Brain Anatomy
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
psych 345
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Glia
-Non neuronal cells in CNS and PNS
-Do not generate action potentials
-Hold Neurons in place, supply nutrients and oxygen, insulate neurons, destroy pathogens & remove dead neurons
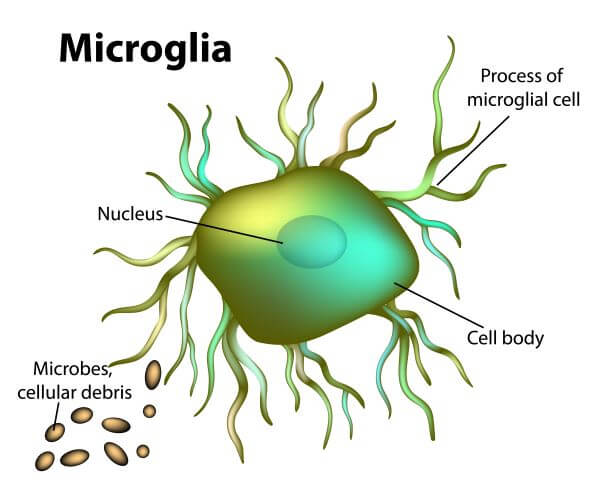
Microglia
-Microglia are specialized immune cells residing within the CNS. Originating from myeloid progenitor cells during embryonic development, they migrate into the brain early in life.
-Microglia function as the primary immune defenders of the brain, actively surveying their surroundings.
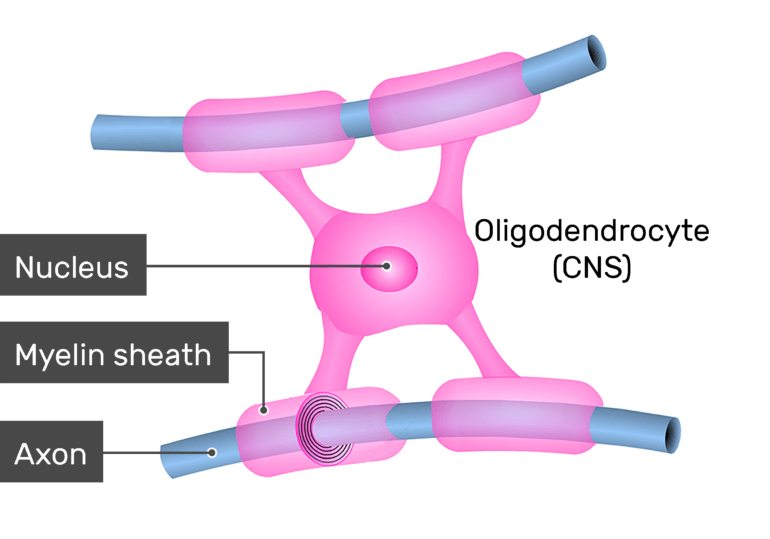
Oligodendrocytes
- are specialized cells in the brain that produce myelin, a fatty substance that insulates nerve fibers and helps electrical signals travel quickly. They also support the metabolic needs of nerve cells, providing them with nutrients and energy.
