HIV Pathogenesis & Therapy
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the specific laboratory tests used to identify and diagnose HIV?
HIV Tests
Antibody test → detects up to 12 wks post exposure but have to wait longer to take (3 wks)
4th gen test (abs + antigens) → detects up to 6 wks post exposure
Nucleic acid test (NATs) → detects up to 1 mo post exposure but only have to wait 1 wk
Specific labs:
CD4 count → detects extent of immune damage (goal = >500)
Plasma viral load (goal = undetectable)
Explain the difference between HIV and AIDS
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
It’s a virus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which help the body fight infections.
A person with HIV can look and feel healthy for many years.
HIV can be controlled with medicine (called antiretroviral therapy or ART), so people can live long, healthy lives.
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
It is the last and most serious stage of HIV.
AIDS happens if HIV is not treated.
Requires CD4<200 or hx of AIDS defining illness (basically any other condition that stemmed from HIV infx because immune system very weak)
Evaluate route of transmission of HIV
🔴Highest Risk
Mother to baby (no medicine) – 24%
Receptive anal sex – 0.3% to 3%
Sharing needles – 0.67%
Needlestick injury (blood exposure) – 0.3%
🟠 Moderate Risk
Receptive vaginal sex – 0.1% to 0.2%
Insertive vaginal sex – 0.03% to 0.14%
Blood to mucous membranes (like eyes or mouth) – 0.09%
🟡 Lower Risk
Insertive anal sex – 0.06%
Receptive oral sex (male) – 0.06%
Female-female oral contact – Very rare (only 4 known cases)
Explain the mechanism of action of antiretroviral medications and how they affect the HIV lifecycle
NNRTIs- Reverse transcription inhibitors
NRTIs- Reverse transcription inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors- inhibit virus integration
Protease inhibitors- inhibits budding (turning immature virus into mature infectious virus)
CIs- Breaks down capsid that holds in virus DNA
What are the pre-treatment tests needed prior to ARV initiation?
HIV test
CD4 count
Plasma viral load (RNA)
CBC
chem panel
BUN, SCr
Glucose/A1C
Lipid panel
Liver function
Urinalysis (if starting tenofovir)
Hep A/B/C, Syphilis, toxoplasma gondii IgG, TB
Identify the classes of antiretroviral drugs
NRTIs (nucleo reverse transcriptase inhibitors)
NNRTIs (nonnuclo reverse transcriptase inhibitors)
PIs (protease inhibitors)
EIs (entry inhibitors)
