Radiology 2 EXAM 1
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
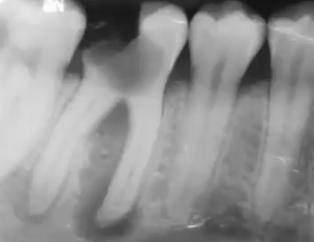
ill-defined
how would you describe the borders of this lesion
well-defined corticated
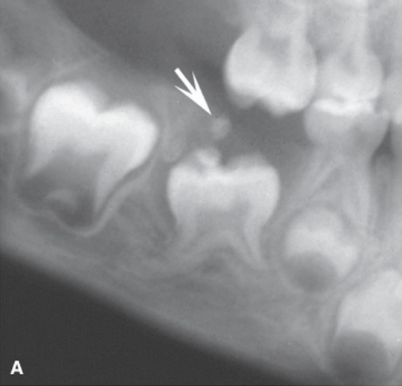
how would you describe the border of this lesion
well defined, non-corticated
how would you describe the border of this lesion
well defined, partially corticated
how would you describe the border of this lesion
blending
gradual, wide zone of radiopaque transition
invasive
wide zone of RADIOLUCENT transition with few or no trabeculae between lesion periphery and normal bone
dentigerous cyst
odontogenic cyst appearing as a well-defined RL area attached to developing tooth’s CEJ, likely to RESORB ROOTs of nearby teeth
tooth displacement/root resorption, expansion of bone, or asymmetrical follicle
how is a dentigerous cyst differentiated from enlarged follicular space
odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
unilocular/multilocular well-defined RL with CORTICATED borders and tunneling growth (no expansion)
odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
grows mesio distally with relatively little buccolingual expansion in body of mandible (expands in ramus and maxilla)
OKC attachs apical of CEJ, no expansion (bucco-lingual), and no resorbed roots
how is an odontogenic keratocyst differentiated from dentigerous cyst
unicystic ameloblastoma
exapansile, unilocular ,RL, displaces/resorbs roots, in young patients
unicystic ameloblastoma
expansile lesion that appears to envelop developing tooth
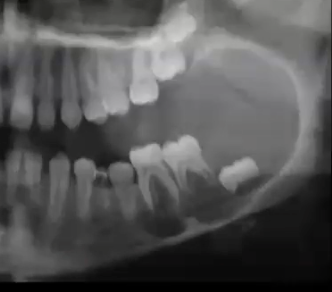
ameloblastic fibroma
non-hydraulic (not round), unilocular, well-defined non-corticated RL , associated with unerupted tooth with INTACT FOLICLE, in young patients
radicular/periapical cyst
well defined RL lesion at apex of non-vital tooth, loss of lamina dura
from peripery inwards
what is the direction of bone growth when a radicular cyst is healing
healing radicular cyst (bone growth after RCT)
what is the diagnosis?
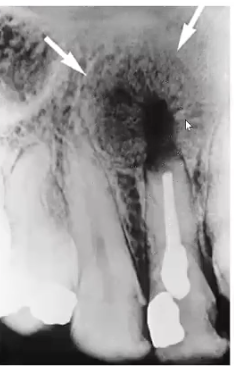
periapical cemento osseous dysplasia
middle aged black female presents with these incidental findings on a pa, teeth are vital, diagnosis?
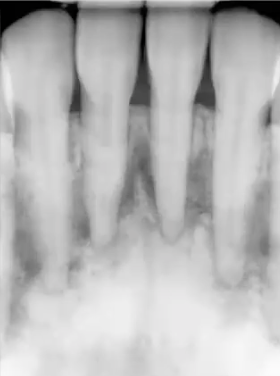
lateral periodontal cyst
developmental odontogenic cyst, lateral to the roots of vital teeth, most commonly in mandibular premolar-canine area
botryoid cyst
multilocular variant of lateral periodontal cyst
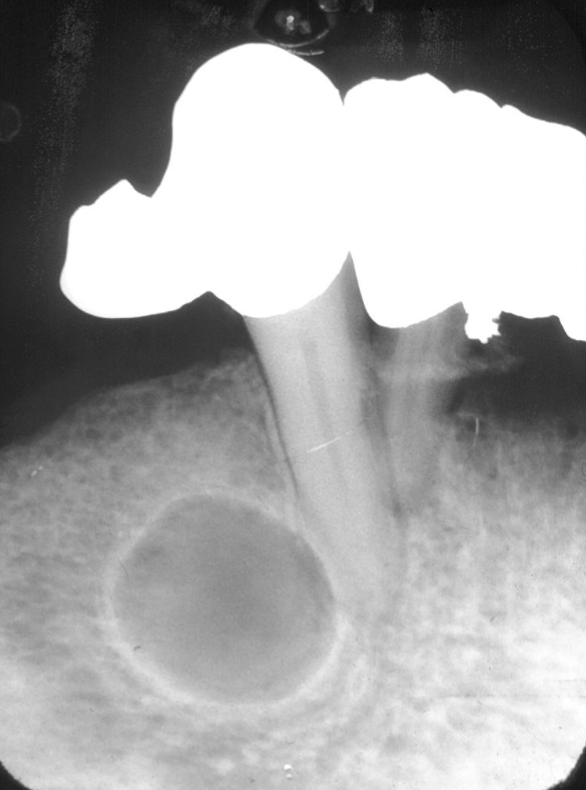
simple bone cyst (traumatic bone cyst)
well-defined, THINLY corticated, uniform radiolucent lesion, scalloping around roots, NO ROOT RESORPTION or displacement. this is probably a:
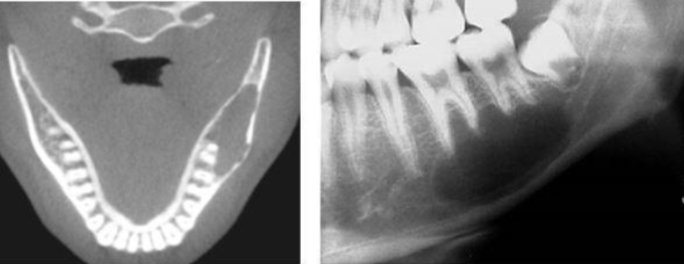
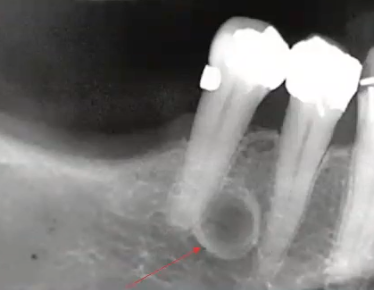
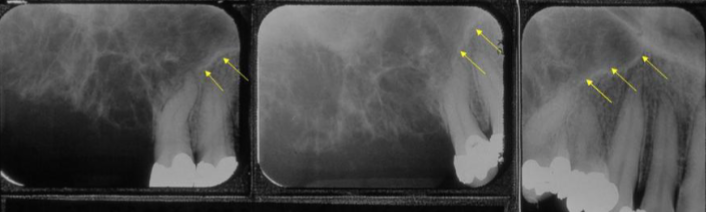
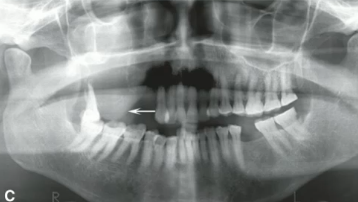
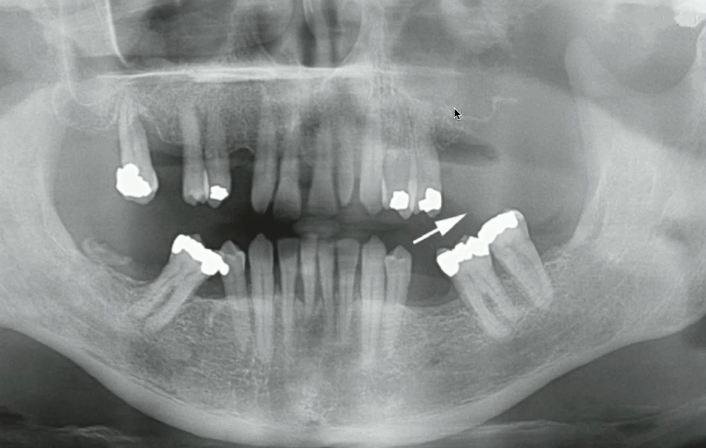
anterior border of lesion or floor of maxillary sinus
what could the radiopaque line that the arrows are pointing to be?
