Zoology Ch. 20: Arthropods 2
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What organisms make up Subphylum Crustacea
Lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, crabs, water flies, copepods, & barnacles(67,000 species)
What are distinguishing characteristics of subphylum crustacea?
“Insects of the sea”
They are diverse and abundant, Mostly marine, but some freshwater and a few Terrestrial species. They have two pairs of antenna, pairs of mandibles, two pairs of maxillae, biramous appendages(two branches), gills for respiration, And Tagama that includes head, thorax and abdomen with typically 16 to 20 segments
Explain the thoracic segments of Subphylum Crustacea
Cephalothorax = One or more thoracic segments feast with the head
A cuticle made up of chitin, proteins, and CaCO3 → Carapace = Used dorsal cuticle of the head that may cover most of the body or just the cephalothorax
Soft, thin, flexible joints
Abdomen ends with the telson that bears the anus
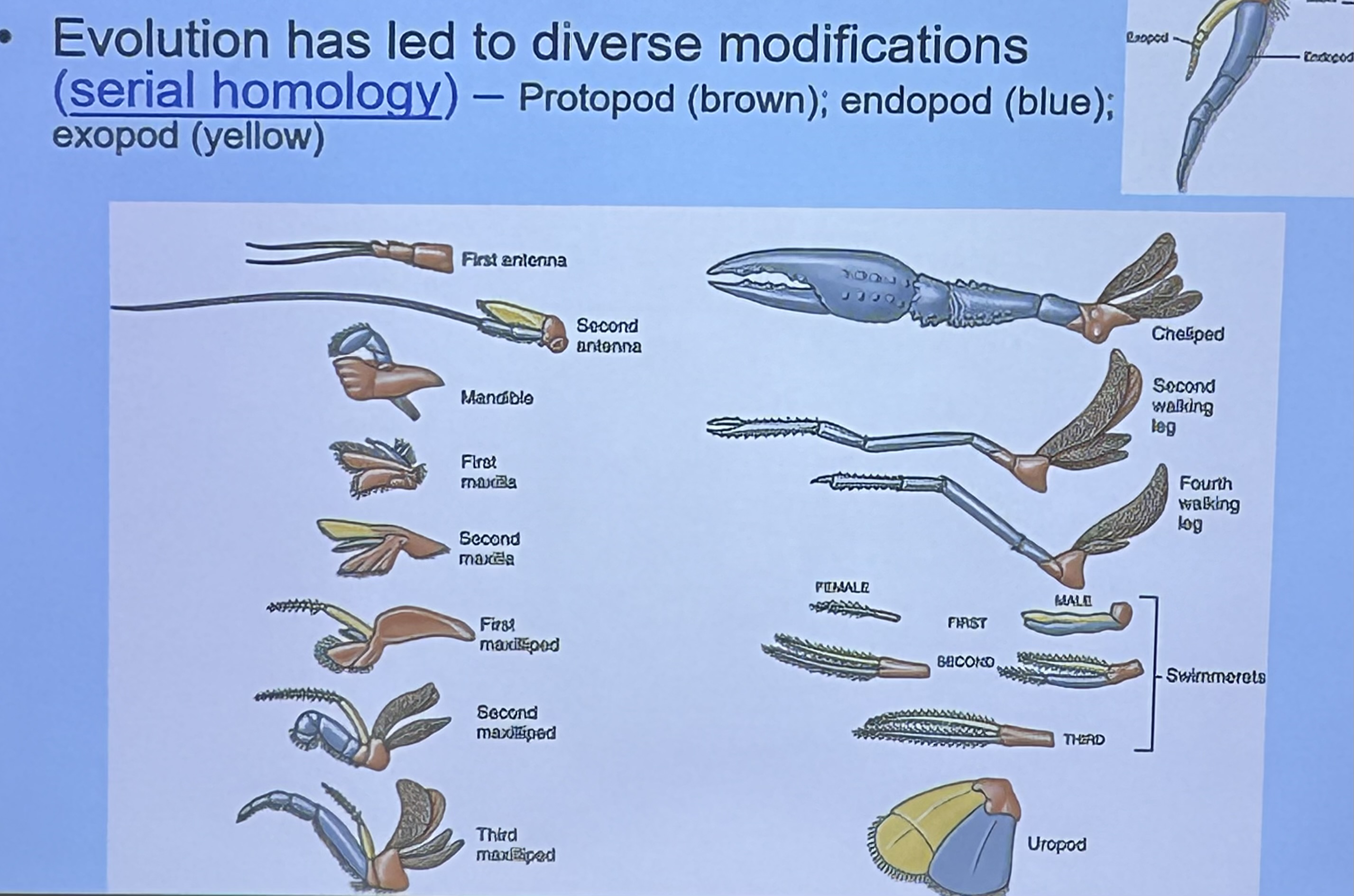
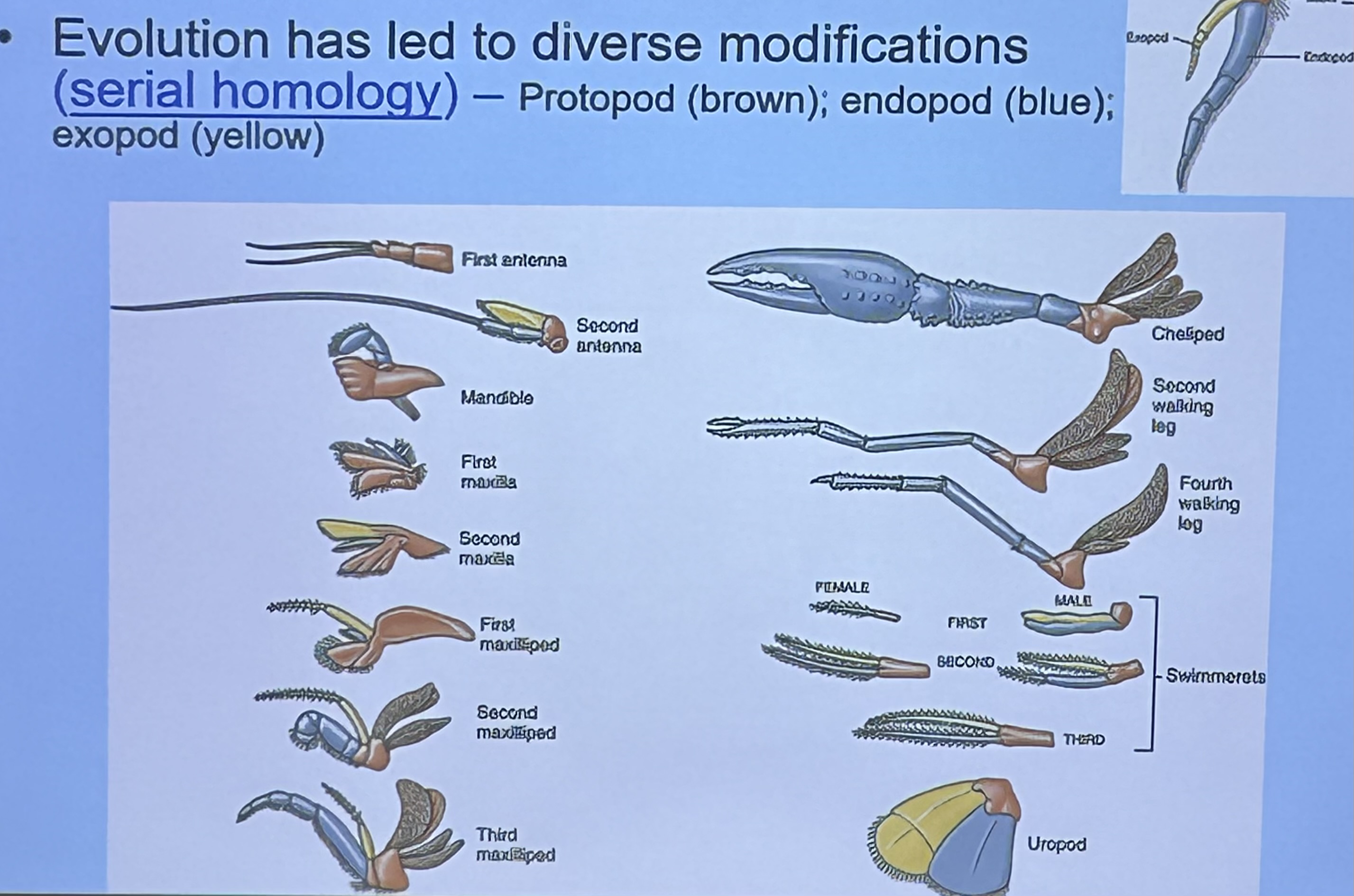
Serial homology in Subphylum Crustea ⭐️
Evolution has led members of this phylum to have similar limbs that evolve into diverse modifications. Each limb will have a Protopod, endopod, and expoed