INSTIs (integrase inhibitors)
CIs (capsid inhibitors)
NRTI drugs
All, Elephants, Love, Tacos
Abacavir
Emtricitabine
Lamivudine
Tenofovir DF
Tenofovir AF
NNRTI drugs
Never, Eat, Really, Dry, Eggs
Nevirapine
Etravirine
Rilpivirine
Doravirine
Efavirenz
Protease inhibitor drugs
Darunavir
Darunavir + Cobicistat
Ritonavir
EIs (entry inhibitors)
~ Every, Monkey, Fights, Infection
Enfuvirtide
Maraviroc
Fostemsavir
Ibalizumab
INSTIs (integrase inhibitors)
-gravirs
CIs (capsid inhibitors):
Lenacapavir (adjunct only)
Cobicistat (boosting agent only NO antiviral activity)
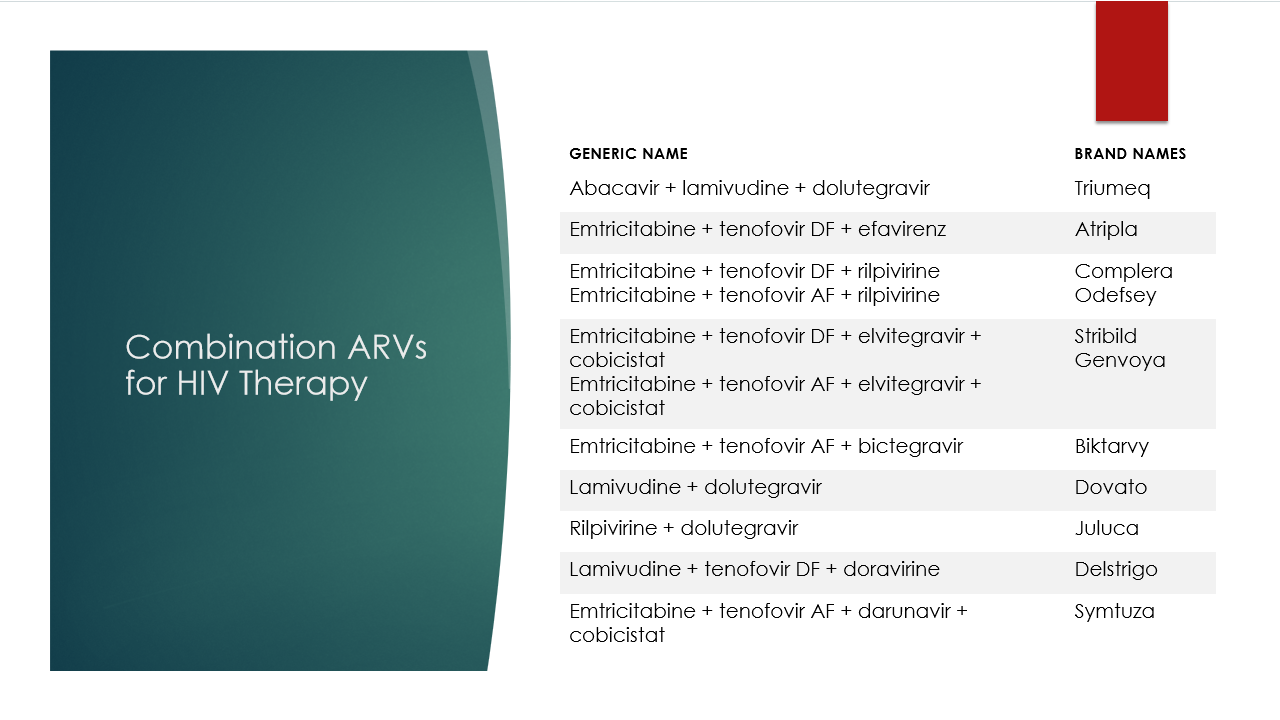
What are the common NRTI combinations and associated brand names?
Abacavir + Lamivudine (Epzicom)
Emtricitabine + Tenofovir
DF (Truvada)
AF (Descovy)
What is the difference between tenofovir DF and AF formulation?
AF has higher bioavailability than DF → lower dose necessary
What are the combination ARVs for HIV therapy including brand names?
When should treatment be initiated in HIV positive patients?
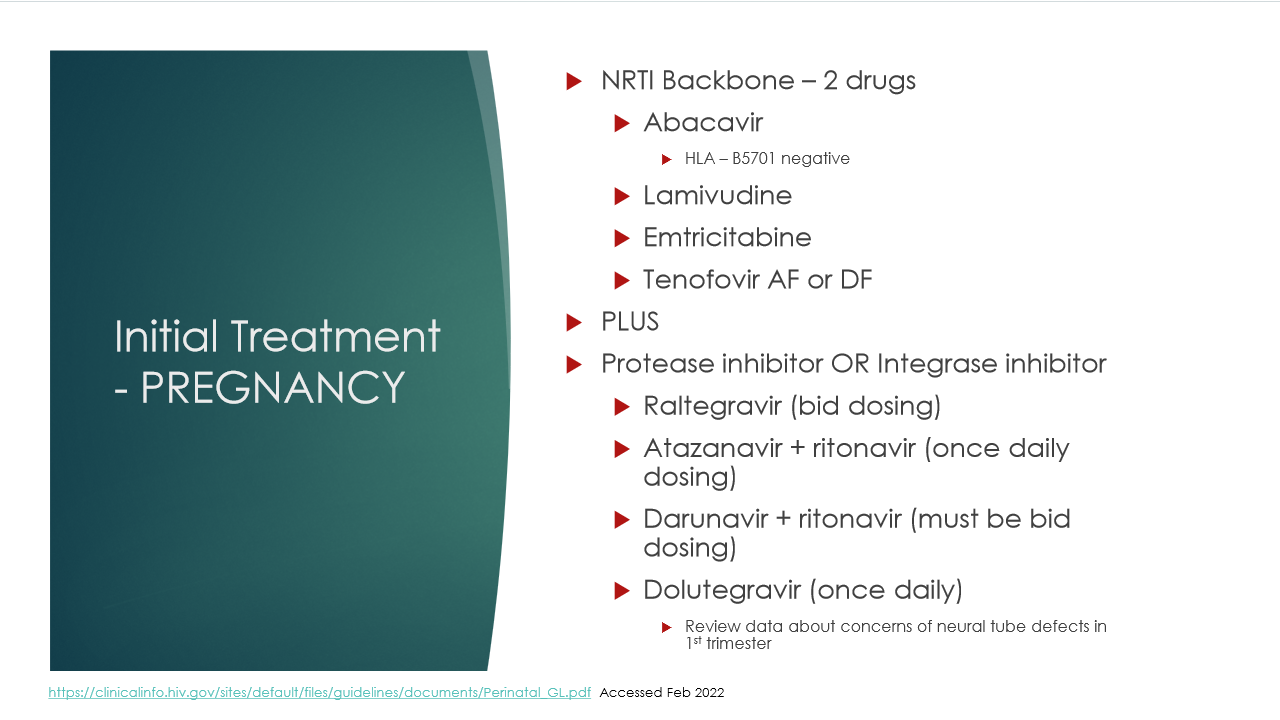
hx of AIDS illness
pregnant
HIV nephropathy
hep b/c coinfection
any CD4 count
everyone!
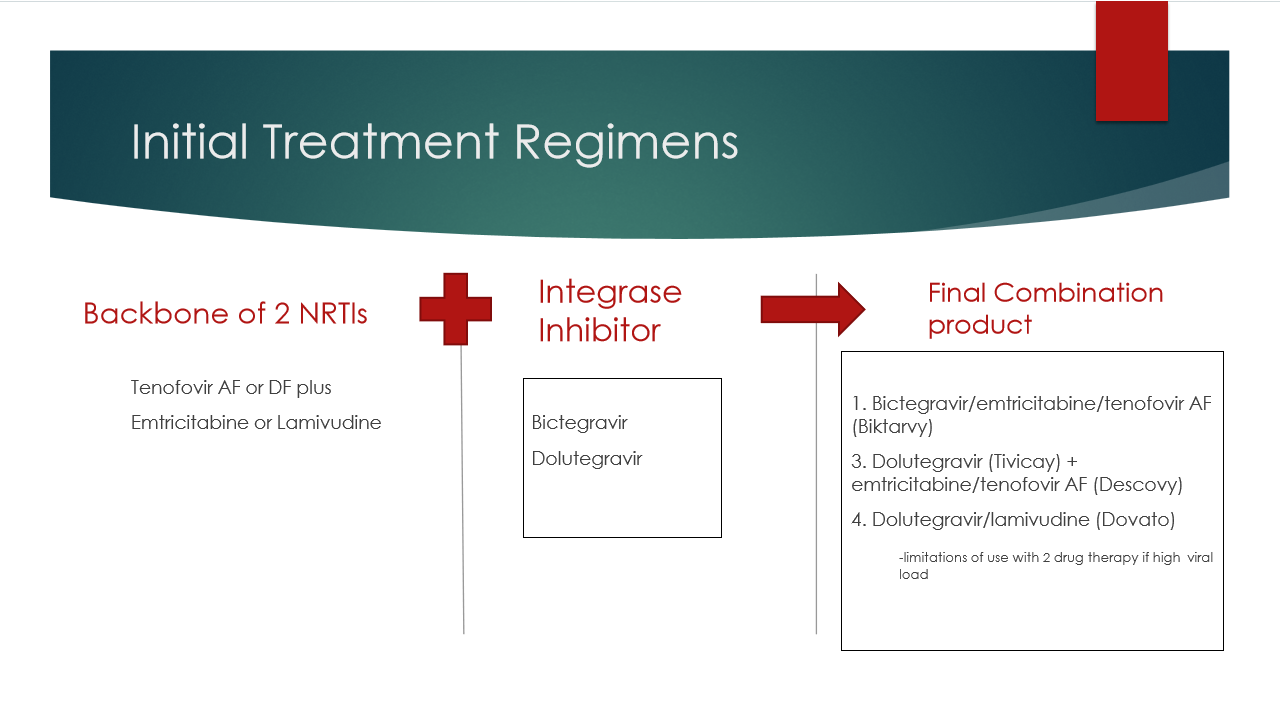
What are the first line treatment initiation options?
