Patho/Pharm 2 (CH 3) - Neurological Drugs PT 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
central acting muscle relaxant
baclofen
baclofen MOA
directly stimulates increase in GABA inhibitory features
- supresses hyperactive reflexes
- NOT DIRECT on skeletal muscle
priority use for baclofen
- relief splacisity in cerebral palsy
- spinal cord injuries
- Multiple sclerosis
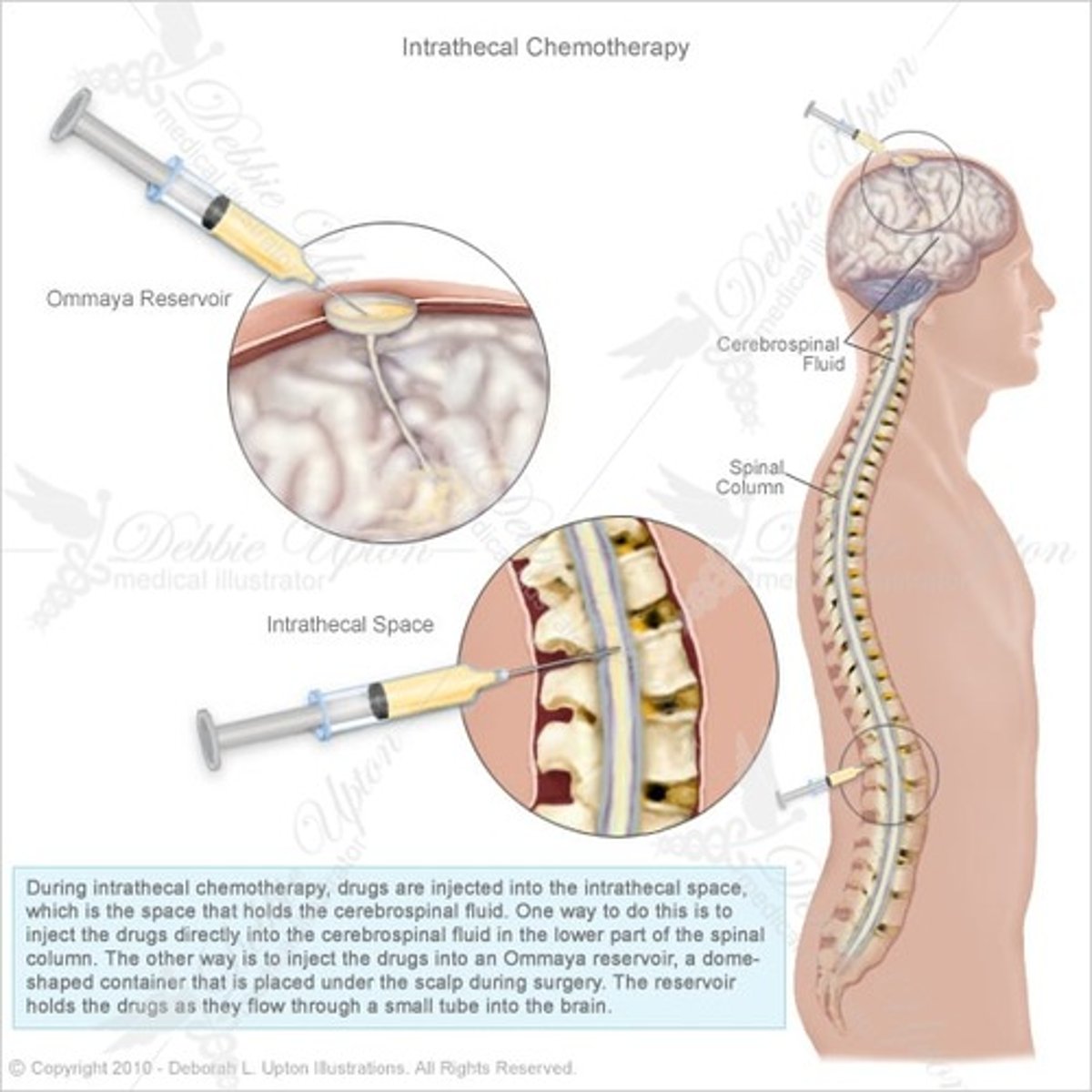
GIVEN via: PO/IV/ and MAINLY INTRATHECAL PUMP
pt education w/ baclofen
- drowsy/dizzy/fatigue
- urinary retention (RARE)
- N/V
- constipation
- REPORT TO PROVIDER if mild laxatives not alleviate constipation
- ABRUPT withdrawel symptoms via PO = SEIZURES / visual hallucinations
- ABRUPT withdrawal symptoms via intrathecal = RHABDOMYLOSIS/ CONFUSION/ RESTLESSNESS
nursing priority for baclofen
- take w/food and milk
- increase fluids
- reposition pt's slowly (prevent dizziness/drowsiness)
- seizure precautions
- strict I/O (urinary rentention s/s)
- tirtate dose up slowly for first time use
- mild laxatives
- DO NOT STOP ABRUPTLY (TAPER OFF 1-2WEEK TIME FRAME)
pt contraindications when taking baclofen
- hypersensitivity
- hx/active use of monoamine/oxydiase/MOAIs (synergic INCREASES CNS effects)
CAUTION W/ (can still take if needed):
- older adults
- children
- mentally ill pts
- hx seizures/CVA
baclofen abrupt intrathecal complications
abrupt stop may cause:
- rebound muscle splasicity FOLLOWED BY FEVER
- muscle damage + hyperactive --> rhabdomylosis (toxins produced) which cause organ failure
