BIO Chapter 3: Organic Molecules and Macromolecules
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What distinguishes organic compounds from inorganic compounds?
Organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen, while inorganic compounds do not.
How are atoms in organic molecules typically connected?
Atoms in organic molecules are usually connected by covalent bonds.
What type of bonds are found in inorganic compounds?
Atoms in inorganic molecules are usually connected by ionic bonds.
What is the primary source of organic compounds?
Organic compounds are made by living organisms.
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
C6H12O6
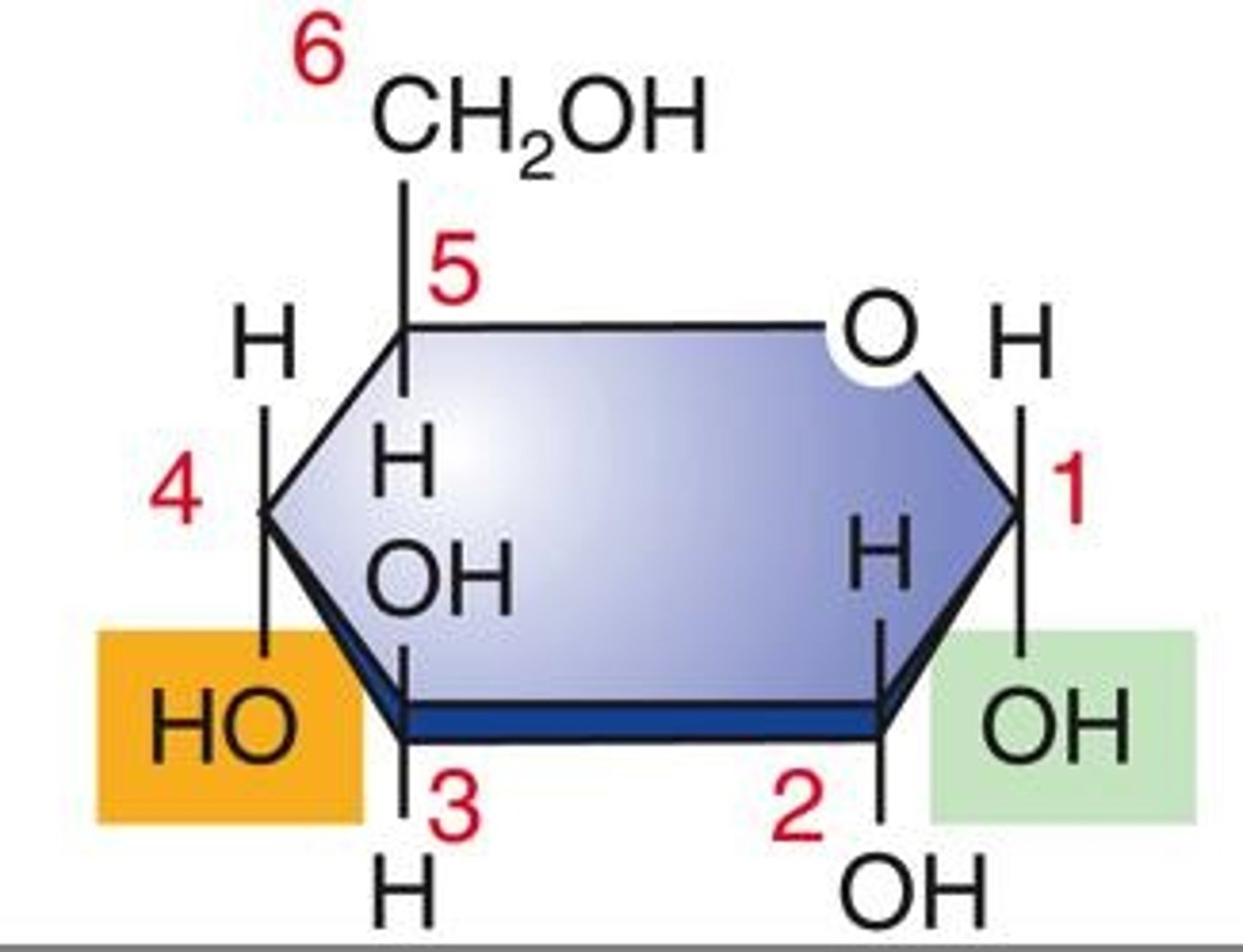
Is glucose an organic or inorganic molecule?
