IB HL ECON
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
demand def
quantity of a good or service that consumers are willling and able to purchase at a given price and at a specific time.
increase of quality demand reasons
income effect: when the price of a product falls, and if peoples income has not changed in momentary terms.
Substitution effect: consumers may switch to alternatives when the price of a good rises and the price of other similar goods are seen as a replacement.
determinantes of demand
price itself is a determinant of the quality demand. All other factors are called non price determinants.
Non price determinants of demand
Tastes and prefrences
Income (normal, demand rise = income rise) and (inferior, demand rise, income fall)
Market size
Expectations
Related goods prices (complimentary, ex:pb&j, shoes&socks) and (substitudes)
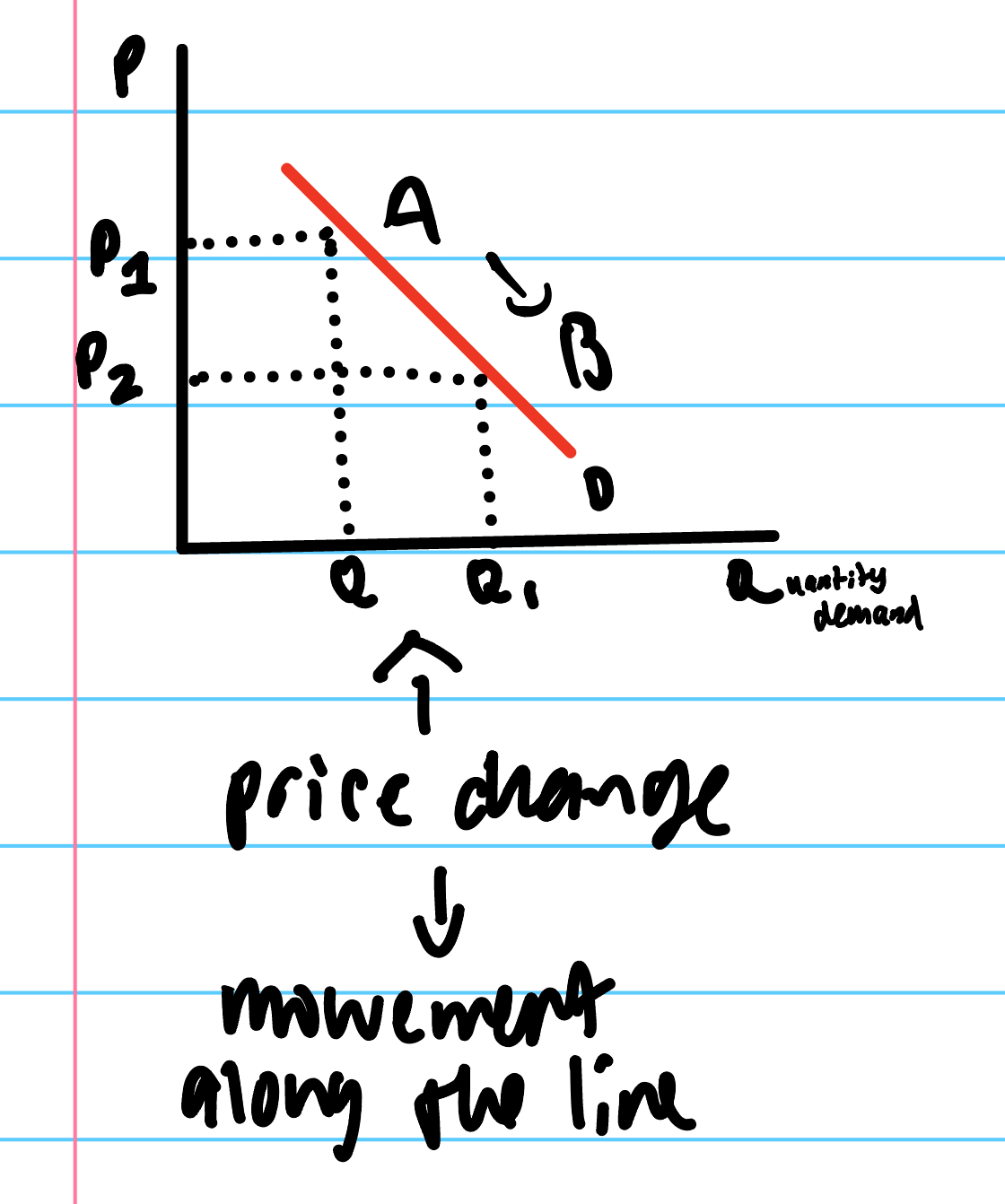
movement along the demand curve caused by…
change in price. (movement along the line)
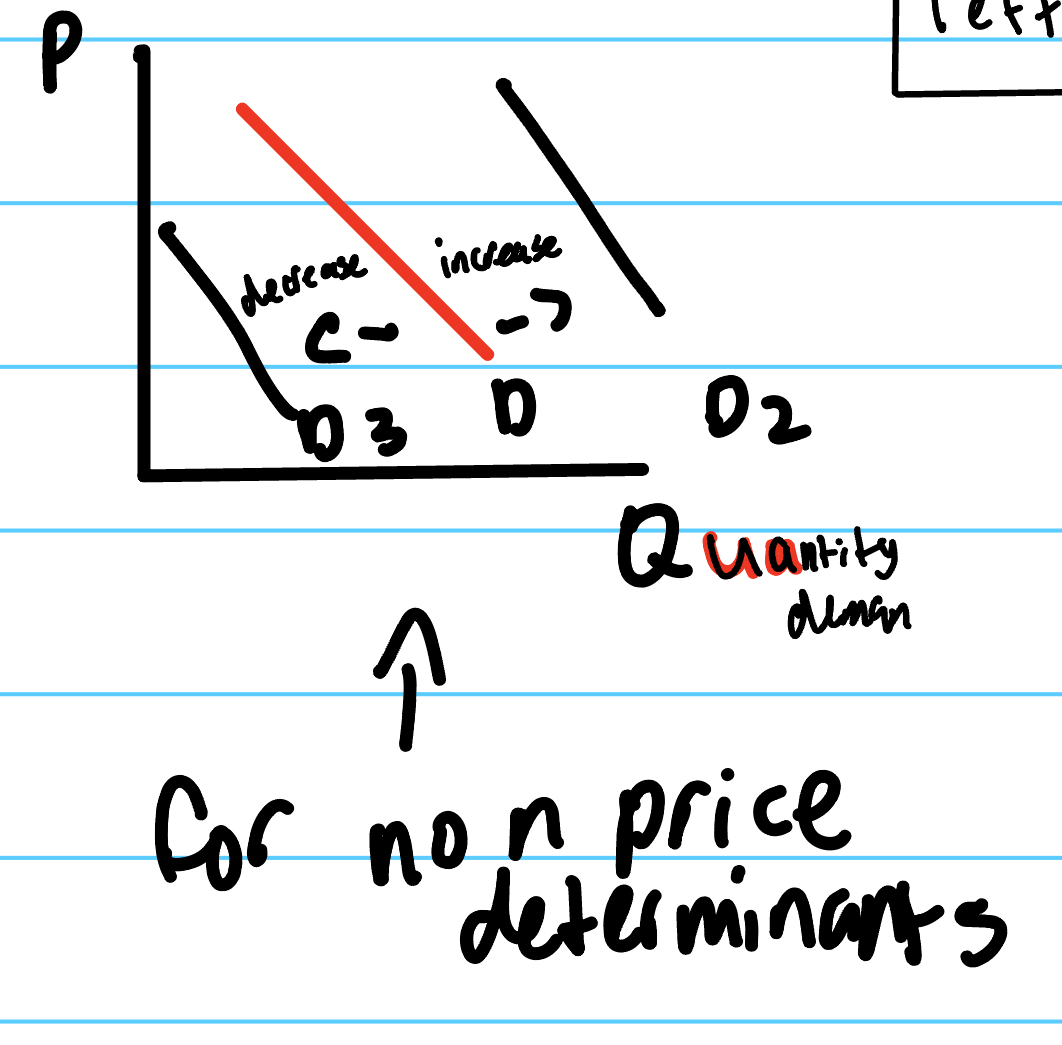
shift in demand curve caused by…
non price determinents
supply def