dantrolene MOA
peripheral acting muscle relaxant
- blocks Ca+ in skeletal muscle to reduce skeletal muscle spasms
primary use for dantrolene
- cerebral palsy
- cardiovascular accident/stroke
- spinal cord injuries
- multiple sclerosis
- prevent AND treat malignant hyperthermia
- GIVEN VIA: PO
treatment for malignant hyperthermia
DANTROLENE
- malignant hyperthermia is caused by Ca+ problems in skeletal muscle causing excessive muscle use
- dantrolene is a Ca+ skeletal muscle blocker relaxing symptoms of malignant hyperthermia
pt education taking dantrolene
- muscle weakness
- drowsiness/dizziness
- diarrhea
- liver toxicity (in high doses + long term therapy)
- caution w/ women >35 years old taking estrogen medications
nursing priorities for dantrolene
- monitor/educate s/s of CNS depression (dizziness/drowsiness)
- diarrhea monitoring
- s/s liver toxicity
- LFTs
- LOW DOSE to start --> titrate up if needed
- for malignant hyperthermia PO 1-2days perioperatively
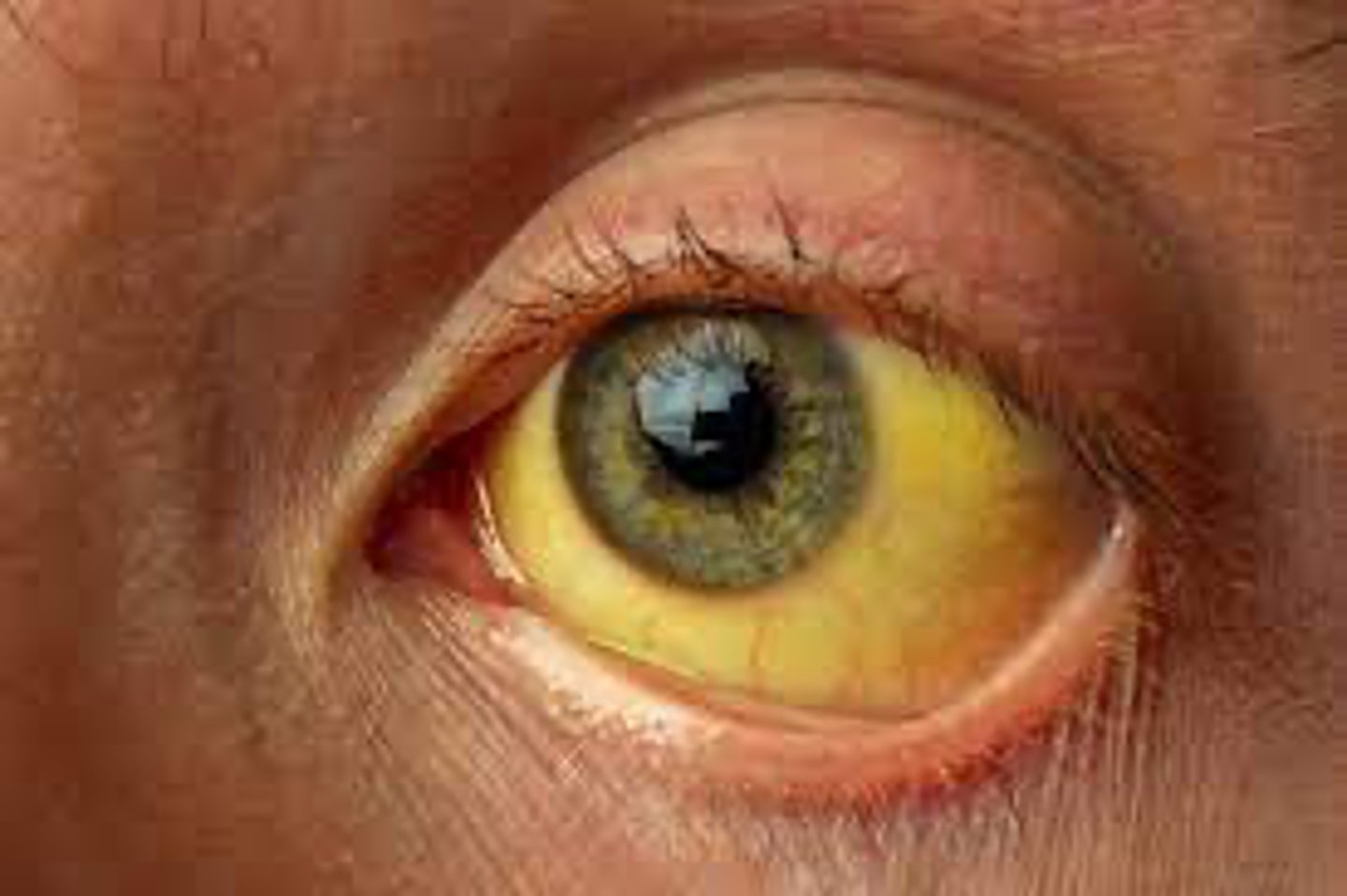
liver toxicity pt education
s/s =
- abdominal pain
- ascites
- N/V
- jaundice
- pain w/ eating
- fever/confusion can occur as well
contraindications for dantrolene
- active liver dysfunction
- HIGH risk > 35y/o (women >35 taking estrogen HIGH risk liver toxicity)
- hx heart, lung, and neuromuscular disorders
- taking/on CNS depressants
- Ca+ channel blockers (severe cardiac dysrhythmias)
Ca+ channel blockers
verapamil
nifedipine
Phenytonin MOA
traditional ASM, decreases neural activity of seizure generating cells