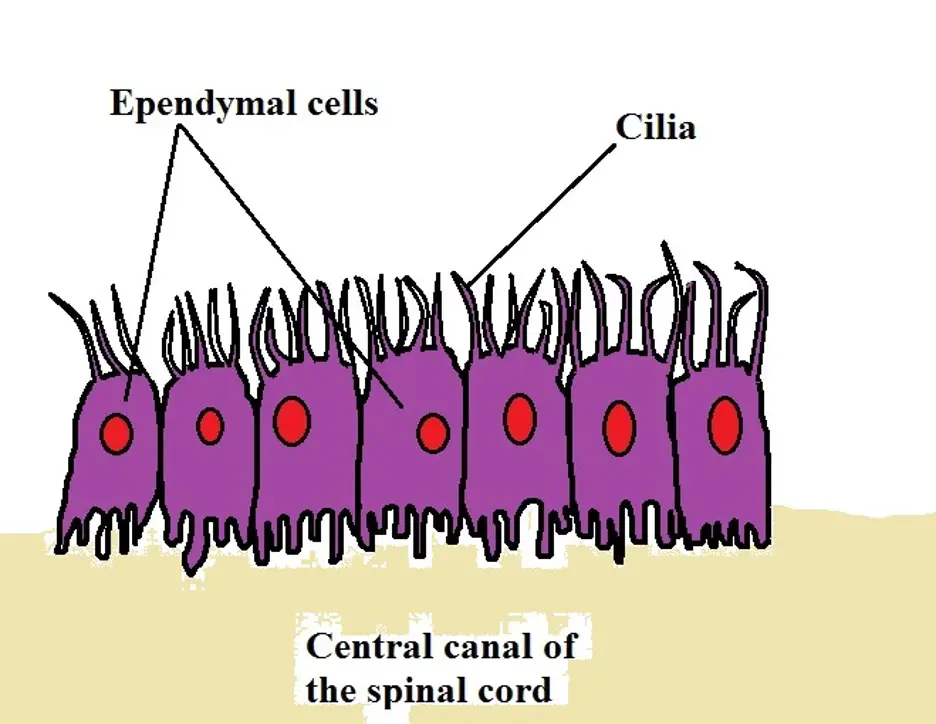
Ependymal
-a thin membrane that lines the ventricles of the brain and the central column of the spinal cord. Their main function is to secrete, circulate, and maintain homeostasis of the cerebrospinal fluid that fills the ventricles of the central nervous system.
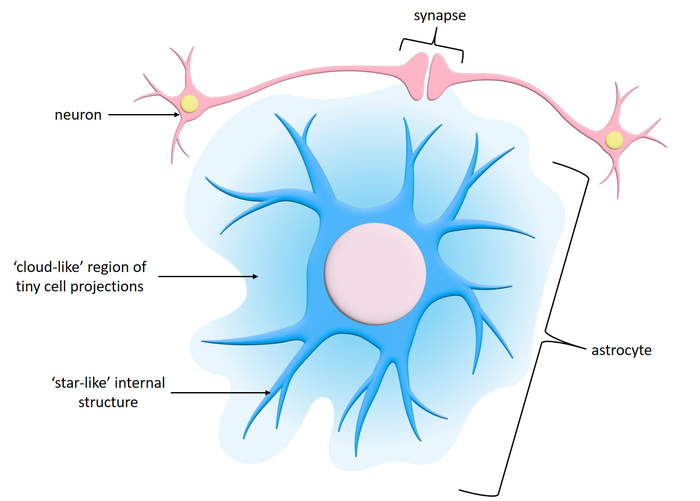
astrocytes
-Fibrous astrocytes are prevalent among myelinated nerve fibers in the white matter of the central nervous system.
-protoplasmic astrocytes occur in the gray matter of the central nervous system.
