Human Development Exam #4
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Define Attachment (p 412)
“Affectional”, emotional bond between two individuals over time and space
serves to join them emotionally
special intimacy that develops toward end of first year
John Bowlby (p. 412-415, 418-421)
Formal theory of Attachment!!
Emotional tie with another person
young kids seeking closeness to caregiver
show separation distress
Affects Emotional AND Cognitive development
"attachment figure serves as a secure base for exploration”
Attachment Theory (**KNOW!!)
forms in relationships where the infant gets…
Needs met consistently
Synchronous stimulation
Affection
Attachment Theory forms a…
secure base for exploration!
Define ‘Secure Base’ for Exploration
According to Bowlby, what purpose does the baby’s crying, clinging, cooing and smiling serve?
4 Phases of Attachment (p.415)
Undiscriminating Social Responsiveness
Discriminating Social Responsiveness
True Attachment
Goal-Corrected Partnership
Phase 1: Undiscriminating Social Responsiveness
birth to 2-3 months
Phase 2: Discriminating Social Responsiveness
2-3 months to 6-7 months
Phase 3: True Attachment
6 months to 3 years
Phase 4: Goal-Corrected Partnership
3 years +
What is social referencing (p. 407)?
Monitoring others’ reactions in ambiguous situations
using this info to regulate one’s own feeling & behaviors
What is emotional regulation (p. 407)?
Konrad Lorenz (p. 412)
Imprinting!!
Imprinting in GEESE
automatic
within critical period
irreversible
Define Imprinting (p. 412)
Joe Hutto: What did the turkey video illustrate?
Turkey Imprinting!!
talking “turkey” to unhatched, incubated eggs
eggs would respond back with “turkey noises”
eggs hatched
first thing the turkey sees is who they identify as their parent or develop a strong attachment to!!
Oxytocin (p414)
Harry Harlow
Contact Comfort!!
Harlow’s Surrogate Mother Experiments
Fear Response & Recovery
What is ‘contact comfort’ (p. 4)?
What 3 things did Harry Harlow’s studies show?
Monkeys preferred contact with CLOTH mother!!
When frightened, baby runs to CLOTH mother
When cloth mother was added, they EXPLORED
(monkeys in strange situations were scared and didn’t explore)
Mary Ainsworth (p.416-417)
Strange Situation Test!!
What is the Strange Situation Test & who invented it?
Mary Ainsworth
Assess quality of infant attachment
categorizes 4 attachment styles!!
secure
resistant
avoidant
disorganized
What specific behaviors are assessed (4 listed in lecture)?
Exploratory behavior
does figure serve as a “secure base,” do they explore?
Stranger anxiety
are they wary or outgoing with strangers?
Separation anxiety
upset to separation? try to follow?
Reaction to reunion
positive, negative, mixed, none
Describe infant behavior for secure and the several insecure attachments when in the Strange Situation Test (p. 325)
?????
4 Attachment Types (p. 416 & table 13.2 p.417)
Mary Ainsworth & Jon Bowlby
Secure
Resistant
Avoidant
Disorganized
3 INSECURE Attachments (+ parental factors)
Resistant (inconsistent)
Avoidant (unresponsive or intrusive)
Disorganized (abusive)
Infant temperaments that contributes to all insecure types
difficult, fearful, reactive
Secure Attachment
65-70%
Mother as secure base
enters room easily, explores
outgoing with strangers when mother is present
normally upset with separation
happy reunion
Infant: easy going
Parent: synchronous interaction, sensitive, responsive
Resistant (insecure) Attachment
10%
Anxious, clings to mother
no exploration
fearful of strangers even when mom is there
extremely upset by separation
ambivalent reunion! (seeks nearness but resentful)
Infant: reactive, difficult, vigorous
Parent: inconsistent, often unresponsive, ex: depressed mom
Avoidant (insecure) Attachment
15%
Indifferent
explores, but play is not as constructive
no separation anxiety
no reaction to strangers
no reaction/ ignores reunion
avoids caregiver
Infant: difficult, reactive, doesn’t show emotional needs
Parent: rejecting/ impatient OR intrusive/ overzealous
Disorganized/ Disoriented (insecure) Attachment
5-10%
No exploration
confused response to strangers
variable separation anxiety
variable reunion (may approach, avoid, both, idk)
Infant: confused, possible neurological problem
Parent: physical abuse, unpredictable, loving one minute, abusive/indifferent the other, can be bc of alcohol, drugs, depression
Define Separation Anxiety
Define Stranger Anxiety
What are the 3 parenting behaviors (listed at the beginning of the lecture -see lecture outline on Canvas) that contribute to a secure attachment?
