GEOL 101 - Chapter 9: Geologic Time
The Importance of a Time Scale
Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth's history
Without a time perspective, these events have very little meaning
Numerical Dates
Specify the number of years that have passed since an event occured
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
The Importance of a Time Scale
Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth's history
Without a time perspective, these events have very little meaning
Numerical Dates
Specify the number of years that have passed since an event occured
Relative Dates
Place rocks in a sequence of formation
Principle of Superposition
In an undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, each bed is older than the one above and younger than the one below
This principle also applies to surface features like lava flows and beds of ash
Principle of Original Horizontality
Layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position
Rock layers that are flat have not been disturbed
Principle of Lateral Continuity
Beds originate as continuous layers that extend in all directions until they eventually thin out or grade into a different sediment type
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
Younger features cut across older features
Inclusions
Fragments of one rock unit that are enclosed within another rock unit
The rock containing this is younger
Conformable
Layers of rock that have been deposited without interruptions
Unconformity
A break in the rock record produced by nondeposition and erosion of rock units
Angular Unconformity
Tilted rocks are overlain by flat-lying rocks
Disconformity
Sedimentary strata on either side of the unconformity are parallel
Nonconformity
Sedimentary strata overlay metamorphic or igneous rocks
Fossils
Traces or remains of prehistoric life preserved in rock
Paleontology
The study of fossils
Permineralization
Mineral-rich groundwater flows through porous tissue and precipitates minerals
Molds and casts
A mold is created when a shell is buried and then dissolved by underground water
A cast is created when the hollow spaces of a mold are filled
Carbonization
Happens when an organism is buried, followed by compression, which squeezes out gases and liquids leaving a thin film of carbon
Impressions
Remain in the rock when the carbon film is lost
Amber
The hardened resin of ancient trees
Trace Fossils
Indirect evidence of prehistoric life
Conditions favoring preservation
Most organisms are not preserved
Rapid burial and the possession of hard parts increases the chances of preservation.
Correlation
Involves matching of rocks of similar ages from different regions
Provides a more comprehensive view off the rock record
Correlation Within Limited Areas
Often accomplished by noting the position of the bed in a sequence of strata
Involves matching of rocks of similar ages from different regions
To correlate over larger areas, fossils are used for correlation
Principle of Fossil Succession
States that fossils are arranged according to their age
Index Fossils
Widespread geographically and limited to a short period of geologic time
Fossil Assemblage
A group of fossils used to determine a rock's age
Environmental Indicators
Fossils can be used to infer information about past environments
Radioactivity
The spontaneous decay in the structure of an atom's nucleus
Alpha Emission
An alpha particle (two protons and two neutrons) are ejected from the atom
Beta Emission
A beta particle (an electron) is ejected from the atom
Electron Capture
An election is captured in the nucleus
Radiometric Dating
Uses the decay of isotopes in rocks to calculate the age of that rock
Half-life
The amount of time required for half of the radioactive isotope to decay
Potassium Argon
Has a half-life of 1.3 billion years
Can date rocks as young as 100,000 years
Potassium-40 (40K) decays to argon-40 (40Ar) and calcium-40 (40Ca)
40Ar is a gas and only present in rocks as the daughter product of the decay of 40K
A complex Process
Determining the quantities of parent and daughter isotopes must be precise
Some radioactive materials do not decay directly into stable daughter isotopes
Sources of Error
The system must be closed
No external addition or loss of parent or daughter isotopes
Fresh, unweathered rocks are ideal to use for radiometric dating
Earth's oldest Rocks
Oldest rocks are found on the continent
All continents have rocks exceeding 3.5 billion years
Confirms the idea that geologic time is immense
Radiocarbon Dating
Uses the radioactive isotope carbon-14 to date geologically recent events
Geologic Time Scale
Encompasses all of Earth History
Subdivides geologic history into units
Originally created using relative dates
Eon
Represents the greatest expanse of time
Phanerozoic Eon
The most recent eon, which begin about 542 million years ago.
