Bivariate and Multivariate Correlational Research
1/537
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
538 Terms
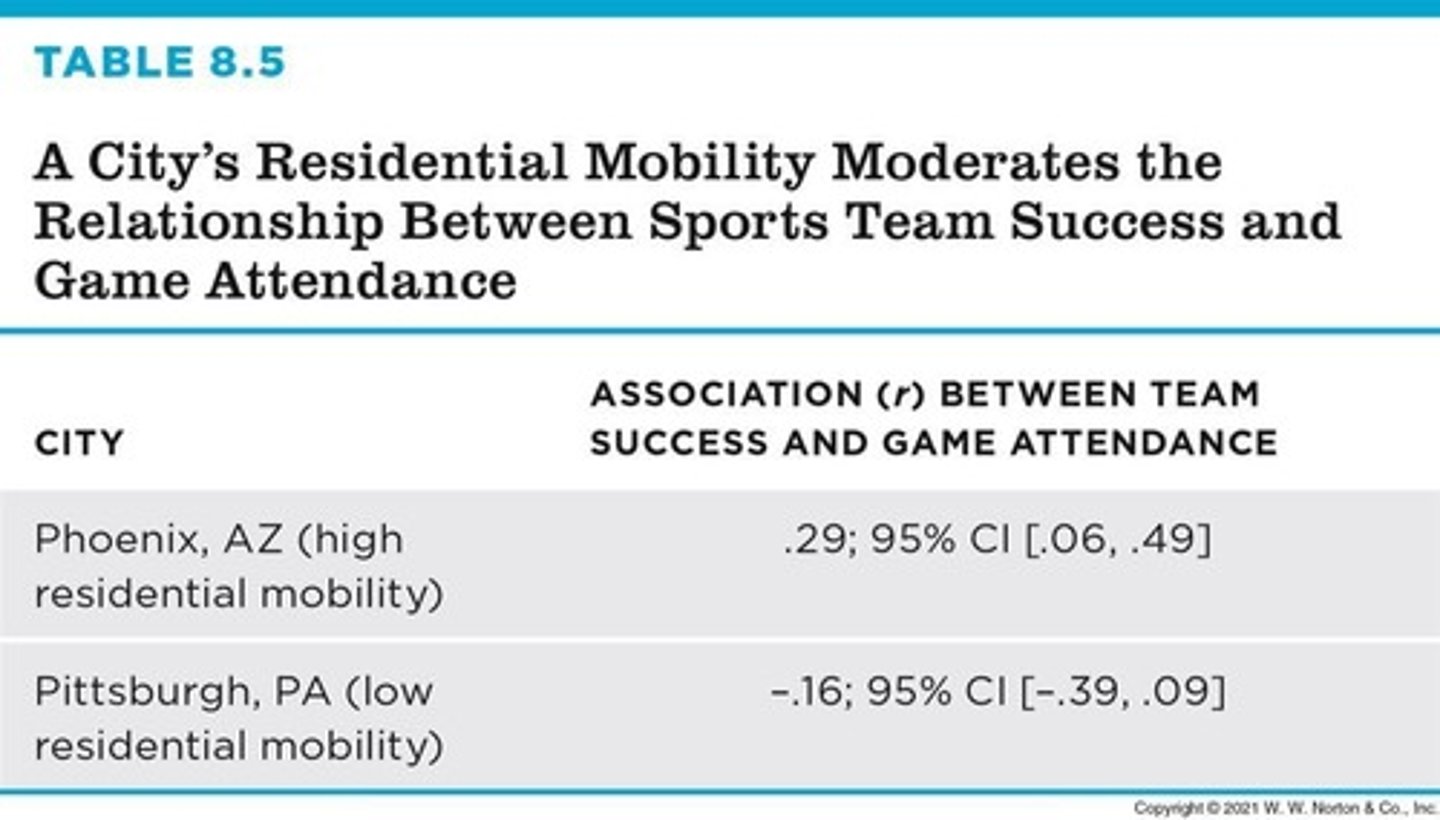
Bivariate Correlations
Associations involving exactly two variables.
Construct Validity
Assessment of how well variables are measured.
