Transformation
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lesson 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Trivial
re-expression of values, but no impact on the shape of distribution
Multiplication of constant
world_density$DensityTimes4 <- 4*(world_density$Density)
This operation scales the values of the density by a constant factor, affecting the magnitude but not the overall distribution shape.
Addition of constant
world_density$DensityPlus100 <- 100+world_density$Density]
This operation shifts the values of the density by a constant amount, altering the location of the distribution without changing its shape.
Nontrivial
Re-expression of values that changes the shape of distribution
Basic power transformation
A method that raises values to a specified power, altering the shape of the distribution and potentially stabilizing variance.

Alternative power transformation
A technique that applies a different power to values, aiming to achieve a more normal distribution and stabilize variance across data.
All of the graphs go through (1, 0) and have the same slope at that point.
All of the curves are increasing in x.
Thus, the order of data are preserved.
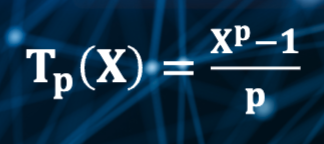
If p > 1
The graph is concaved up, and as p moves away from 1, the curve becomes more curved, which means that the concavity increases.
The transformation will expand the scale more for large xx than for small xx
If p < 1
the graph is concaved down
the transformation will compress the scale more for large xx than for small xx.
if p = 1
the graph is linear
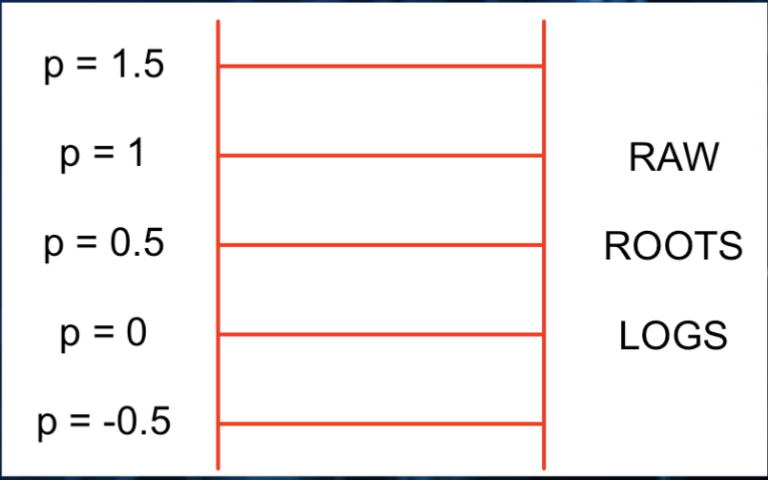
Tukey’s Ladder of power
Create a stemplot
stem(df$attribute)
Create histogram
ggplot(CO2emissions, aes(CO2emissions)) + geom_histogram(color = "blue", fill = "white", bins=15) + geom_density(aes(x = CO2emissions)) + theme_classic(base_size = 15) + labs(x = "CO2emissions")
letter values
lvals ← lval(df$attribute); lvals
Symmetric Data
the mids does not show any trend
Right skewness
the mids are increasing and the tailis on the right side.
Left skewness
the mids are decreasing and the tail is on the left.
Plotting the mids
lvals %>% mutate(LV = 1:8) %>% ggplot(aes(LV, mids)) + theme_classic(base_size = 25) + geom_point()
getting the square root of the attribute you want t re-express
df$attribute ← sqrt(df$attribute)
Hinkley’s quick method
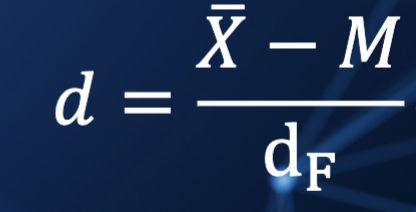
Hinkley code
hinkley(df$attribute)
Inspect the mids
logval ← lval(df$attribute) logva
Symmetry Plot
plot showing the symmetry of a batch
STEPS
Arrange the values, from y(1), y(2), y(3),…, y(n).
If M is the median, then plot
𝒖𝒊 = 𝒚(𝒏)𝟏+𝒊) − 𝑴 on the vertical axis, versus
𝒗𝒊 = 𝑴 − 𝒚(𝒊) on the horizontal axis
for 𝑖 = 1, 2 , 3, ... 𝑛/2 if 𝑛 is even and (𝑛 + 1)/2 if 𝑛 is odd.Add the line 𝒖 = 𝒗 to the graph as the line of symmetry
Symmetry Plot code
example ← c(4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 9, 10, 14, 18, 19) stemplot(example)
Editing a function in R (default)
edit(function)
Editing a function in R (editing the symplot)
edit(symplot)
Modify the symplot function
symplot ← (paste the script you just highlighted)
Comparison of re-expressed data
boxplot(data.frame(CO2emissions$CO2emission,
CO2emissions$sqrtCO2,
CO2emissions$logCO2,
CO2emissions$recrootCO2,
CO2emissions$CO2p))