Glucose is an organic molecule because it contains carbon and hydrogen.
What is the classification of NaCl?
NaCl is classified as an inorganic compound because it does not contain carbon or hydrogen.

What is HCl classified as?
HCl is classified as an inorganic compound.
What are the macroelements essential for life?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHONPS).
What are microelements and their role?
Microelements include Mg, K, Mn, Ca, Fe, and Cu, and they are needed in smaller amounts, usually as cofactors for enzyme function.
What type of bond is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms.
What is a disulfide bond?
A disulfide bond is a covalent bond between two sulfur atoms.
What characterizes a hydrogen bond?
A hydrogen bond is a bond between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules?
Polar molecules have a partial charge due to unequal sharing of electrons, while nonpolar molecules have an even distribution of charge.
What are the functional groups that are polar?
Polar functional groups include hydroxyl (R-OH), carbonyl (R-C=O), carboxyl (R-COOH), amino (R-NH2), sulfhydryl (R-SH), phosphate (R-PO4), and sulfate (R-SO4).
What are the two main types of reactions for macromolecule formation?
The two main types of reactions are dehydration synthesis (to connect subunits) and hydrolysis (to break down polymers).
What is produced during dehydration synthesis?
A molecule of water is produced when two monomers are connected.
What occurs during hydrolysis?
During hydrolysis, a covalent bond between two subunits is broken, producing two smaller molecules and consuming a molecule of water.
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
The general formula for carbohydrates is CH2O.
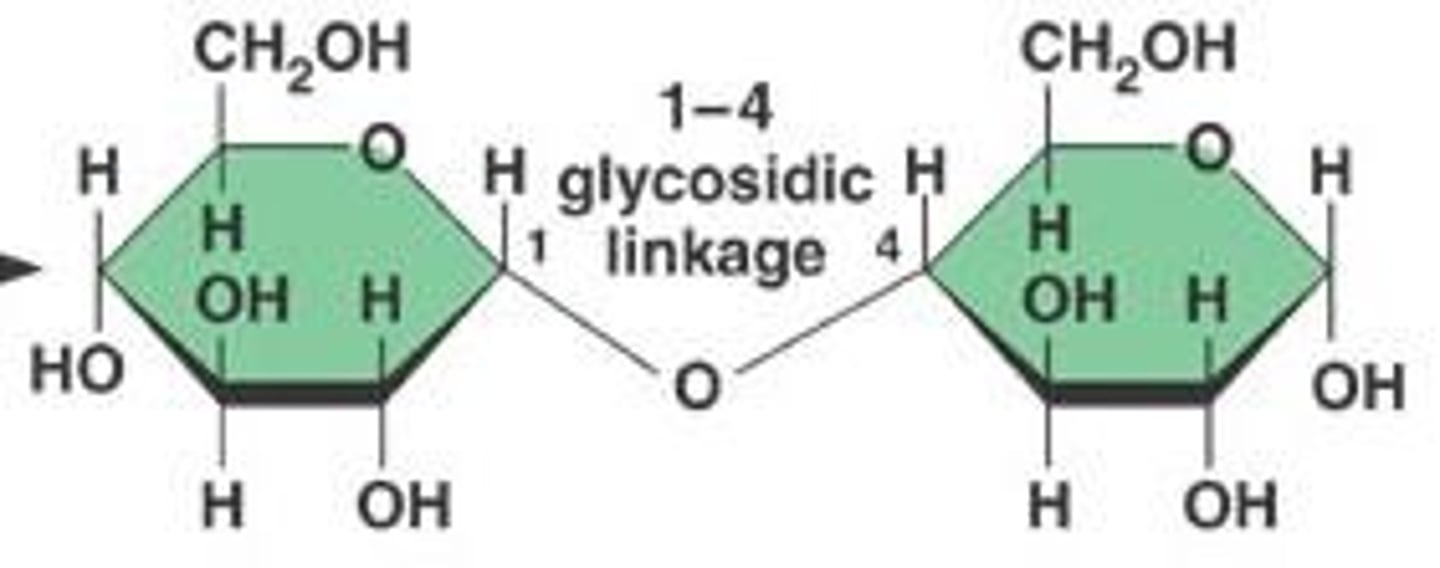
What type of bond connects sugars in disaccharides?
Sugars in disaccharides are connected by a covalent bond called a glycosidic bond.
