PT7130- Orthopedics in Acute Care
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
2 different; WB; ROM; wait
Orders and Chart Review:
- May see physical therapy orders from ________________________ physicians
- Always refer to orthopedic guidelines:
→ ___________________ status (i.e., For every extremity affected, what is WB status?)
→ ____________________ guidelines
→ Exercise restrictions (i.e., no SLR after hip fracture and repair)
- What tests and measures did the physician order: x-ray, CT, MRI → _______________________ till post-op imaging has been completed
All joints; sensation; transfers; gait
Exam and Eval:
- Screen _____________________ ROM and strength
- Screen _______________________
- Assess edema/swelling
- Assess bed mobility and _______________________
- Assess balance, ______________________, and stairs
WB status
Always explain the ________________________ to the patient!
Weight-bearing; equipment use; community; fatigue
Other Considerations:
- Prior level of function
- Compliance /c current ________________________ restrictions
- Compliance /c ________________________ and safety
- Ability to self monitor, risks for falls, insight and judgement (consider evaluation environment)
- Speed and velocity of functional movement → More important for _________________________ ambulators
- Onset of ________________________
- Body mechanics
Orthopedic consult; holding
If a fracture is present, an _________________________ is almost always indicated.
- Follow orthopedic guidelines/restrictions/precautions
- Conservative or surgical management
- May require _____________________ on a PT consult (short-term)
Hospitalist
99% of the time, PT is held until orthopedics has been involved. If ______________________ can manage the fracture (i.e., pinky fx, great toe fx), then ortho is not consulted.
Non-urgent
- Stable fracture
- Intact neurovascular system
Elective
Failed conservative treatment.
Urgent