How is attachment assessed?
What does your text say about German and Japanese babies put through the strange situation test (p. 418- 419) – what might explain those differences??
What effect does attachment style have on your future personality, memory, and cognition?
Personality
3 yrs SECURE:
bold, socially competent, sensitive, initiates play activities
Memory
securely attached: positive details
insecurely attached: negative details
Malleable????
50% changes from one testing to the other
later secure attachment may compensate
How do mother’s and father’s interaction with the child differ?
What does your text say about childcare and attachment (p. 420)?
Adult romantic relationships are a result of what?
infant attachment!
4 ADULT Attachment Types
Secure
Preoccupied
Dismissing
Fearful
Adult: Secure Attachment
(secure infant attachment)
Healthy balance of attachment and autonomy
not afraid of intimacy or abandonment
share thought and feelings
longer lasting relationships
responsible, comfortable
trust and positivity
Adult: Preoccupied Attachment
(resistant infant attachment)
Clingy, worry about abandonment, express anxiety/ anger
Crave closeness
Overly dependent on partner
may view self as unworthy of it
Highly fearful of abandonment
Adult: Dismissing Attachment
(avoidant infant attachment)
Avoid intimacy, “self-reliant”
positive view of self but do not trust others
Do not trust partners and keep them at a distance
Shut down emotions
Value personal independence and sense of worth
Adult: Fearful Attachment
(disorganized infant attachment)
Need relationships but doubts/ fears intimacy, lacks coherent strategy
Suspicious and anxious
Avoid any type of intimate relationships
Adult Attachment Revisited
Experience strong affection for partner
Seeks proximity
Takes comfort from the bond to the attachment figure
Upset by separation
Define Peer (p. 413)
Social EQUALS
similar level of behavioral complexity, (age)
Peer relationships have equal power (appreciate & negotiate)
Mildred Parten’s 6 ways of Play (3 categories)
NONSOCIAL
Unoccupied - not playing, wandering around
Solitary- by yourself
Onlooker - observing other people play
PARALLEL
Parallel- playing with each other, doing same thing, but NOT interacting
TRUE SOCIAL
Associative - doing same thing, but NOT towards common goal
Cooperative - working together for a common goal
Play Age Development
6 months
smile, babble, offer toys, gesture
18-24 months
turn-taking, reciprocal
social imitation
offer toy if receiving one
chase, then be chase d
6-7 years: Rule-Governed Play
games with rules
hobbies with instructions
Basis of Friendship across lifespan
Early childhood- preschool
Middle-late childhood
Adolescent
Adult
Early Childhood- Preschool Friendships
Common activities
someone who likes you and you play with
more emotionally expressive
give and receive more reinforcement (greetings, praise)
Middle-Late Childhood Friendships
Chumships (9-12 yrs)
Mutual relationship: “best friend”
trust and mutual loyalty
like personal qualities
responds to each other’s needs
same age, gender
breaches of trust (ex: breaking promises, gossip)
Adolescent Friendships
Intimacy and Self Disclosure
similar psychological qualities
“Collectives”:
unique values and standards
leadership
Peer Culture:
specialized vocab, dress code and place to “hang out”
seek group membership
Adult Friendships
Confidant
Feel attachment
can share your thoughts and feelings
Cliques
Same-sex friendship groups
provides secure base for peer relationships
venturing into romantic relationships
Heterosexual Cliques
group of popular dating pairs
Crowd
Collection of several heterosexual cliques together to organize social activities
ex: party
True or False: Young adults (esp. single) have more friends.
