CH 37 The Endocrine System
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Hormone
Regulatory chemical that is secreted into extracellular fluid, carried by the blood and can act at a distance from the source. These regulatory chemicals are found in multicellular organisms and aid in homeostasis. They travel to the cell that has a receptor and attach to the receptor to induce cellular response.
Endocrine system
Organs and tissues that produce hormones
Lipid-deprived hormones
Cholesterol and steroid hormones such as testosterone and estradiol are examples of?
the amino acid tyrosine.
The hormone epinephrine, which triggers the fight-or-flight response is derived from what amino acid?
the amino acid tryptophan
The hormone melatonin, which regulates circadian rhythms, is derived from what amino acid?
oxytocin
Look at the image. What peptide hormone is this?
growth hormone
Look at the image. What peptide hormone is this?
folliclestimulating hormone
Look at the image. What peptide hormone is this?
Neuroendocrine system /Nervous system
this system controls the body through nerve impulses conducted by axons. These responses occur within milliseconds. This system also causes relatively local, specific effects. Stops when stimulus stops and adapts quickly.
endocrine system
this system controls the body through hormones transported in the blood. It may have widespread general effects. Responses occur after seconds to days, are more prolonged and adapts slowly.
They need a receptor to work. Receptors change with cellular activity. They may be found on many different cells or limited to a small number of specialized cells. Hormone receptors may also be found within the cell or on the plasma membranes. Number of receptors can change.
Why are hormones very specific?
Lipid-derived hormones (intracellular hormone receptors)
bind to transport proteins. Once they reach the target cell, they are released from their carrier protein and pass through the plasma membrane and bind to a target within the cell. The hormone/receptor complex regulates transcription by increasing or decreasing the synthesis of mRNA.
Lipophilic
cross membrane and bind to intra-cellular receptor
Excretory System
Maintains water balance & releases the antidiuretic hormone
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Regulates amounts of water excreted by kidneys therefore regulating blood pressure
Released when water levels of bloodstream are lower
(function of osmo-receptors)
Underproduction causes diabetes insipidus
released with the function of osmo-receptors
Aldosterone (steroid hormone)
This hormone is produced by adrenal cortex. It is the Main regulator of water and electrolytes such as sodium and potassium in the body. It Promotes reabsorption of water and is Released due to the signaling of the renin angiotensin system, whereas ADH is released with the function of osmo-receptors.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
what type of hormone promotes the maturation of sperm cells in males and promotes the development of egg cells in females?
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
what type of hormone promotes the production of testosterone in males and in females creates the surge that causes ovulation?
oxytocin
hormone that stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth is __
insulin (metabolism)
Produced by beta cells of pancreas. It lowers blood sugar through the increase of cellular uptake and utilization by cells. A deficiency in this hormone results in diabetes mellitus.
glucagon (metabolism)
Antagonist to insulin. Produced by alpha cells of pancreas and raises blood sugar by targeting liver to break down glycogen.
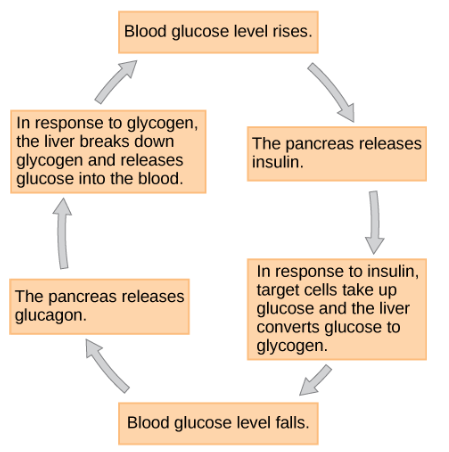
metabolism
Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels. This is called__
Basal metabolism rate
(amount of calories required by body at rest). It is determined by thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Released from thyroid gland in response to stimulation by Thyroid Stimulating Hormone.
Hypothyroidism
= low metabolic rate
Weight gain, sensitivity to cold, lethargy
Hyperthyroidism
= high metabolic rate
Weight loss, irritability, increased heart rate
the parathyroid hormone (PTH) which is released in response to low blood calcium levels and increases calcium levels.
Calcium is regulated by?
Calcitonin
this hormone is the antagonist of (PTH) & has opposite effects in the body because it decreases calcium levels
the Growth Hormone (GH) which releases and inhibits other hormones from hypothalamus
Growth and cell replication are regulated by:
GH (Growth Hormone)
Stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration
Increases rate of protein synthesis
Is glucose sparing
Short Term Stress
Epinephrine for “fight or flight” from adrenal gland is what type of stress?
Long Term Stress
Cortisol from adrenal gland (Anti-inflammatory) is what type of stress?
Hypothalamus
Integrates the endocrine and nervous systems.
Synthesizes and secretes regulatory hormones that control endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary.
pituitary gland
Also known as the hypophysis. Hangs by a stalk from the hypothalamus & Consists of two parts:
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
Appears glandular and is NOT part of the brain. Hypothalamus releases neurohormones, it causes the gland to release tropic hormones (these hormones then work on other endocrine glands)
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
Appears fibrous because it contains axons from Hypothalamus& IS part of brain. 2 hormones are produced in the hypothalamus, and stored in special cells which are then released: ADH and oxytocin
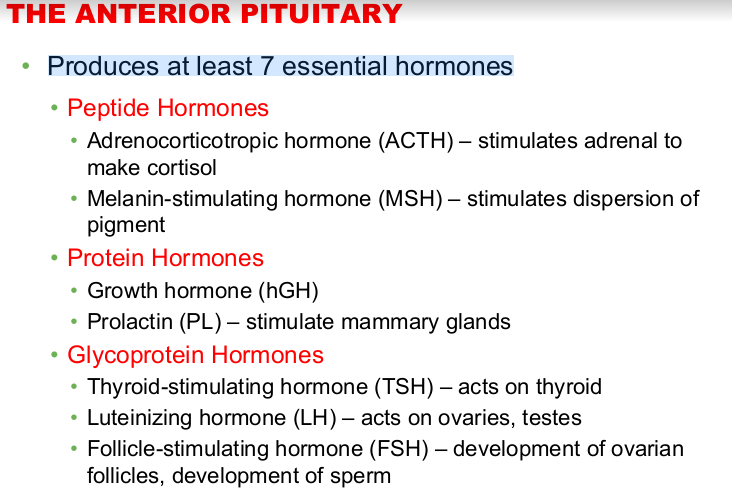
anterior pituitary gland
Produces at least 7 essential hormones classified into 3 groups: peptide hormones, protein hormones, & glycoprotein hormones