- inhibits Na+ going through Na+ channels
primary use for phenytonin
- simple partial + complex partial seizure
- tonic clonic seizures (PRIMARY USE)
GIVEN VIA: PO, IM, IV
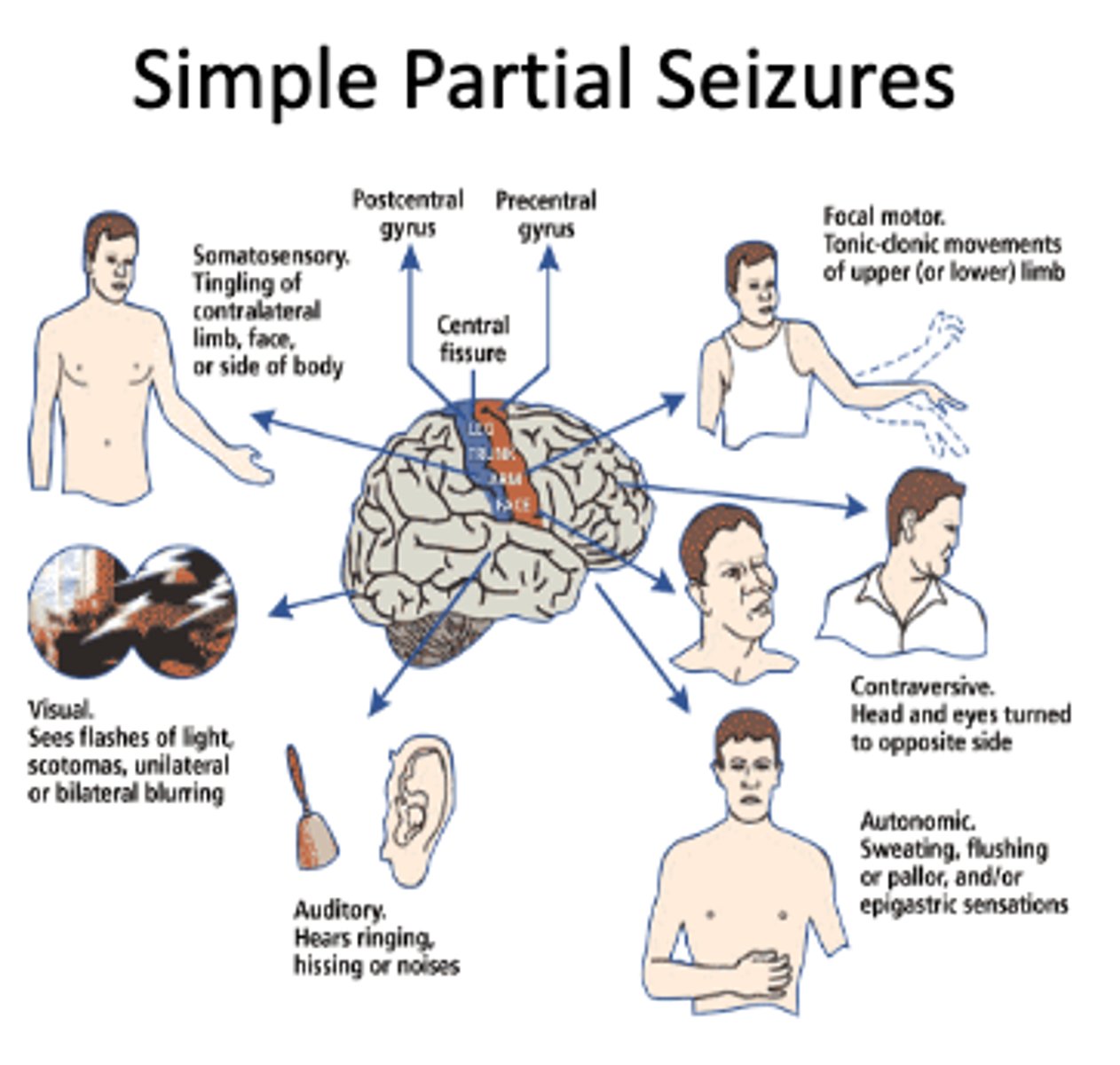
simple partial seizure
a partial seizure, starting from a focus and remaining localized, that does not produce loss of consciousness
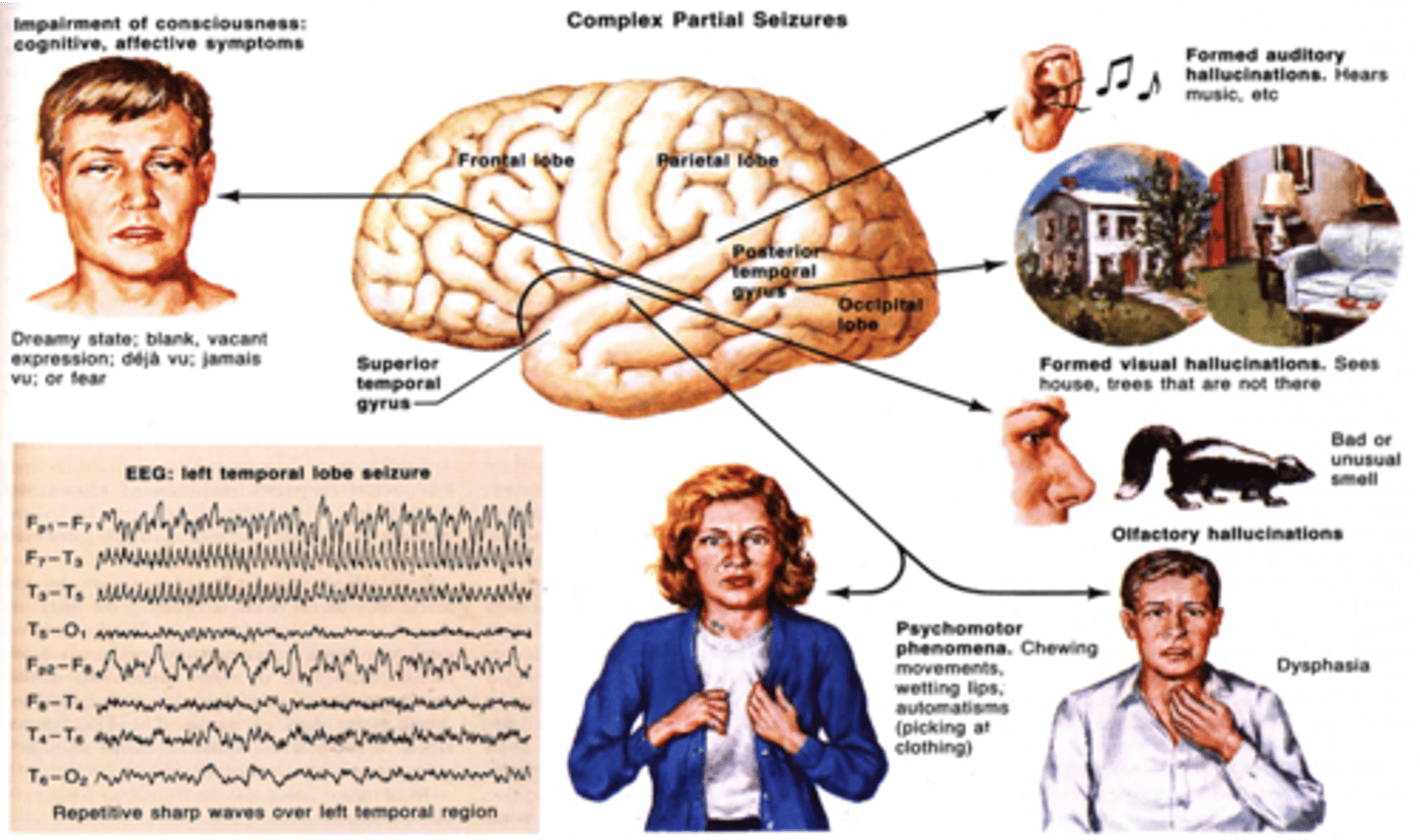
complex partial seizure
in epilepsy, a type of seizure that doesn't involve the entire brain and therefore can cause a wide variety of symptoms
phenytonin pt education
- mild drowsiness combined w/ CNS depressants
- gingival hyperplasia w/ CHILDREN + TEENS
- occasional SKIN RASH (STEVENS-JOHNSONS SYNDROME)
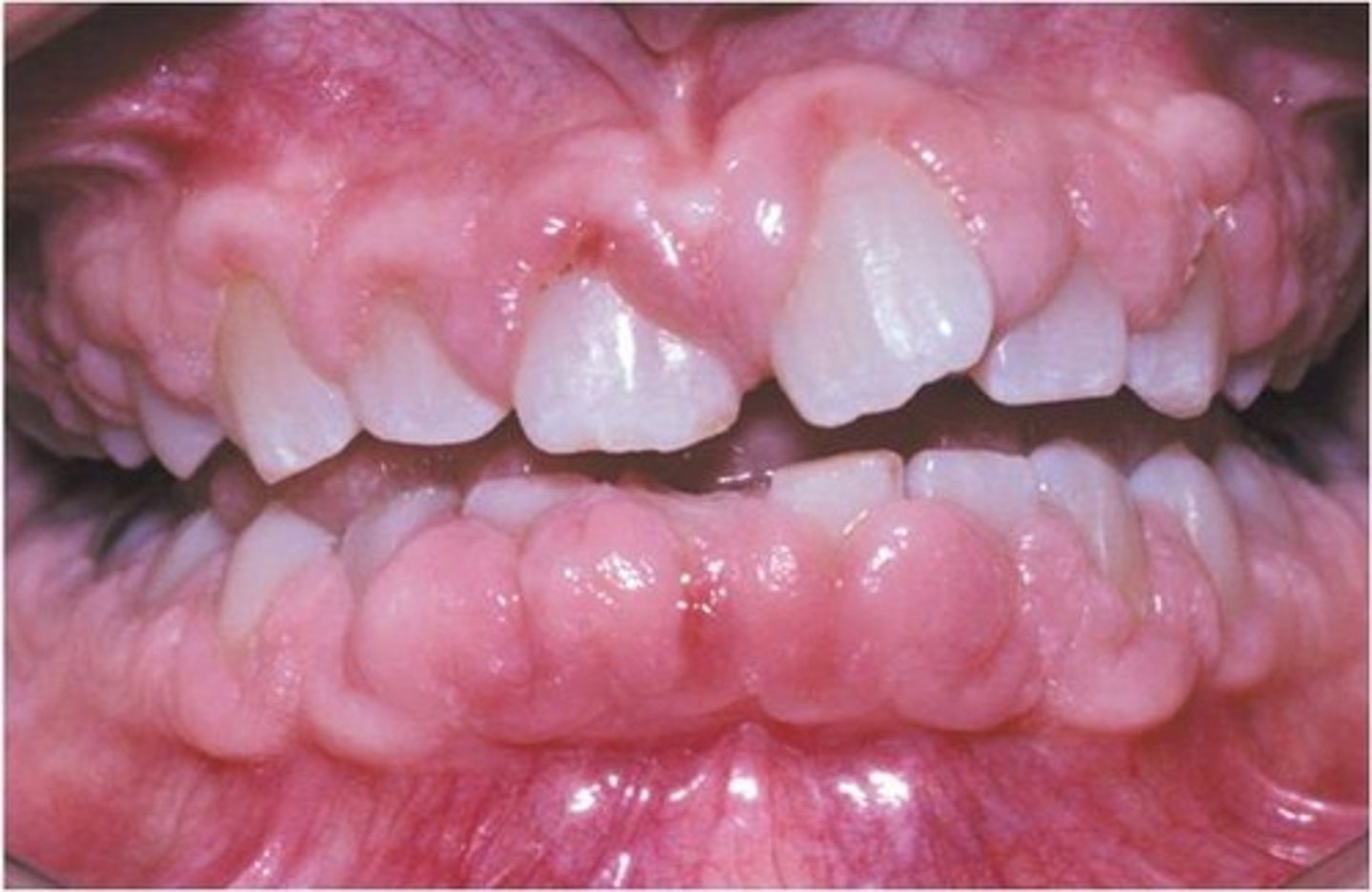
nursing priorities for phenytonin
- THERAPUETIC RANGE = 10 - 20mcg/dL
- CNS/neuro checks (depression toxicity)
- gum assessments in children/teens
- rash monitoring
- PO take w/ food
- IV MAX DOSE = 50mg/min
- 25mg/min in eldery
- IV increases risk cardiac collaspe is pushed too fast
nursing interventions for phenytonin usage
- IV MAX DOSE = 50mg/min
- 25mg/min in elderly
- IV increases risk cardiac collaspe is pushed too fast
- constant drug level checks
- DO NOT STOPE MED ABRUPTLY (unless SJ syndrome shows)
- gradually stop med over a couple weeks
SJ syndrome (from phenytoin)
- fever
- massive skin damage/peeling off
- internal organ damage
- sepsis
DISCONTINUE THE MEDICATION IMMEDIATLY IF RASHING OCCURS
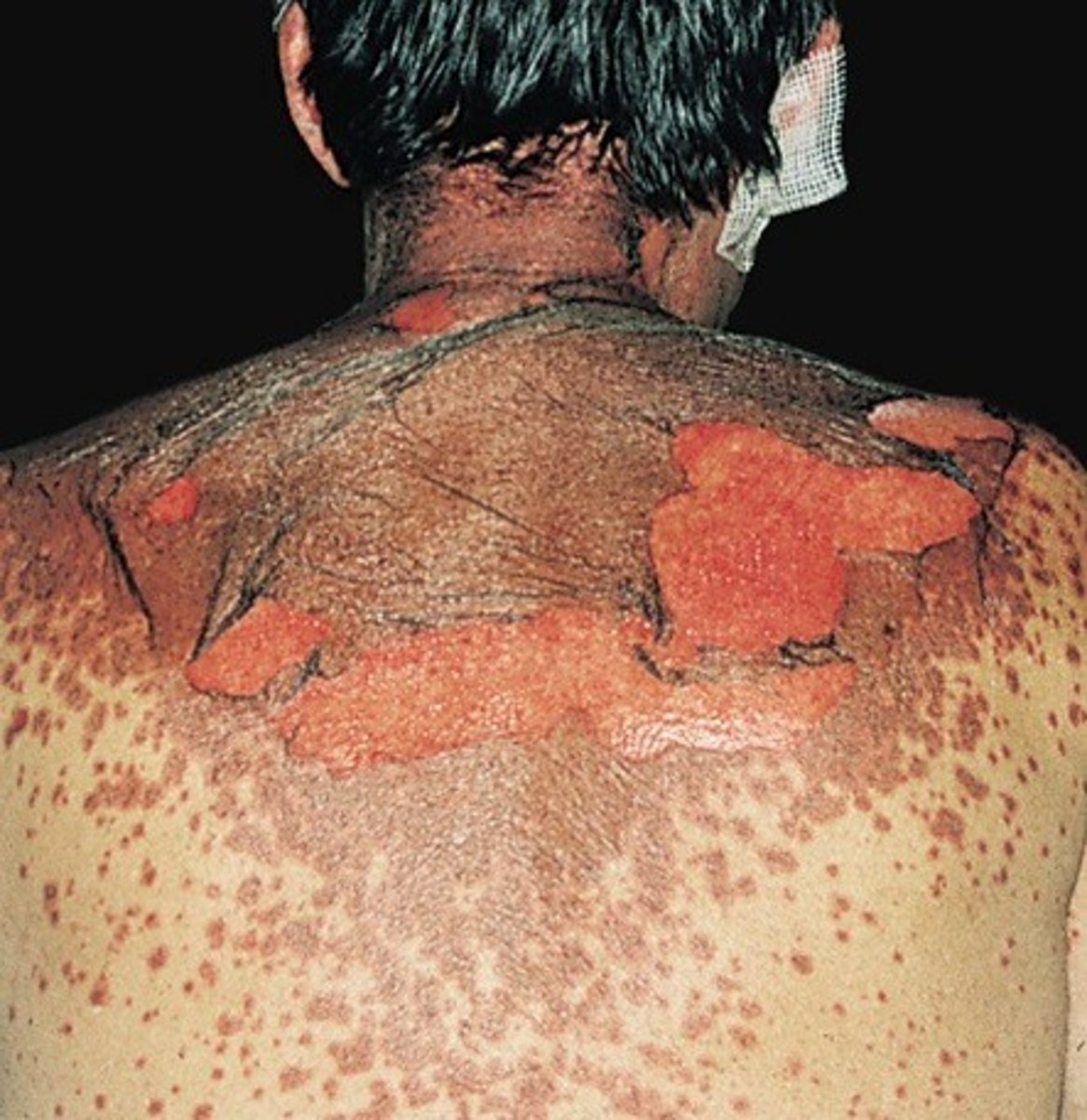
phenytonin toxicity s/s