TRUE
have more friends than middle & older adults
Social stimulation & new information
What is the Socioemotional Selectivity Hypothesis?
(Remember story of Dr. Michalski’s parents and their 50th wedding anniversary)
Adult social networks SHRINK
quantity for quality
we actively narrow social network to those who best meet our needs
less desire for social stimulation & new info
Know (and be able to reproduce) Sternberg’s triangle of love p. 432 (Know the LECTURE VERSION!!)
Intimacy, Passion, Commitment

Sternberg’s Intimacy
EMOTIONAL part of love
Liking
feelings of warmth, comfort, closeness, respect, understanding towards another person
Trust, open communication
Concern about other’s well-being
Happiness
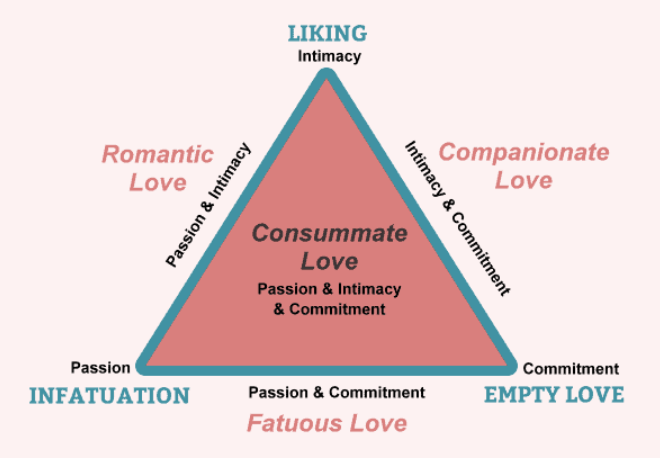
Sternberg’s Passion
PHYSICAL part of love
Infatuation
chemistry
sexual attraction
excitement
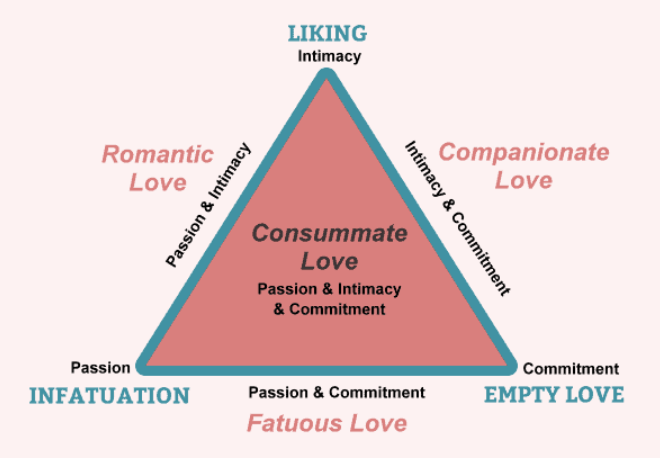
Sternberg’s Commitment
COGNITIVE aspect of love
Empty
deciding to maintain love
long-term relationship
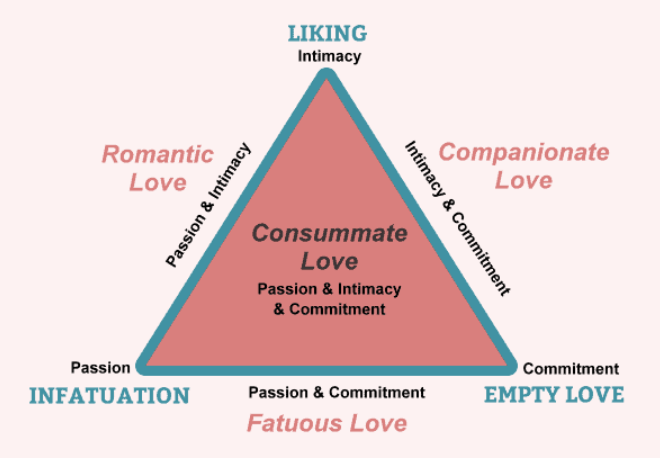
Sternberg’s Romantic
passion & intimacy
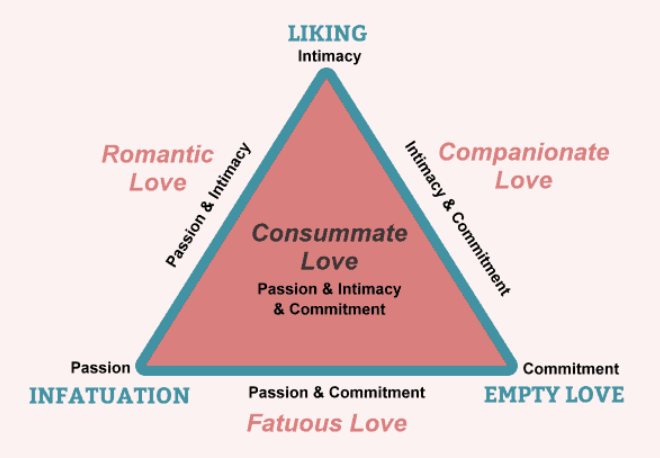
Sternberg’s Compasionate
intimacy & commitment
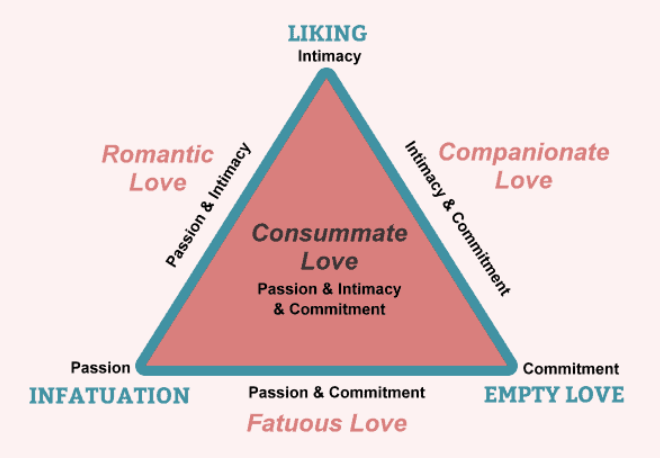
Sternberg’s Fatuous
passion & commitment
Sternberg’s Consumate