complex odontoma
the differential for this incidental finding on an asymptomattic patient should include the following EXCEPT:
lateral periodontal cyst
odontogenic keratocyst
residual cyst
complex odontoma
simple bone cyst/cavity
well defined RL, thinly corticated, scalloping around roots, intact lamina dura, DOES NOT displace teeth
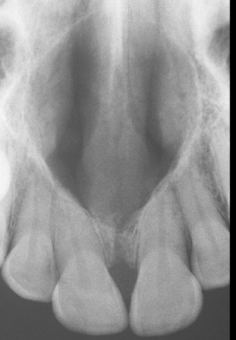
nasopalatine duct cyst
well-defined corticated heart-shaped lesion in the anterior maxilla (may be on midline or slightly off center)
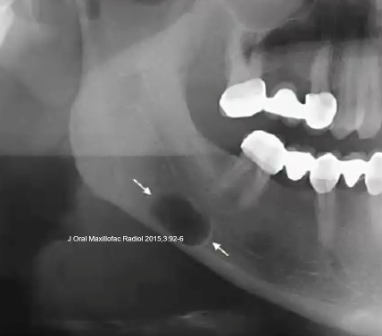
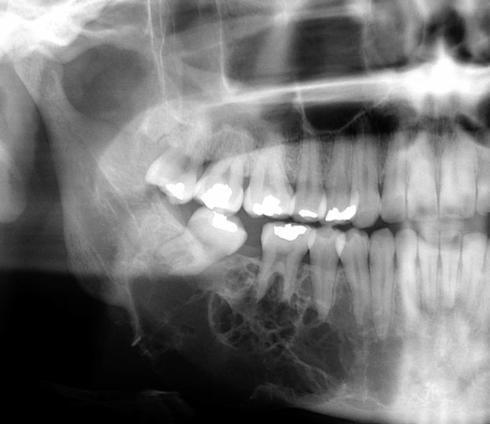
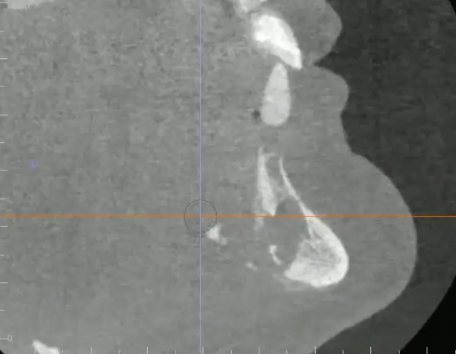
stafne bone defect/ lingual salivary gland depression
a well-defined corticated ovoid RL in the posterior mandible, BELOW IAC
odontogenic Myxoma, Ameloblastoma, CGCG, Hemangioma, OKC, osteoporotic bone marrow (MACHO)
well-defined RL multilocular lesions in differential diagnosis
odontogenic myxoma
likely diagnosis of this lesion
odontogenic myxoma
well-defined RL multilocular lesion in posterior mandible with characteristic “tennis racket” septa
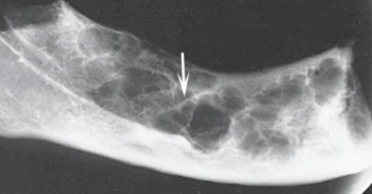
odontogenic myxoma
less well defined in maxilla with “honeycomb appearance”
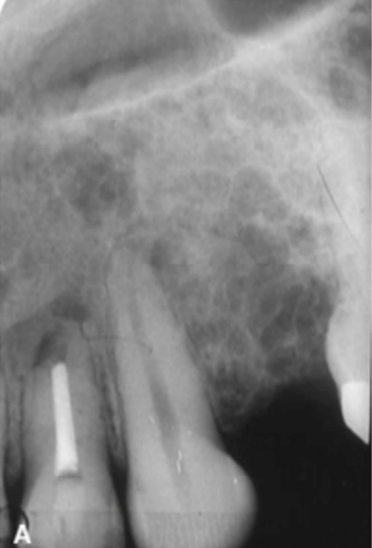
ameloblastoma
aggeressively EXAPANSILE lesion RL lesion with thick curved septa and “honeycomb” or “soapbubble” appearance
ameloblastoma (root resorption, honeycomb appearance)
most likely diagnosis?
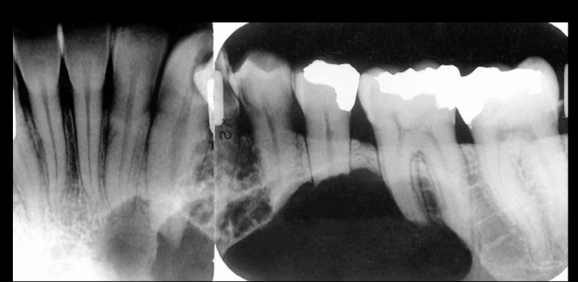
ameloblastoma
likely diagnosis of this AGGRESIVE lesion in maxilla
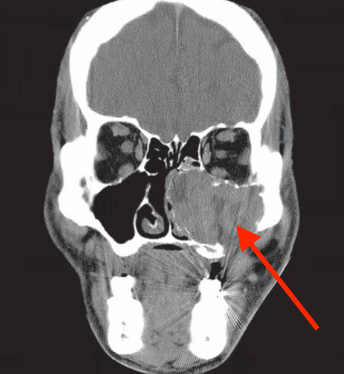
cental giant cell granuloma (CGCG)
EXAPANSILE multilocular RL lesion with faint wispy septa, more common in anterior mandible, in YOUNGER age group
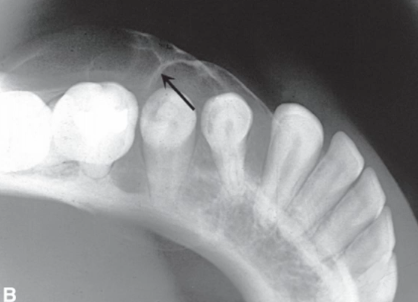
central giant cell granuloma (CGCG)
septation at right angle to mandibular border likely indicates?
vascular malfomation (hemangioma)
likely diagnosis?
