Lecture 22: Large Intestine
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Large Intestine
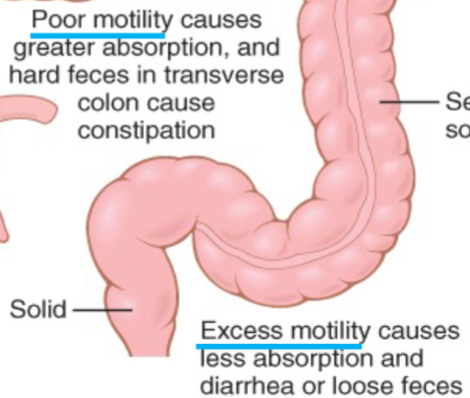
Role: Drying & Storage
Motility influences absorption
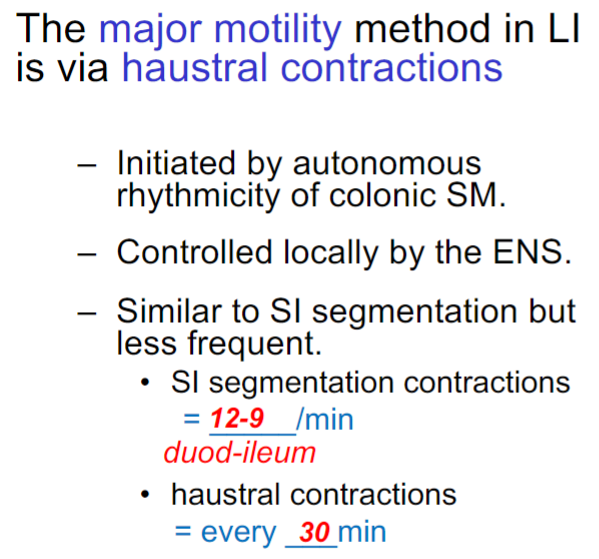
Haustral Contractions Overview

Haustral Contractions
Mass Movements
Propel colonic content
Mass movements occur 1 - 3 /day
High amplitude propagating contractions
Contents moved over a large distance in one movement
Typically start in cecum and sweep towards the rectum
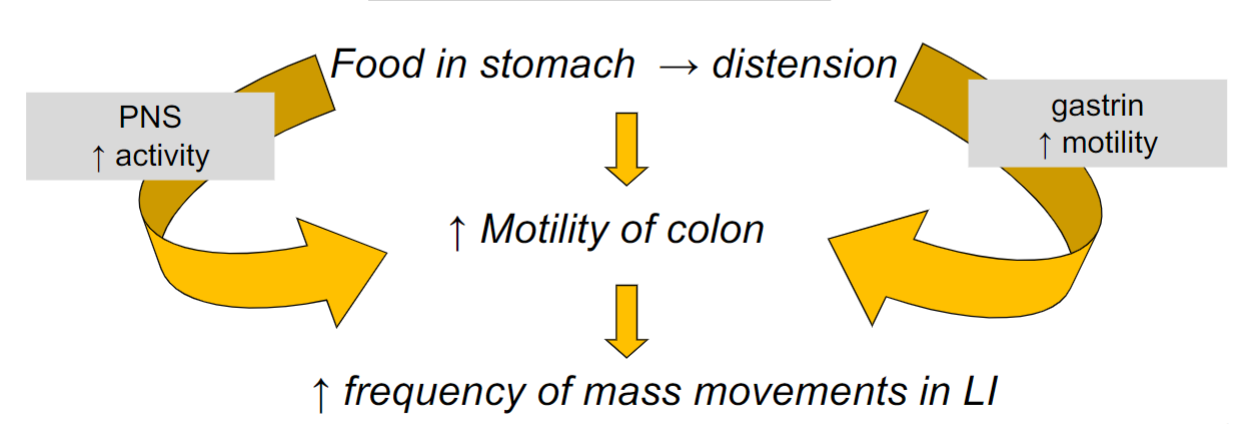
Gastrocolic Reflex
Receptive Relaxation

