Chapter 10 - Cell Division and Mitosis
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Slide 2 - 10.1 The Cycle of Cell Growth and Division: An Overview
Single-celled prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms ______ and ________ as long as environmental conditions allow
grow
divide
Slide 2 - 10.1 The Cycle of Cell Growth and Division: An Overview
In multicellular eukaryotes, cell division is under strict control to __________
develop and maintain different subpopulations of cells
Slide 2 - 10.1 The Cycle of Cell Growth and Division: An Overview
Three parts of cell’s life cycle are
Cell growth and activity, including replication of DNA
Nuclear division (mitosis)
Division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
Slide 3 - Two Types of Nuclear Division
_______ (Mitosis/Meiosis) is a growth process
Mitosis
Slide 3 - Two Types of Nuclear Division
Meiosis is a process of __________
sexual reproduction
Slide 3 - Two Types of Nuclear Division
A process divides the replicated DNA equally and precisely, generating daughter cells, which are exact genetic copies of the parent cell is ___________
Mitosis (a growth process)
Slide 3 - Two Types of Nuclear Division
produces daughter nuclei with half the number of chromosomes of the parental nucleus
Meiosis (a process of sexual reproduction)
Slide 3 - Two Types of Nuclear Division
In Meiosis, the arrangements of genes on chromosomes are different from those in the _______
parent cell
Slide 4 - The Products of Mitosis
Mitosis partitions replicated DNA ___________ and _____________
equally
precisely
Slide 4 - The Products of Mitosis
___________ is a master program of molecular checks and balances
Mitosis
Slide 4 - The Products of Mitosis
DNA synthesis replicates each DNA chromosome into _____ copies with ____________
two
almost perfect fidelity
Slide 4 - The Products of Mitosis
_________ separates replicated DNA molecules precisely into the daughter cells
Mitotic cytoskeleton
Slide 4 - The Products of Mitosis
What are chromosomes?
The nuclear units of genetic information divided and distributed by mitotic cell division
Slide 5 - Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, the hereditary information within the nucleus is distributed among ________
individual, linear DNA molecules
Slide 5 - Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, the hereditary information within the nucleus is ______
distributed among individual, linear DNA molecules
Slide 5 - Chromosomes
DNA molecules combine with ________ that stabilize the DNA molecules, assist in ___________ during cell division, and influence the expression of __________
proteins
packaging DNA
individual genes
Slide 5 - Chromosomes
In a cell, each chromosome is composed of __________ and ___________
In a cell, each chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule and its associated proteins
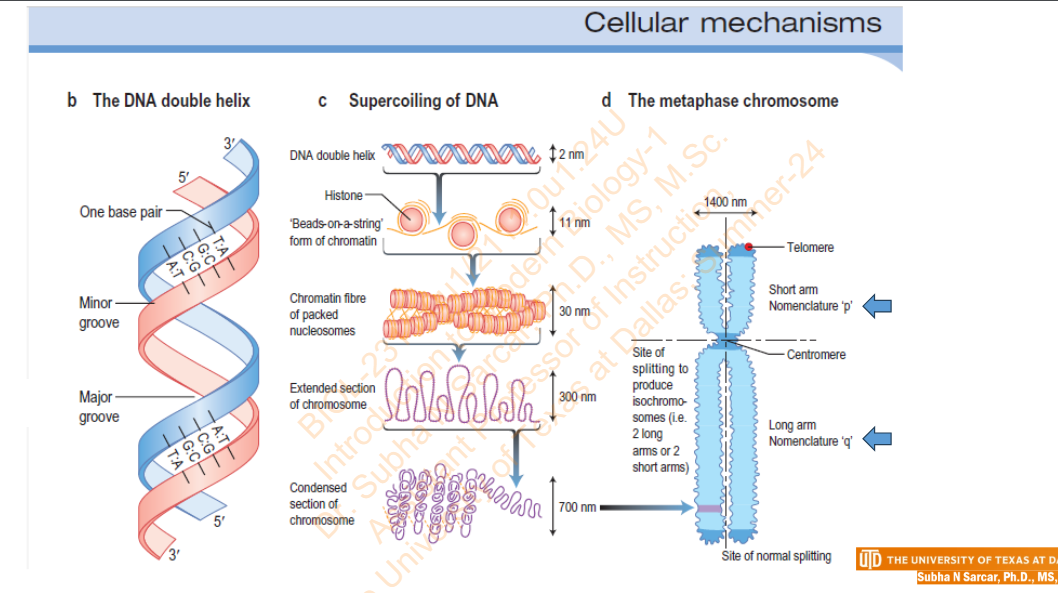
Slide 6 - Packing DNA (1 of 2)