- Time frame for management: 24-72 hours
- Closed, unstable fractures
- Intact neurovascular system
Emergent
- Requires immediate attention
- Open fractures
- Fracture/dislocation with impaired neurovascular system
- Spinal injuries with deteriorating neurologic deficits
Fracture reduction
Alignment of fracture fragments.
Closed reduction
Noninvasviely /c manual manipulation.
Open reduction
Surgical stabilization /c hardware.
Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)
Uses screws, plates, rods, and pins internally to promote immobilization for healing. → May requires additional external support /c external fixation.
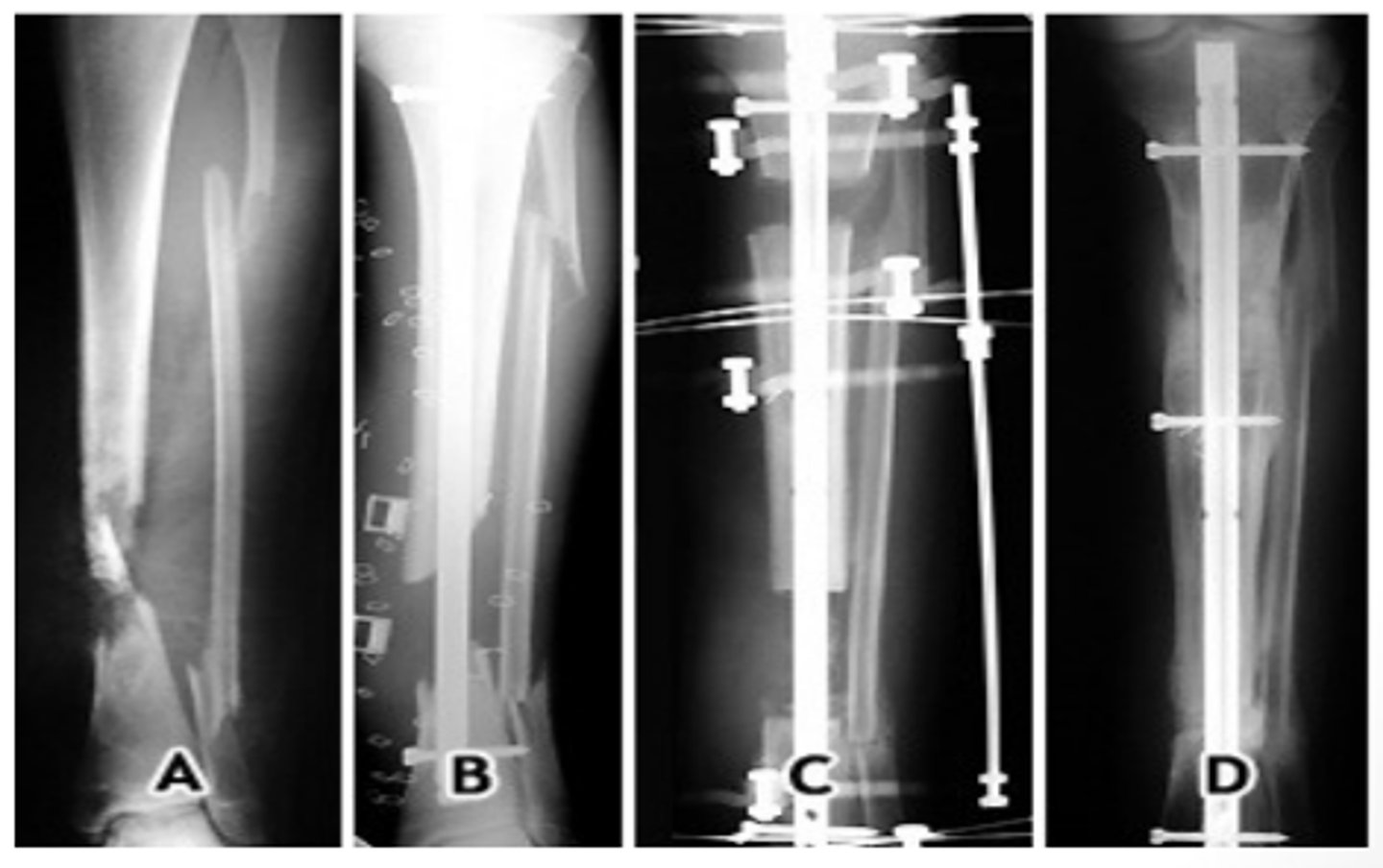
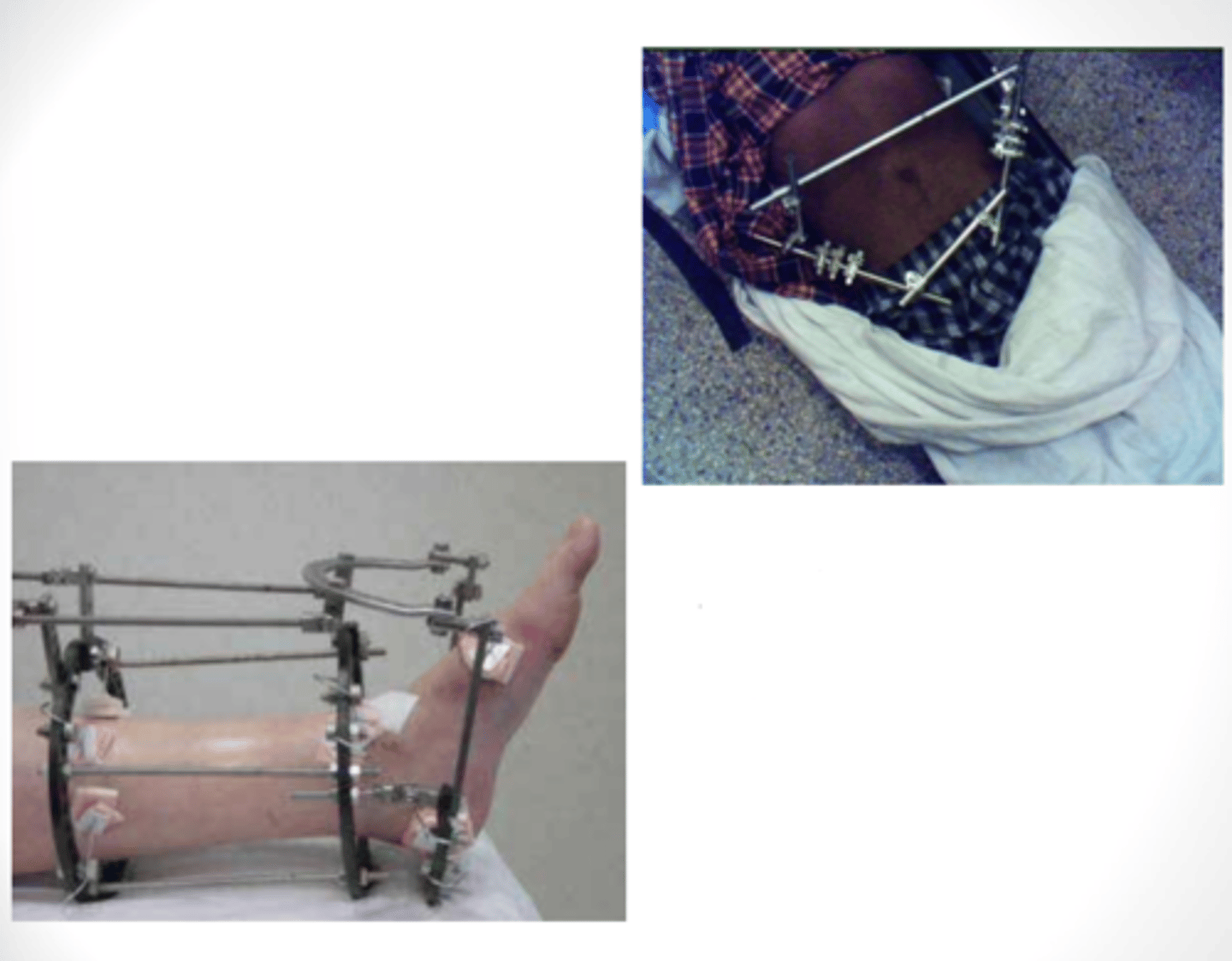
External fixation
Provides alignment forces to fracture fragments and maintains reduction while healing.
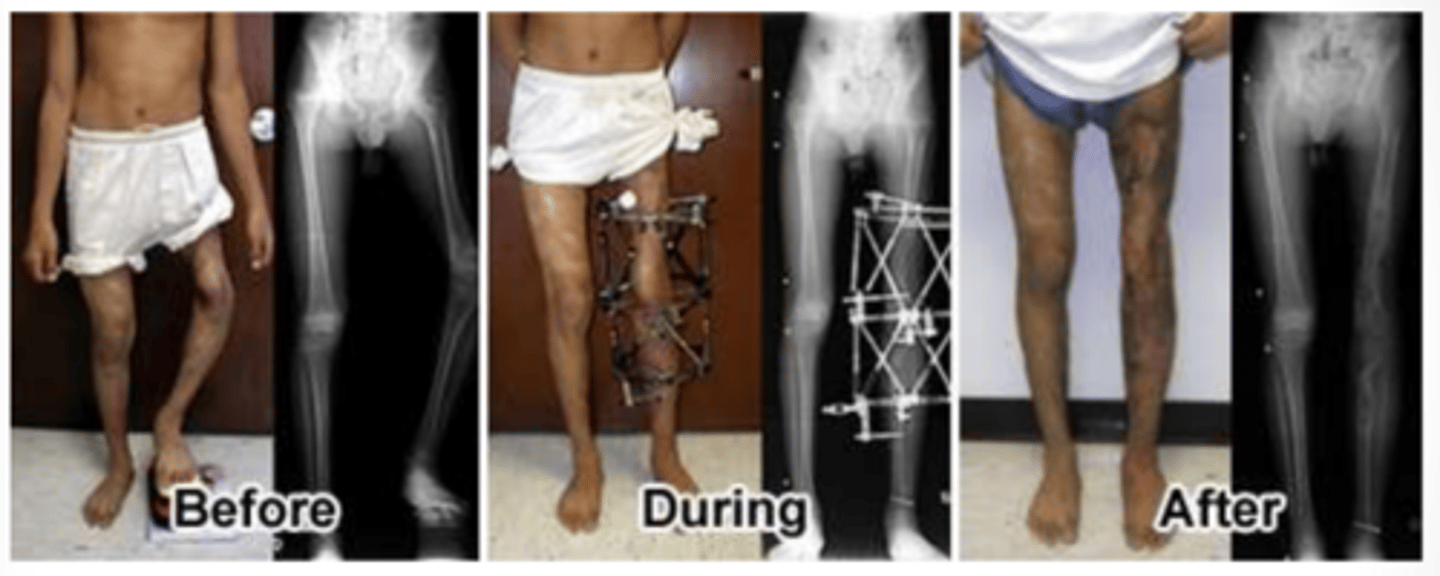
Comminuted; open
External fixation is appropriate for severely _________________________ or _________________________ fractures.