- hystamus (rapid fluttering of the eyes)
- ataxia (drunk walk/ uncoordinated)
- sedation
- blurred/double vision
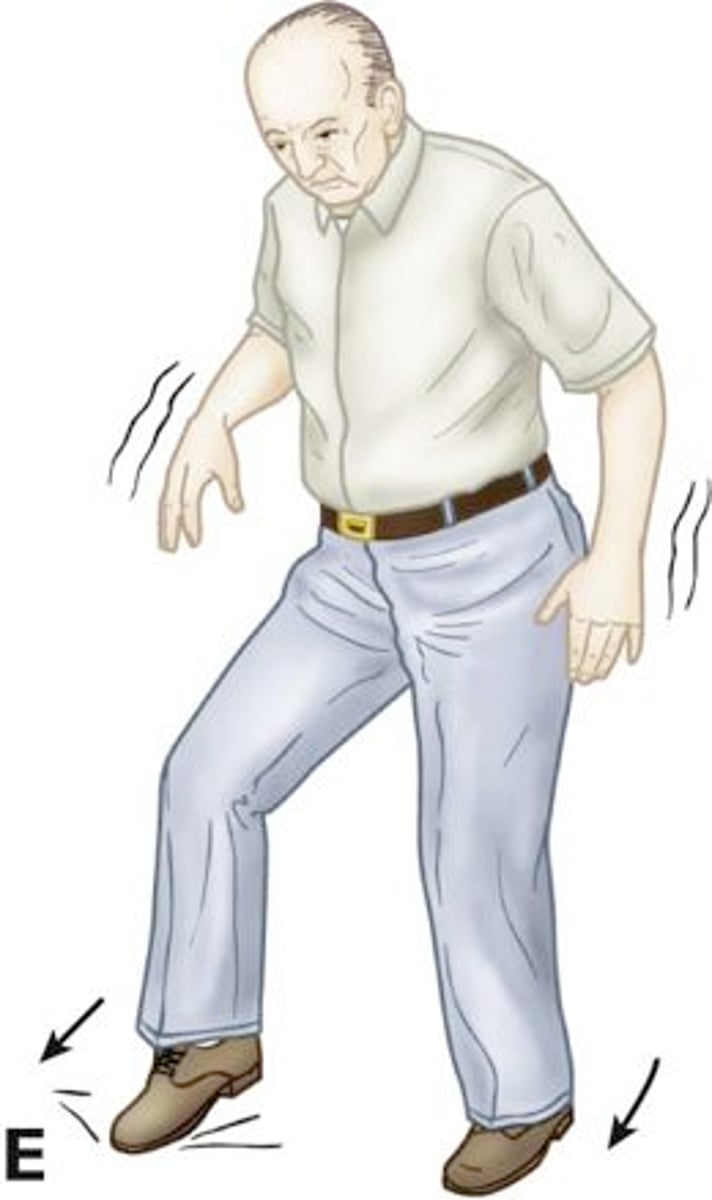

priority pts when monitoring phenytonin
- Category D pregnancy
- Hx resp, liver, and cardiac dysfunction
- diabetes (increases insulin resistance)
- older adults
- hx alcohol abuse
- actively on contraceptives (lower phenytoin levels)
(DECREASE phenytoin levels)
- w/ phenybartibital
- w/ carbamezepine
contraindications for phenytonin
- skin rashing
- heart block pts
- seizure induced via low blood sugars
med interactions:
(SYNGERGIC = phenytonin toxicity)
- diazapem
- isoniazid
- cimetidine
- valporic acid
carbamazepine MOA
traditional ASM, lowers amount of Na+ going into Na+ channels
- slows down neuron discharge
priority use for carbamazepine
- all subtypes of partial seizures (focal, focal-aware, focal-impaired)
- tonin clonic seizures
- bipolar mood stabilizer
- trigimineal neuralgia
GIVEN VIA: PO
pt education taking carbamazepine
- CNS effects (headache, axtaxia, hystamus, blurred vision)
- FLUID RETENTION
- SJ syndrome
- photosensitivity (WEAR SUNSCREEN)
- BONE MARROW SUPRESSION
- educate immunocompromised, anemia, thrombocytopenia
- take w/ meals (sustained release med GI distress)
nursing priorities for carbamazepine
- monitor fluid retention (ESPECIALLY W/ HX OF CARDIAC/KIDNEY DYSFUNCTION)
- administer low dose and SLOW
- take w/ meals (sustained release med GI distress)
- monitot Na+ levels (hyponatrermia s/s)
- monitor CBC levels/ and bruising s/s
- monitor signs of rash