DNA fits into a nucleus because it is packed into a shorter length by __________ proteins
histone
Slide 6 - Packing DNA (1 of 2)
Other _______ proteins also associate with DNA; the complex of DNA and all its associated proteins is _______
nonhistone
chromatin
Slide 6 - Packing DNA (1 of 2)
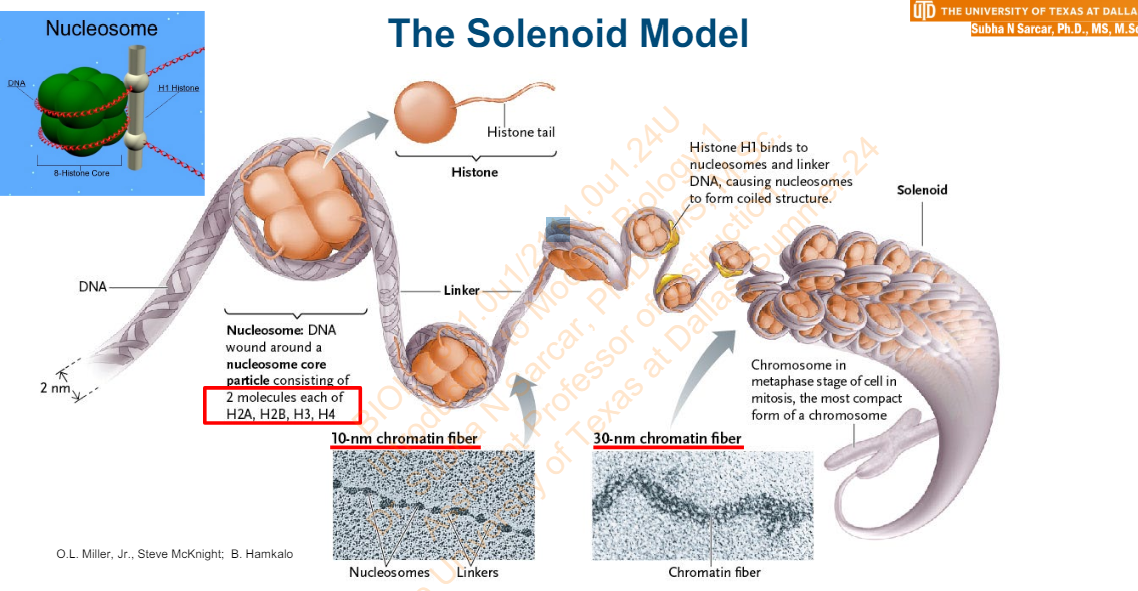
In a __________, an eight-protein _______ forms when DNA winds around the histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
nucleosome
nucleosome core particle
Slide 6 - Packing DNA (1 of 2)
What segment of DNA connects nucleosomes?
A short linker segment
Slide 7 - Packing DNA (2 of 2)
Nucleosomes and linkers appear as _________ on a string under electron microscopes
beads
Slide 7 - Packing DNA (2 of 2)
The ______________ is named from the diameter of the beads and compacts DNA by a factor of about ——
10-nm chromatin fiber
7
Slide 7 - Packing DNA (2 of 2)
Further packing occurs in the __________ when the nucleosome and linker are bound by the _________ protein H1
30-nm chromatin fiber
fifth histone
Slide 7 - Packing DNA (2 of 2)
The ________ model predicts the nucleosomes spiral helically with about _____nucleosomes per turn
solenoid
six
Slide 7 - Packing DNA (2 of 2)
Chromatin packing continues at higher levels, with _______ being loosely packed and ___________ showing dense packing
euchromatin
heterochromatin
Slide 8 - DNA Functions as an InformationContaining Molecule (1 of 2)
Watson and Crick’s model revealed ________ as the biological reservoir of information
DNA
Slide 8 - DNA Functions as an InformationContaining Molecule (1 of 2)
As per Watson and Crick’s model __________ stores information required for an organism’s ___________
DNA
growth and reproduction
Slide 8 - DNA Functions as an InformationContaining Molecule (1 of 2)
Information consists of sequences of _________ in nucleic acid
nucleotides
Slide 8 - DNA Functions as an InformationContaining Molecule (1 of 2)
Four __________ function like letters in an alphabet
_________ has meaning, like the order of letters in a word
nitrogenous bases
Sequence of bases
Slide 9 - The Solenoid Model
Slide 10 - Cellular Mechanism
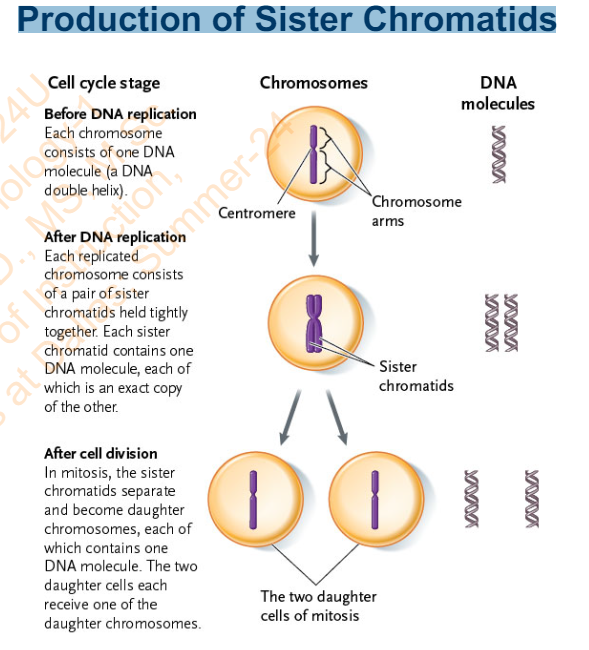
Slide 11 - Sister Chromatids
How and when are sister chromatids produced?
Before a cell divides in mitosis, duplication of each chromosome (and its proteins) produces two identical copies called sister chromatids
Slide 11 - Sister Chromatids
Sister chromatids are held together by ________
sister chromatid cohesion
Slide 11 - Sister Chromatids
What separates the sister chromatids?
mitosis separates them, placing one in each of two daughter nuclei
Slide 11 - Sister Chromatids
_________ hold the sister chromatids together until they are removed
Cohesins (protein)
Slide 11 - Sister Chromatids
The equal distribution of chromosomes into each of two daughter nuclei is called __________
chromosome segregation
Slide 11 - Production of Sister Chromatids
Slide 12 - Ploidy
What is Ploidy?