supply is defined as the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer at a given price, at a specific time period (ceteris paribus)
demand law
as the price rises, the quantity demand falls
supply law
as prices rise, the quantity supplied rises
types of supply
individual = the supply of one product from one firm at every price
market = the market supply is the sum of all the individual supplies of a product at every price
law of diminishing marginal returns
marginal returns refers to the additional output gained from adding an additional unit of input to a production process
the law of diminishing marginal returns states that adding more of one factor of production, while holding at least one other factor of production constant, will at some point yield lower marginal returns (outputs/product)
example: too many cooks in the kitchen, so must charge more because returns decrease
increasing marginal cost of production
marginal cost refers to cost of producing one more unit of a good
a producer will only want to increase the quantity supplied if she can receive a higher price in the market for selling the product.
therefore, to make more they much charge a higher price
Determinants of supply
higher price = higher quantity supplied
price is a determant of quanity supplied
Non-price determinant of supply
Subsides and taxes (goverment intervenence in markets)
Technology
Other related goods prices (competitive supply ex: Charlotte Tilbury and elf) ( joint supply ex: two or more goods from same product, so not possible to produce more of one without the other)
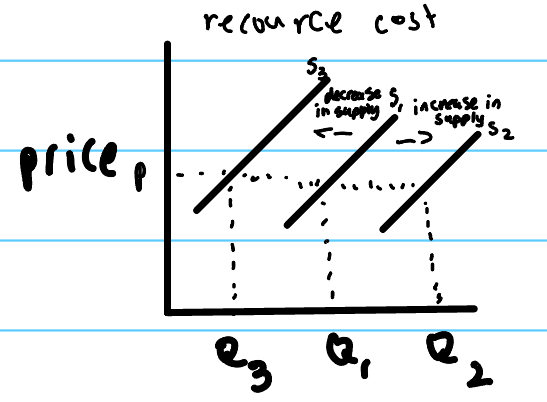
Resource cost (change in the cost of factors in production of the goods or services firms produce)
Expectations/weather
Size of market
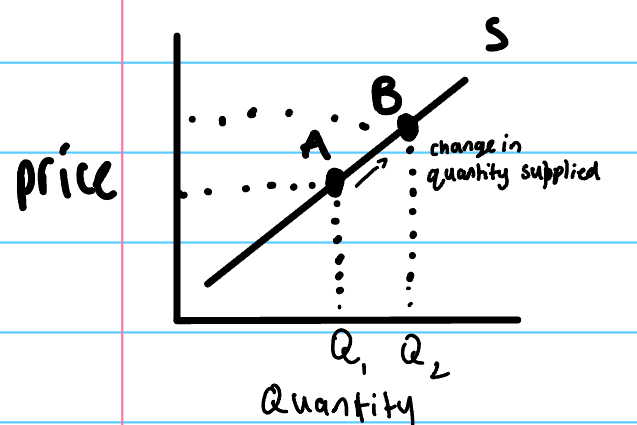
movement along supply curve caused by …
a change in price.
a shift of the supply curve caused by…
a change in a determinant of supply
market equilibrium
it occurs at the point where the supply curve of a good or service crosses the demand curve
equilibrium price
the price at which the quantity demand of a good equal the quantity supplied, so that there are no surpluses nor shortages at that price. It is the market clearing price, as everything that is offered is at that price, is sold.