Eras
Eons are divided into this
Paleozoic Era
Ancient Life
Mesozoic Era
Middle Life
Cenozoic Era
Recent Life
Periods
Each Phanerozoic era is divided into this
Epochs
Each period is divided into this
Precambrian
The 4 billion years prior to the Cambrian period are divided into two eons and often collectively refereed to as this
Precambrian Time
During this time, simple life-forms that lacked a hard part (algae, bacteria, worms, fungi) dominated.
Rocks are highly deformed metamorphic rocks
Terminology and the Geologic Time Scale
Precambrian is an informal name for the eons before the Phanerozoic
Hadean refers to the earliest interval of Earth's history
Geologic timescale is continuously updated
A ______ is formed when magma intrudes between existing sedimentary layers.
Silll
If a limestone, shale, and sandstone are deposited in that order without interruption, which of the following is true?
The limestone is the oldest and the succession is conformable.
What scenario requires a geologist to use the principle of cross-cutting relationships?
A dike truncates layers in a sedimentary succession.
Which of the following is associated with an erosive surface?
A stream running across an irregular surface.
An igneous dike across existing sedimentary layers and erupts at the surface, creating a layer of basalt, as well as all the layers below, are then cut by a fault. Which statement is true?
The fault is the youngest because it cuts through all the sedimentary layers and basalt.
A sandstone contains inclusions of metamorphic rock. An igneous dike cuts both the sandstone and inclusions. List the rocks from youngest to oldest.
Igneous dike, sandstone, metamorphic rock
If a sequence of sedimentary units is cut by a fault, what does the principle of cross-cutting relationships tell a geologist?
All of the sedimentary units must have been deposited and lithified before being cut by the fault.
Which of the following describes the principle of original horizontality?
Folded sedimentary layers were originally laid down flat and later deformed.
An undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks is exposed in a large river canyon. Which two principles would be demonstrated by the rocks?
Principles of superposition and lateral continuity
An igneous dike cuts through limestone, but not through the overlying sandstone. Which of the following statements is most accurate?
First, the limestone was laid down, then intruded by the igneous dike, and lastly the sandstone was deposited.
Following the deposition of a sequence of sedimentary rocks, which event is the first to occur to produce an angular unconformity?
Deformation
A(n) _______ exhibits sedimentary layers that are parallel to each other above and below an erosive surface
Disconformity
Which of the following is accurate description of nonconformity?
Younger sedimentary strata overlie uplifted and weathered igneous or metamorphic rocks
The sedimentary layers above a erosive surface are _____ relative to all rocks present below the surface.
Younger
Which of the following is common feature that all unconformities exhibit?
Erosive surface
What is the definition of relative dating?
Putting events in order form first to last
Petrified wood is an example of what type of fossil preservation?
Permineralization
Which conditions favor fossil preservation?
The organism is buried quickly.
A worm burrow is an example of which typeof fossilization?
Trace Fossil
Which of the following includes all common types f radioactive decay?
Alpha particle emission, beta particle emission, electron capture
Which of the following statements regarding radioactive decay is true?
More daughter products accumulate over time.
If one half-life has lapsed, what is the radioactive parent to stable daughter isotope ratio?
50:50
Radioactive decay in mineral shows that two half-lives has elapsed, giving an age of approximately 1.4 billion years. Using Table 11.1 as a reference, what is the correct radioactive parent and stable daughter isotope pair?
U^235, Pb^207
What are the characteristics of an index fossil?
Limited to a short span of geologic time, but widely distributed
What is the best definition of fossil range?
The period of time when an organism first and last appears in the sedimentary record.
Which of the following characteristics is the most desirable for constraining the relative age of rocks?
Organisms with overlapping ranges and geologically short lifespans
Which organism from the video is the least useful for relative dating?
Scallop
If a rock contains ten different kinds of fossils, which of the following must be true?
All of the organisms had to be alive when the rock was deposited.
How is the geologic time scale related to the fossil record?
The periods of time scale were constructed based on ranges of fossil organisms.
What is correlation?
Matching up rocks of similar age in different regions
The Principle of ________ states that organisms succeed one another in a definite, determinable order that can be used to recognize a specific time period.