ROM; vibrations; swelling
Therapy Implications of External Fixation:
- Maintain full _______________________ of all joints above and below external fixator
- Avoid any type of _________________________
- Clear drainage, slight bleeding, redness, and __________________________ at pin sites is normal
Chuck's pad
Do not lift /c rods of external fixation device! Use _______________________ to create a sling when possible.

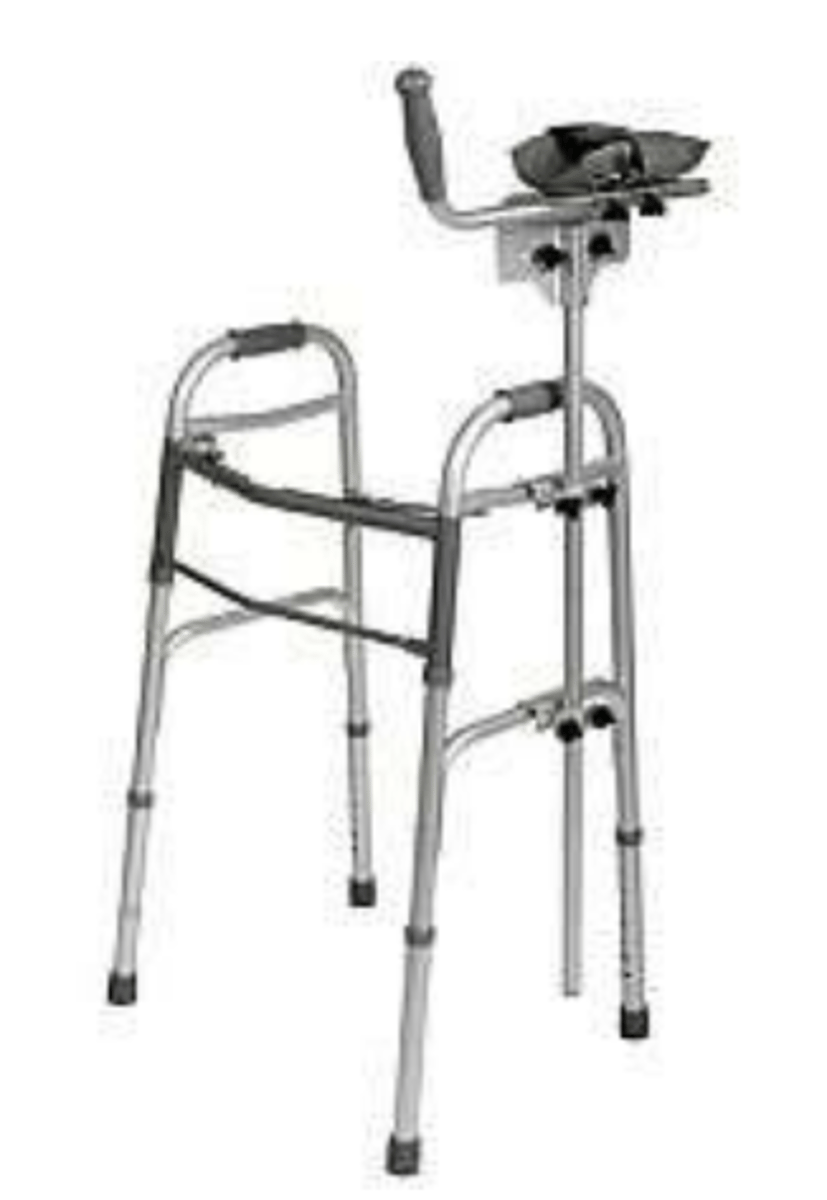
Platform walker
What does image show?

Total joint arthroplasty
Used for severe degenerative arthritis or severe damage to joint. Also used when conservative measures are failed, such as pain medication, using assistive devices, activity/lifestyle modification, cortisone injections, lubrication injections.
Bilateral
Total joint arthroplasty can be elective vs. non-elective and/or _________________________.
Days; surgeons
Bilateral joint replacement → Either spread across several ______________________ in hospital. -or- Two different _____________________ on knees at same time in operating room.
Pre-op
Total joint arthroplasties may have PT _____________________ and post-op.