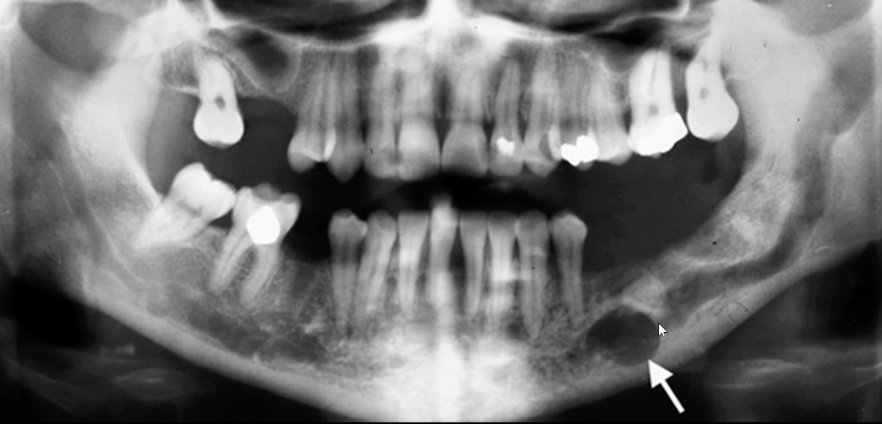
vascular malformation (hemangioma outside IAC)
honeycomb with coarse trabecullation
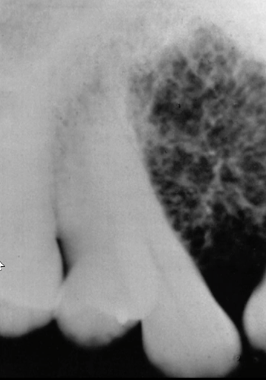
phleboliths (vascular malfomation in soft tissue)
likely diagnosis of these “bulls-eye" lesions
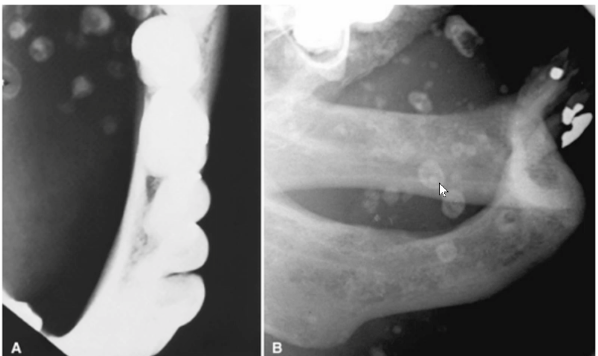
odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
perforated inferior border, EXAPANSILE, NO ROOT RESORPTION, likely diagnosis?
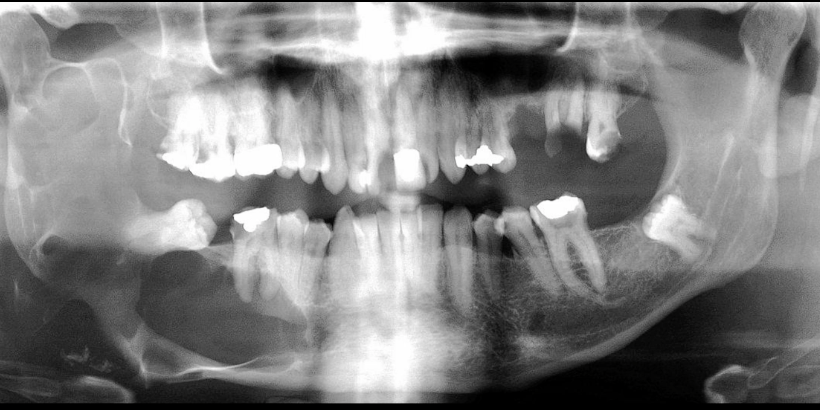
odontogenic keratocyst (no root resorption)
most likely diagnosis of this EXANSILE LESION ?
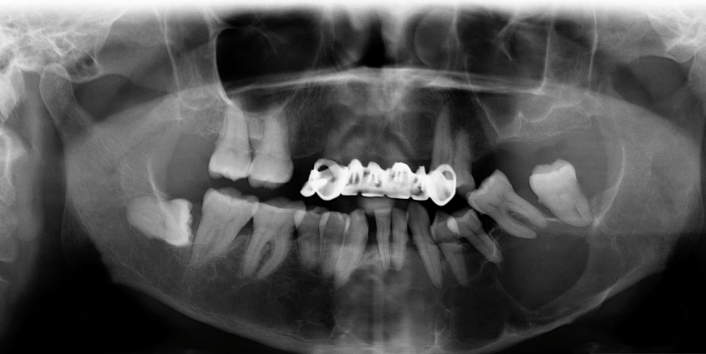
ossifying fibroma
EXPANSILE RO lesion causing tooth and IAC displacement, likely diagnosis?
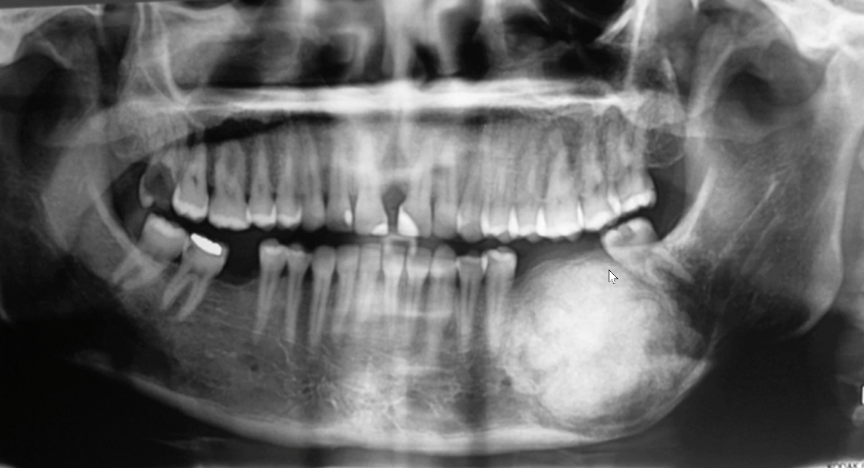
ossifying fibroma
well defined, thin radiolucent rim, RL to RO EXPANSILE lesion, resorbs roots, loss of lamina dura
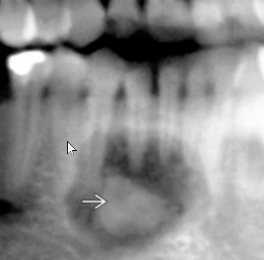
maxilla
where do lesions tend to be more aggresive?