Adaptive Relaxation

Internal Anal Sphincter relaxes via
NO and VIP
Hirschsprung’s Disease
Megacolon
Genetic M>F
Loss of ENS in distal part of colon
Involves the internal anal sphincter
Normal defecation reflex doesn’t occur → Fecal build
Symptoms: little to no bowel movement, abdominal distension, lethargic & vomiting
Tx: surgical removal of the aganglionic region (resection) restores the ability to defecate
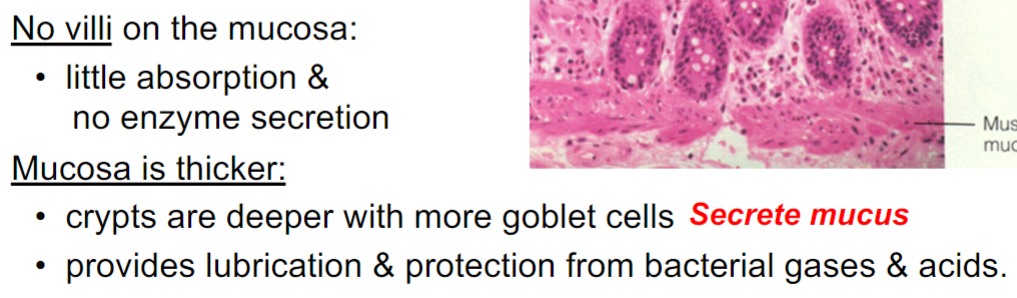
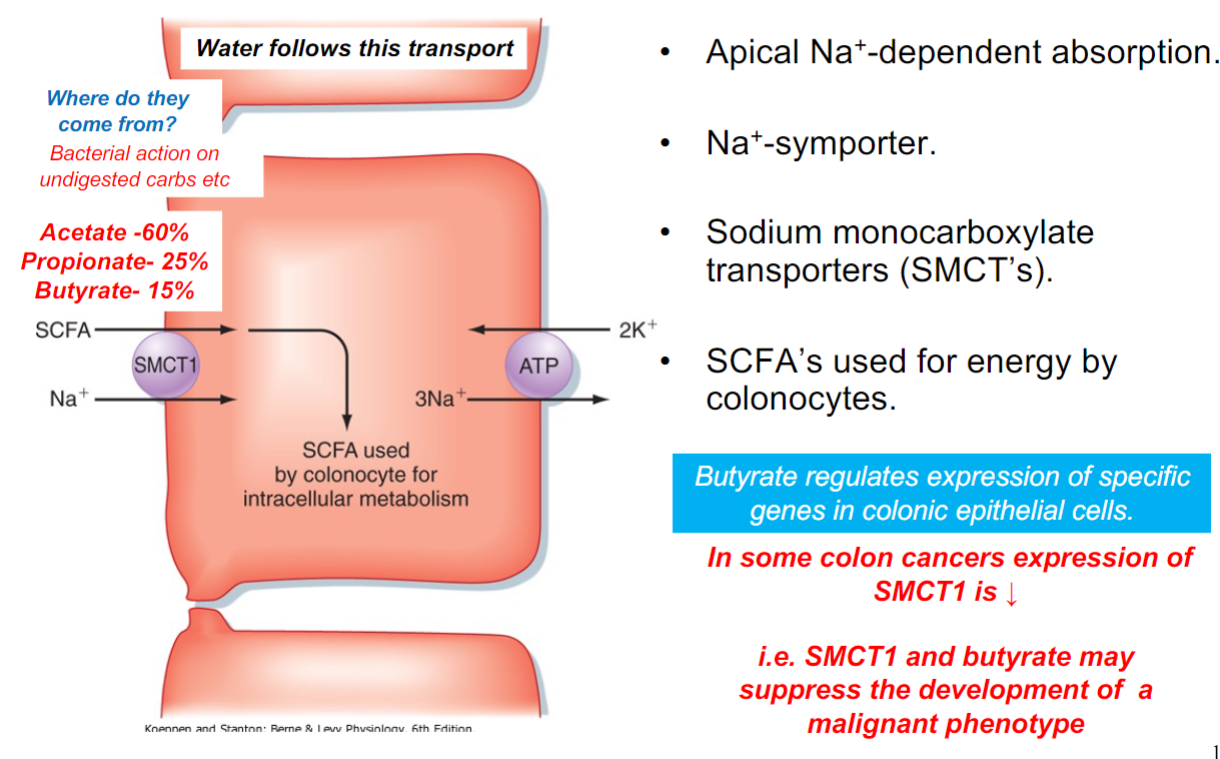
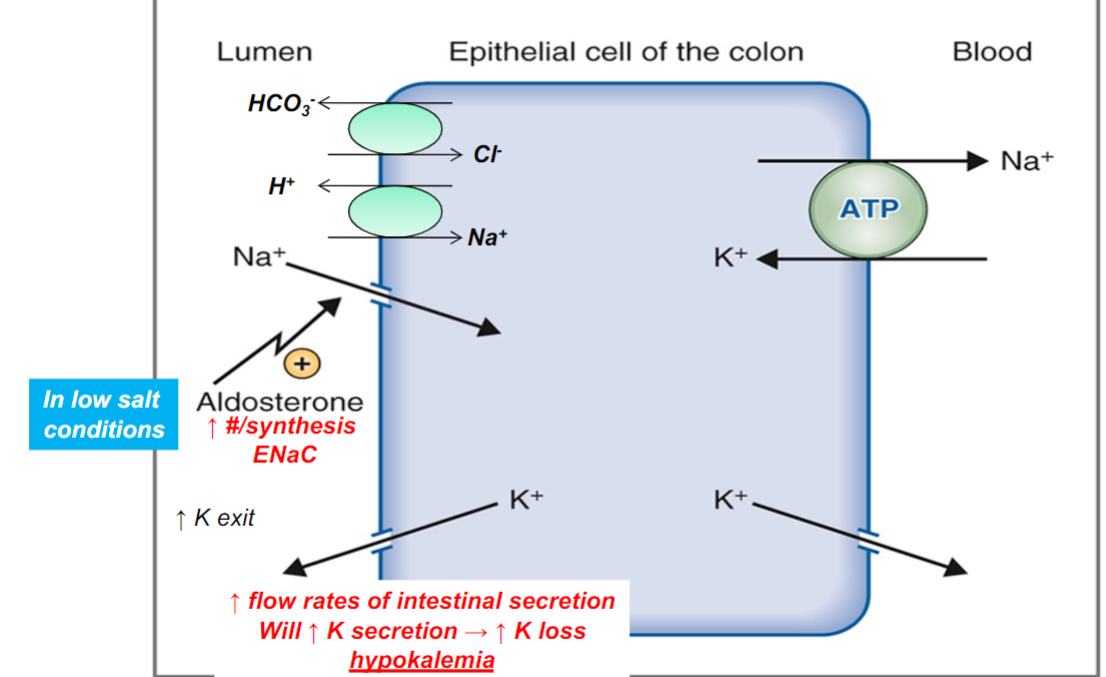
Colonic secretion
Alkaline (HCO3- ) mucus solution
Absorption of short chain fatty acids
Ion Transport in Colon
Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis
Haustra are readily apparent radiologically and give the colon a lobed
appearance.
Loss of the haustra is a common observation in both Crohn's disease and chronic ulcerative colitis
The colon will have a symmetric, tubular appearance
The loss of haustration is associated with a loss of colonic motility
Crohn’s disease