- HLA-B*1502 gene testing
- THERAPUTIC DOSE = 4-12mcg/dL
hyponatremia s/s
N/V
Muscle cramps
Confusion
Muscular twitching,
coma
Seizures
Headache
priority pts taking carbamazepine
- category D pregnancy
- hx cardiac, hepatic disease
- hx alcohol abuse
(MEDS DECREASE EFFECTIVENESS):
- oral contraceptives
- phenytonin
- rifampin
- theothyline
- barbiturates
- cisplastin
pt contraindications w/ carbamazepine
- hx of hematologic disorders
- hx/active heart failure pts
- HLA-B*1502 gene in asian decent (increases risk for SJ)
(SYNERGIC MEDS):
- antifungals
- grapefruit
- erythromycin
- isonizid
- antiretrovirals
- MOAIs
- valporic acid
valporic acid MOA
traditional ASM
- inhibits influx of Ca+ and Na+ into channesl
- enhances inhibitory effects of GABA
primary use for valporic acid
- ALL TYPES of seizures
- controls mania induced bipolar episodes
- PREVENTATIVE for migraines
GIVEN VIA: PO, IV
pt education taking valporic acid
- liver toxicity
- hyperammonemia leading to hepatitis
- prancreatitis
- bone marrow supression
- GI distress/indigestion w/ PO
- take w/ food
BB WARNING - hepatitis/pancreatitis leads to SEVERE DEATH IN 6 MONTHS if untreated
nursing priorities for valporic acid
- PO sustained release DO NOT crush
- IV MUST be diluted
- DO NOT MIX IV MED w/ other meds
- REPORT hyperammonemia immediately
- s/s hepatitis/pancreatitis
- LFTs
- amylase tests (pancreatitis rise in amylase)
- platelets, bleeding time, and ammonia levels
- skin monitoring
hyperammonemia s/s
- episodes of N/V, confusion, LOC