focal osteoporotic bone marrow
RL multilocular lesion commonly seen in middle aged women with osteoporosis
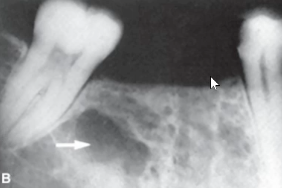
acute osteomyelitis
infiltrative, irregular, ill defined radiolucency associated with infection/trauma
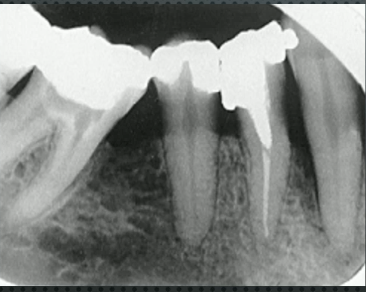
osteomyelitis
can present as osteolytic, sclerotic, sequestrum, or with periosteum bone formation (onion skin)
osteomyelitis (periosteal bone formation, fresh EXT site)
what is the likely diagnosis of this ill defined RL
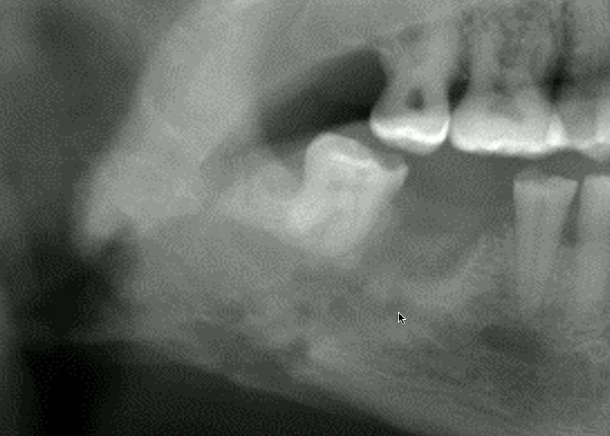
periosteal bone formation
what is indicated by the white arrow
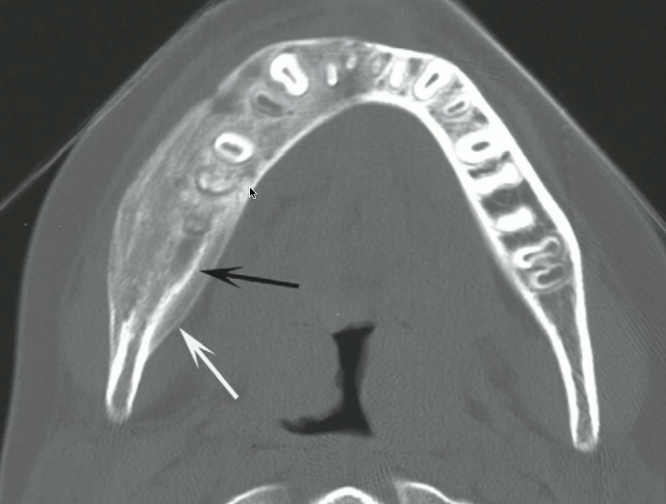
chronic osteomyelitis
bone infection with mostly SCLEROTIC reaction
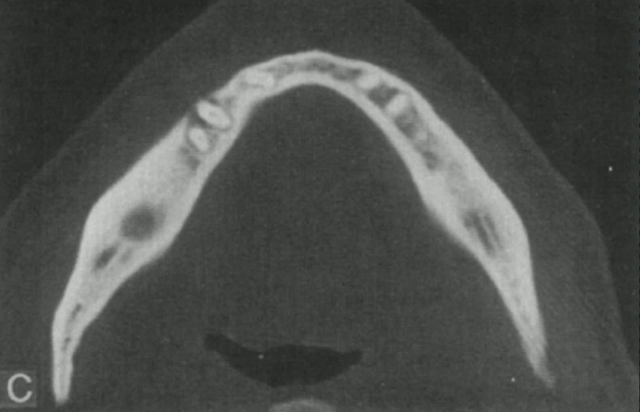
chronic osteomyelittis
sclerosis, WIDENING of bone, periosteal bone formation, and sequestrum indicates?
chronic osteomyelitis (sclerosis and widening of bone)
what is the likely diagnosis of the lesion in the left mandibule
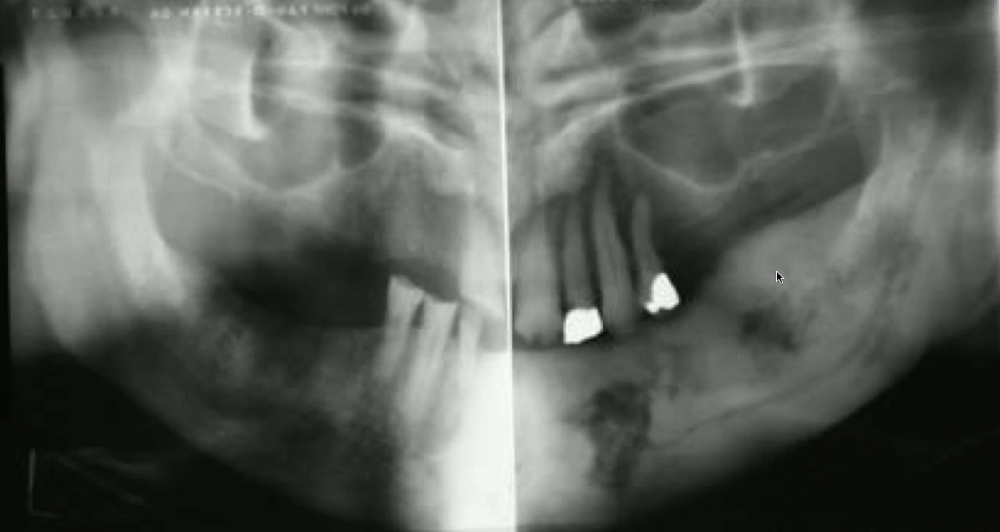
chronic osteomyelitis (sclerosis, widening, and onion skin)
what is the likely diagnosis of the lesion in the right mandible
osteoradionecrosis
lesion in posterior mandible with LOSS of LINGUAL CORTEX, sequestrum, and HISTORY of RADIOTHERAPY
MRONJ
LARGE sequestrum in jaws associated with antiresorpative medications
sqeamous cell carcinoma arising from soft tissue
soft tissue mass with destuction of bone
squamous cell carcinoma (from soft tissue)
what is the cause of this bone destruction
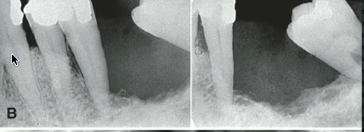
squamous cell carcinoma
well-defined NON-corticated lesion with CORTICAL DESTRUCTION and NO EXPANSION (unlike cyst/tumor)
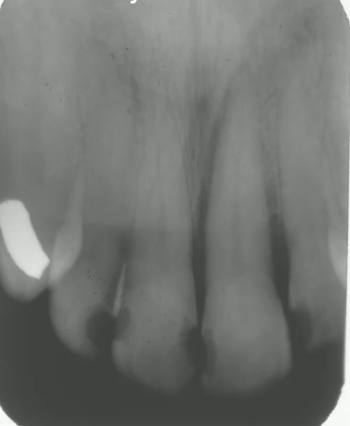
irregular PDL widening of tooth #9
identify the anomaly in this image
squamous cell carcinoma (from soft tissue)
likely cause of these “floating teeth”
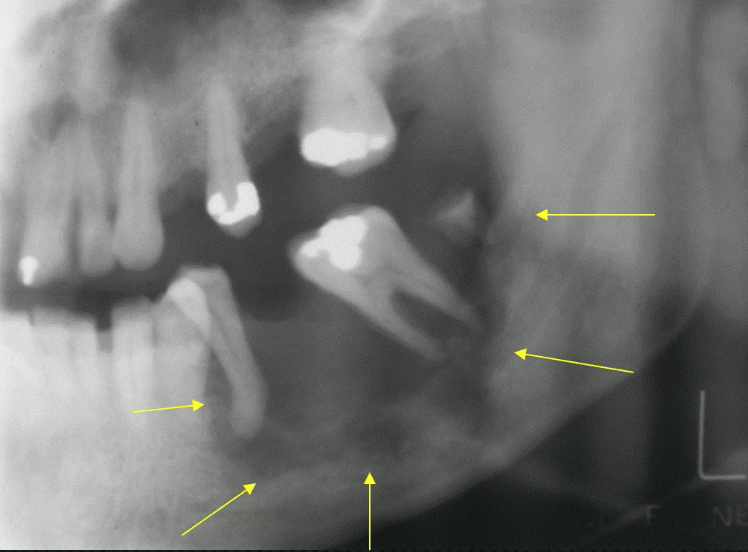
erosion (vs invasion)
what would smooth borders of malignant lesion indicate?
