Bio 14 Week 2 Nervous System Pt. 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Synapse
The junction between one neuron and another neuron or effector cell
Electrical Synapses, Chemical Synapses
The types of Synapses
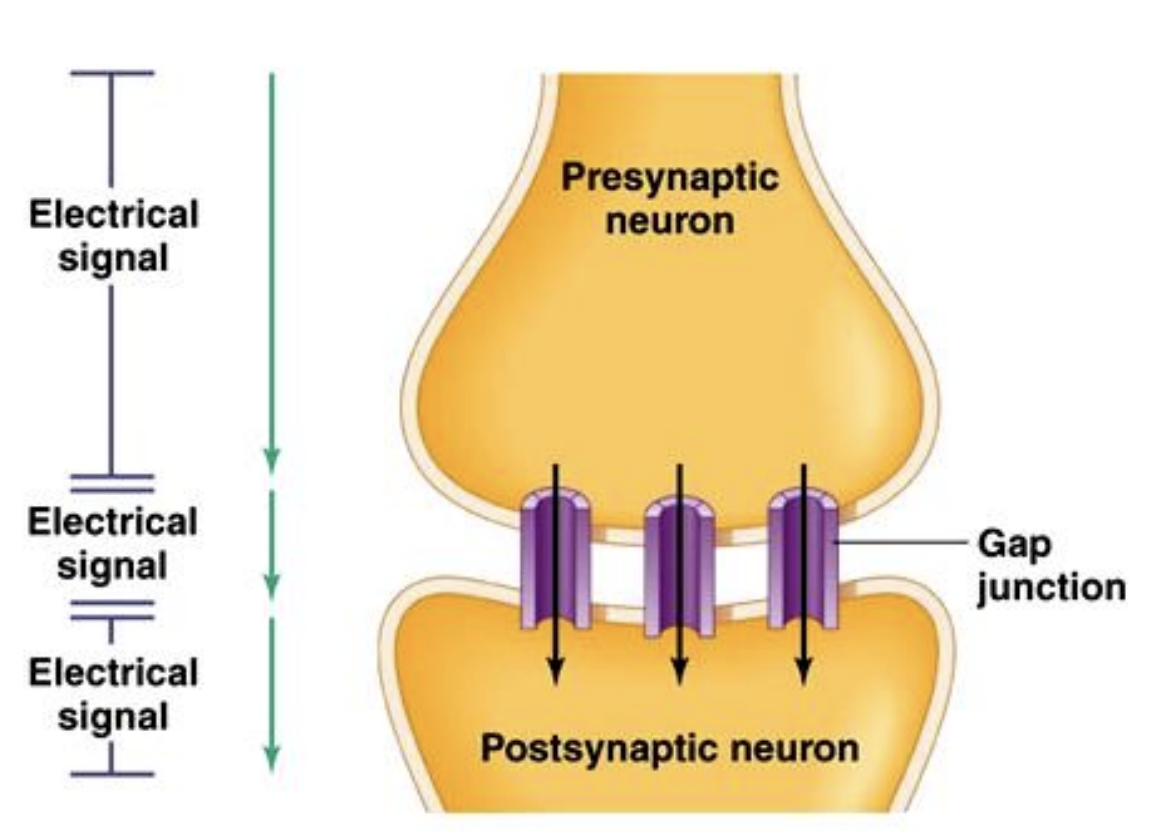
Electrical synapses
Type of synapses with gap junctions which allow ions to flow from one cell to another
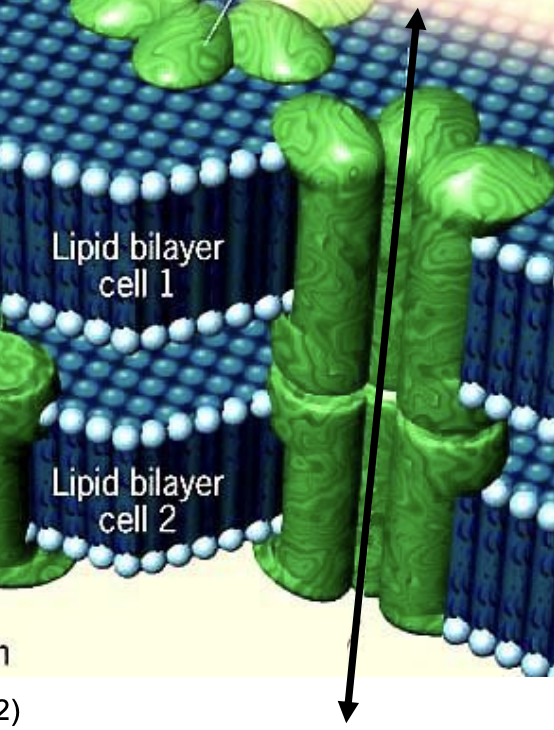
Gap junctions
multi-subunit channels that connect the interior of two adjacent cells.