equilibrium base graph
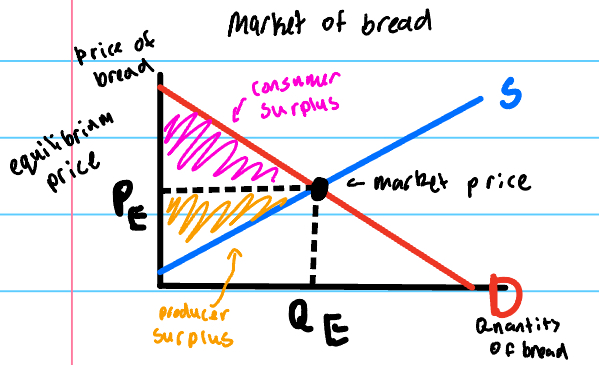
consumer surplus
the highest price consumers are willing to pay for a good minus the price actually paid
producer surplus
the price received by firms for selling their good minus the lowest price that they are willing to accept to produce the good
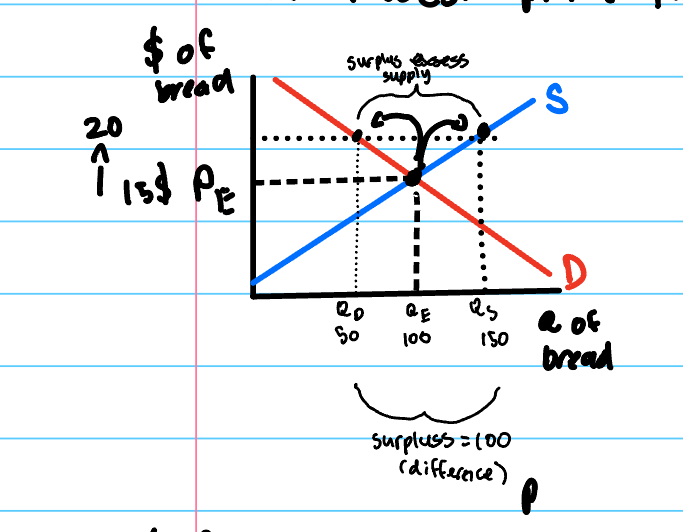
excess supply
the situation where, at a specific price, above the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded of a good is smaller than the quantity supplied producing a surplus in the market
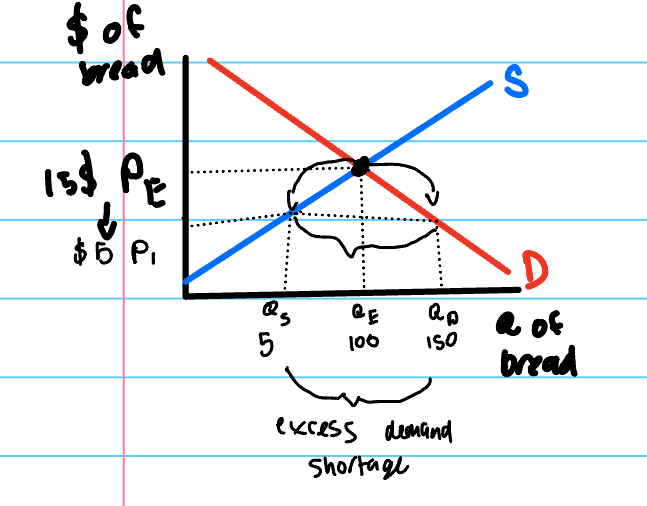
excess demand
the situation where at a specific price, below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded of a good is greater than the quantity supplied producing a shortage in the market.