meninges
-brain’s protective covering
Dura mater
-strong and durable
-the outermost layer
archanoid
-”spider like” layer
-spongey like
-2 layer of meninges
Pia mater
-inner most layer of meninges
-clingy and closest to brain
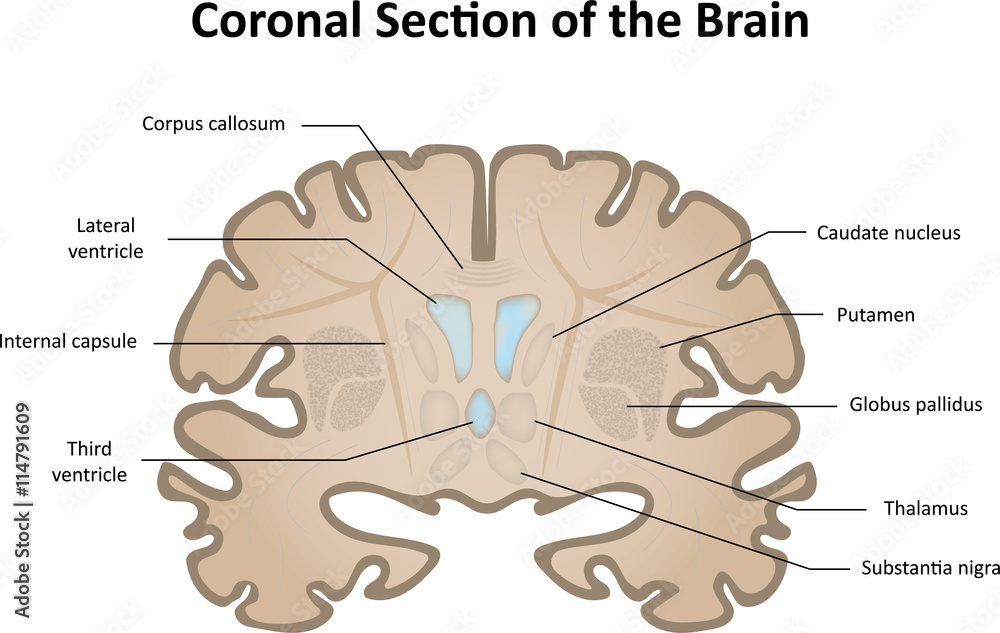
Coronal
-Anterior and posterior
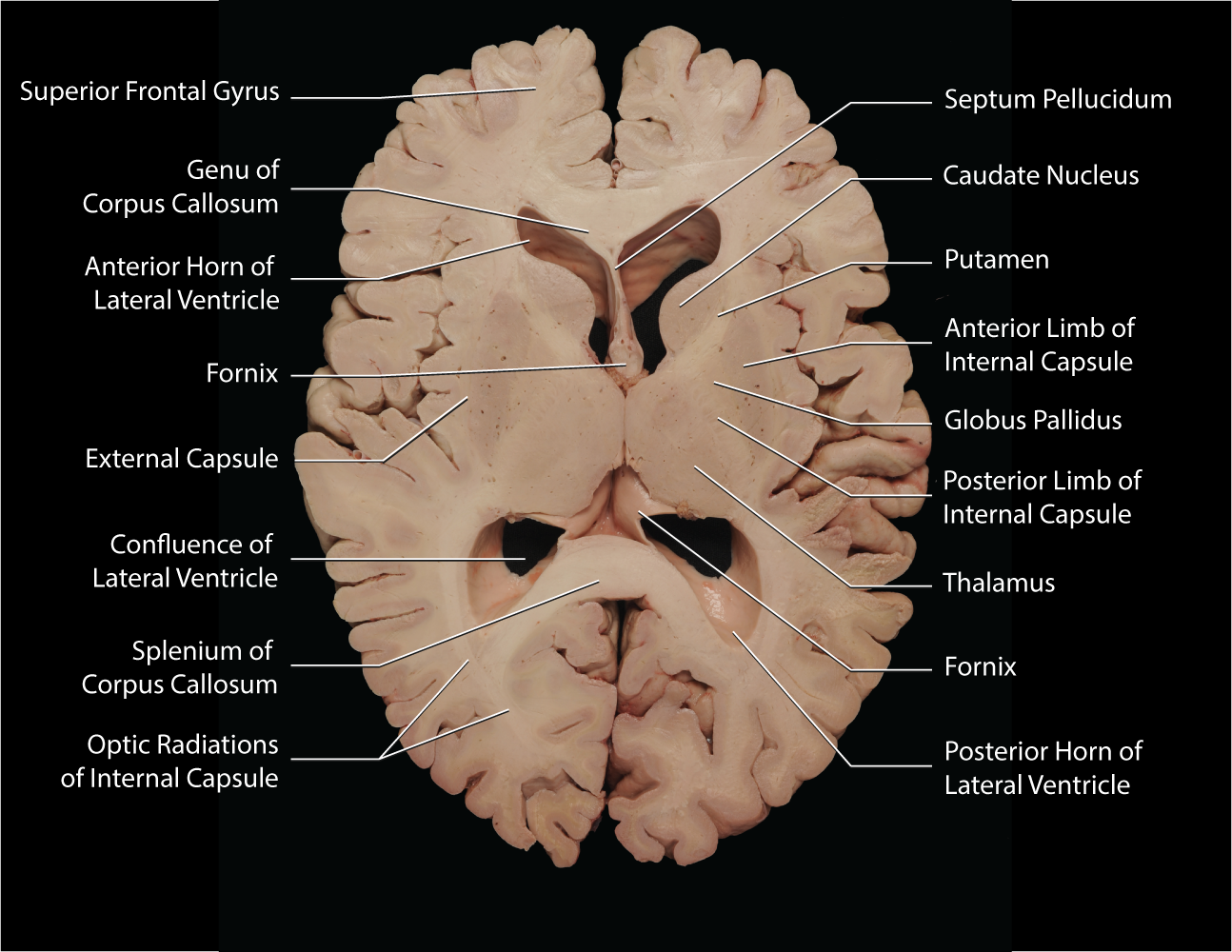
Horizontal
-Dorsal and Ventral
sagittal
-Right and left hemisphere
Gray Matter
-Neuronal Cell bodies(glia too)
-forms nuclei and cortex
white matter
axons and myelin(glia too)
Cortex
-Ribbon of tissue around the surface of the brain
White matter Tracts
-Large collection of axons travelling toward or away from a nuclear layer in CNS
U-fibers
-Subcortical U-fibers, also known as short association fibers, represent connections between adjacent gyri of the brain, located within the cortex or immediately deep to it in the very outer parts of the subcortical white matter 1.
Fasciculi