pancreatitis s/s
- abdominal pain
- N/V
- fever
- jaundice
- weight loss
- skin bruising
priority pts on valporic acid
- pregnancy (must take folic acid supplements to prevent fetal deformaties)
- children < 2y/o
- active kidney disease
- older adults
contraindications when on valporic acid
- hx/active liver disorders
- thrombocytopenia
- hyperammonemia levels
- w/ other anticonvulstants
(MED INTERACTIONS)
- w/ phenytonin increases phenytoin levels
- w/ phenobacterial meds increase med levels
- topiramte increases risk of hyperammonemia
oxycarbazepine MOA
2nd/3rd generation ASM similar to the structure of carbamazepine
- Anticonvulsant binds to Na+ channels used w/ adjunct therapy for seizures
- blocks glutamine release (excitatory neurotransmitters)
primary use for oxycarbazepine
- mood disorders
- migraines
- neuralgia (nerve pain)
GIVEN VIA: PO
pt education taking oxycarbazepine
- allergy to carbamepizine can causes hypersensitivity to this med
- hyponatremia
- SJ syndrome
- dizziness/drowsiness
- blurred vision
- ataxia
- LONG TERM USE CAUSES HYPERTHYROIDISM
- photosensitivity
nursing priorities for oxycarbazepine
- monitor electrolyte levels (especially if on diuretics)
- monitor s/s of SJ syndrome (rashing)
- TITRATE IV med slowly in LOW DOSES
- monitor WBC
- WITHHOLD MED IF ANY CBC levels are out of range / notify provider
- - HLA-B*1502 gene testing
contraindications for ozycarbazepine
- therapy w/diuretics = SEVERE hyponatremia INCREASING RISK of seizures
(MED INTERACTIONS):