price change will cause either a shortage or surplus
words to include in description
signals: “the market signals what it should do”
incentives = financial motivation to consumers and producers
rationing def
refers to the controlled distribution of resources. how it is distributed. (price is typically best rationing function)
elasticity def
a measure of the responisivness of the quantity demanded or supplied of a good service, to changes in any of the factors that determines it (very responsive)
price elasticity of demand def (PED)
measure of how much the quanitity demanded of a good changes, when there is a change in its own price
inelastic def
people will pay whatever as product is needed (not very responsive)
price of elasticity demand formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
sign does not matter
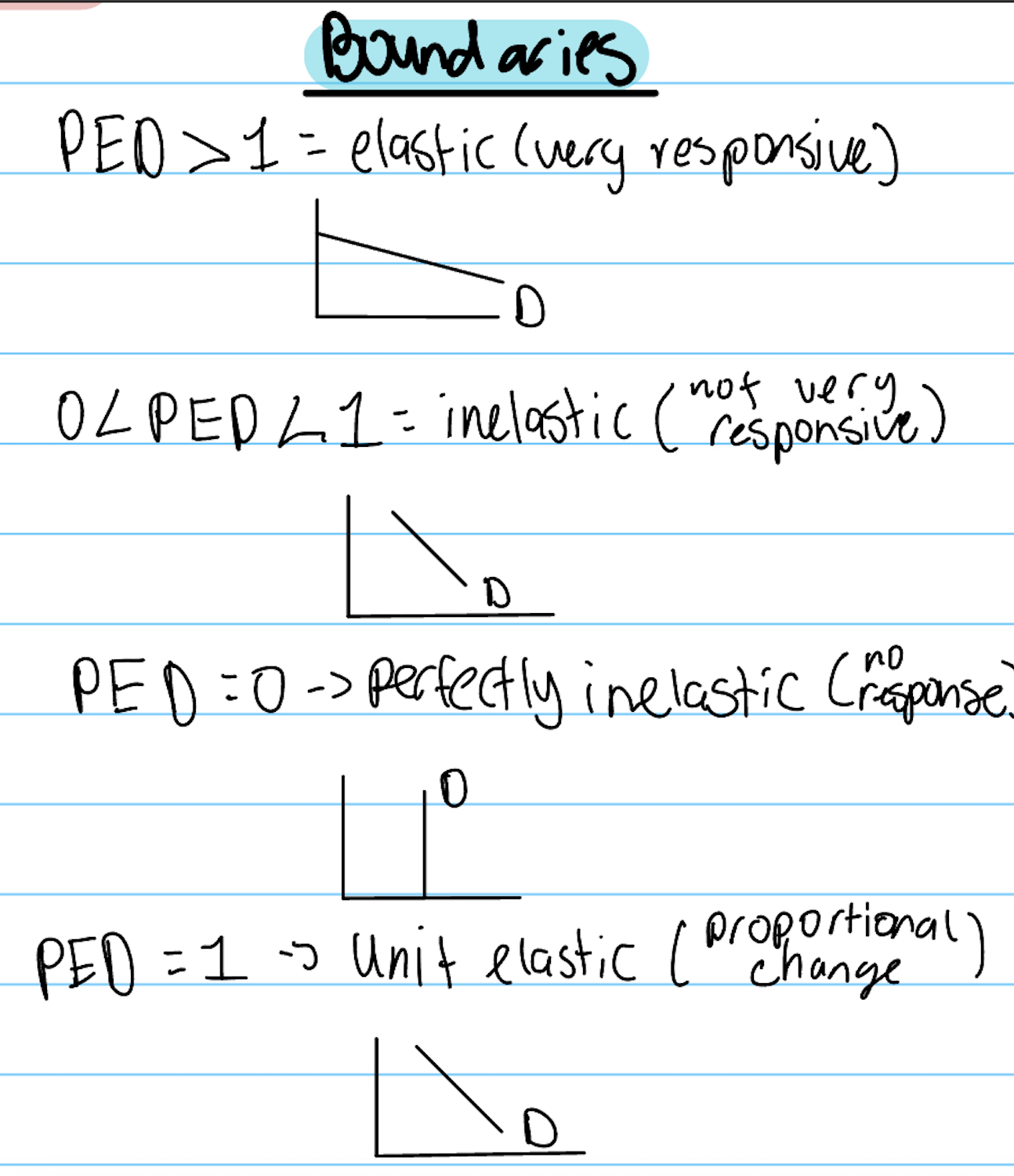
Elasticity boundaries
PED> 1 = elastic
0<PED<1 = inelastuc
PED is 0 = perfectly inelastic/no response
PED is 1 = unit elastic
Determinants of price elasticity of demand
Time (length of time, longer the time period in which it takes to make a purchasing desicion = more elastic)
Income proportion (higher the proportion/more expensive the product = elastic)
Necescity (how nessacary it is, more necacarry=inelastic)
Substitutes (number and clossness of substitudes available, how many options, more substitutes=more elastic)
Total revenue fromula
PxQ=total revenue
old P and Q - new P and Q = revenue