Fossil Succession
What happens during radioactive decay?
Parent isotopes turn into daughter isotopes.
What is the scientific definition of half-life?
The amount of time over which the number of parent isotopes decreases by half.
Two containers hold the same radioactive isotope. Container A contains 1000 atoms, and container B contains 500 atoms. Which of the following statements about containers A and B is true?
The rate of decay of atoms in container A is greater than the rate of decay of atoms in container B.
A container hold 100 atoms of an isotope. This isotope has a half-life of 1.5 months. How many total atoms will total atoms will be in the container after 3 months?
100 atoms
A container holds 100 atoms of an isotope. This isotope has a half-life of 1.5 months. How many atoms of the radioactive isotope will be in the containers after 3 months?
25 atoms
A rock sample contains 75 atoms of a parent isotope and 25 atoms a daughter isotope. The half-life of the parent isotope is 100 years. How old is this rock?
50 years
What is an isotope?
An atom that has more or fewer neutrons than it should.
______ is a term used to define 88% of Earth's history prior to the start of the Paleozoic Era.
Precambrian
Which rock is best suited for radiometric dating?
Granite
The fossil record is biased toward preserving organisms with hard parts.
True
The first life on Earth developed during the Cambrian Period.
False
In southeast Utah, the San Juan River and its tributaries have cut through hundreds of feet of Paleozoic sedimentary rocks. The photo below shows the Honaker Trail Formation, the Halgaito Formation, and the Cedar Mesa Sandstone. Each unit is composed of rocks that were deposited in distinct environments, and record the transition from a marine to continental setting.
The Honaker Trail Formation is made up of predominately carbonates, which record deposition in a shallow marine setting.
The Halgaito Formation is located above the Honaker Trail Formation. This unit is composed of siltstones and sandstones deposited in channel and flood plain environments on a coastal plain.
The layers of the Cedar Mesa Sandstone make up the steep cliffs of this region. This unit is composed of sandstones, which accumulated mostly in an eolian, or wind-blown environment.
Use the information above and your knowledge of relative dating to rank the geologic events from oldest to youngest. Pay particular to the sediments and depositional environments for each formation.
Oldest Event - Youngest Event
1.Carbonate sediments were deposited in a shallow marine depositional environment.
2. Sediment was deposited in stream and floodplain depositional environments.
3. An abundance of sand was transported and deposited by wind in a large dune field.
4. The San Juan River and tributaries incised downward into preexisting sedimentary rock units.
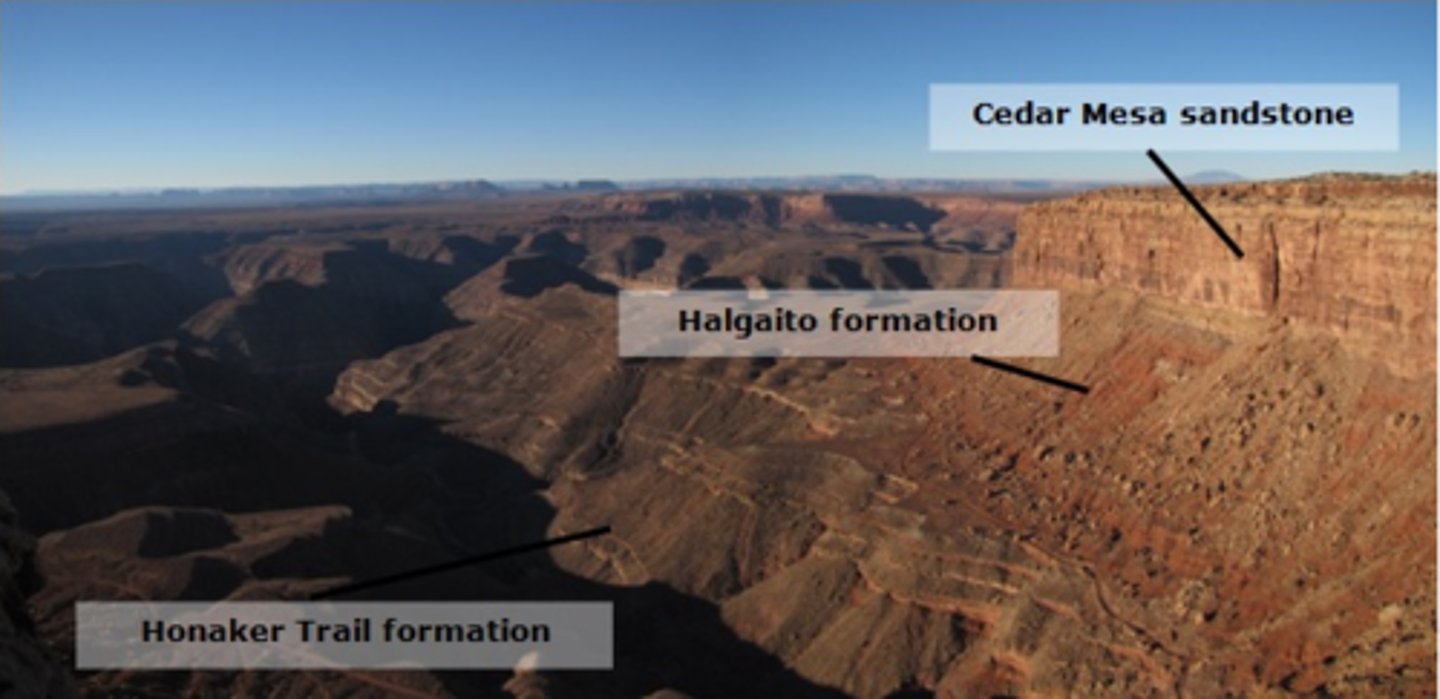
Which principles of relative dating did you use to answer the previous question?
Superposition and Cross-Cutting Relationships