-are bundles of nerve fibers that connect different areas of the brain, playing crucial roles in various functions.
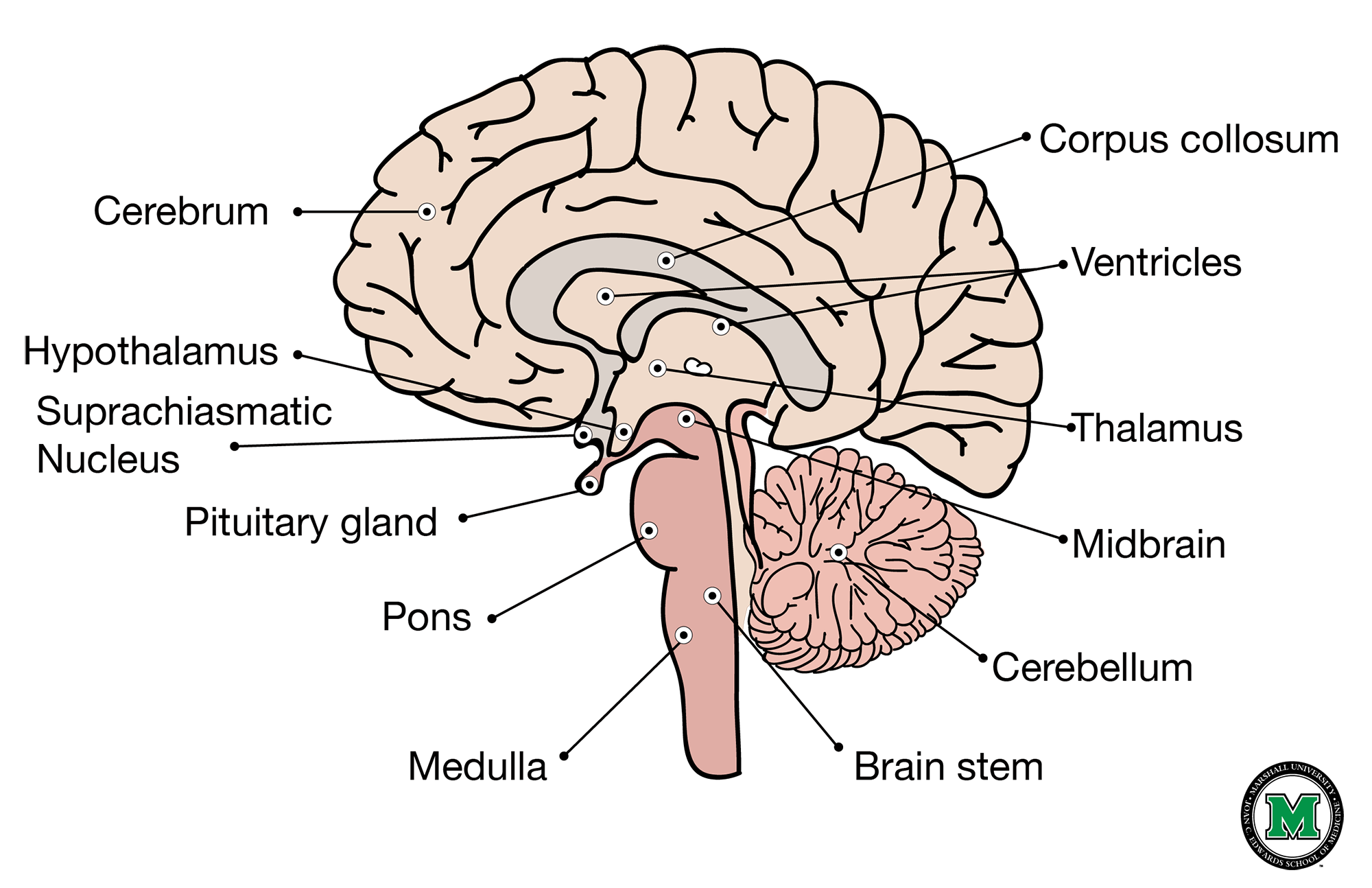
Corpus Callosum
-connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres
diffusion tensor imaging
-Iimages brain’s white matter tracts by tracking the direction/orientation of
water molecules within white matter
Brainstem
-begins where the spinal cord enters the skull
-extends to lower areas of forebrain
Cerebellum
-motor learning and coordination
Damage: equilibrium problems, postural defects, impairments in motor activity, ataxic gait(staggering, unsteady)
Reticular Formation
-controls sleep and waking
Damage: Permanent unconsciousness
Medulla
-involuntary functions
-breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
Damage: Breathing stops, heart stops
Pons
-vital body movements
-Relays signals from cerebellum to forebrain
Damage: Locked-in syndrome
Superior Colliculus
-receives projections from the retina to control eye movements
-helps locate objects in space
Inferior Colliculus
-receives projections from the ear to control eye movements
-helps locate objects in space
Diencephalon
-at the junction of the midbrain and forebrain
Hypothalamus
-Maintains balance of the internal environment(homeostasis), hunger, thirst, body temp, fatigue
-Mamillary body part of memory circuitry
Thalamus
-sensor gateway
-all sensory modalities make connection is thalamus (except olfaction) then go to primary sensory areas in cortex
Forebrain
-3 main nuclei (globus pallidus, caudate, putamen)
-motor control, reward processing, memory interacts extensively with cortical areas
-responsible for motivation, learning, emotion, and memory
-Phylogenetically youngest structure
Diseases: Huntington’s, Parkinsons
Forebrain crude functionality
-Frontal (voluntary motor control)
-Occipital (visual)
-Parietal (Somatosensory
-Temporal(Auditory)
fissure
-deep cleft
Sulcus
-Shallow cleft
Gyrus
-Ridge
Decussations
Crossings