two connexons/six connexons
A gap junction consists of ________ (each formed from ______ subunits).
one
___ connexon is located in each of the adjacent cells, and when they align, they form a channel allowing ions and small molecules to pass through.
Electrical synpases/rapid
________ allow for extremely _____ signal transmission
invertebrate/vertebrate
Electrical synapses are more common in _____ nervous systems than in ________ nervous systems.
coordination of rhythmic activity
Electrical synapses in vertebrates are involved in the _________ essential for controlling breathing patterns.
Chemical synapses
Synapses where neurotransmitter release occurs between a presynaptic and a postsynaptic cell.
Slight delay in the transmission of the action potential from one neuron to another.
Ligand-gated receptors
Chemical synapses utilize _______ while electrical synapses utlilize gap junctions
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after the action potentials arrive at axon terminal?
Ca2+ enters the cell
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after the
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open?
Ca2+ signals to the vesicles
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after Ca2+ enters the cell?
Vesicles move to membrane
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after
Ca2+ signals to the vesicles
Docked vesicles release neurotransmitter by exocytosis
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after vesicles move to membrane
diffuses/receptors
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, after the docked vesicles release neurotransmitter by exocytosis, neurotransmitter _____ across the synaptic cleft and binds to _____
signal transduction pathways activated
For Chemical Synaptic Transmission, what happens after the neurotransmitter is bound to the receptors of the postsynaptic cell?
omega shapes
Electron microscopy provides evidence of vesicle fusion (“____________”)
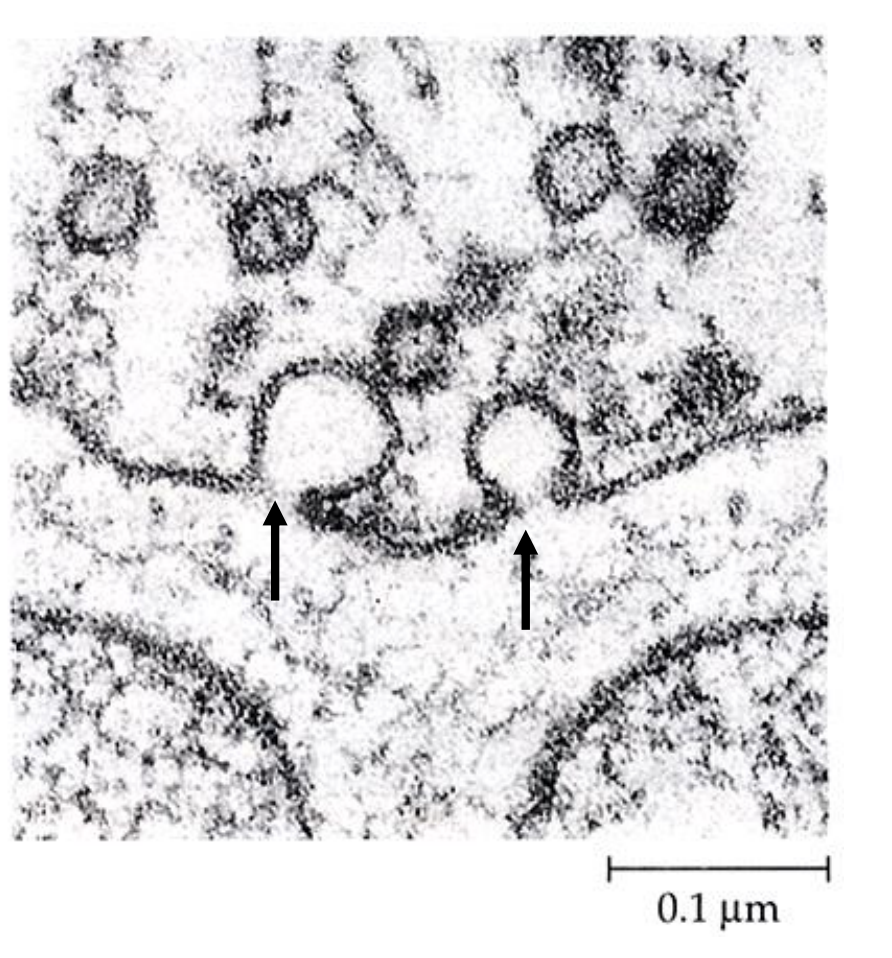
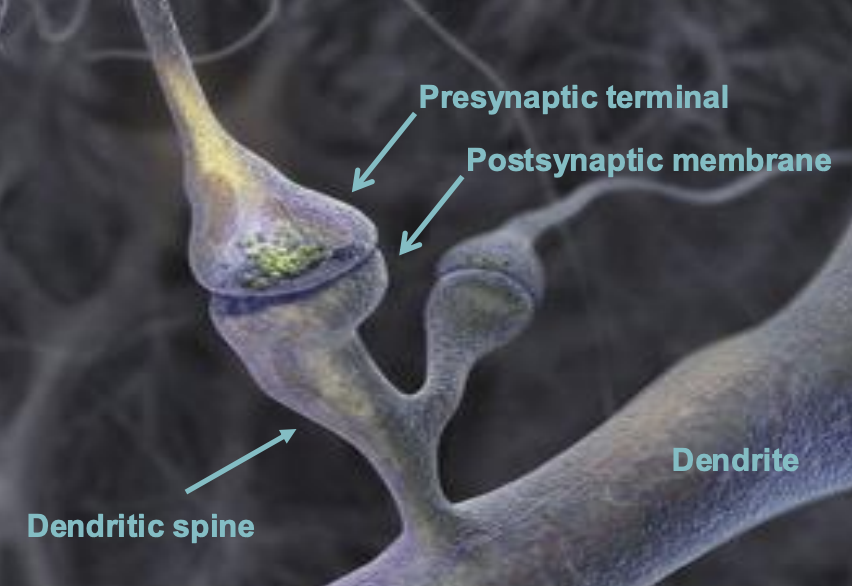
dendritic spines
Synapses are often located on _________
dendritic spines
small, bulbous protrusions on dendrites (the receiving part of a neuron) that serve as the primary location for excitatory synapses
thousands
Neurons have ________ of synapses
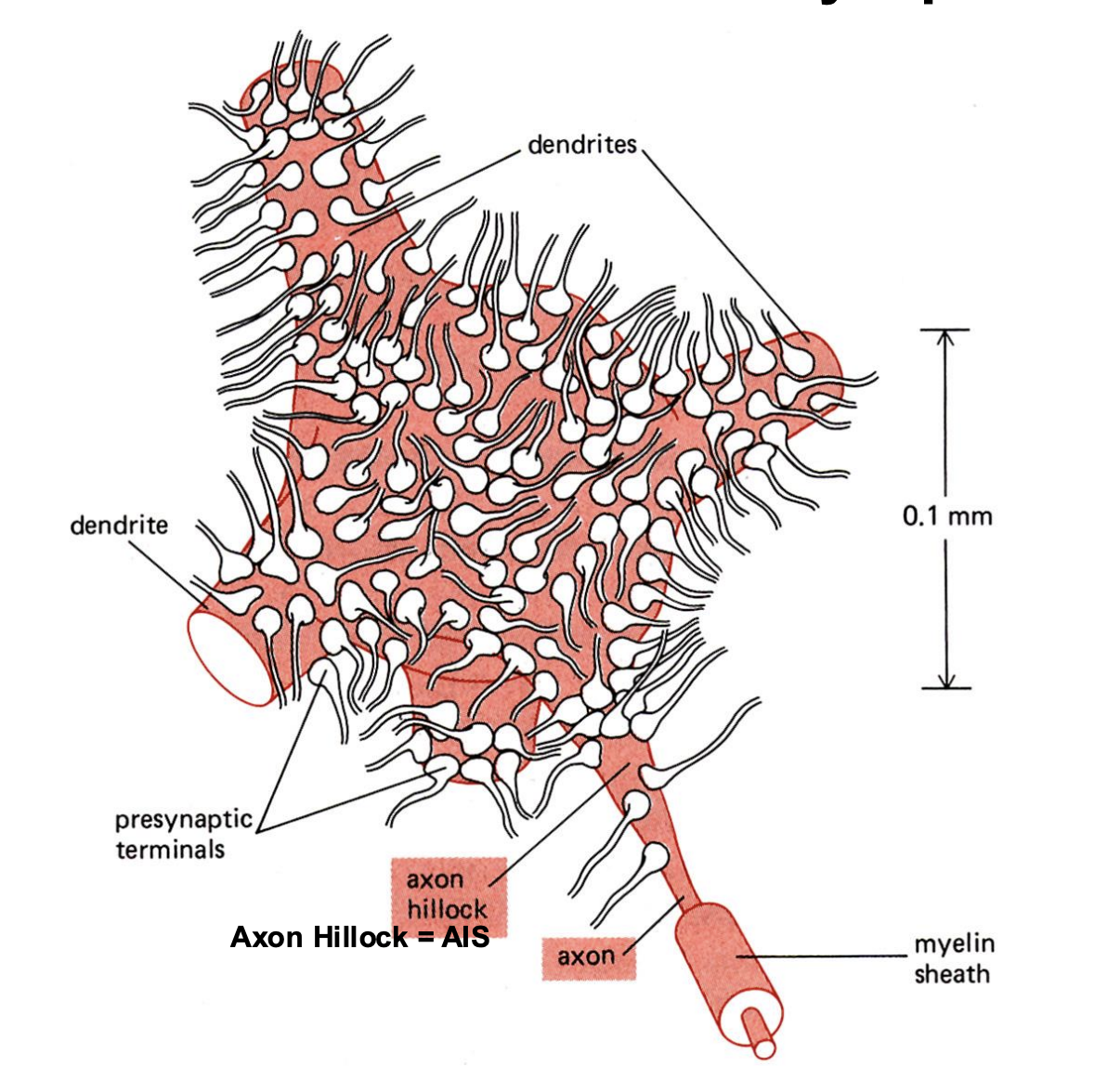
Axon hillock
What is another name for the axon initial segment?
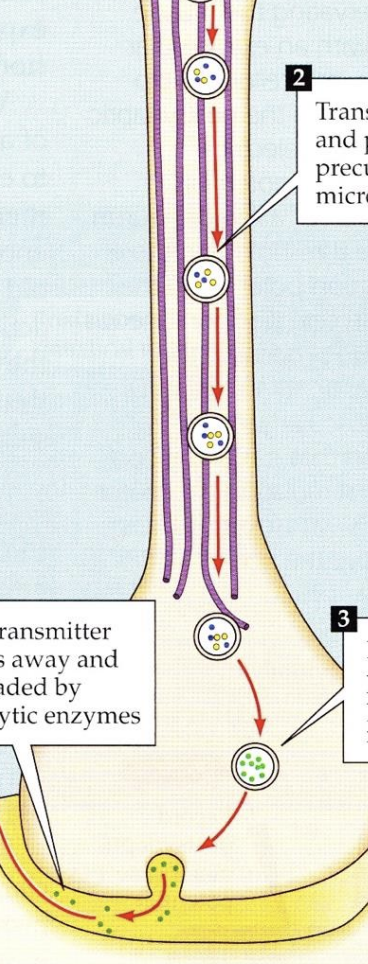
Neurotransmitter Synthesis
The process by which neurotransmitters are synthesized in the neuron, typically starting in the soma (cell body) and ending with the transport to the axon terminals for release into the synaptic cleft.