What is the storage form of energy in cells?
The storage form of energy in cells is starch.
What type of glycosidic bonds connect sugars in starch?
Sugars in starch are connected by alpha (α) glycosidic bonds.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are long polymers made of sugar subunits, which can be straight or branched.
What are the two main types of carbohydrate storage in plants and animals?
Plants store carbohydrates as starch, while animals store them as glycogen.
What type of glycosidic bonds are found in starch and glycogen?
Both starch and glycogen contain alpha (α) glycosidic bonds.
What is cellulose and how does it differ from starch and glycogen?
Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide with glucose polymers connected by beta (β) glycosidic bonds, making it stable and unbreakable by most organisms.
What are glycoproteins?
Glycoproteins are proteins that have sugars covalently attached to them.
What are the three main functions of carbohydrates?
1. Food/Energy: Used to create short-term chemical energy. 2. Storage: Serve as a stored form of chemical energy. 3. Structure: Act as structural components in cells.
What is the structure of amino acids?
Amino acids consist of an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and an R group.
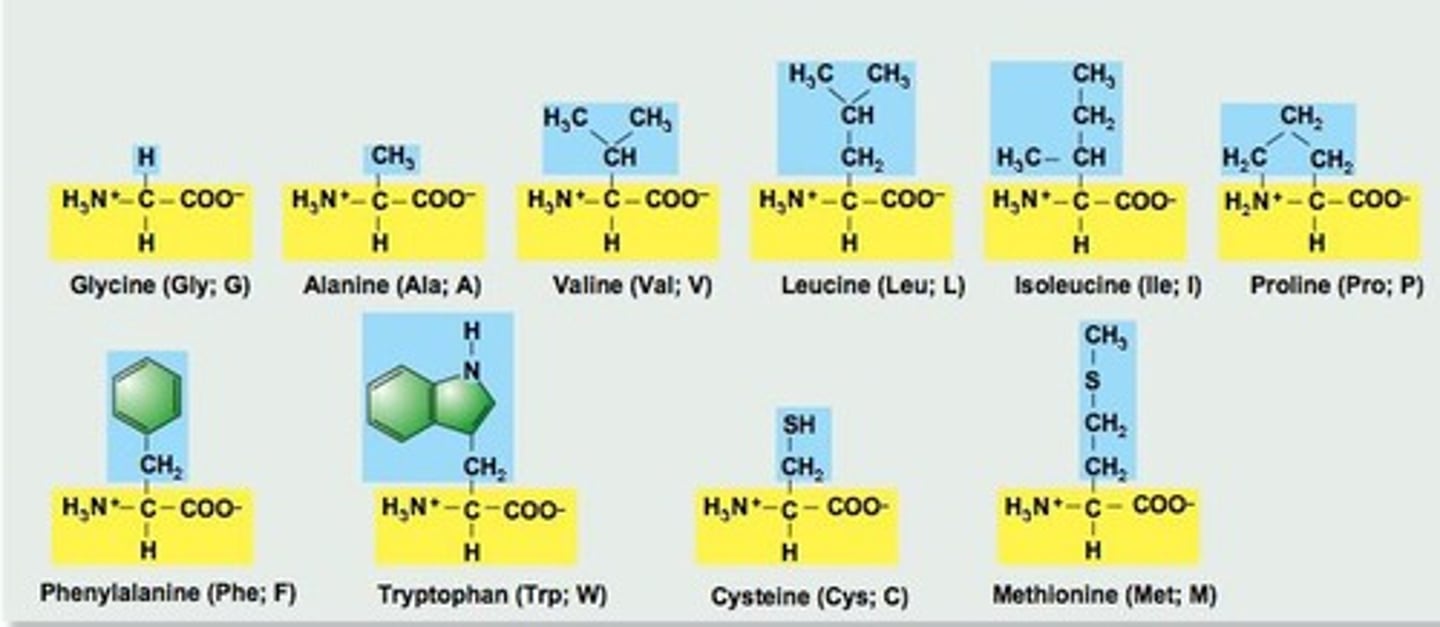
What are the three types of amino acids based on polarity?
1. Nonpolar or uncharged amino acids. 2. Polar (uncharged) amino acids. 3. Polar (charged) amino acids.
What connects amino acids together?
A peptide bond connects amino acids.
How is a peptide bond formed?
A peptide bond is formed when the OH of one amino acid combines with an H from another amino acid, releasing a molecule of H2O in a dehydration synthesis reaction.