The number of chromosome sets in a cell or species is called its ploidy
Slide 12 - Ploidy
microorganisms that have only one copy of each type of chromosome in their nuclei are __________ or ______
haploid
n
Slide 12 - Ploidy
Explain Polyploid
Many plant species, have three, four, or even more complete sets of chromosomes in each cell – They are polyploid
Slide 12 - Ploidy
What are diploid?
Most eukaryotes have two copies of each type of chromosome in their nuclei – they are diploid, or 2n
Slide 12 - Ploidy
The two chromosomes of each pair in a diploid cell are called ____________ – one is from the mother, the other from the father
homologous chromosomes
Slide 12 - Ploidy
Homologous chromosomes have the ______ genes in the _______ order in the DNA of the chromosomes
same
same
Slide 13 - What Is a Chromosome? (1 of 3)
What is a chromosome?
Single long double helix of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones
Slide 13 - What Is a Chromosome? (1 of 3)
DNA encodes cell’s __________
genetic information
Slide 13 - What Is a Chromosome? (1 of 3)
Gene”
___________ in chromosome
________ for specific RNA
Region of DNA
Codes
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
Chromosomes _________ into compact structures
condense
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
________ is distributed to each of the _____ cells
One copy of each chromosome
two daughter
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
What is a chromatid?
Each double-stranded DNA copy is called a chromatid
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
Chromatids are attached along their entire length by proteins called ________
cohesins
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
Once mitosis begins, they are attached only at __________
centromere
Slide 14 - What Is a Chromosome? (2 of 3)
Before mitosis, each chromosome is replicated. What are the steps involved in ?
• Chromosomes condense into compact structures
• One copy of each chromosome is distributed to each of the two daughter cells
• Each double-stranded DNA copy (chromatid) are attached along their entire length by proteins called cohesions
• Once mitosis begins, they are attached only at centromere
Slide 15 - What Is a Chromosome? (3 of 3)
Chromatid copies that remain attached at centromere are _______
sister chromatids
Slide 15 - What Is a Chromosome? (3 of 3)
Two attached sister chromatids are still considered a __________
single chromosome
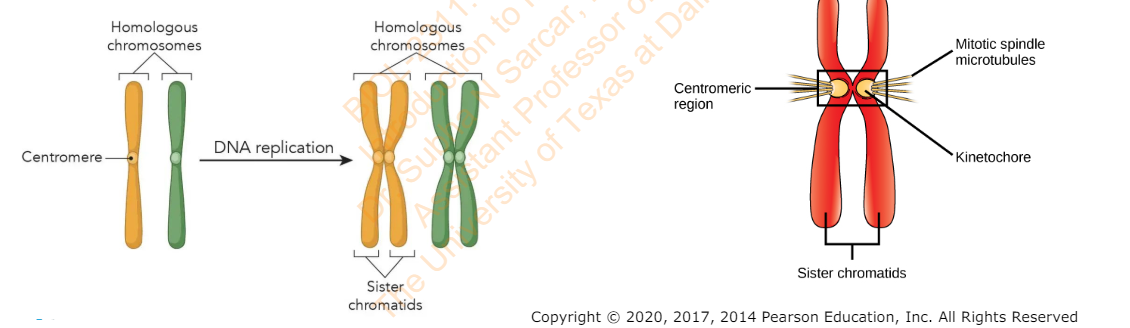
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
A structure containing genetic information in the form of genes
Chromosome
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
The material that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes; consists of a DNA molecule complexed with histone proteins
Chromatin
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
The two attached, double-stranded DNA copies of a replicated chromosome.
Sister chromatids
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
When chromosomes are replicated, they consist of two genetically identical _________
sister chromatids
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
When sister chromatids separate during mitosis, they become _________
independent chromosomes
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
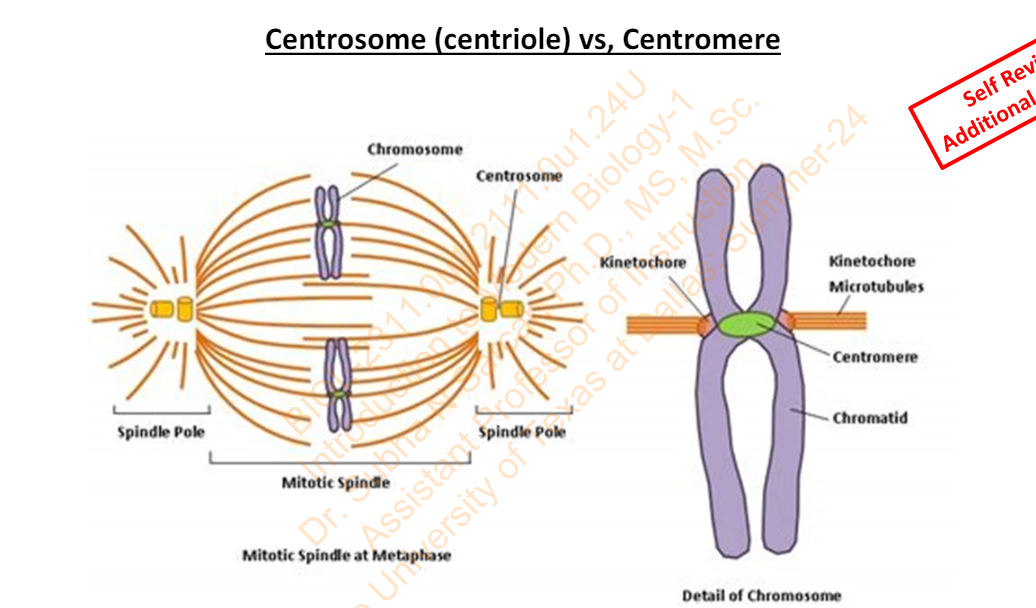
Specialized regions of chromosomes where sister chromatids are most closely joined to each other
Centromeres
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
The structures on sister chromatids where microtubules attach
Kinetochores
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
What is the microtubule-organizing center in animals and certain plants and fungi.