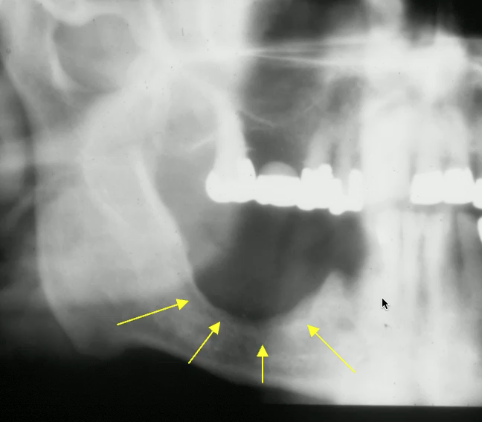
destruction of left sinus border
what indicates that this soft tissue mass may be malignant (squamous cell carcinoma)
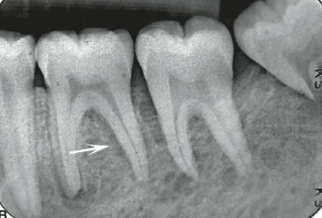
leukemia
no expansion, ill defined patchy RL that can enlarge
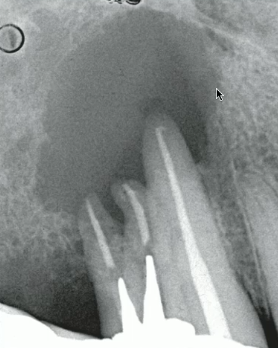
non-hodgkins lymphoma
ill defined/ relatively well defined with irrregular NON-corticated INVASIVE border
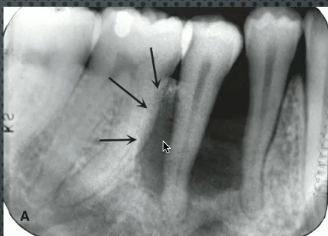
breast cancer
most common metastasis to POSTERIOR mandible
langerhans cell histocytosis
well defined, NON-corticated SCOOPED out appearance with epicenter at MID-ROOT in YOUNG patient
multiple myeloma
punch out lesion with sharp boundary but NON-CORTICATED
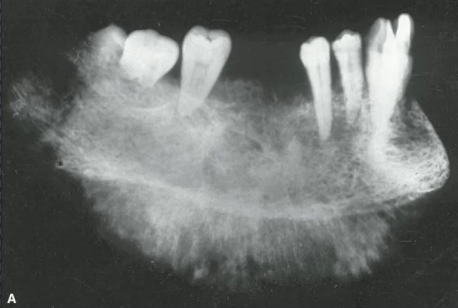
fibrrous dysplasia
blending EXPANSILE RO lesion with ground-glass appearance
osteosarcoma
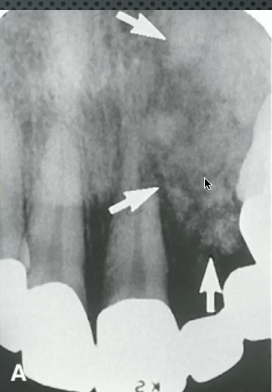
this “sunrray” periosteal reaction could indicate:
osteosarcoma
RL/RO lesion with IRREGULAR border and DESTRUCTION of CORTEX and lamina dura
chondrosarcoma
INVASIVE, mixed RL/RO, EXPANSILE, root resorption and displacement
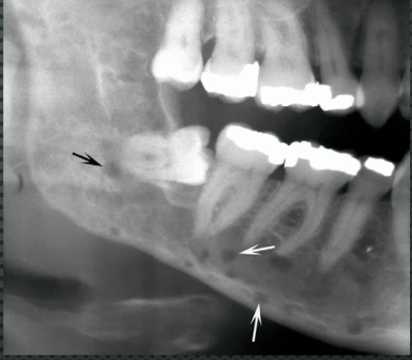
osteomyelitis
no history of antiresorpative medications, PAINFUL , what is the likely diagnosis?
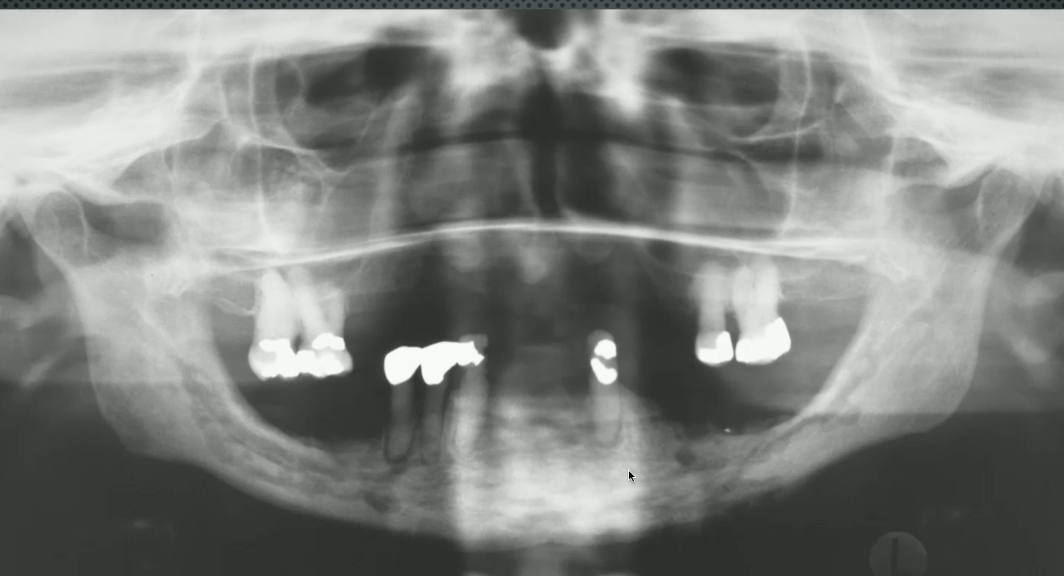
left maxillary (loss of sinus floor)
where is the lesion?