What is a polypeptide?
A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids.
What are the N terminus and C terminus of a protein?
The N terminus is the front end of a protein with an amino group, while the C terminus is the rear end with a carboxyl group.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds.
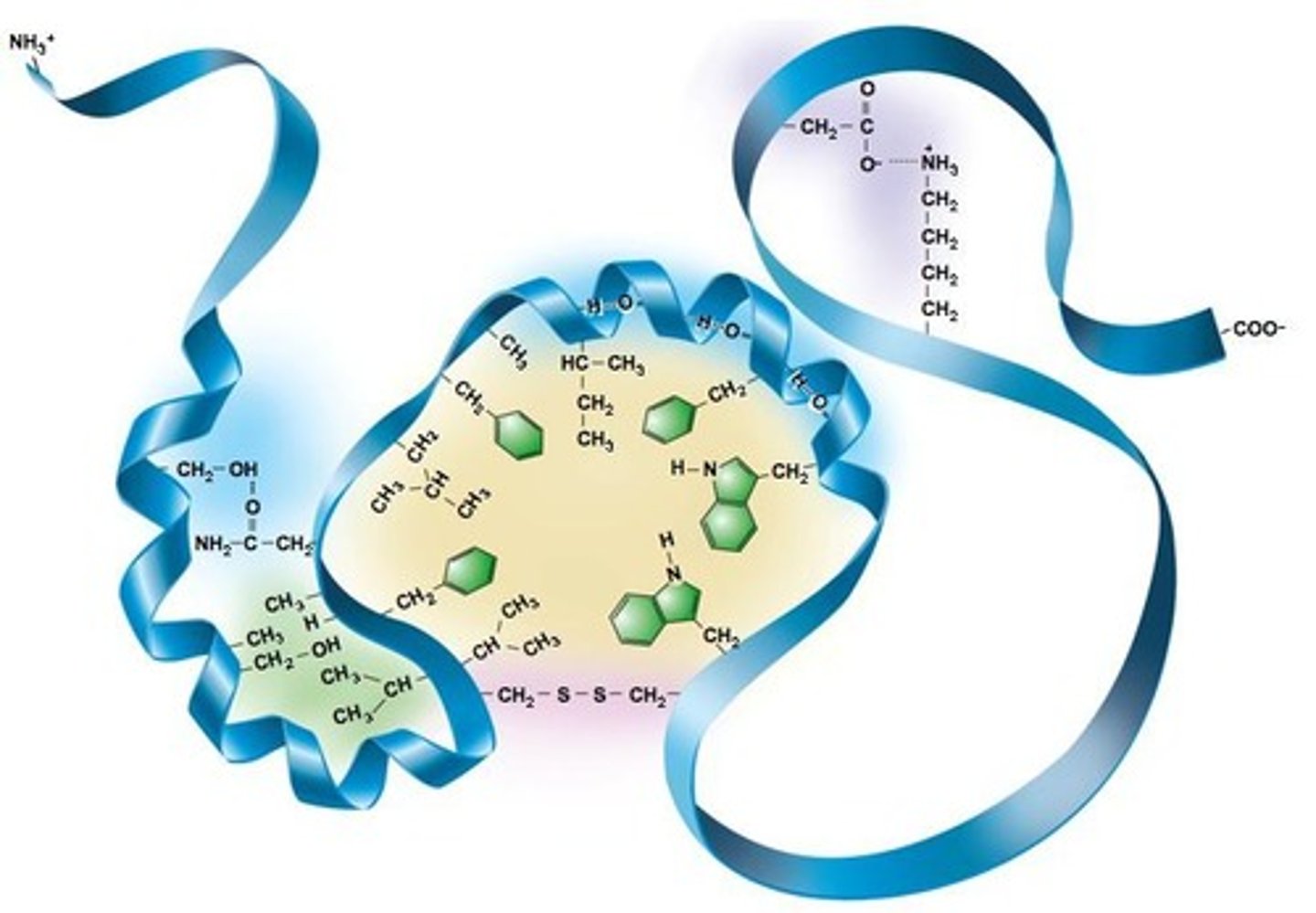
What characterizes the secondary structure of proteins?
Localized folding of the polypeptide chain, mainly due to hydrogen bonds, with examples including alpha helices and beta sheets.
What defines the tertiary structure of a protein?