What are these limbs modified for? ⭐️
First antenna & second antenna
Sensory
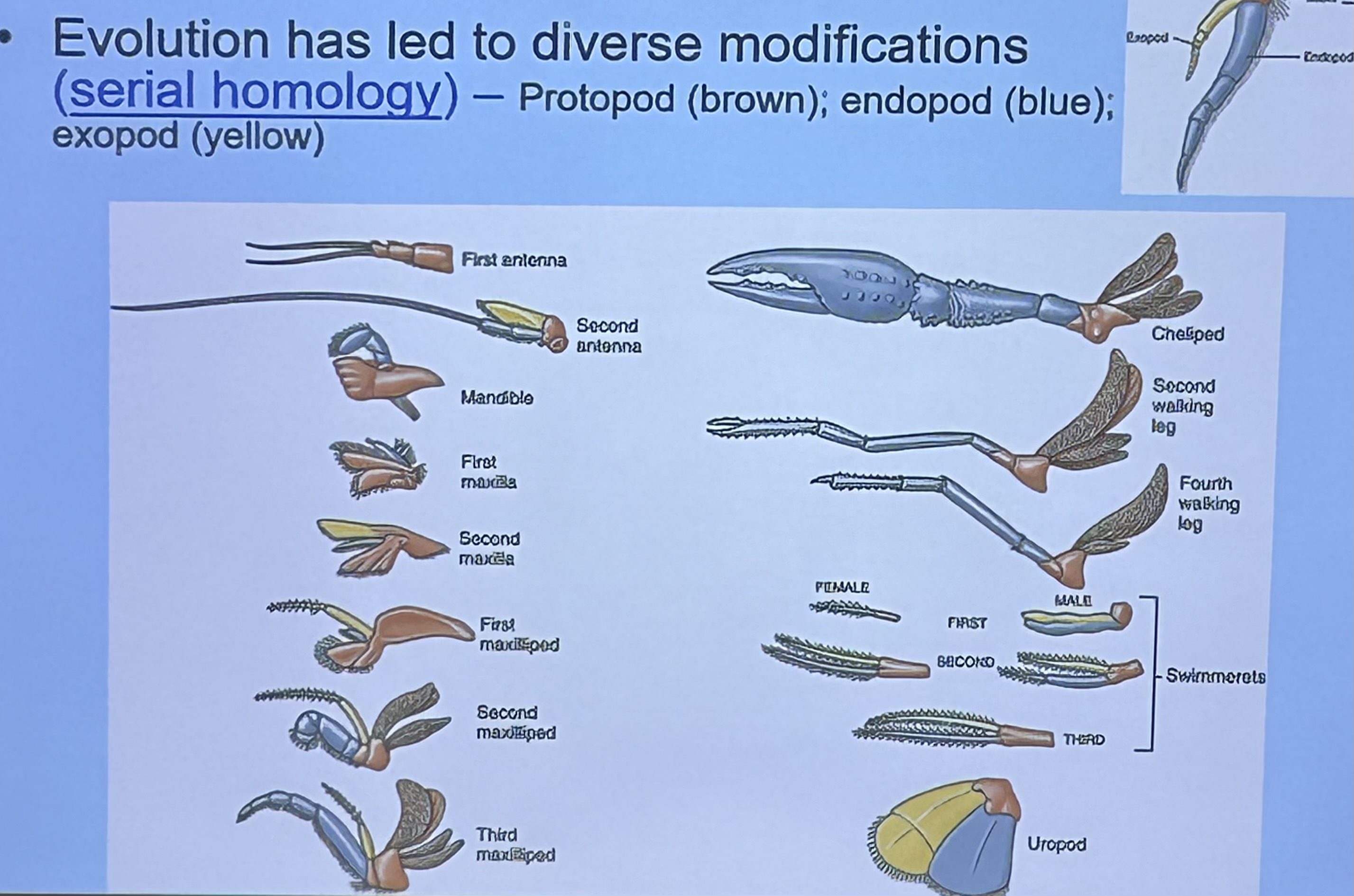
What is this limbs modified for? ⭐️
Mandible
Crushing food
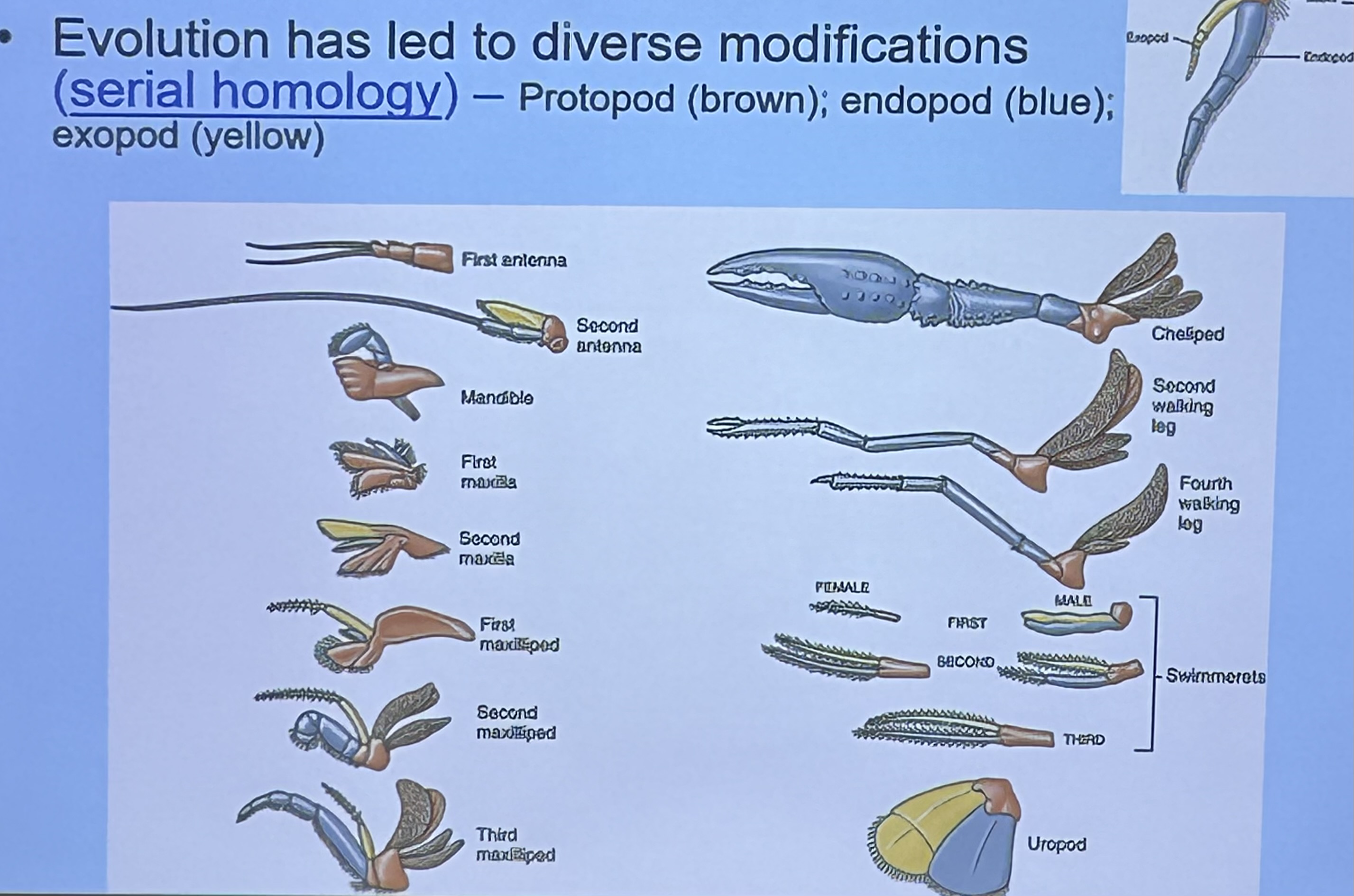
What is/are this/these limbs modified for? ⭐️
First maxilla
Shredding food
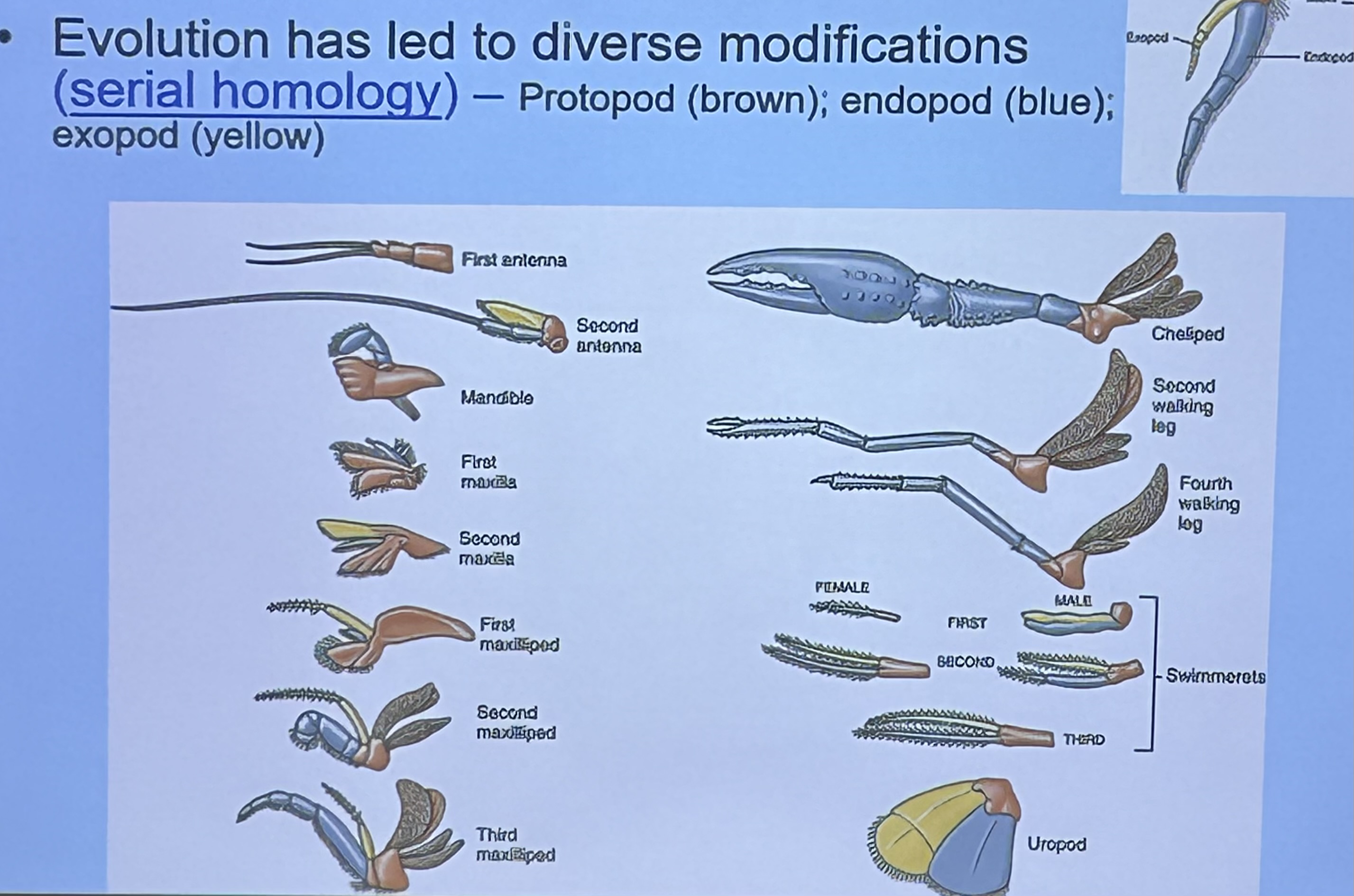
What are these limbs modified for? ⭐️
First, second, and third Maxilliped
Manipulating food and sensory
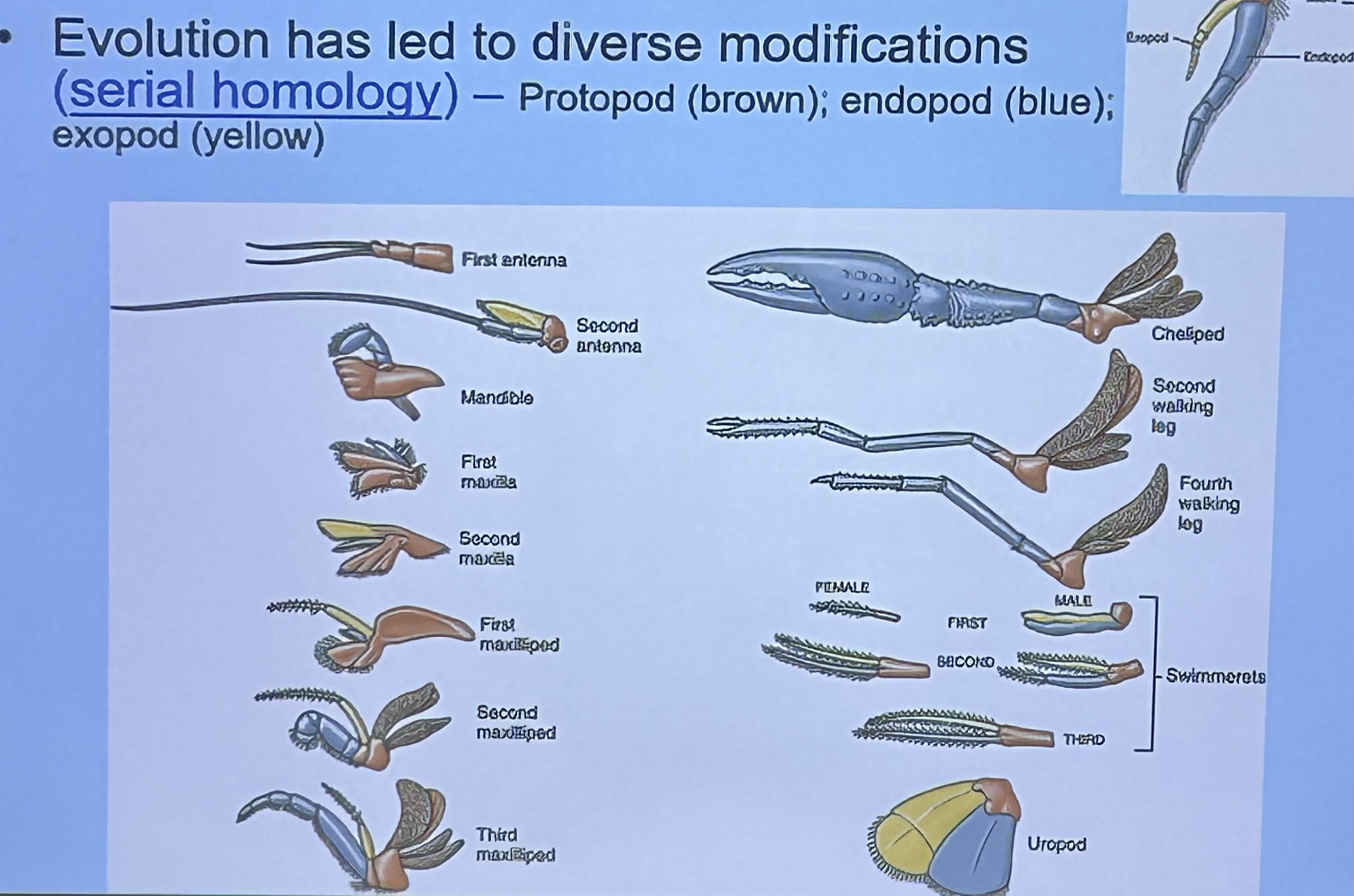
What is this limb modified for? ⭐️
Cheliped
Offense & defense
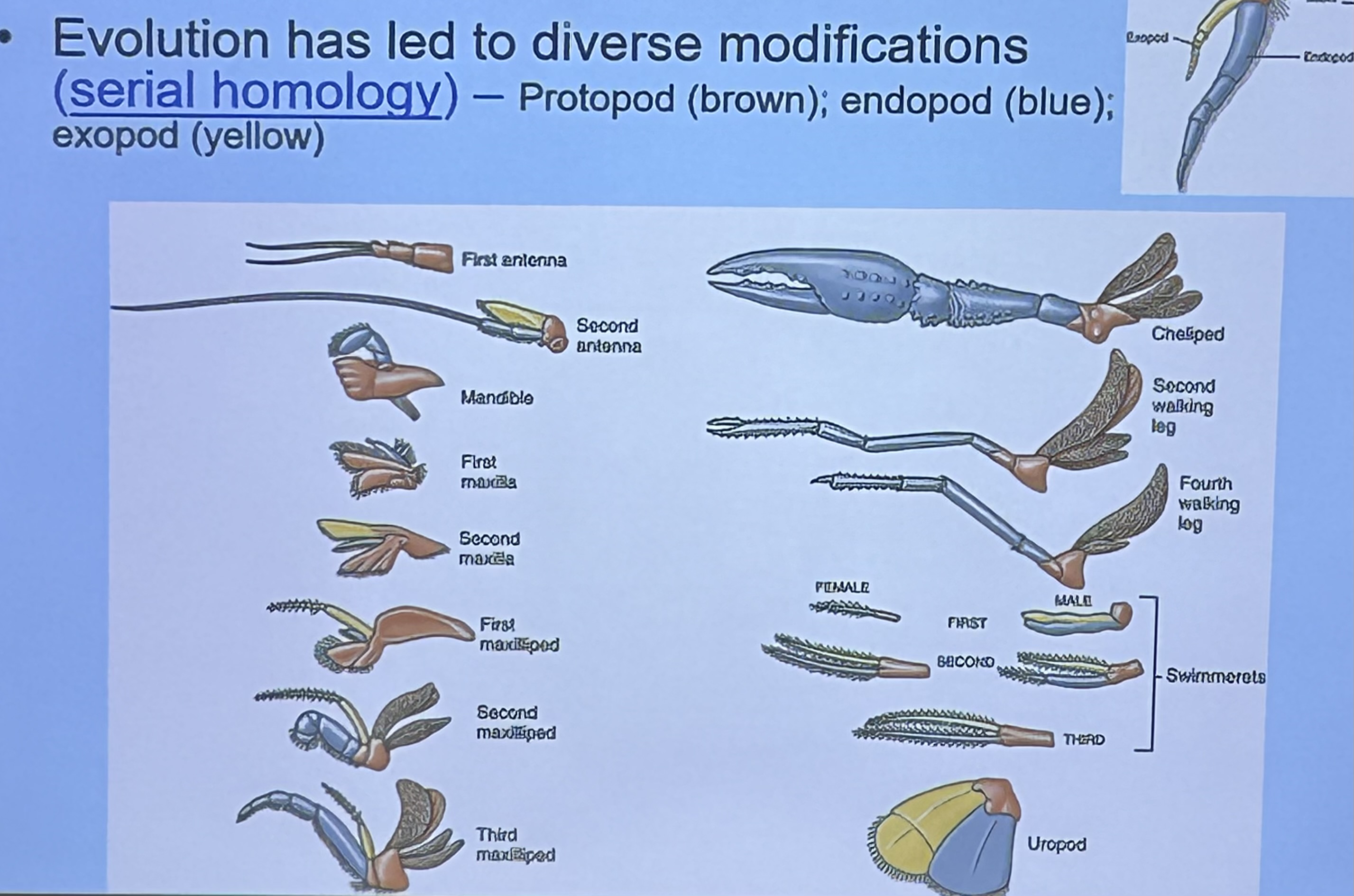
What is this limb modified for? ⭐️