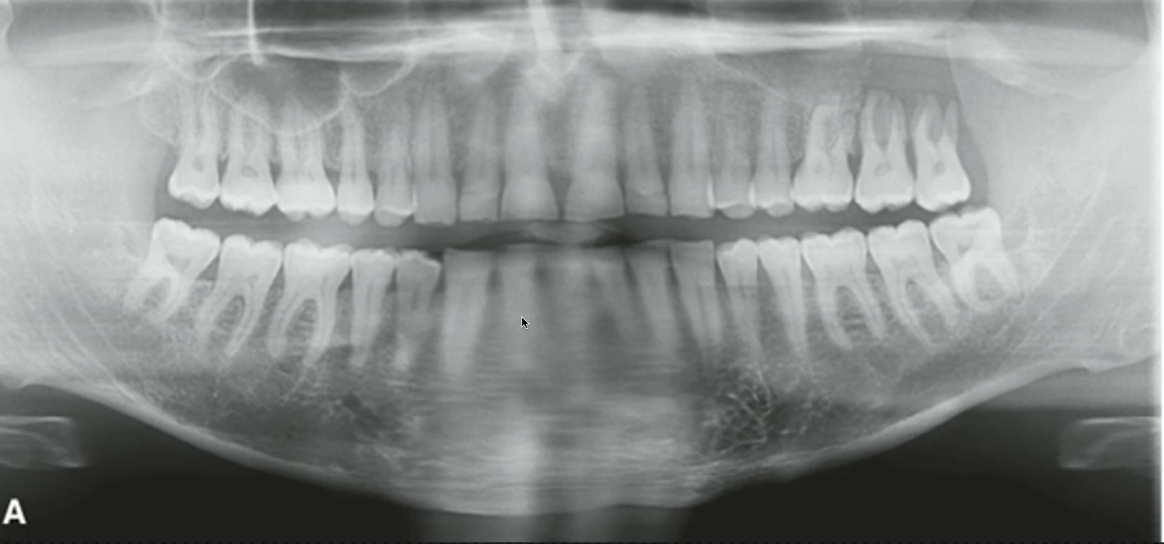
squamous cell carcinoma
most likely diagnosis?
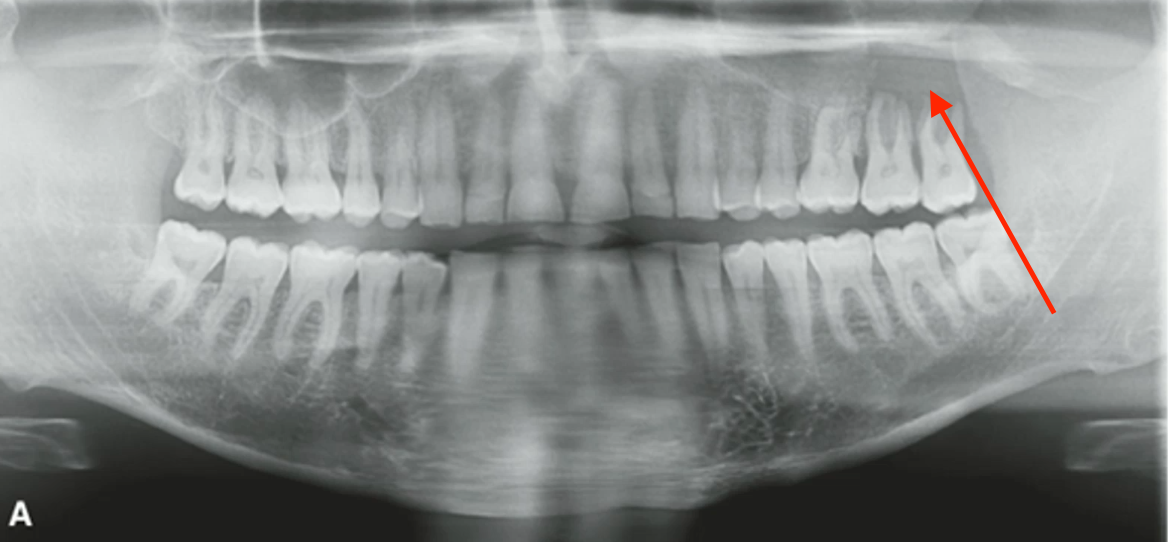
metastatic disease
no history antiresorptative medication, no history of cancer, no pain most likely diagnosis?
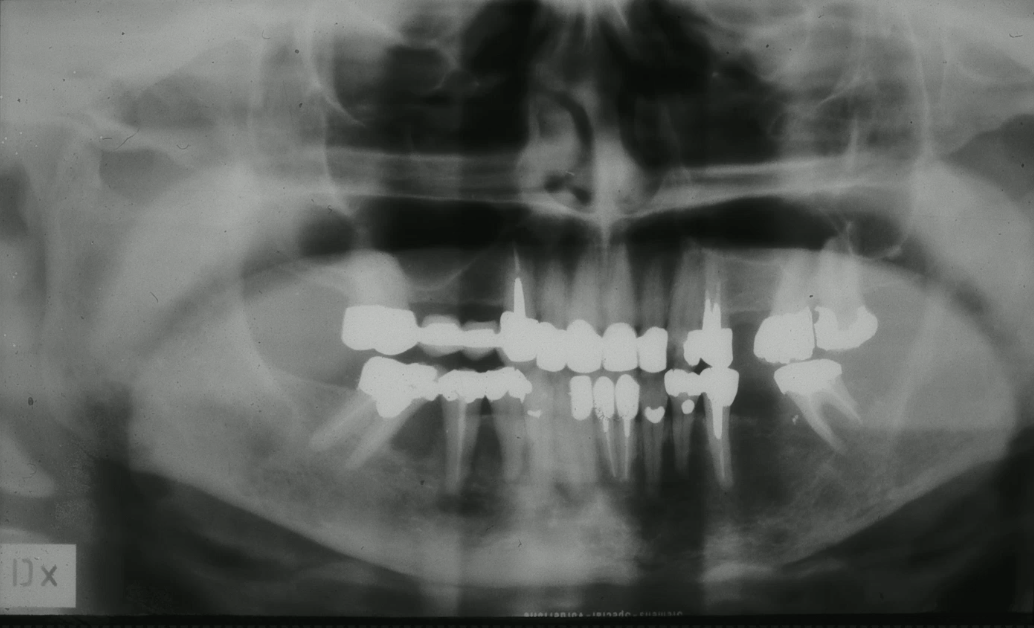
squamous cell carcinoma
left facial swelling, numbness V2 for 3 months, intraoral soft tissue swelling, most likely diagnosis?