c. Numerous sedimentary beds can be observed driving through the Valley of the Gods in southeast Utah. These sedimentary rocks are in their originally horizontal position, which means they have not been deformed. The spectacular spires and buttes that you see are the result of erosion driven by wind and water.
The Principle of Lateral Continuity states that sediments are deposited as continuous beds across a wide area until they transition to another sediment or thin at the edge of a basin. Using this principle, geologists can correlate units across areas where erosion has occurred.
Pay close attention to the rock units exposed along these buttes. Using the Principle of Lateral Continuity, can you connect the sedimentary beds in this photo? (image not shown)
Below are a series of sketches that show rock units organized by color, and traced across valleys with dotted lines. The keys include information on rock types and relative ages. Remember creating a clear and accurate key is important when sketching in the field. Pay special attention to the keys in these drawings when you make your choice. Select the correct sketch below.
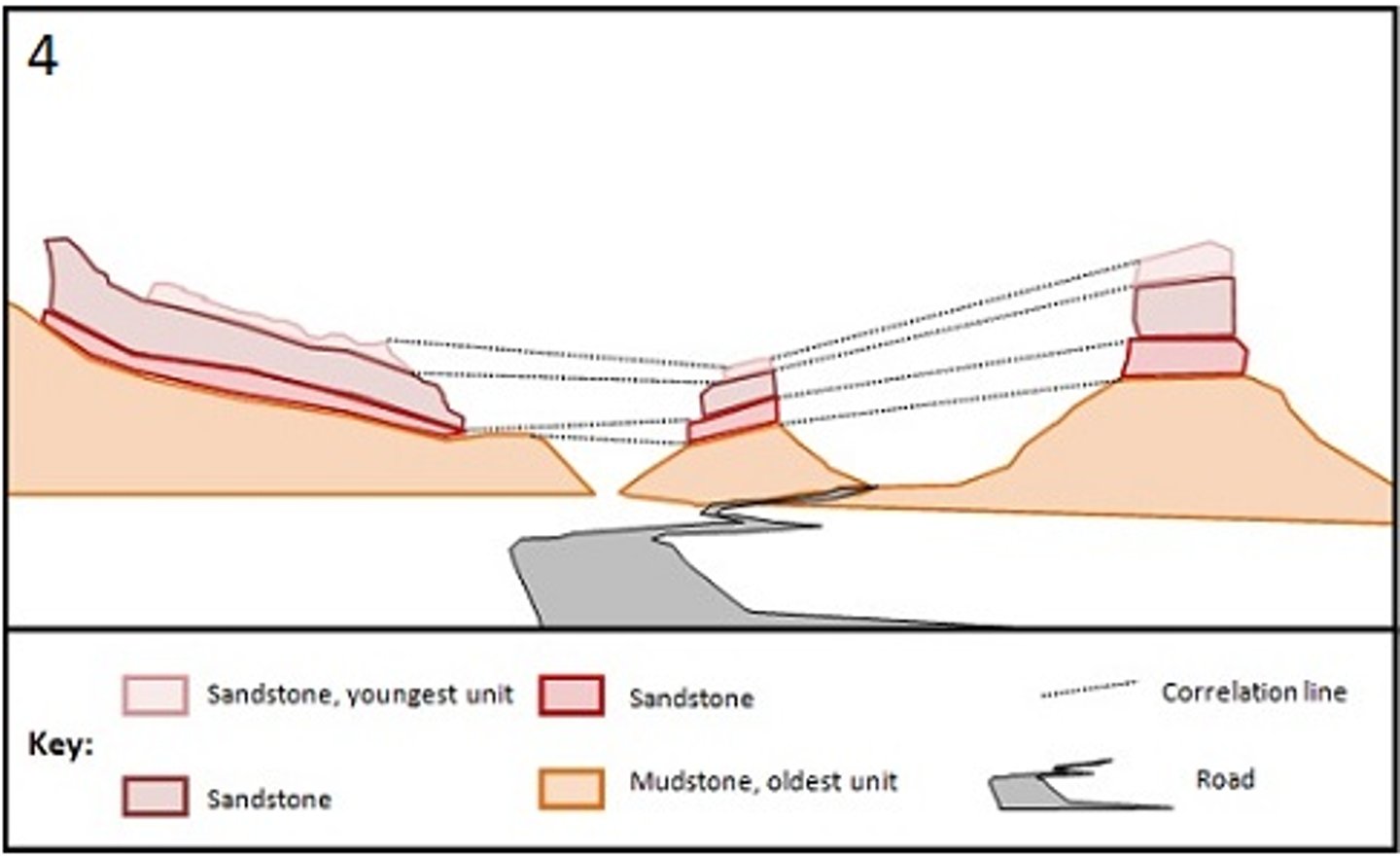
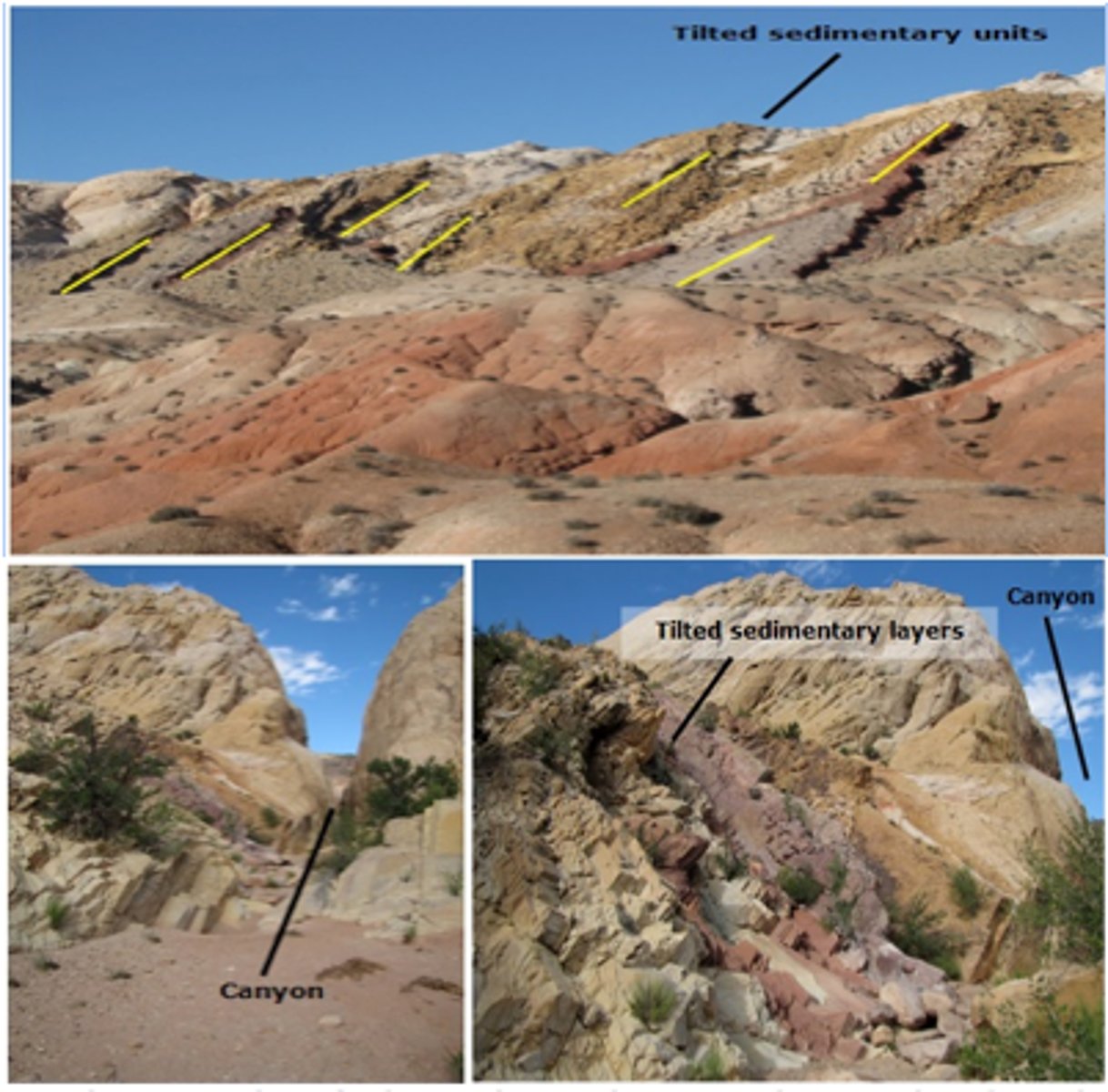
The San Rafael Swell is a monocline, or large step-like fold, located in central Utah. The photos below were taken on the east and southeast portion of this fold, and show tilted sedimentary beds and canyons from different perspectives.
Use the principles of relative dating that were discussed in the video to fill in the blanks of the sentences below.
The "Principle of Cross Cutting Relationships" can be used to determine the relative ages of the sedimentary rocks versus canyon formation.
The sedimentary beds were initially deposited in a(n) "horizontal" orientation.
The process of stream "incision" is younger compared to the folding of the rock units.
The "Principle of Original Horizontality" says that folded sedimentary beds have been disturbed since deposition.
The sedimentary layers are "older" than both folding and stream incision.

A dike, which is a tabular intrusive igneous body that cuts across existing rock structures, is shown below. Notice that this feature cuts through horizontal layers of sandstone, or country rock (outlined in yellow).
The inset photograph shows an inclusion, which is a fragment of unmelted crustal rock that was incorporated into a body of magma before it crystallized as a dike. During intrusion, magma caused the crustal rock to fracture and pieces were mixed into the magma. The magma then cooled, preserving the inclusion encased in igneous rock. You can see that the inclusion is different in composition than the surrounding rock.
Using principles of relative dating, classify the statements according to whether they are "true," "false," or there is "not enough information to tell."
True - The sandstone country rock is older than the dike.
True - The intrusive igneous rock making up the dike is the youngest in age.
False - The dike is older than the inclusion.
Not Enough Information to Tell - The inclusion is older than the sandstone country rock.