The final 3D structure of a polypeptide chain, involving interactions between distant amino acids.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The interaction between different protein subunits to form the whole protein, applicable only to proteins with more than one subunit.
What types of bonds are involved in the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of proteins?
Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals forces.
What happens during protein denaturation?
Proteins unfold and no longer function properly due to the breaking of bonds involved in their 3D structure.
What are the main functions of proteins?
Enzymes, structural proteins, receptor proteins, transport proteins, and hormones (e.g., insulin).
What are nucleic acids composed of?
Nucleotides, which consist of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
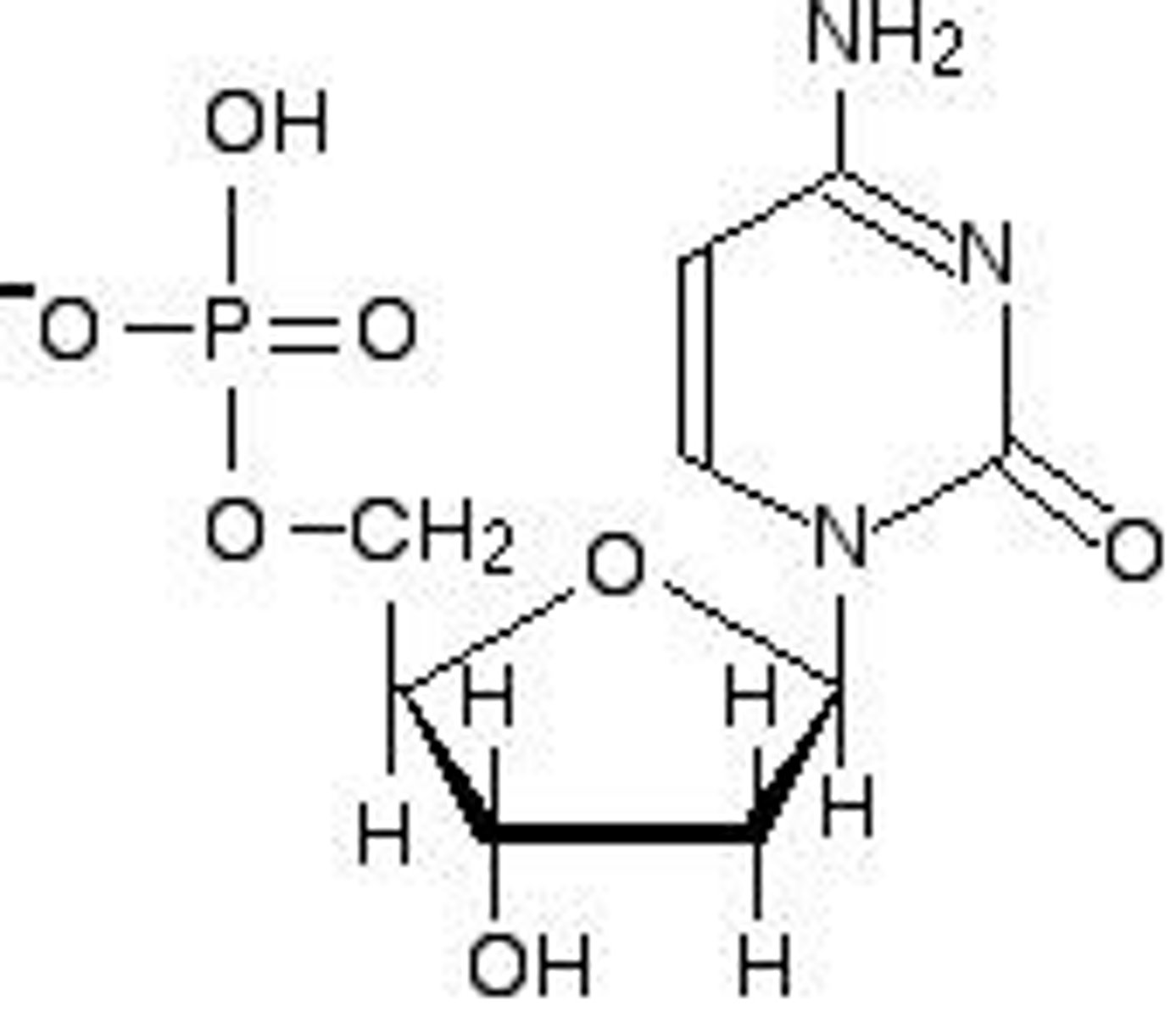
What distinguishes RNA from DNA in terms of sugar?