Uropod
Egg protection & swimming
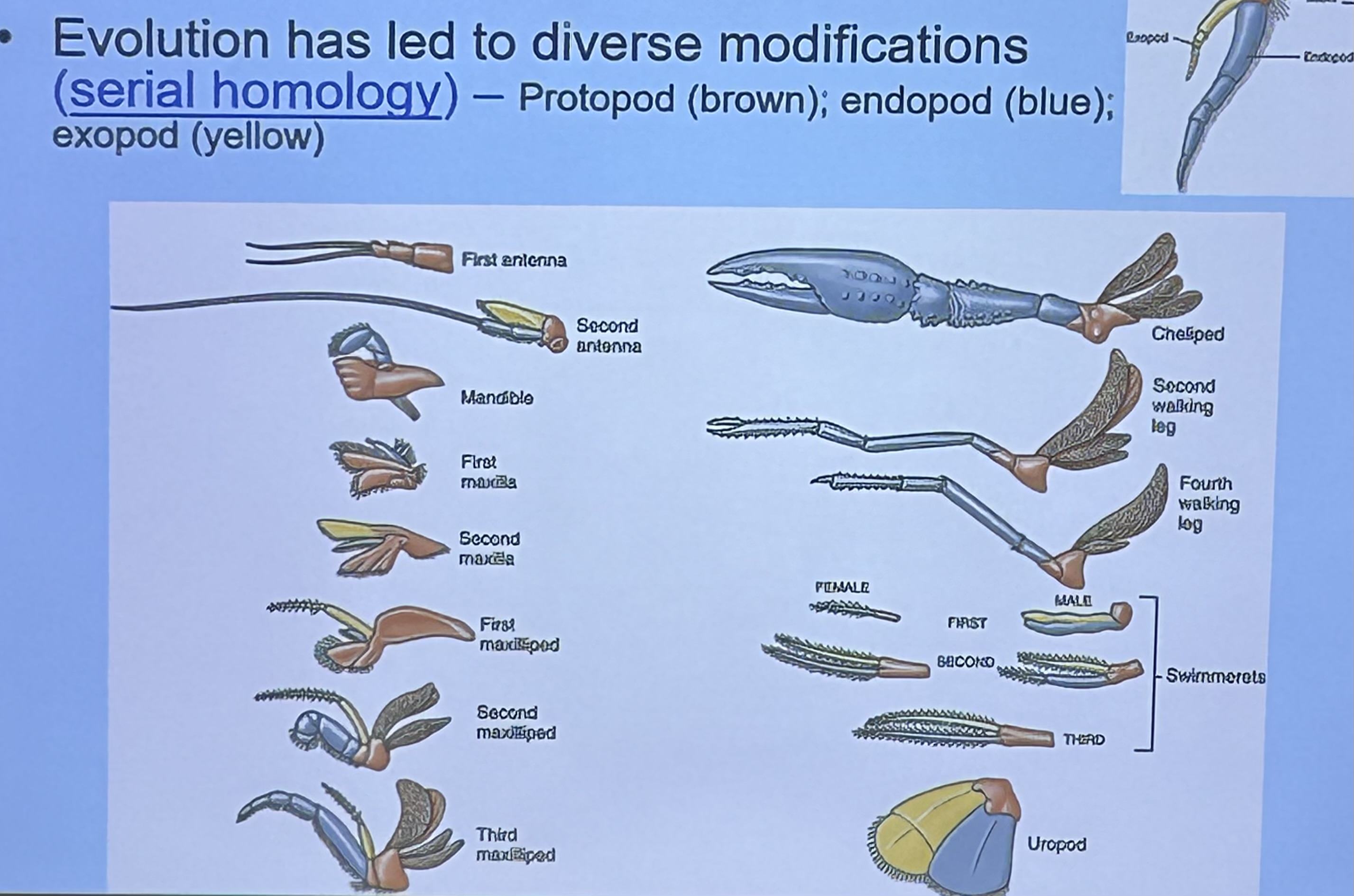
What are these limbs modified for? ⭐️
Swimmerets
Respiration, swimming, holding offspring, sperm transfer
Respiration in Subphylum Crustacea
In small crustaceans, respiration occurs via gas exchange via diffusion across the cuticle, while in large crustaceans gills are used for respiration
Circulation in subphylum Crustacea
Open circulatory system with heart and some arteries pumping hemolymph
Hemolymph
Circulatory fluid(blood) of invertebrates
Excretory system of Subphylum Crustacea
Antennae glands(Green glands) used for osmoregulation & ion regulation. Nitrogenous waste(mostly ammonia) diffuses through gills