endoplasmic reticulum/golgi network
The _________ is involved in synthesizing neurotransmitter precursors and enzymes in the cell body. It then transports these molecules to the ________
enzymes
After the transport of enzymes/peptide precursors down the microtubule tracks, _______ modify precursors to produce peptide neurotransmitter
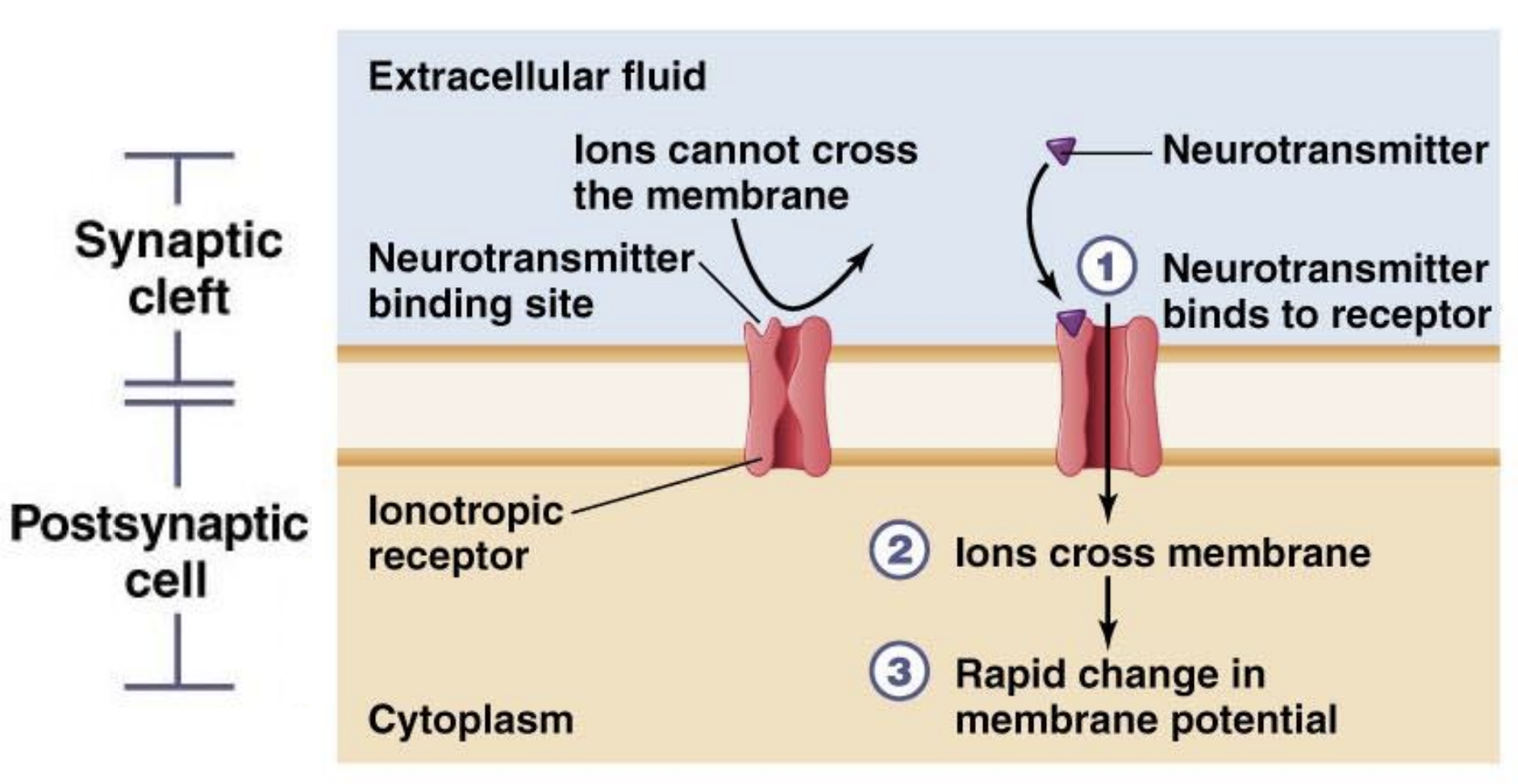
Ionotropic Receptors
Membrane-bound receptors that, when activated by neurotransmitters, open ion channels to allow ions to flow across the membrane, leading to a rapid change in the membrane potential. These receptors typically result in fast synaptic responses.