RNA contains ribose, while DNA contains deoxyribose.
What are the nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil (AGCU).
What are the nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine (AGCT).
How are nucleotides in the same strand of DNA connected?
By phosphodiester bonds.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is double-stranded with antiparallel strands, where bases in opposite strands are connected by hydrogen bonds.
What is the function of DNA?
To serve as the genetic blueprint, containing genes that code for proteins.
What is the function of mRNA?
To code for proteins.
What is the role of tRNA?
To bring amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
What is the structural role of rRNA?
To form part of the ribosome.
What distinguishes saturated fats from unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature with single bonds in fatty acids, while unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature with at least one double or triple bond.
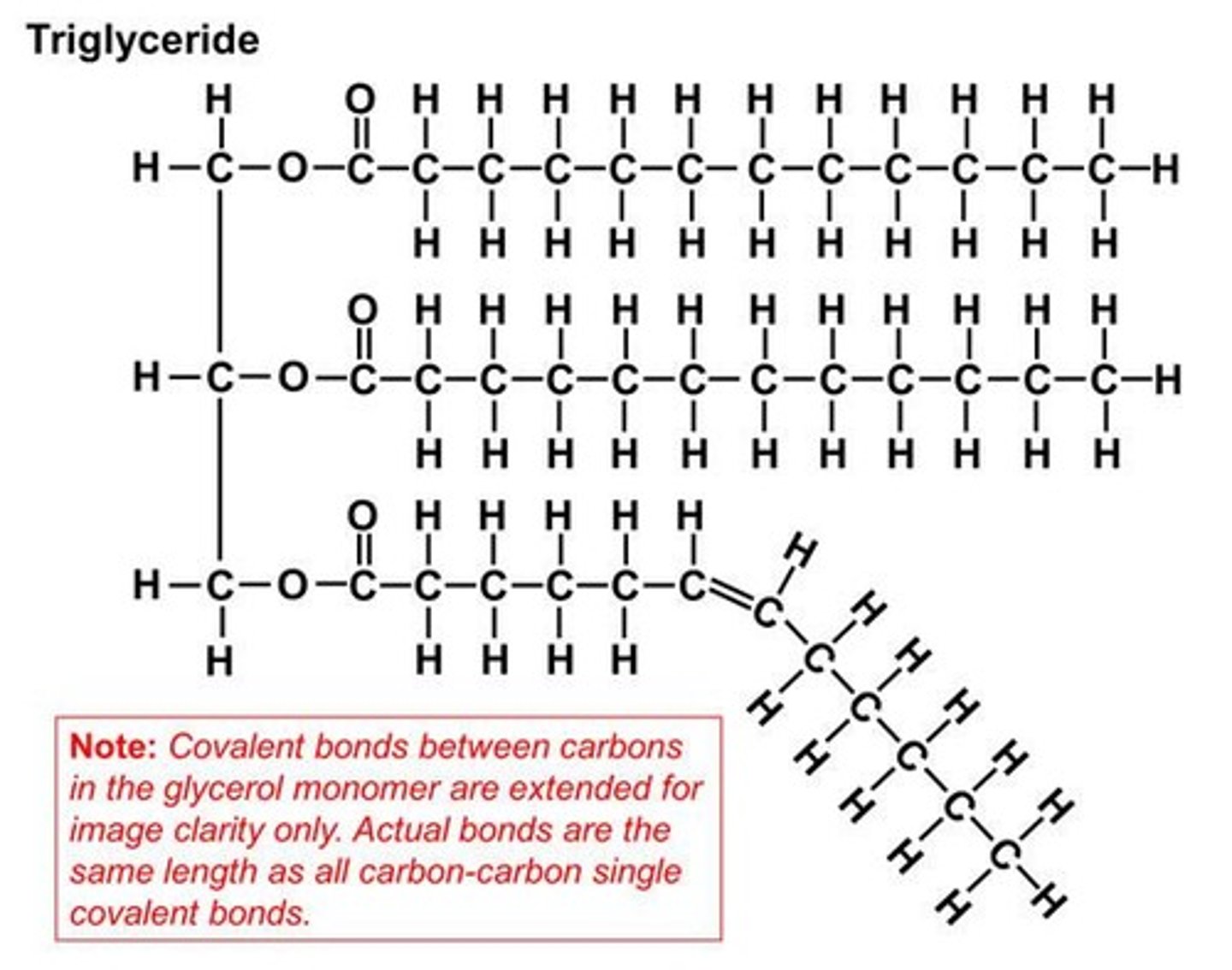
What is the structure of triglycerides?
