2 - F=ma
An egg breaking when it drops and hits the ground is an example of Newton's ___ law.
No. 3 - Action ~ Reaction pair
A soccer ball sits motionless in the middle of a field. This is an example if Newton's ____ and ____ laws
No. 1 - Law of Inertia (An object will remain stationary unless acted upon by an unbalanced force)
No 3. - Action ~ Reaction pair (downward gravitation force is paired with an equal but opposite force from the ground)