centrosome. Each pole in the spindle apparatus is a centrosome
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
What is the cytoskeletal filaments that form the spindle apparatus, which consists of polar microtubules, kinetochore microtubules, and astral microtubules
Microtubules
Slide 16 - Structures Involved in Mitosis
The dynein and kinesin motors that participate in moving chromosomes and the poles of the spindle apparatus
Microtubule motor proteins
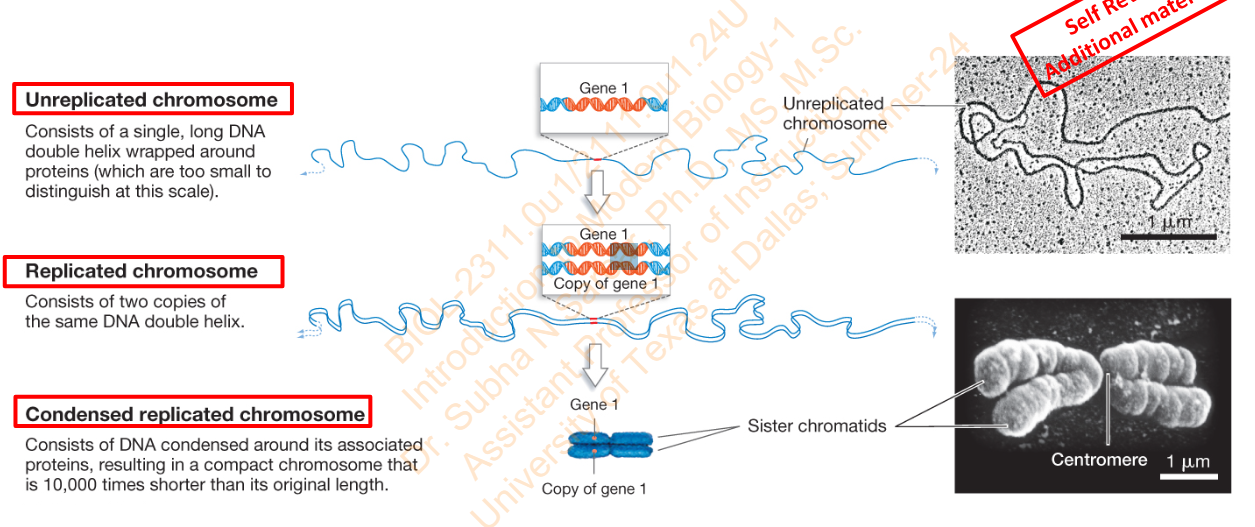
Slide 17 - 12.1 Changes in Chromosome Morphology
What is it that consists of a single long DNA double helix wrapped around proteins (which are too small to distinguish at this scale)
Unreplicated chromosome
Slide 17 - 12.1 Changes in Chromosome Morphology
What is it that consists of 2 copies of the same DNA double helix
Replicated Chromosome
Slide 17 - 12.1 Changes in Chromosome Morphology
What is it that consists of DNA condensed around its associated proteins resulting in a compact chromosome that is 10,000 times shorter than its original length.
Condensed replicated chromosome
Slide 17 - 12.1 Changes in Chromosome Morphology
Diagram
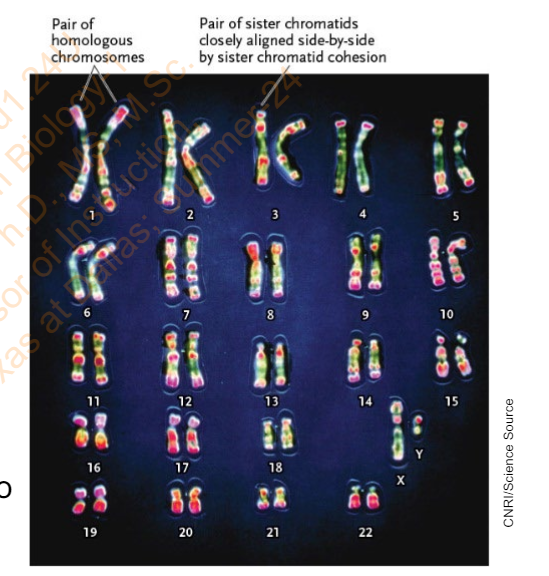
Slide 18 - Research Method: Preparing a Human Karyotype
List the protocols to prepare a human karyotype
Add sample to culture medium that has stimulator for growth and division of cells (white blood cells in the case of blood). Incubate at 37oC.