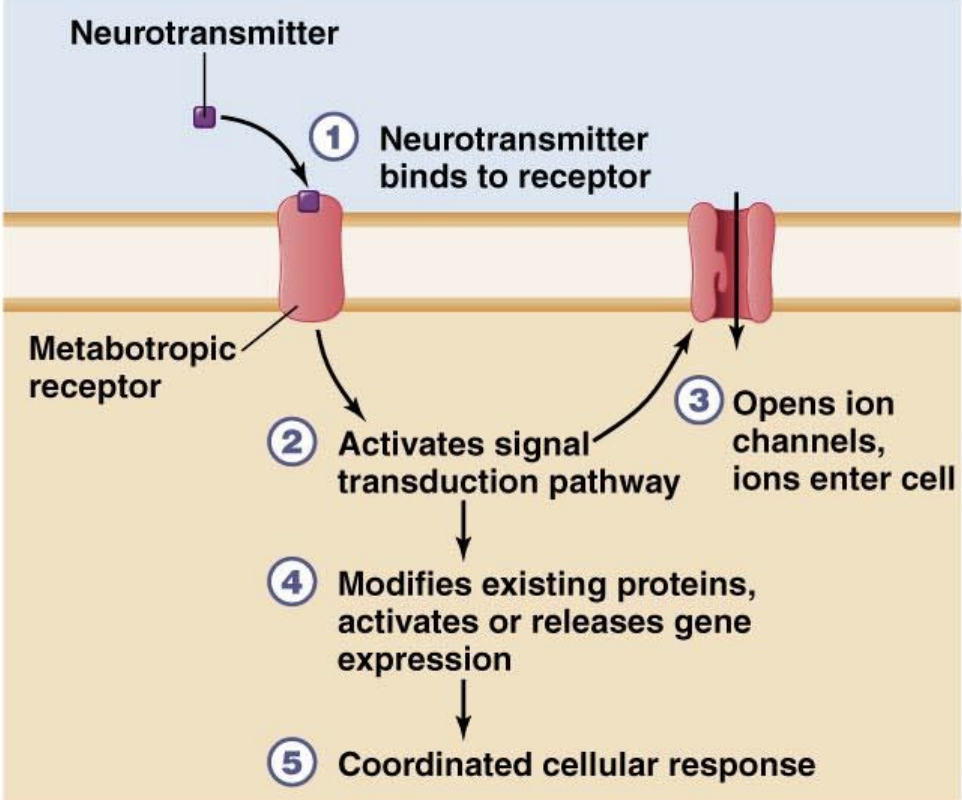
Metabotropic Receptors
Membrane-bound receptors, that instead of opening ion channels directly, they initiate signal transduction pathways that often lead to a slower and more complex cellular response. These pathways can alter existing proteins or regulate gene expression, causing a coordinated cellular response.
Glutamate
Most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is the most abundant neurotransmitter. It plays a crucial role in cognitive functions such as learning and memory.
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
Most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It regulates brain activity, affecting anxiety, concentration, sleep, depression, and other aspects of mental health.