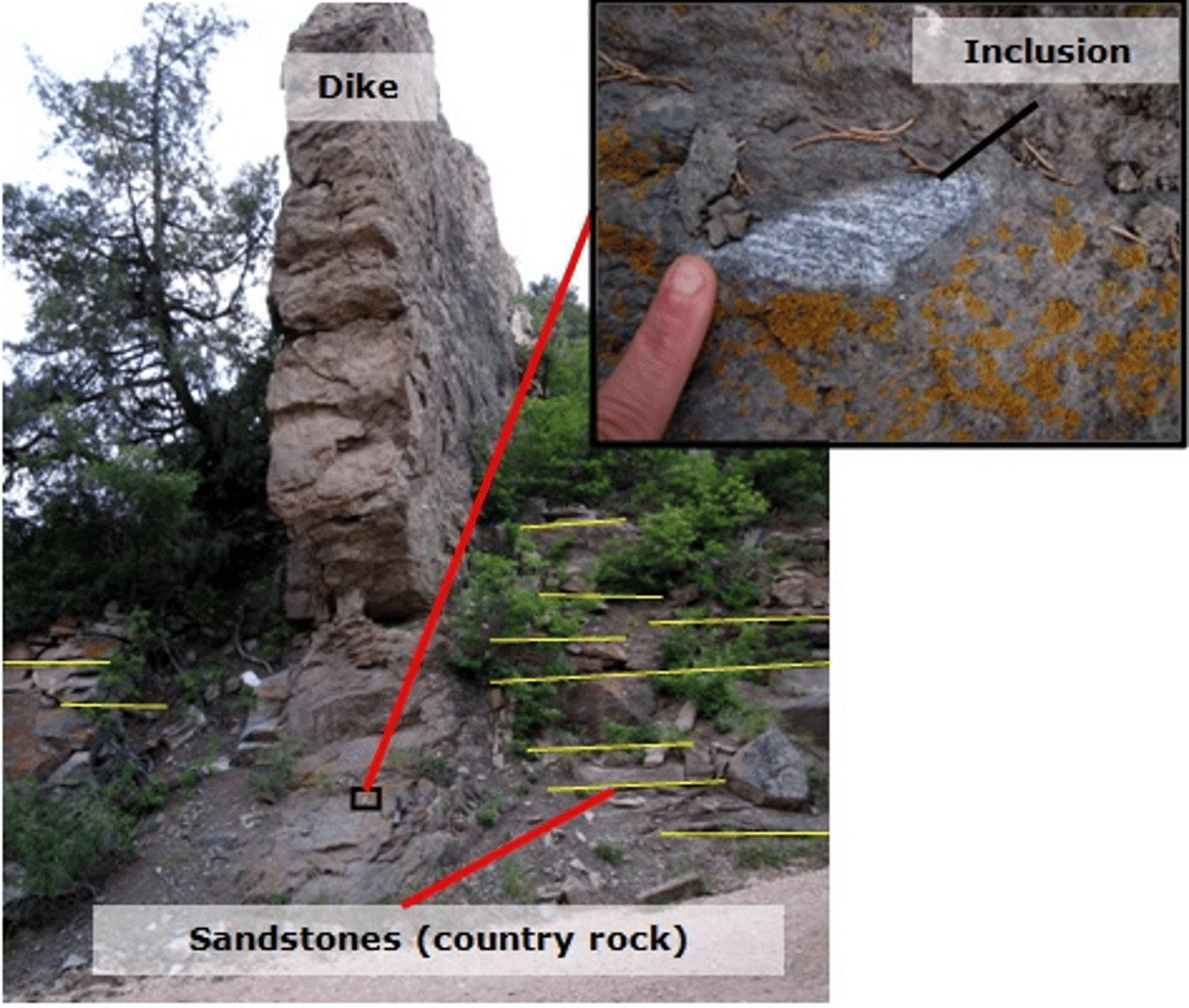
The Principles of ______ and ______ were used to determine relative ages in the previous question.
Inclusions, Cross-Cutting Relationships
How is the atomic number of an atom determined?
Counting the number of protons in the nucleus.