Stain the cells so that the chromosomes are distinguished.
View the stained cells under a microscope equipped with a digital imaging system and take a digital photograph
Slide 18 - Research Method: Preparing a Human Karyotype
Interpreting the Results: The karyotype is evaluated with respect to the _________
scientific question being asked.
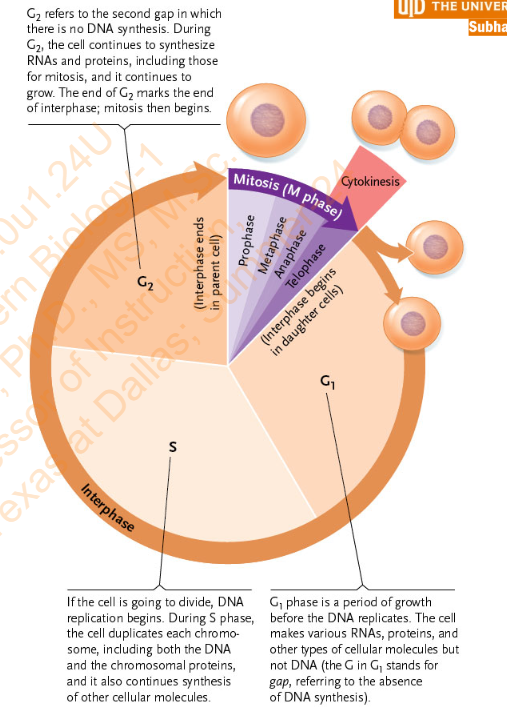
Slide 19 - 10.2 The Mitotic Cell Cycle
What are the three main events in a cell cycle:
interphase,
mitosis (M phase),
and cytokinesis
Slide 19 - 10.2 The Mitotic Cell Cycle
What are the phases of Interphase?
• G1 phase, in which the cell grows
• S phase, in which DNA replicates and chromosomal proteins are duplicated
• G2 phase, in which cell growth continues and the cell prepares for mitosis
Slide 19 - 10.2 The Mitotic Cell Cycle
In which phase of the Interphase does the DNA replicates and chromosomal proteins are duplicated?
S Phase
Slide 19 - 10.2 The Mitotic Cell Cycle
In which phase of the interphase does the cell prepares for mitosis and in that phase what happens to the cell growth?