Length of stay; cost; function; milestones
Guidelines and Order Pathways:
- ↓ _________________________
- ↓ __________________________
- Improve ______________________ while mandating clinical activities
- ________________________ expected on certain post-op days
Total hip arthroplasty
Replace femoral head and acetabulum.
OA, AVN, infection, congenital disorders, trauma
What are some indications for THA?
Restricted; WBAT
THA Weight Bearing Restrictions:
Uncemented → WB almost always _______________________
Cemented → ________________________
Functional mobility
THA has total hip precautions and implications for __________________________.
Posterolateral approach
THA has highest risk of dislocation acutely /c __________________________ → Fall risk reduction.
Cemented THA
- Most common
- Widely accepted over last 20 years
Early; tolerated
Cemented THA Precautions:
- Allows _____________________ WB
- Activity as _________________________
Uncemented THA
- Attaches directly to bone without cement
- Implant has a topography that is conducive for new bone growth
- Bone grows into surface of implant
Limited; limited; longer
Uncemented THA Precautions:
- ____________________ WB initially
- ____________________ ROM initially
- _____________________ healing time
No hip flexion >90°, no IR, no adduction past neutral
What are THA precautions for posterolateral approach?
No hip extension past neutral, no ER, no adduction
What are THA precautions for anterolateral approach?
0 or 1; foot drop; quad; education; stairs; pivoting
Physical Therapy for THA:
- Post-op day ______________________ pending no complications
- Check sensation and strength → Sciatic n. and femoral n. palsy can lead to ______________________ and _____________________ weakness (always check ankle DF)
- Focus on gross mobility /c relation to new hip precautions → _______________________ on do's/don'ts /c regard to functional implication
- Focus on gait and _________________________, assistive device training and safety; avoid _________________________
