Plants (17 & 18) - Egan BISC-120
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What do macroalgae anatomically consist of?
Holdfast — root-like structure that attaches algae to a hard surface
Stipe — stem-like structure
lamina/blade — leaf-like structure
What are plants?
Plants included organisms that photosynthesize, have cell walls, spores, and sedentary behaviors
How are viridiplantae/chlorobionta united?
they are chloroplast containing organisms
What are embryophytes?
plants that live in terrestrial environments; they have waxy cuticles, specialized gametangia, and experience alternation of generations
What are tracheophytes?
plants that have vascular tissue
What three groups compose tracheophytes?
seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms, angiosperms
What are some pieces of key evidence that land plants are associated with charophytes?
rings of cellulose-synthesizing complexes
structure of flagellated sperm
the polymer sporopollenin
high similarities between nuclear, chloroplast, and mitochondrial DNA sequences
What is cellulose synthase?
it’s an enzyme crucial for plant structure — it synthesizes cellulose and builds cell walls
How does cellulose synthase build cell walls?
Cellulose chains are formed and pushed out through a channel created by cellulose synthase, and the chains assemble into microfibrils, strengthening cell walls
What differentiates algae and plants living on water and land?
Alga absorb minerals, water, and CO2 from the water and is simple.
Plants are complex structures, from the root absorbing nutrients and water, the leaf photosynthesis, and the cuticle and stomata allowing the plant to function as well as possible
How were land plants aided by mycorrhiza-like structures?
They acted as the first roots of land plants before land plants evolved their own roots
What are four traits that appear in nearly all land plants but are absent in charophytes?
alternation of generations
apical meristems
multicellular gametangia
walled spores in sporangia
What is the alternation of generations in land plants?
They alternate between gametophytes (n) and sporophytes (2n).
A gamete and a different plant’s gamete meet and fertilize to make a zygote
a zygote develops into a sporophyte (2n)
sporophyte goes through meiosis and releases spores
spore develops into a gametophyte (n)
gametophyte makes a gamete
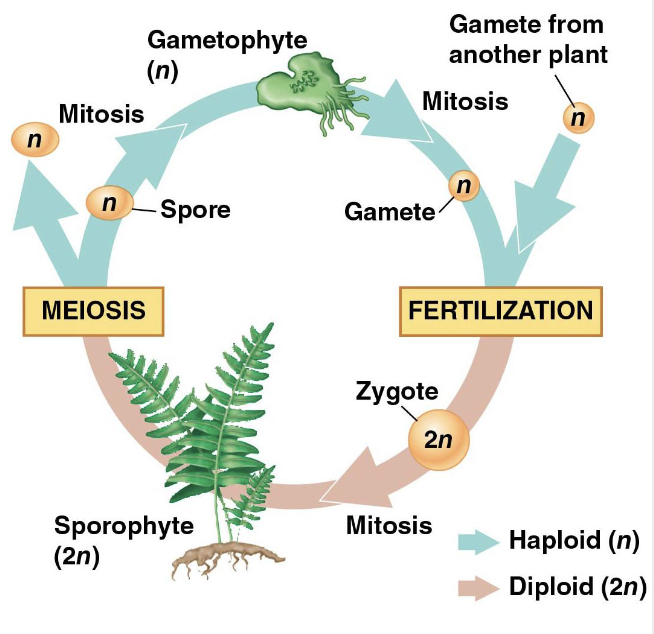
What do sporophytes do?
Meiosis, sporophytes produce haploid spores and mitotic division of spore cell produce a multicellular gametophyte.
How do plants sustain continual growth?
apical meristems
Where are apical meristems found?
at the tips of all roots and stems
What are three primary meristems?
protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium
Where and how do land plants grow?
They grow by rapid cell division at the apical meristems, crafting a solid mass of parenchyma tissue
What do cuticles do for plants?
it’s a waxy covering of the epidermis that reduces water loss
what do stomata do for plants?
they are pores that facilitate gas exchange between the outside air and internal plants
When trees grow higher, what happens to alternation of generations?