G2 Phase and the cell growth continues in that phase
Slide 19 - 10.2 The Mitotic Cell Cycle
Diagram
Slide 21 - Figure 12.4 An Overview of the Cell Cycle
Diagram
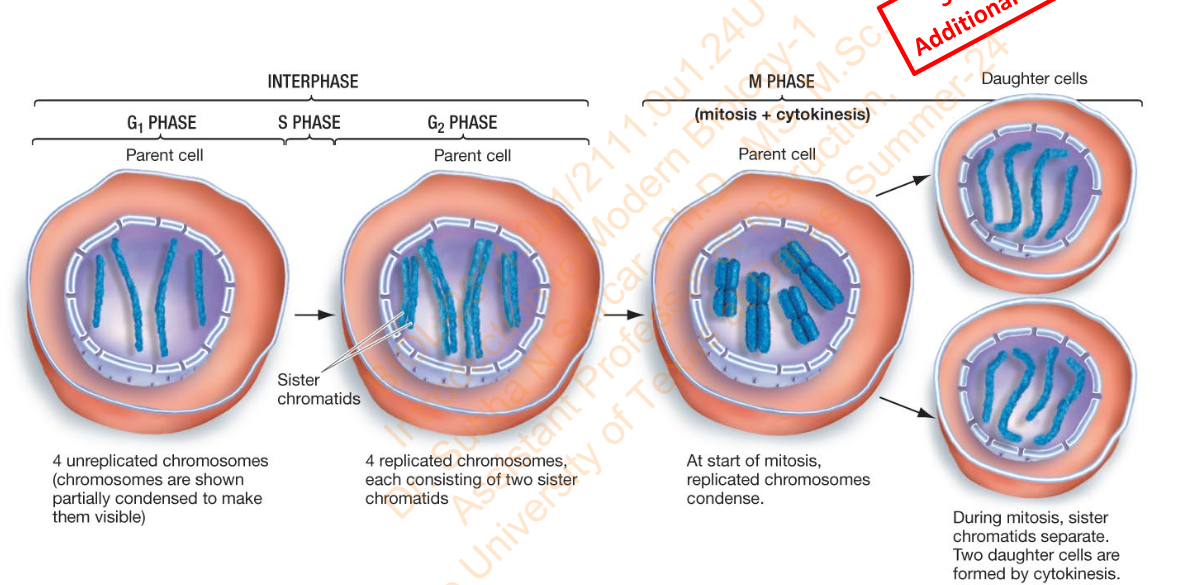
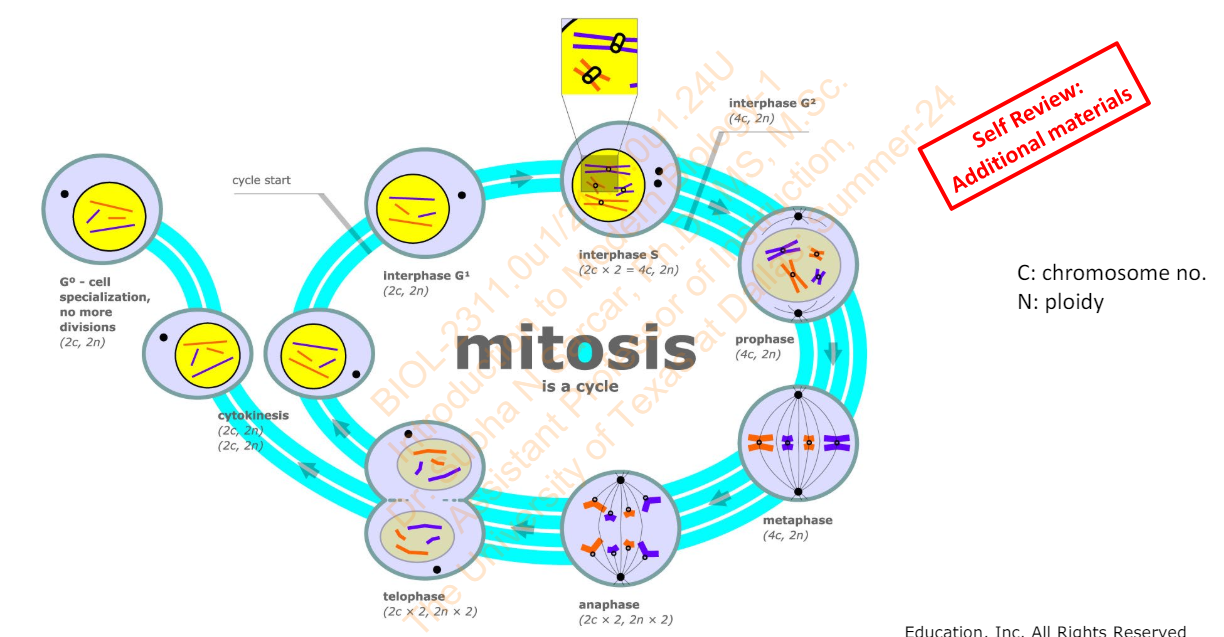
Slide 22 - How the chromosome no. and ploidy changes during the mitotic cell cycle - Diagram
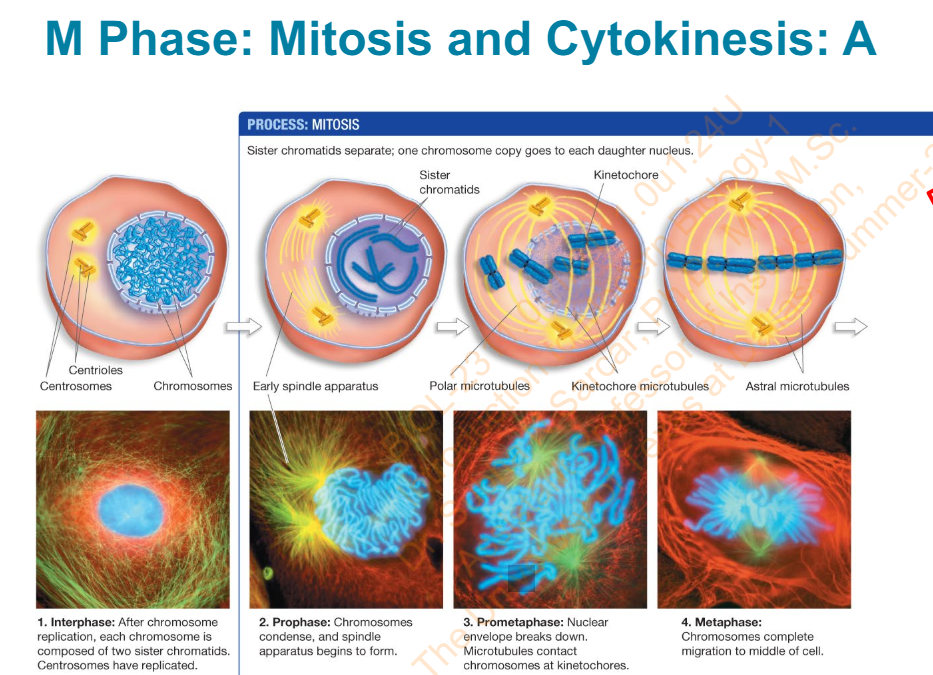
Slide 23 - M Phase: Mitosis and Cytokinesis: A
What are phases and explain them?
Interphase
After chromosome replication, each chromosome is composed of 2 sister chromatids. Centrosomes have replicated
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and spindle apparatus begins to form
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope breaks down. Microtubles contact chromosomes at kinetochores
Metaphase
Chromosomes complete migration to middle of cell
Slide 23 - M Phase: Mitosis and Cytokinesis: A - Diagram
Slide 24 - M Phase: Mitosis and Cytokinesis: B - Diagram
What are the phases?