- phenytonin (increases risk phenytonin toxicity)
- phenobarbtial decreases effectiveness
- carbamazepine (decreases effectiveness)
- med can decrease effectiveness of oral contraceptives
lidocaine MOA
local anesthetic blocks Na+ influx in Na+ channels
- prevents depolarization
primary use for lidcaine
- SMALL areas ONLY
- body anesthesia
- minor surgeries
- clients who are unable to tolerate general anesthesia
GIVEN VIA: LOCAL IV, EPIDURAL SPACE (LABOR)
pt education taking lidocaine
- HIGH doses = LIFE THREATENING cardiac dysrhythmias
- hypotension in SPINAL ANAESTHESIA
SYSTEMIC ABSORPTION=
- high seizure risk
- respiratory distress
- restlessness
- tremors
- confusion
- CNS depression (rare)
- paraesthesia
nursing priorities for lidocaine
- frequent vitals/ monitor hypotension
- EPI or phenylephrine @ the ready
- frequent neuro checks
- respiratory assessments
contraindications for lidocaine use
- hx hypersensitivity
- hx hypersensitivity w/ similar anesthesia
- viscous lidocaine NEVER w/ children < 3y/o
- bradycardia
- heart block
- cardiac arrest UPON HOSPITAL ASMISSION
priority pts taking lidocaine
(MED INTERACTIONS:)
- beta blockers (increase lidocaine levels)
- cimetidine (increase lidocaine levels)
- quinidine (increase lidocaine levels)
- phenytonin (increase cardiac effects)
- procainamide (increases CNS + cardiac effects)
methohexital sodium MOA
general anesthesia, rapidly introduces anesthesia and hypnosis,
- increases GABA inhibitory effects
primary use for methohexital sodium
- "propofol" #1 COMMON INDUCING ANESTHESIA