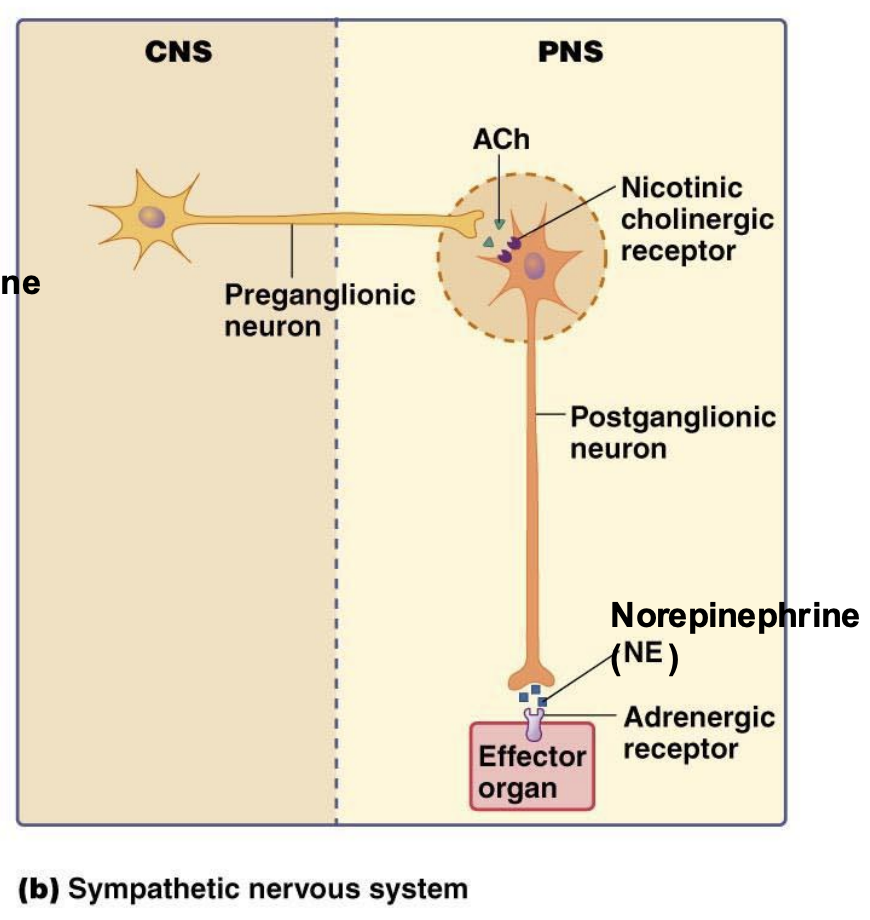
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter that regulates the autonomic nervous system. It plays a role in motor functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, gut function, and also impacts muscle contractions, memory, sleep, and learning.
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, sleep patterns, anxiety, appetite, and pain. It is crucial for emotional balance and well-being.
Glycine
inhibitory neurotransmitter primarily found in the spinal cord. It helps in regulating functions related to hearing processing, pain transmission, and metabolism.
spinal cord
Glycine is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in your ____
GABA/Glycine
______ are the major Inhibitory neurotransmitters
Glutamate/Acetylcholine
_______ are the major excitatory neurotransmitters
two
Acetylcholine can bind to _____ different receptors
Agonists
substances (such as drugs or neurotransmitters) that bind to a receptor and activate it, mimicking or enhancing the natural biological activity of the receptor. They can increase or facilitate the normal action of the receptor, leading to physiological changes in the body.
Antagonists
substances that bind to a receptor but do not activate it. Instead, they block or inhibit the receptor's normal function by preventing agonists or natural neurotransmitters from binding. Antagonists reduce or block the biological activity of the receptor.
Nicotine
agonist that binds to nicotinic receptors in the body.
Mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh), activating these receptors and inducing excitatory effects on the nervous system.
Curare
Antagonist of acetylcholine that binds to nicotinic receptors, preventing acetylcholine from activating the receptor. It blocks neuromuscular transmission, which results in paralysis.
Muscarine
Agonist of acetylcholine that binds to muscarinic receptors. It mimics acetylcholine’s effects, activating G-protein-coupled receptors in the body and inducing parasympathetic responses like increased salivation and slowed heart rate.
Atropine
antagonist of acetylcholine that binds to muscarinic receptors and blocks their activation.
Increases heart rate and reduce salivation during surgery
Nicotinic Receptor
ionotropic receptors that respond to acetylcholine and nicotine.
Found at neuromuscular junctions and are involved in fast synaptic transmission, allowing for the influx of sodium ions and depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane.
Muscarinic Receptor
metabotropic receptors activated by acetylcholine and muscarine. These receptors are involved in slower, G-protein-coupled signaling pathways, primarily in the parasympathetic nervous system, and control functions such as heart rate and digestion.
Adrenergic
Muscarinic and ________ receptors are both metabotropic (GPCRs)
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
graded potentials occurring in the dendrites and cell body of a neuron when excitatory neurotransmitters (like glutamate) bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. This causes positive ions (e.g., Na⁺) to flow into the cell.
hundreds of thousands
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials represent __________ of channels opening
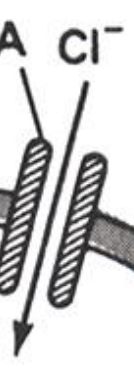
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Graded potentials that occur in the dendrites and cell body when inhibitory neurotransmitters, such as GABA, bind to their respective receptors.