Composed of glycerol and three fatty acids.
What is the function of phospholipids?
To form the phospholipid bilayer, a key component of cell membranes.
What is an amphipathic molecule?
A molecule that has both a polar end and a nonpolar end, such as fatty acids and phospholipids.
What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The fatty acid tails.
What reaction connects two amino acids to form a peptide bond?
Dehydration Synthesis, producing a molecule of H2O.
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary.
What defines the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds.
What characterizes the secondary structure of a protein?
Localized folding of the polypeptide chain, mainly due to hydrogen bonds, with examples like alpha helix and beta sheet.
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The final 3D structure of a polypeptide chain, involving interactions between distant amino acids.
What happens to proteins during denaturation?
They unfold and no longer function properly due to broken bonds involved in their 3D structure.
What are the functions of proteins?
Enzymes, structural proteins, receptor proteins, transport proteins, and hormones like insulin.
What are nucleic acids made of?
Nucleotides, which consist of a 5-carbon sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base.
What is the difference between RNA and DNA in terms of sugar?
RNA contains ribose, while DNA contains deoxyribose.
What are the purines and pyrimidines in nucleic acids?
Purines: Adenine and Guanine; Pyrimidines: Cytosine, Thymine (DNA), and Uracil (RNA).
How are nucleotides connected in a strand of nucleic acid?
By phosphodiester bonds.
What are the complementary base pairs in DNA?
A pairs with T, and G pairs with C.
What are the functions of RNA?
mRNA codes for proteins, tRNA brings amino acids to ribosomes, rRNA is a structural part of ribosomes, and snRNA is involved in RNA splicing.
What are the key differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded with deoxyribose and contains thymine; RNA is single-stranded with ribose and contains uracil.
What is the general formula for lipids?
CHO (mostly carbon and hydrogen, with very little oxygen).
What are the types of lipids?
Triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
What is the structure of phospholipids?
Glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group with a polar head group.
What is the hydrophobic effect in relation to phospholipids?
Phospholipids assemble into a bilayer with hydrophobic tails facing each other and polar head groups exposed to water.
What is the difference between ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleotides?
Ribonucleotides contain ribose sugar, while deoxyribonucleotides contain deoxyribose sugar.
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases?
Purines (two rings, e.g., adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (one ring, e.g., cytosine, thymine, and uracil).
How are nucleotides connected in a nucleic acid strand?
By phosphodiester bonds, forming a sugar-phosphate backbone.
What is the function of RNA?
RNA codes for proteins (mRNA), brings amino acids to the ribosome (tRNA), and is a structural part of the ribosome (rRNA).
What are the main differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded, contains deoxyribose, and has thymine; RNA is single-stranded, contains ribose, and has uracil.
What are the types of lipids mentioned?
Triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
How do phospholipids arrange in a membrane?
They form a bilayer with hydrophobic tails facing each other and polar headgroups exposed to water.
How are phospholipids arranged in a membrane?
Hydrophobic parts are arranged tail to tail in the middle, while hydrophilic parts are on the outer and inner surfaces.
What is the structure of cholesterol?
Cholesterol consists of 4 characteristic rings plus a side chain.