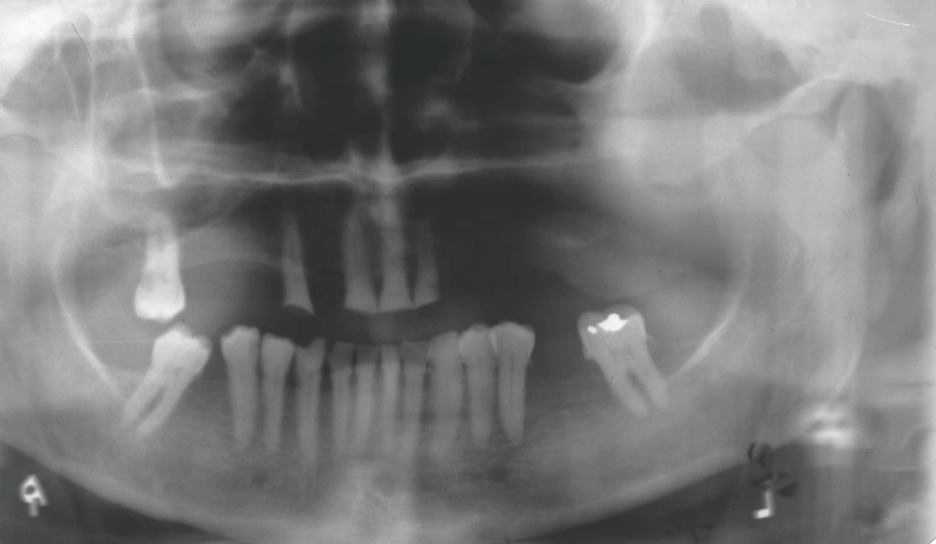
osteomyelitis
osteolytic, small sequestrum, and periosteal bone formation, likely diagnosis?
soft tissue or PDL space
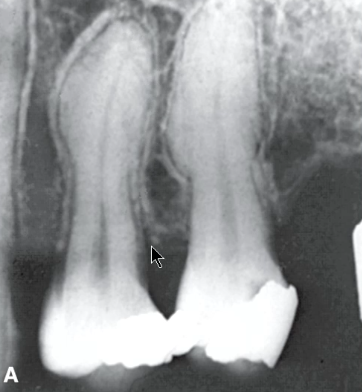
what could a lucent rim around a lesion represent?
root remenants
well defined RO with radiolucent PDL space
hypercementosis
irregular bulbous enlargment of root
hard palate and lingual mandible
locations of tori
palatal tori
what is the likely diagnosis of the radiopacity
lingual tori
likely diagnosis of these radiopaque lesions
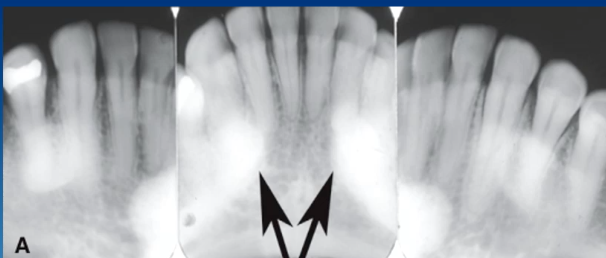
exostoses
what are these radiopaque lesions?
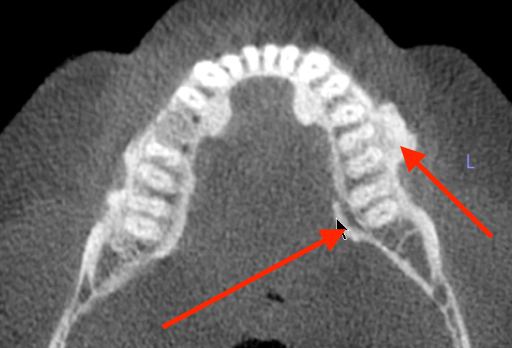
bone graft
granular appearrance in edentulous sites with loose fragments of bone within soft tissue
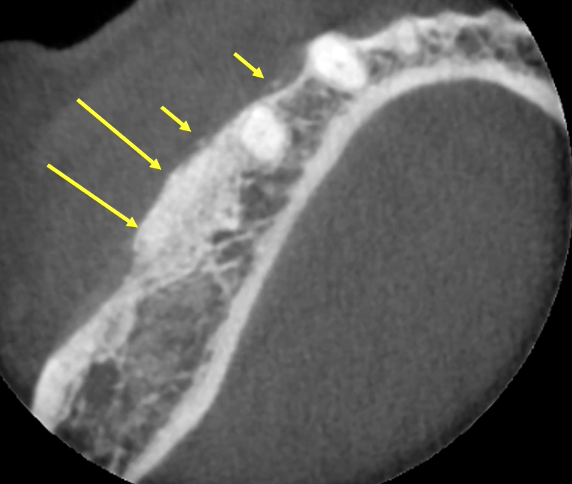
bone graft
what could be the cause of this uniform elevation of the sinus floor
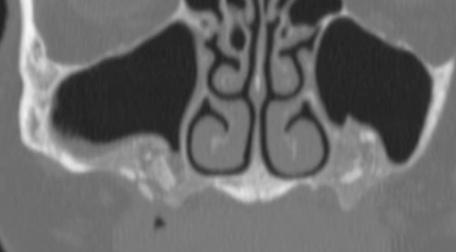
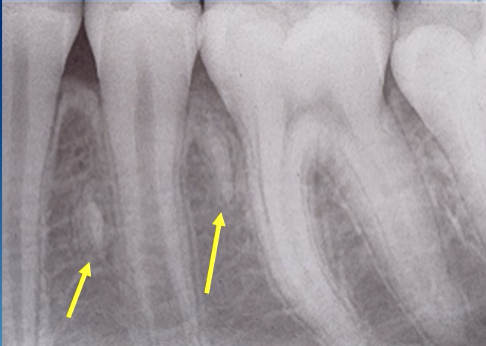
dense bone island/ idiopathic osteosclerosis
localized area of increased radiopacity within the jaw, typically asymptomatic and teeth are VITAL
idiopathic osteosclerosis/ dense bone island (normal PDL space)
most likely diagnosis?