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate into daughter chromosomes which are pulled to opposite poles of spindle apparatus
Telophase
Nuclear envelope re-forms and chromosomes de-condense
Cell division begins:
Actin-myosin ring case plasma membrane to begin pinching in
Cell division is complete:
Two daughter cells form
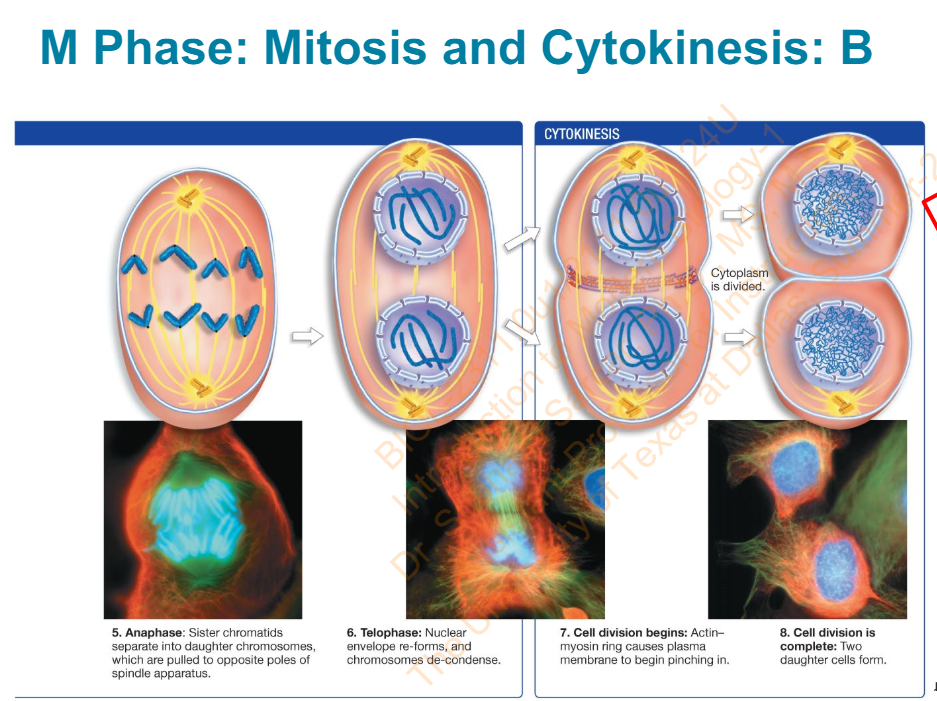
Slide 24 - M Phase: Mitosis and Cytokinesis: B - Diagram
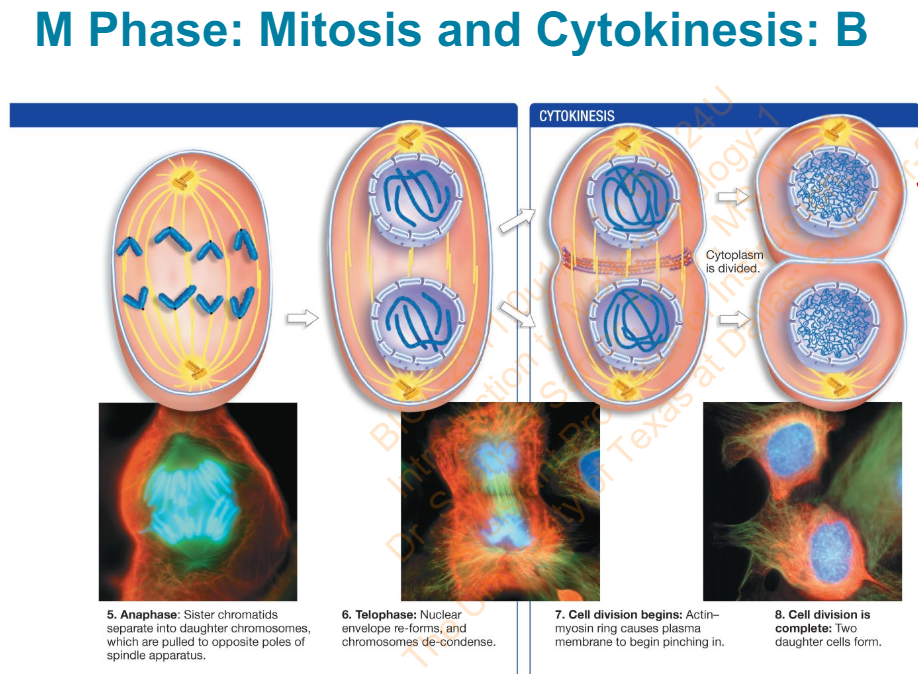
Slide 25 - Interphase
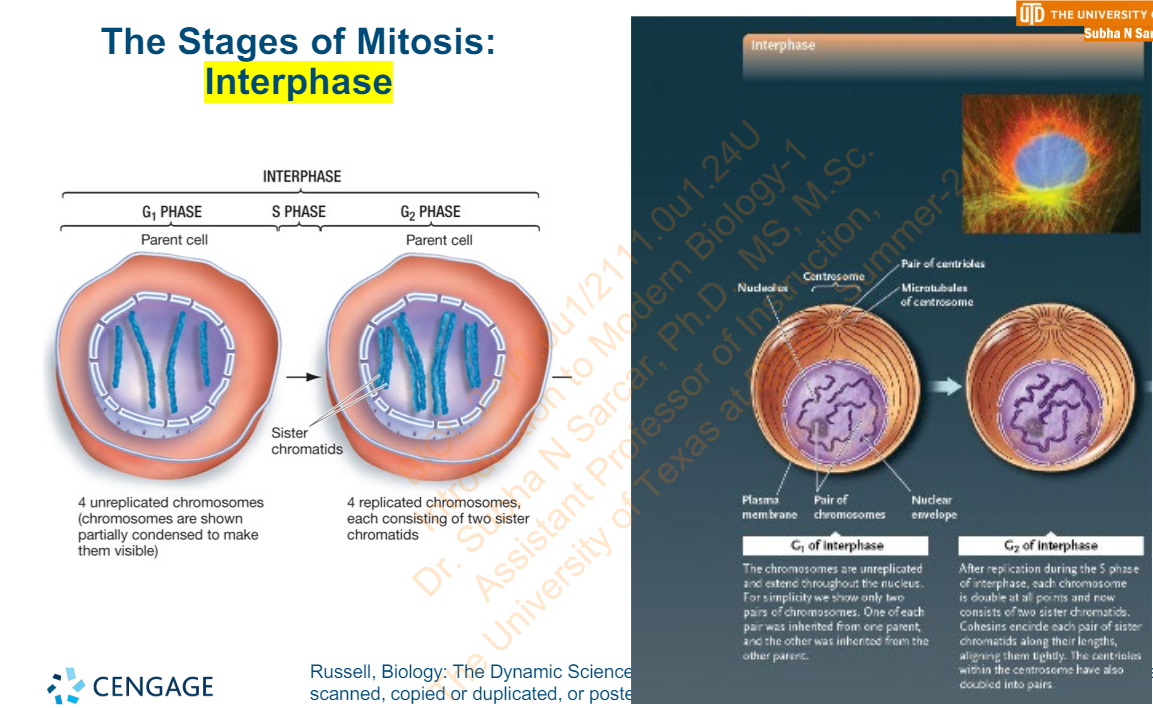
Usually, ________ is the only phase of the cell cycle that varies in length – other phases are typically uniform in length
G1
Slide 25 - Interphase
G1 is also the stage in which many cell types __________ and are ______________ into a G0 phase
stop dividing
shunted
some cells in G0 reenter G1, others never resume the cell cycle
Slide 25 - Interphase
___________ trigger each phase of the cell cycle and regulate the ____________ that a cell goes through
Internal regulatory controls
overall number of cycles
Slide 26 - The Stages of Mitosis: Interphase - Diagram
Slide 27 - Mitosis proceeds in Five Stages
Following interphase, mitosis can be divided into five sequential stages:
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Slide 27 - Mitosis proceeds in Five Stages
Which phase of mitosis does Cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis coincides with?
telophase
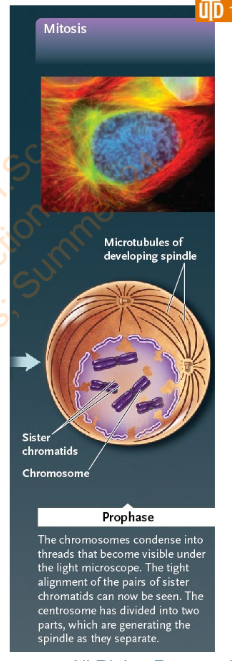
Slide 30 - Prophase