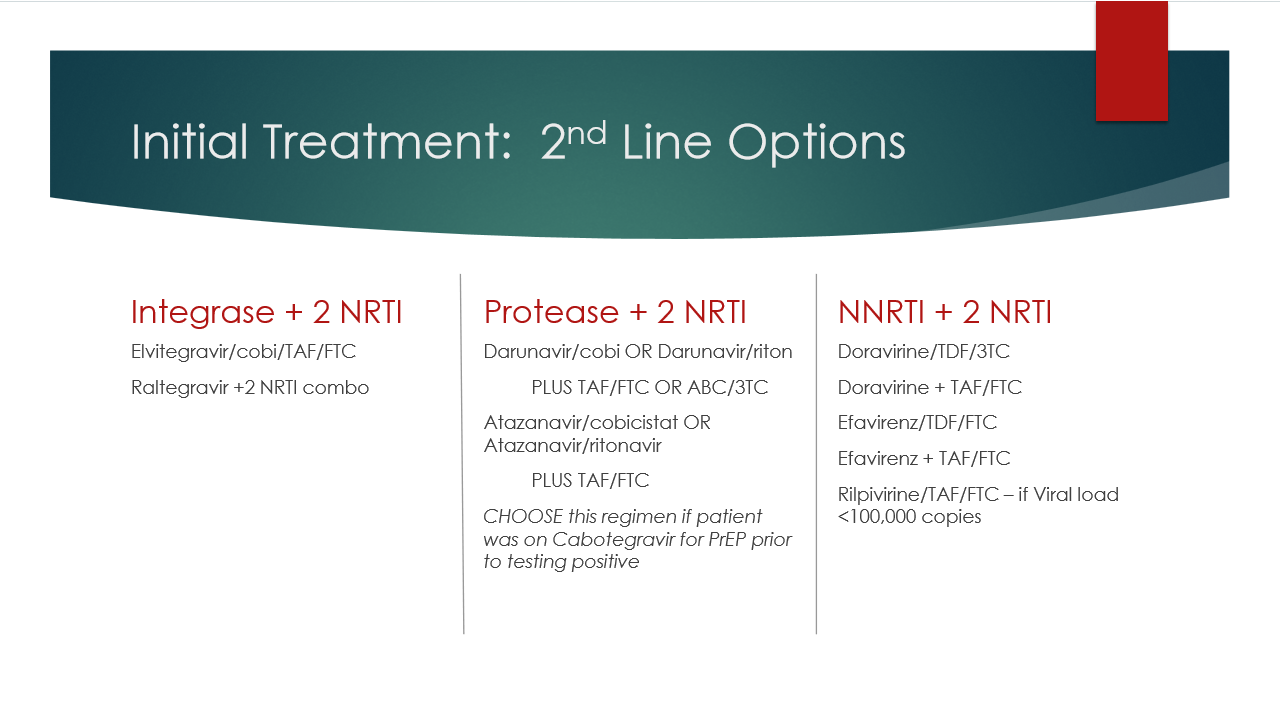
Second line treatment options
Pregnancy treatment options