- for inducing anesthesia in surgeries
- most misused med to induce sleep
pt education on methohexital sodium
in LARGE DOSES =
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- resp depression
- apnea/death
- extravasation (very common in poor venous access)
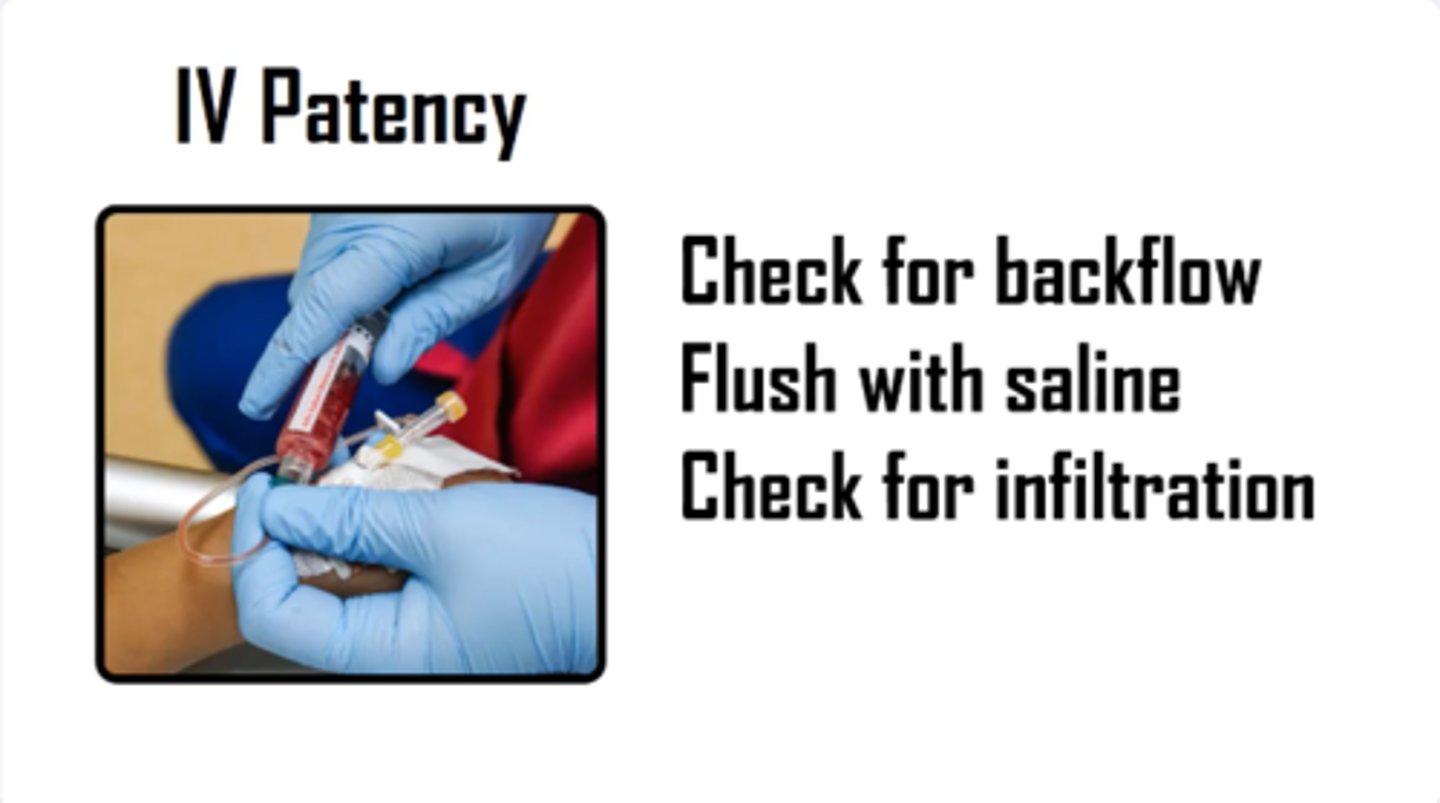
nursing priorities for methohexital sodium
- monitor IV site (PRIORITIZE IV PATENCY)
- PRIORITIAZE CENTRAL LINES w/ large bore IVs are next choice (18-20' gauge)
- frequent vitals
-stop infusion w/ s/s of infiltration
- recitation @ THE READY
contraindications for methohexital sodium
- Allergy to barbiturates
- CAUTION W/ HX HEPATIC/RENAL DISORDERS
(SYNERGIC MEDS):
- CNS depressants
- benzodiazepines (duplicate therapy) (ex: moazolam)
moazolam MOA
benzodiazapine anesthesia
- CNS depressant
- Increases GABA inhibitory effects
primary use for moazolam
- general anesthesia
- sedation
- hypnotic
GIVEN VIA: PO, IV, IM
pt education taking moazolam
- respiratory arrest
- cardiac arrest
- amnesia (memory loss)
nursing priorities for moazolam
- monitory vitals frequently
- slow IV push w/ 2min pauses between doses
- recitation @ the ready
- PRIOTIZE CAUTION W/ PTs hx of neuromuscular, cardiac, pulm, renal disorders
cardiac arrest s/s
- sudden collaspe/LOC
- gasping for air/SOB
- no pulse
- heart palaptions
contraindications w/ moazolam
(MED INTERACTIONS):
- anticonvulsants (SYNGERIC CNS effects)
- cimetidine (increases med toxicity)
- HERBAL PRODUCTS can lower or raise effects of meds
- pregnancy
- delivery
- lactation