Explain the different stuff that happens in Prophase
Chromosomes condense into chromatin
Nucleolus becomes smaller and disappears
The mitotic spindle begins to form between the two centrosomes as they migrate toward the opposite ends of the cell, where they will form spindle poles
Slide 31 - Prophase
Spindle apparatus consists of ___________
microtubules
Slide 31 - Prophase
Spindle apparatus forms from ________
microtubule-organizing center
Slide 31 - Prophase
MTOCs define [#] poles of spindle apparatus
_____ ends of microtubules grow out from each pole
two
positive
Slide 31 - Prophase
_______ extend from each spindle pole and overlap with each other
Polar microtubules
Slide 31 - Prophase
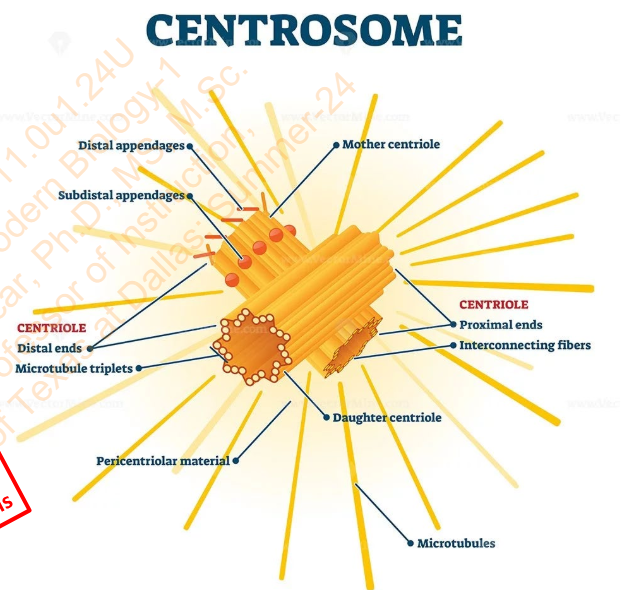
Structure that contain centrioles?
Centrosome
Slide 31 - Prophase
Centrosome replicates during _________ Phase
S Phase
Slide 32 - Centrosome (centriole) vs, Centromere
Slide 33 - Prometaphase
Prometaphase - Begins when the ________
nuclear envelope breaks down
Slide 33 - Prometaphase
in Prometaphase - __________ grow from centrosomes at opposite spindle poles toward the center of the cell
Spindle microtubules
Slide 33 - Prometaphase
Prometaphase: A __________forms on each sister chromatid at the __________(the point where chromatids are joined in sister chromatid adhesion)
kinetochore
centromere
Slide 33 - Prometaphase
Kinetochore microtubules attach to the ___________
Chromosomes are pushed and pulled by ____________ until they reach ________
kinetochores
microtubules
the middle of spindle