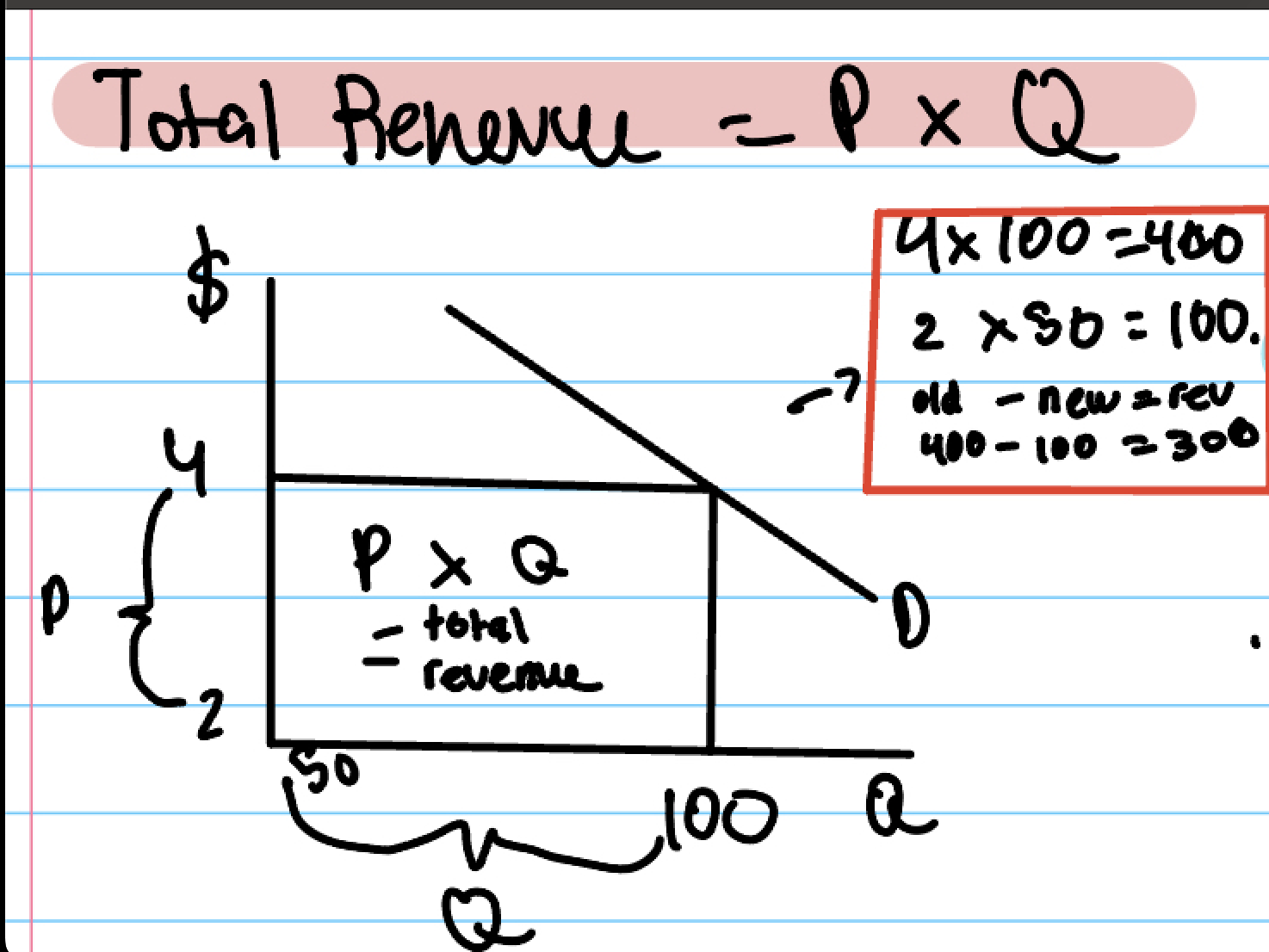
revenue def
how much you earned
elastic product to make more revenue…
lower price
inelastic product to make more revenue…
higher price
primary comodities def
goods that are natural resources ex: corn, forests (inelastic)
manufactured products
produced by labour with capital ex:cars (elastic)
income elasticity of demand (YED)
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good will respond to a change in a consumers income
income elasticity of demand formula (YED)
% change in the quantity demanded of good x / % change in peoples income
sign matters
income elasticity of demand (YED) values
negative = inferior = income increase, demand decrease
positive (0<YED<1) = necessity(normal good) = income increases, demand increases
positive (YED>1) = luxury (normal good) = income increases, demand increases
Engel curve def
as an income rises, the demand for example potatoes may increase, then become constant, and then fall as people begin to buy superior products instead such as pasta.
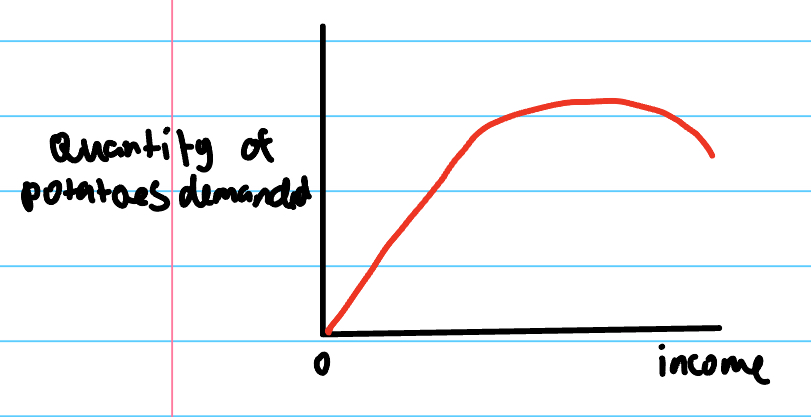
engels law
as households incomes rise, the percentage spent on some purchases ex: food decreases, while the proportion spent on other goods (such as luxury goods) increases.
Price elasticity supply (PES) def
a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good changes when there is a change in its own price, therefore it implies a movement along the supply curves
Price elasticity supply (PES) formula
% change in the quantity supplied of goods X / % change in the price of good x
ranges of values of price elasticity supply (PES)
PES>1 = elasticity (very responsive)
0<PES<1 = inelastic (not very responsive)
PES = 0 = perfectly inelastic (no response)
PES = 1 = unit elastic (proportional change)
Determinants of Price elasticity of supply (PES)
Time period (the more time you have to produce that product = more elastic)
Unused capacity ( the greater the space (un used) capacity = more elastic the supply is)
Mobility (the more mobile factors of production can be = more responsive a firm can be in)
Store ability (the greater ability to store stock = more elastic changes)
primary commodities and manafactured products PES
most primary commodities have a lower PES (inelastic supply) than manufactured products. this is because of the long time period or the high levels of investment needed to increase production, which affects the ability of supply to react to price changes
primary produceres revenue
price flunctuations are sustainabilly larger in the case of inelastic apply, big price fluctuations = larger revenue fluctuations and unstable total revenues for primary producers
veblen goods
super luxury goods and their instrinsic value comes from there worth or snob value rather than their functional value (ex:bags)
speculative goods
you buy more to hope and expect them to make more value in the future