Gametophytes are reduced.
What features stands out in bryophytes?
They are non-vascular, have rhizoids not roots, and their gametophytes are larger and longer-living than sporophytes
What does the alternation of generations look like for bryophytes?
the gametophyte generation is much longer and can live independently of sporophytes; sporophyte generation depends on gametophyte after fertilization
Since bryophytes do not have vascular tissue, what does this mean for them?
they are highly dependent on water and only found in moist environment
What is xylem?
unidirectional movement of water
what is phloem?
bi-directional movement of sugar and solutes
Why were leaves essential for newly evolved vascular plants?
It increased plant surface area, meaning it also increased capture of solar energy for photosynthesis
What are the two types of leaves?
Microphylls (have a single mid vein) and megaphylls (have a highly branched vascular system)
Seedless vascular plants have what qualities?
They are the first to have vascular tissue
developed true roots
still reproduce with spores and need film of water for sperm
What does the alternation of generations look like for seedless vascular plants?
their life cycle is dominated by sporophytes
Seed plants have what qualities that differ from other plants?
They have seeds, reduced gametophytes, heterospory, ovules, and pollen
That is the male gametophyte enclosed in?
enclosed in a pollen wall, a pollen grain
How does pollination occur?
pollen grains germinate
germinated pollen grain produces pollen tube
pollen tube grows into the ovule and discharges sperm into the female gametophyte
What does an ovule consist of?
a megaspore (n) within a megasporangium (2n) surrounded by protective integuments
What are gymnosperms?
“naked seeds,” the seeds are exposed on sporophytes that form cones
The mesozoic era features what three periods and what evolutionary development (pertaining to this course)?
Three periods: triassic, jurassic, cretaceous and the age of gymnosperms
How important were gymnosperms in the Mesozoic era?
Gymnosperms dominated terrestrial ecosystems and served as food for herbivorous dinosaurs, however angiosperms began to replace gymnosperms near the end of the era
What are angiograms?
They are seed plants that produce flowers and fruits
flowers produce gametes
fruits are product of fertilization
What group is the most widespread and diverse of all plants?
Angiosperms
What are the four parts that make up a flower, and what are their functions?
sepals: enclose the flower
petals: brightly colored and attract pollinators
stamens: which produce pollen (male gamete)
carpels/pistils: which produce ovules (female gamete)
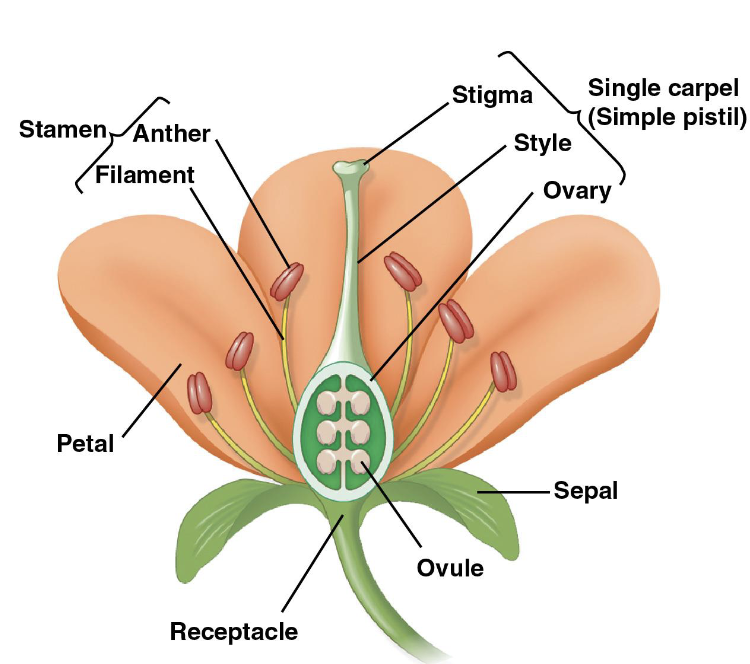
How are fruits made?
As seeds develop, the ovary wall thickens and the ovary matures into a fruit