Precuations; elevated; abductor pillow
Physical Therapy for THA Cont'd:
- Gentle HEP of AROM/PROM/AAROM hip within _________________________
- DME recommendations: _________________________ toilet, BSC, etc.
- Car transfers and rolling → Cannot roll onto operative side, can roll onto non-operative side /c __________________________ secured in place to maintain hip precautions.
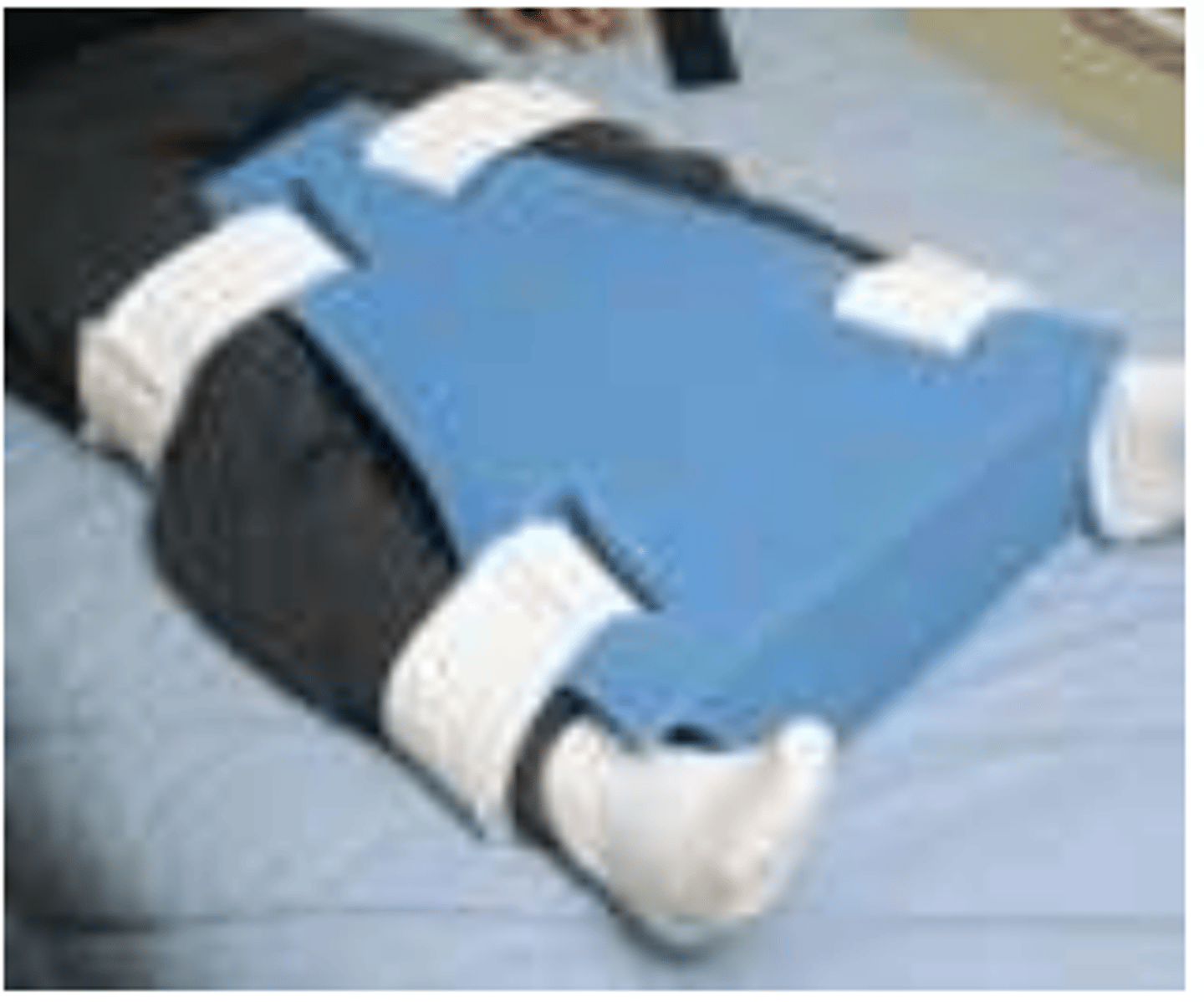

Sensation; stand patient up
Anesthesia for THA:
Regional Nerve Block → Spinal (Epidural) -or- General Anesthesia
If spinal (epidural) was administered, check bilateral _______________________ along entire LE, do not ________________________ if sensation has not fully returned.
Total knee arthroplasty (tricompartmental)
Replacement of both condyles, tibial plateau, dorsal surface of patella.
Partial knee arthroplasty (unicompartmental)
Replacement of the worn femoral and tibial articulating surfaces (medial or lateral compartment) → 1/2 of femur
Quicker
Partial knee arthroplasty has ______________________ rehab, but usually depends on patient's pain tolerance and progress.
OA; traumatic; nonseptic
Indications for TKA:
- Severe _____________________
- RA
- _______________________ arthritis
- _______________________ arthropathy
Stair; assistive device; supine
Physical Therapy for TKA:
- ROM and strengthening exercises → Educate on exercises but let patient know that you don't expect them to do them post-op day 1
- Functional mobility, gait training, _______________________ training
- ________________________ safety
- Education on positioning while __________________________
ER; to sky; flexion; pillow
Post-TKA Positioning while Supine:
- No hip _______________________ → Bolstering to side of knee
- "Toes and knees ______________________ at all times"
- No prolonged knee _______________________ to avoid hamstring contracture
- No _________________________ beneath knees
Continuous passive motion (CPM) machine
What does image show?