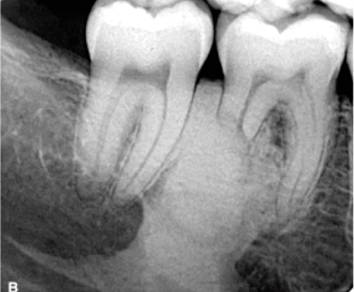
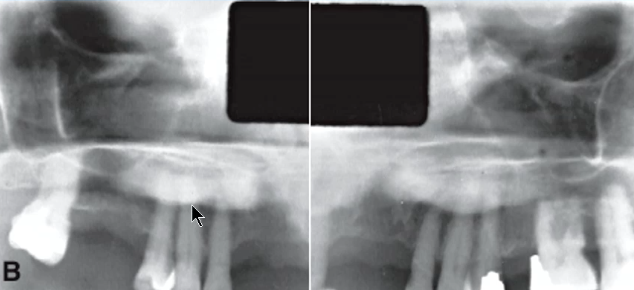
condensing osteitis
most likely diagnosis?
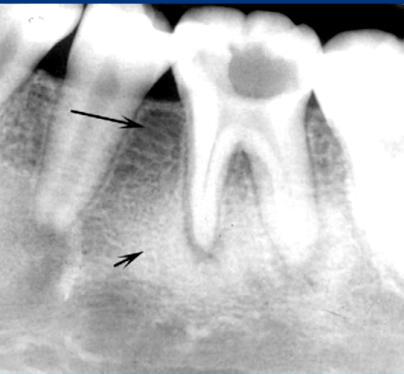
osteoma
benign tumor of bone, well-defined radiopaque, often asymptomatic, and can occur in various locations (MOST COMMON IN SINUS) including the jaw.
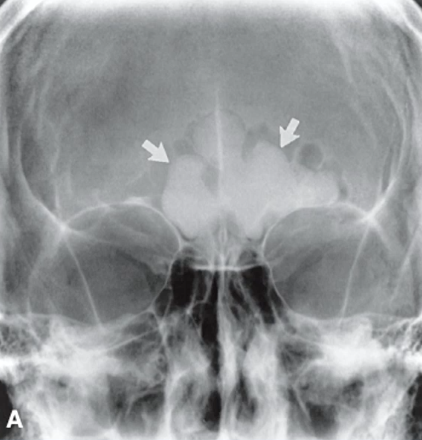
osteoma
homogeneously radiopaque lesion with NO PERIPHERAL lucent rim
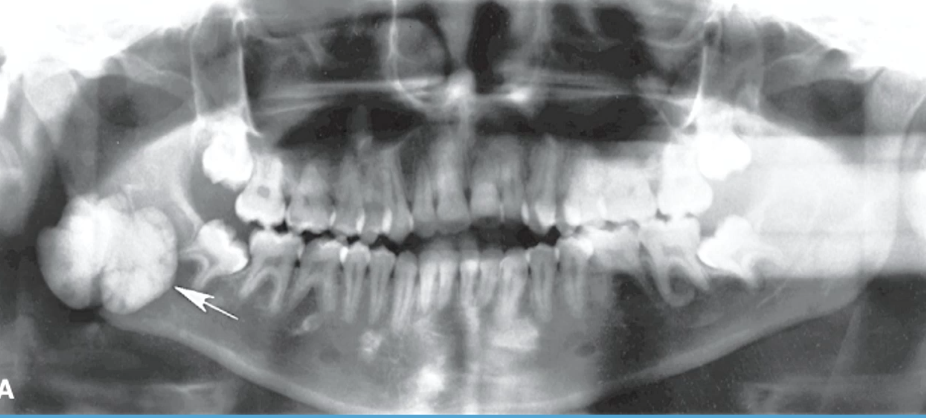
fibrous dysplasia
poorly defined RO, BLENDING trabecular bone, EXPANDS maintaining anatomical shape
focal COD
most likely diagnosis
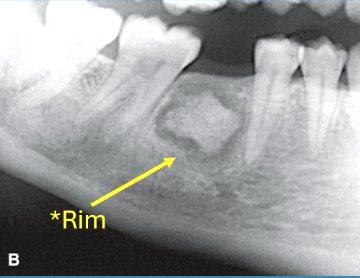
florid COD with simple bone cyst
most likely diagnosis
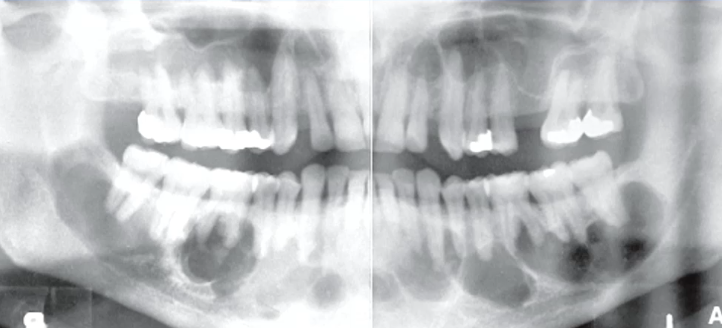
cementoblastoma
RO center mass fused to root with RL RIM, ROOT RESORPTION
cementoblastoma
most likely diagnosis?
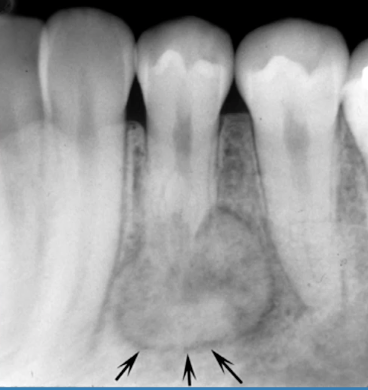
compound odontoma
tooth like structures with radiolucent rim, most likely diagnosis
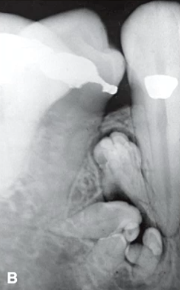
complex odontoma
irrregular mass with enamel density and lucent rim
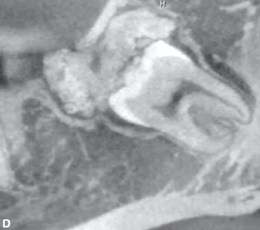
ossifying fibroma
corticated border with WIDE zone of transition, lucent rim
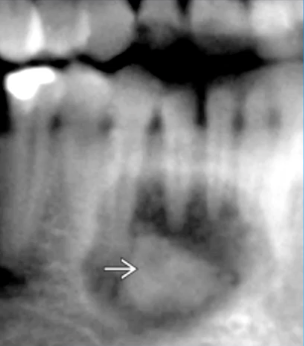
ossifying fibroma
RO/RL well-defined concentric lesion with WIDE zone of transition, causes ROOT RESORPTION and DISPLACES teeth and IAC
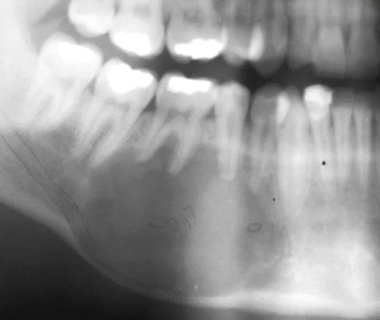
ameloblastic fibro-odontoma (AFO)
non-corticated mixed RL/RO lesion in CHILDREN