ALL 3!! (passion, intimacy and commitment)

Define Personality
Characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and behaving
self-concept
self esteem
“Temperament” in infancy/ childhood
present at birth
corresponds to “traits” as an adult
Self-Concept
your PERCEPTION of yourself (+ or -)
Self-Esteem
your EVALUATION of yourself
based on self-concepts
5 people of CHANGE THEORY
Freud: psychoanalytic, psychosexual
Erickson: psychosocial
Marcia: status
Bandura: social learning, situational
Erikson’s Stages
(positive/ healthy or negative outcome)
Trust v. Mistrust
Identity v. Role Confusion
Intimacy v. Isolation
Generativity v. Stagnation
Integrity v. Despair
Erikson: 1) Trust v. Mistrust
0-1 year
Needs met, attachment formed
HOPE!!
learns about the world and themselves
Erikson: 5) Identity v. Role Confusion
12-20 yrs
Develop sense of self
FIDELITY!!
Who am I? Where am I going? How do I fit in?
societal roles
groups you are a part of
Identity Crisis (Erikson stage 5)
Difficulty expressing your values, attitudes and beliefs
harder when they are different from those around you
its’s likely to create conflict
ex: Religion, politics, career choice, sexual orientation Moving out, marriage
Erikson: 6) Intimacy v. Isolation
20-40 yrs
Emotional closeness, adult attachment
LOVE!!
