Science 9: Biological Diversity BD1 & BD2 Vocabulary
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Biological Diversity
The number and variety of organisms.
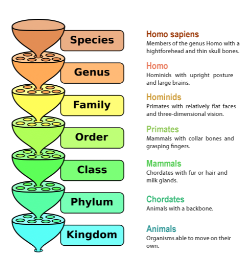
Species
A group of organisms with similar characteristics that are capable of interbreeding. The offspring have to be fertile offspring.
Variation
Any differences between living organisms caused either by genetic differences or environmental factors.
Intraspecies Variation
Variations between members of the same species.

Interspecies Variation
Variations among different species.

Natural Selection
The process by which favourable traits become more common in successive generations of a population, and unfavourable heritable traits become less common.
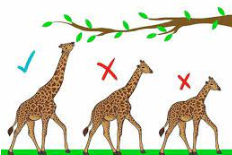
Structural Adaptation
A specific body part of an animal that helps an animal survive in its environment.

Behavioural Adaptation
Something an animal does to survive in its environment.

Niche
The role a species has in its environment, how it meets its needs, where it lives, and all interactions.
Specialist Species
Narrow niche, few food sources, live in small areas, do not tolerate changing conditions, intraspecies competition (some species), small populations

Generalist Species
Broad niche, eat a variety of foods, lives in many ares, tolerates changing conditions, interspecies competition (different species), larger populations

Dependency
When an organism needs to rely on something in order to survive.

Competition
Species competing for the same resources (food, space, water, sunlight, mates, etc).

Symbiosis
A close, long term relationship between species, based on dependency between organisms.
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms where one organism benefits and the other organism is unaffected.

Mutualism
Two organisms working together in a way where both benefit from the relationship.

Parasitism
Involves one organism, a parasite, living off energy supplied by another organism, a host. Some parasites only attach themselves to feed while others are permanently attached. Some live attached to the outside of the host while others live inside of the host. The parasite benefits and the host is harmed.

Asexual Reproduction
The formation of a new individual from a single organism.
Sexual Reproduction
Creating a genetically unique offspring with 2 parents involved.
Clone
An identical copy of a molecule, gene, cell, or entire organism.
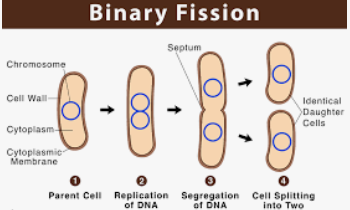
Binary Fission
Single cell organisms duplicates contents and divides, resulting in indentical daughter cells (Bacteria).
Budding
An asexual reproduction precess in which a bud forms on an organism, grows, and eventually breaks away to become a new organism independent of the plant (Hydra and Yeast).
Spores
A single-celled reproductive structure from which an individual offspring develops through mitosis (Plants, Algae, Fungi, etc.).
Vegetative Reproduction
Asexual reproduction in plants using meristems at the tips of roots and stems, which are rapidly reproducing cells (Cutting, Runners, Tubers).
Gametes
A reproductive cell (egg or sperm) containing half the number of chromosomes of a somatic cell.
Zygote
The new cell formed by the process of fertilization (Egg).
Ovule/egg
Ovule: The plant part that develops into a seed.
Egg: Female gamete, also a developing embryo enclosed in a shell or membrane and produced by animals that do not give birth to live young.
Sperm cells
Male gamete.
Fertilization
Female gamete (egg) and male gamete (sperm) combine to fertilize an egg/ovule.
Embryo
A multi-cellular organism during early development.
Pollination
After pollen reaches the pistil of a flower, the sperm nucleus travels down the pollen tube to fertilize the egg, then grows a zygote, to an embryo.
Heritable Characteristics
Passed from parent to offspring. (Hair Colour, Skin Colour, Freckle)
Non-heritable Characteristics
Not passed from parent to offspring. (Tattoos, scars, piercings)
Discrete Variation
There are a small number of variations (2-4). You cannot go in between categories. (Ability to roll tongue, blood types, sex)
Continuous Variation
There are many variations. (Eye colour, height, hair colour)
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Molecular blueprint for living things, controls all the structures and functions of the cell, responsible for the variations between and among species
Genetic Code
Sequence of Nitrogen bases, controls production of proteins in cells
Nucleotide
A segment of DNA with one phosphate, one sugar, and a nitrogen base
Base pairs
A matching pair of nitrogen bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine)
Chromosomes
Tightly packed strands of DNA
Gene
A section of DNA that determines a specific characteristic or trait
Allele
Possible forms that a gene may take on (Black hair, tongue rolling)
Mitosis
Somatic cells (anything but gamete) have to be replaced very often, before dividing, a copy of each chromosome is made, new cell is genetically identical (same amount of chromosomes)
Meiosis
Forming new gametes by dividing cells, gametes only have 23 chromosomes
Somatic Cells
Any cell in your body that is not a gamete (sex cell)
Heritable Trait
A child receives at least one allele from each parent indicating what form of the trait the child will have
Dominant trait
The trait will always show up in the phenotype, even if only one copy is present, not always more frequent, is represented by a capital letter
Recessive Trait
The recessive trait will only show up in the phenotype if there are two copies (one from each parent)
Genotype
The genetic code for an individual’s traits (TT, tt, Tt)
Phenotype
The physical representation of the genotype (red hair, tongue rolling)
Purebred (Homozygous)
When there are two of the same version of the allele, either both dominant or both recessive
Hybrid (Heterozygous)
When there are two different versions of the allele, one dominant and one recessive
Co-domiance
Both parental traits are present in the phenotype, two versions of the same gene are expressed seperately to create a different trait
Incomplete dominance
An intermediate (mix) between the two parental traits
Chromosomal variation
Abnormalities in chromosomes when one is missing, extra, switched to another chromosome, or turned upside down, will result in disorders such as Down Syndrome
Punnett Square
A method to help figure out possible offspring combinations
GMO
Genetically modified organism that has altered genes to produce a new genotype