These lead to the opening of chloride (Cl⁻) channels, allowing chloride ions to enter the postsynaptic cell
Neural output
________ is the sum of excitatory and inhibitory inputs
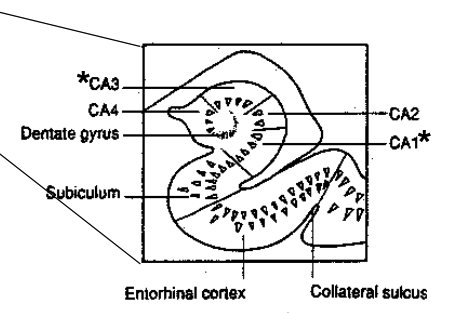
Hippocampus
The _________ is an important model for neural plasticity
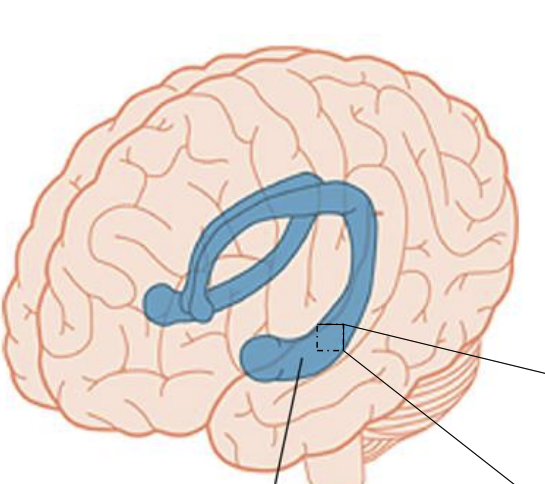
Dentate Gyrus
A part of the hippocampus involved in the formation of new memories and the processing of spatial memory.
Subiculum
The part of the hippocampus that links to other brain regions, facilitating the flow of information.
Entorhinal Cortex
A part of the brain that functions as the main interface between the hippocampus and the neocortex.
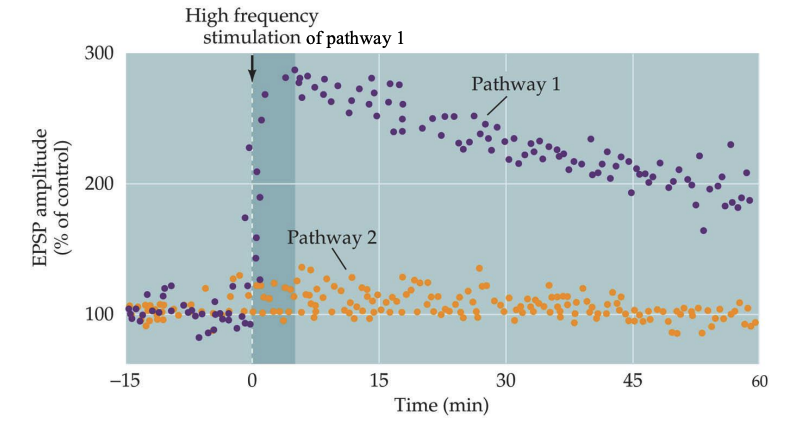
Tetanus
A repetitive, high frequency burst of stimuli
Schaffer collaterals
axons of the neurons in the CA3 regions of the hippocampus that form synapses in the CA1 regions
Synaptic plasticity
The functional properties of individual synapses can be modified by a variety of factors, including elevated electrical activity (experience)
Long-Term Potentiation (LTP)
lasting increase in the strength of synaptic transmission, often observed after high-frequency stimulation of a synapse. It's considered a fundamental mechanism for learning and memory.
Perforant Pathway
Critical neural pathway in the brain, particularly in the context of the hippocampus. It connects the entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus, which is part of the hippocampal formation.
Perforant Pathway
Entorhinal cortex → dentate gyrus → CA3 → CA1 → subiculum → entorhinal cortex