INTIMACY
formed identity, comfortable in relationships
trust themselves and others
cooperative
emotional ties without fear
ISOLATION
hesitant to get close, lack of trust
low tolerance for differences
give little of themselves, competitive
Erikson: 7) Generativity v. Stagnation
40-65 yrs
Sense of purpose and productivity
CARE!!
genes
generate
generation
Genes (Erikson stage 7)
Am I producing something that lives on after me?
Generate (Erikson stage 7)
Universal sense of responsibility toward human beings
Provide strength and support to the next generation
so it can come to face ultimate concerns in its own way
Generation (Erikson stage 7)
Am I being productive or stagnating?
Erikson: 8) Integrity v. Despair
65+ yrs
Evaluation of life: Satisfaction or failure
WISDOM!
INTEGRITY
content with life, approach with gratitude
self-confident
life story made, have meaning and purpose
DESPAIR
regret
fear of death
blame others for situation
easily pushed around
See ‘Life Review’/ Define identity
James Marcia’s expansion of Erikson’s identity stage (p.320-321)
(expanded 5th stage: Identity vs. Role Confusion)
Adolescent Identity Development
Research to explore political, religious, and occupational views
2 key elements
4 identity statuses
Marcia’s 2 key factors
Exploration
Commitment
Marcia’s 4 states of identity achievement
Diffusion
Foreclosure
Moratorium
Identity Achievement
Identity Achievement: Diffusion
postponement of identity crisis
NO exploration
NO decision
life may be chaotic, disorganized
low intimacy
Identity Achievement: Foreclosure
identity chosen in early adolescence
NO exploration
MADE decision!!
family goals, traditions
external locus of control
truly limited options
Identity Achievement: Moratorium
unable to make decisions and commitments
NO decision
STILL exploring
sense of urgency
anxious but open to new experiences
Identity Achievement: Identity Achievement
individual commits to option that best fits them
EXPLORATION & COMMITMENT!
most mature
40% of college students
What percent of college students have achieved a clear sense of identity?
40%
MAMA
Marcia’s Expansion in Adulthood (go through every 7 years)
moratorium
identity achievement
moratorium
identity achievement
STABILITY (psychometric/ trait) THEORY!!
“Big Five” OCEAN Dimensions of Personality
Openness
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
assessed by: personality inventories, peer ratings, factor analysis
Trait Theory
stability theory
Personality is relatively ENDURING PATTERNS of thought, feelings & behavior called ‘traits’
Genetically based
Characteristic pattern of behavior
Typical way of thinking or feeling
Self-proclaimed motives
Psychometric Theory
stability theory
Personality can be MEASURED
pencil/ paper tests
Big 5: Openess
(stability theory)
from curiosity and interest to a preference for sameness
Imaginative vs. practical
Preference for Variety vs. Preference for Routine
Independent vs. Conforming
Big 5: Conscientiousness
(stability theory)
from discipline and organization to lack of seriousness
Organized vs. Disorganized
Careful vs. Careless
Disciplined vs. Impulsive
Big 5: Agreeableness
(stability theory)
from compliance and cooperativeness to suspiciousness
Soft-Hearted vs. Ruthless
Trusting vs. Suspicious
Helpful vs. Uncooperative
Big 5: Extraversion
(stability theory)
from sociability and outgoingness to introversion
Sociable vs. Retiring
Fun-Loving vs. Sober
Affectionate vs. Reserved
Big 5: Neuroticism
(stability theory)
from emotional stability to emotional instability
Calm vs. Anxious
Secure vs. Insecure
Self-Satisfied vs. Self Pitying
Bandura: Social Learning / Reciprocal Determinism (p. 311)
Personality is influenced by the situation/social context
& person’s interpretation of the situation
person, behavior and environment are connected!!
assessed by observations of people’s behavior in certain situations
questionaries about feeling of control