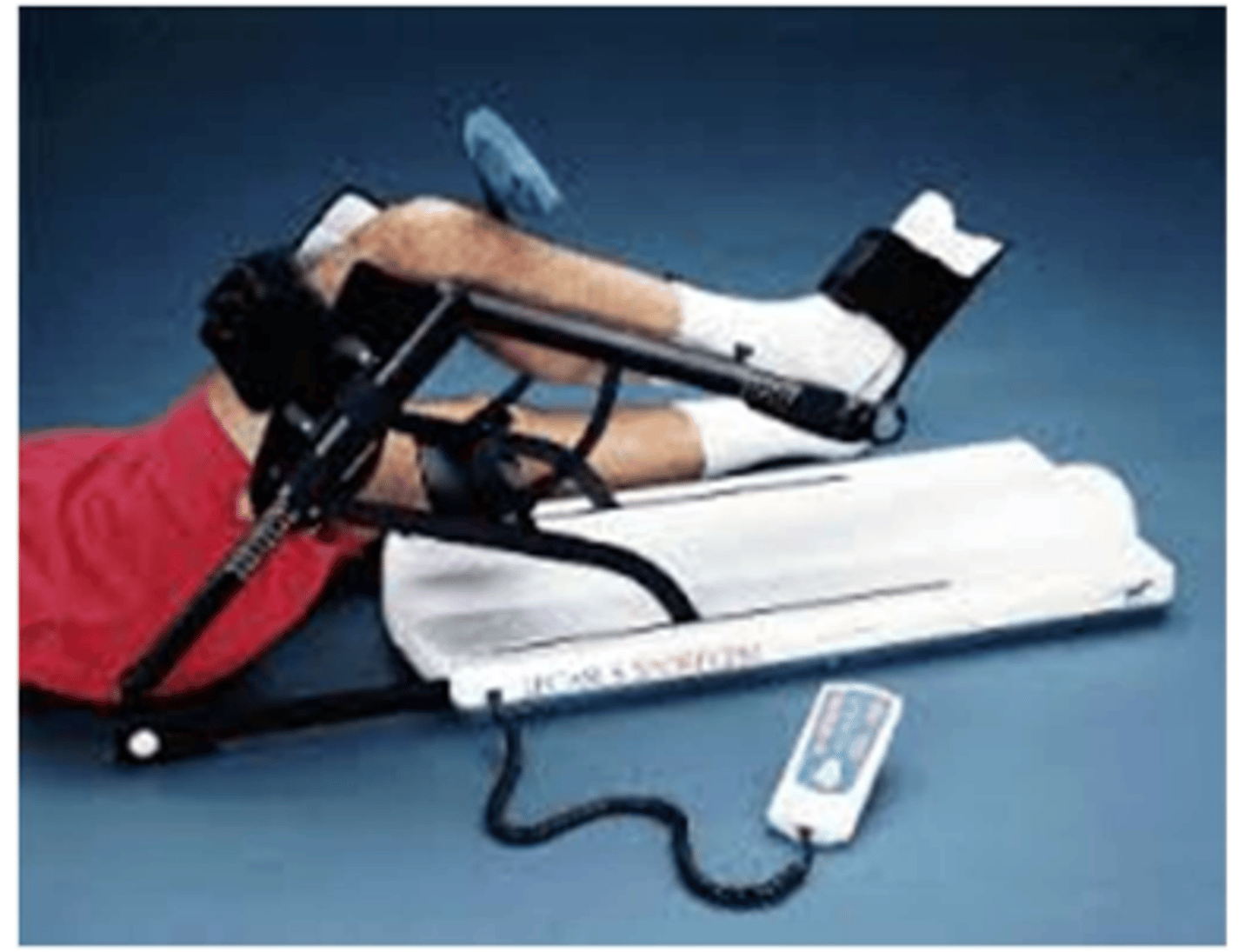

Joint line
For CPM, _____________________ needs to line up /c joint of machine → May be responsibility of PT.
Conflicting; surgeon; should not
Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) Machine:
Not covered by insurance
- Evidence is _________________________
- __________________________ preference
- Uncomplicated TKA who does HEP _________________________ need this
3-6 hours; 100 ft ambulation; anesthesia
Rapid Recovery Programs:
Early mobilization ________________________ after operation
- Sitting EOB → _________________________
- Performed in recovery room /c adequate monitoring and close observation of vitals and tolerance
- May need to wait till __________________________ wears off to perform PT
Analgesic; quadricep; ↓
Benefits of Rapid Recovery Programs:
- Less _______________________ effects → Nausea and vomiting, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness
- Improved strength and ROM of ________________________
- _______________________ length of stay in hospital
Fail; obstructive sleep apnea
Most people are rapid recovery program patients unless:
- ___________________ PT day of
- Diagnosis of ______________________
Sepsis; antibiotic; cement spacer; immobilizer; leg length discrepancy