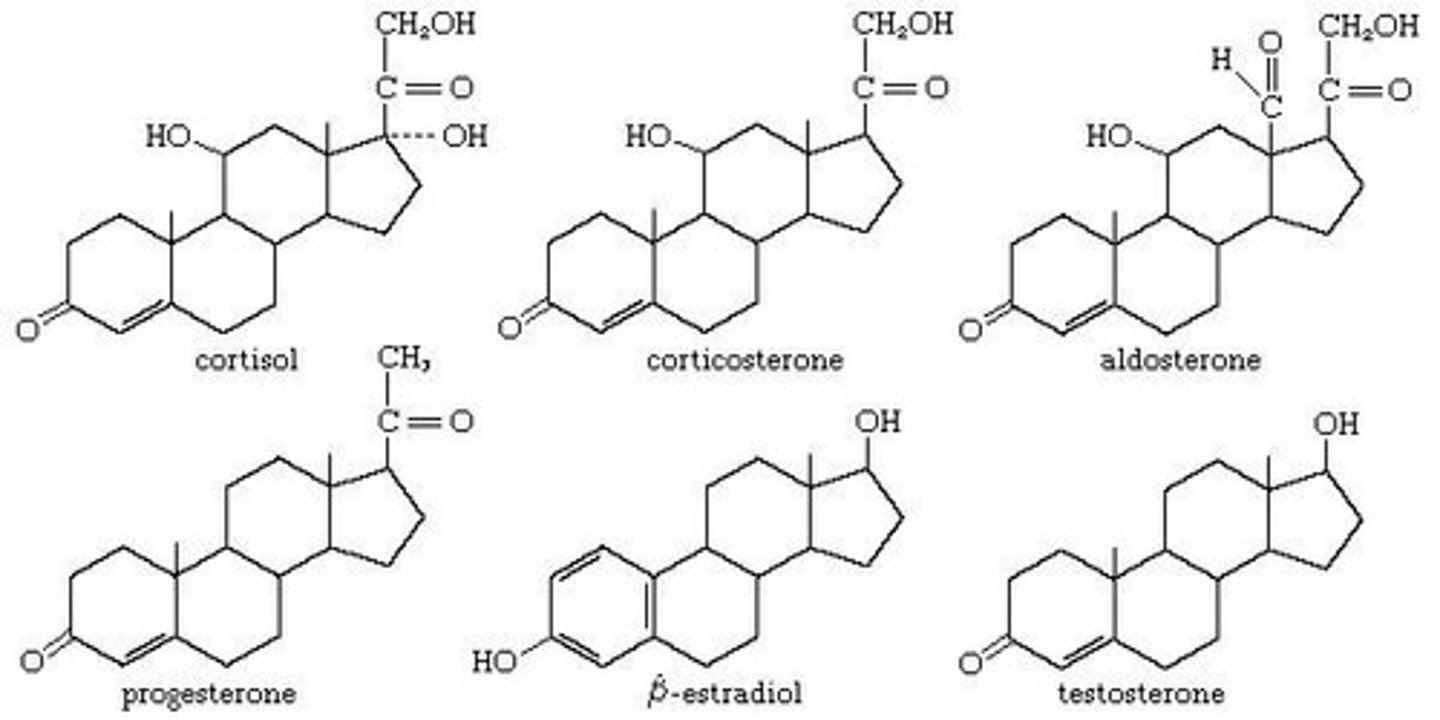
What are the functions of cholesterol in biological membranes?
Cholesterol acts as a component of membranes and functions as a hormone.
What types of hormones are some steroids classified as?
Some steroids are classified as sex hormones.
What are the main functions of lipids?
Membrane structure (phospholipids, cholesterol), energy storage (triglycerides), hormones (steroids), and pigments (chlorophyll, carotene).
Name five functional groups you should be able to identify.
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Carbonyl, Amino, Phosphate, Sulfhydryl, Methyl.
What types of molecules should you be able to identify in diagrams?
Sugar (disaccharide), amino acid, nucleotide, fatty acid, triglyceride, phospholipid, steroid.
What is the composition of an amino acid?
An amino acid contains CHON (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen), an amino group, a carboxyl group, a central carbon, and an R group.
What characterizes a disaccharide?
A disaccharide consists of 2 sugars connected together, typically in ring form, and contains CHO in a CH2O ratio.
What elements are found in nucleotides?
Nucleotides contain CHONP (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus).
What is the structure of a triglyceride?
A triglyceride consists of glycerol and 3 fatty acids and contains mostly carbon and hydrogen.
What is the structure of a steroid?
A steroid consists of 4 rings joined together and contains mostly carbon and hydrogen.
What is the charged form of a carboxyl group?
The charged form of a carboxyl group is -COO⁻.
What is the significance of nitrogen in amino acids and nucleotides?
Only amino acids and nucleotides contain nitrogen (N).
Why is a molecule not classified as a nucleotide if it lacks sugar and phosphate?
A molecule is not classified as a nucleotide if it lacks a sugar and a phosphate group.
What functional groups are present in an amino acid?
An amino acid contains an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group.
What functional groups are present in a nucleotide?
A nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the chemical formula ratio for sugars?
Sugars have a chemical formula in the CH2O ratio.