Ulcerative Colitis

Hematochezia
Passage of blood through anus, bloody stools
Can result in hemorrhage
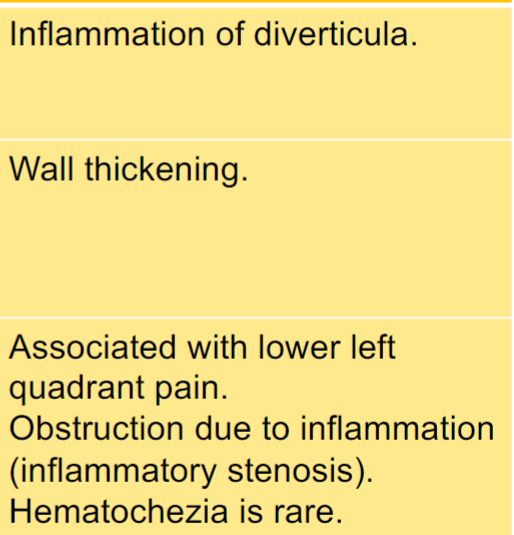
Diverticulosis and diverticulitis
Diverticulosis occurs when small, bulging pouches (diverticula) develop in the LI
Diverticulitis occurs when one or more of these pouches become inflamed or
infected
Diverticulosis

Diverticulitis