Nervous system of Subphylum Crustacea
They have a brain made up of a pair of supraesophagel ganglia, and possess a double ventral nerve cord and well developed sense organs
Sympathetic nervous system = digestive tract
Well developed sense organs of Subphylum Crustacea
Compound eyes & statocyst, tactile hairs, and antennae for taste & smell
Reproduction of Subphylum Crustacea
Most are dioecious with a complex life cycle of Nauplii larvae(ancestral state) or direct development.
Some are parthenogeneic(offspring develop from an unfertilized egg without the need for a male's genetic contribution) and barnacles are monoecious(cross fertilize)
What are the steps of Ecdysis
Epidermis begins to secrete a new epicuticle
Enzymes are released and dissolve old cuticle
Salts and other soluble products are reabsorbed from old cuticle and stored
New cuticle forms inside old one
Old cuticle, ruptures, animal backs out
New cuticle is stretched and hardens
What is ecdysis controlled by
It’s initiated by environmental stimuli perceived by the central nervous system and controlled by two hormones:
Molt-inhibiting hormone = production declines
Molting hormone = concentration increase
Feeding habits of Subphylum Crustacea
Suspension feeders, predators, scavengers, omnivores
Coloration Subphylum Crustacea
Their body color is produced by chromatophores(Pigment containing cells in epidermis). When the pigment granules are at the center of the cell they appear lighter, and when the granules disperse, they will appear darker
Androgenic glands Subphylum Crustacea
Sexual characteristics only found in males that produce A hormone that plays a crucial role in male sexual differentiation and development
Characteristics of Class Malacostraca
20,000 species worldwide, largest and most diverse group
Head has five fused segments, eight thoracic segments and six abdominal segments with paired appendages
Important groups of Class Malacostraca
Isopoda, Amphiopods, Euphausiaceans, Decapods
Characteristics of Isopods
Marine, freshwater, terrestrial; Dorsoventrally flattened; no carapace; sessile compound eyes; Gills or lung like organs on abdominal appendages; Many can roll into a ball for protection; Mostly direct development; sow bugs, pill bugs, parasites
Characteristics of Amphiopods
No carapace; Sessile compound eyes; Compressed laterally; Gills in thorasic region; Direct development; Marine, freshwater, parasitic; many are detritivores