Total Joint Resection and Infection:
- ______________________ → Irrigation + debridement to clear infection, amputation as last resort
- Aspirate joint, take cultures
- _____________________ treatment, debridement, amputation
- Removal of joint for re-implantation
- ____________________ for the knee to maintain joint space, tissue length, and improve WB
- Knee __________________ for stability while joint is removed
- Education on shoe lift, gait training d/t ______________________
- May see varied WB status and bracing
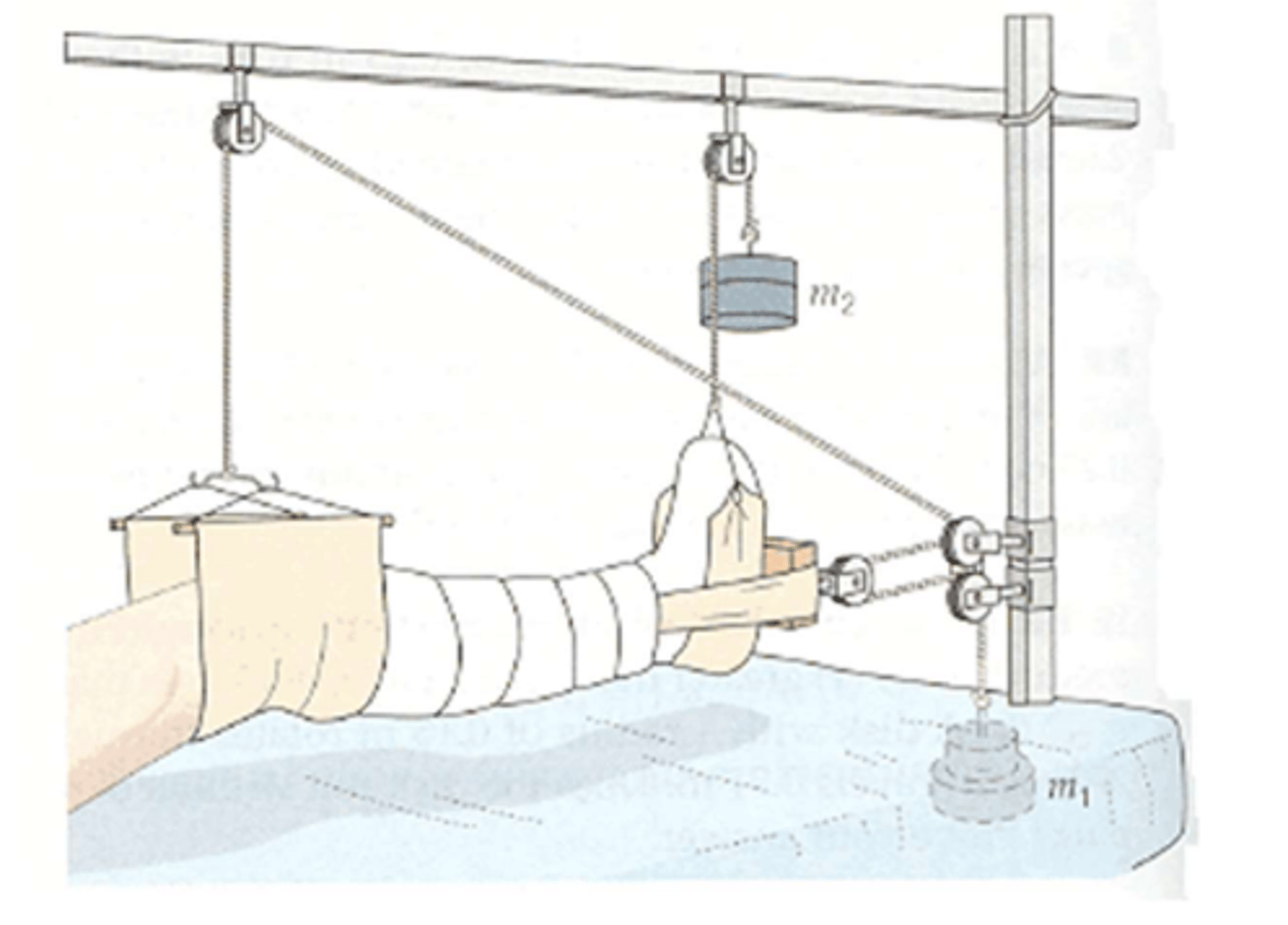
Traction
Distractive force on an extremity to reduce a fracture, immobilize a joint, or decrease muscle spasm.
Alignment
Traction uses weights and pulleys to restore ________________________.
Skeletal traction
Pins and needles through bone.
Strict bedrest
What are PT implications of skeletal traction?
Skin traction
Boots, slings, belts applied directly to skin.
Can be removed intermittently
What are PT implications of skin traction?
Freely; isometric
PT Implications of Traction:
- Do not change positioning of HOB, FOB, placement of blankets, etc.
- Keep weights haning __________________________
- __________________________ or active exercise of uninvolved extremities