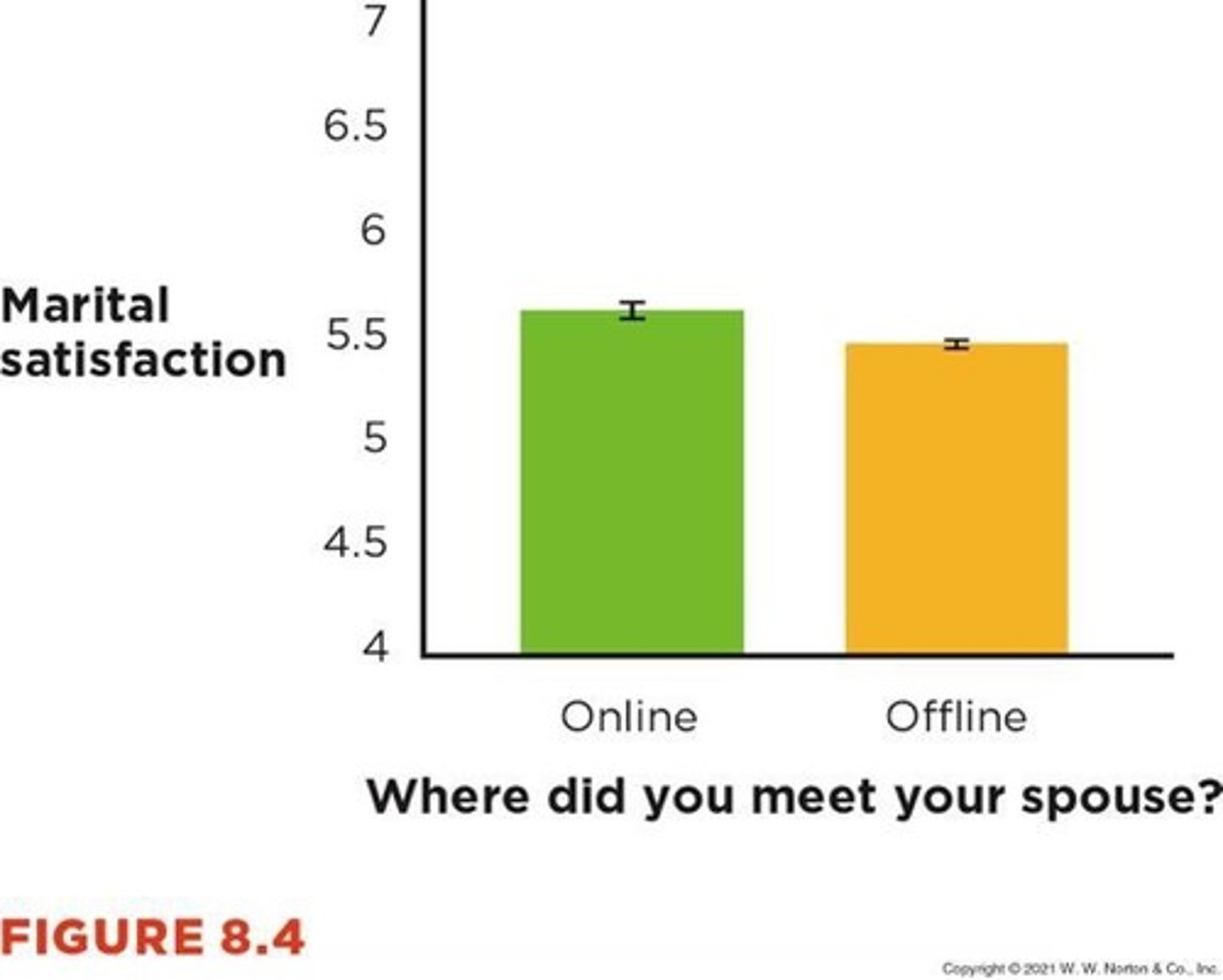
Effect Size
Describes strength of an association.
Sample Size
Number of observations in a study.

95% Confidence Interval
Range where true correlation likely falls.
Statistical Significance
Finding unlikely from a population with zero association.
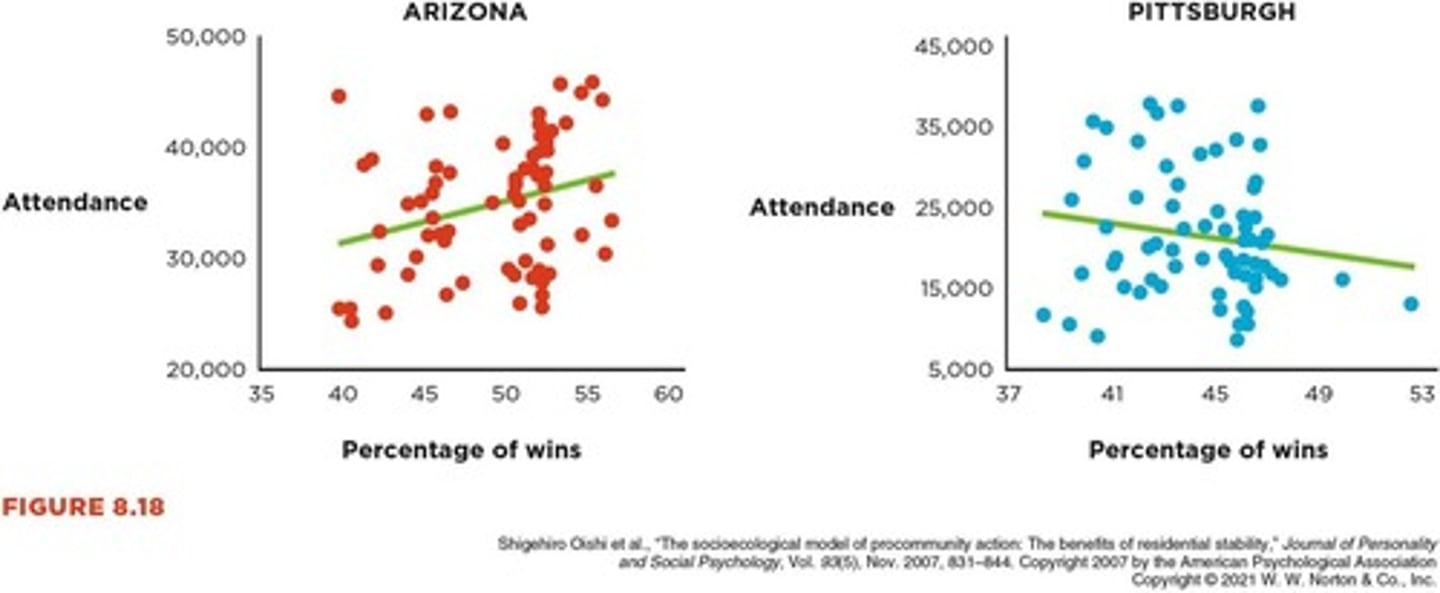
Moderating Variables
Variables altering the relationship between two others.
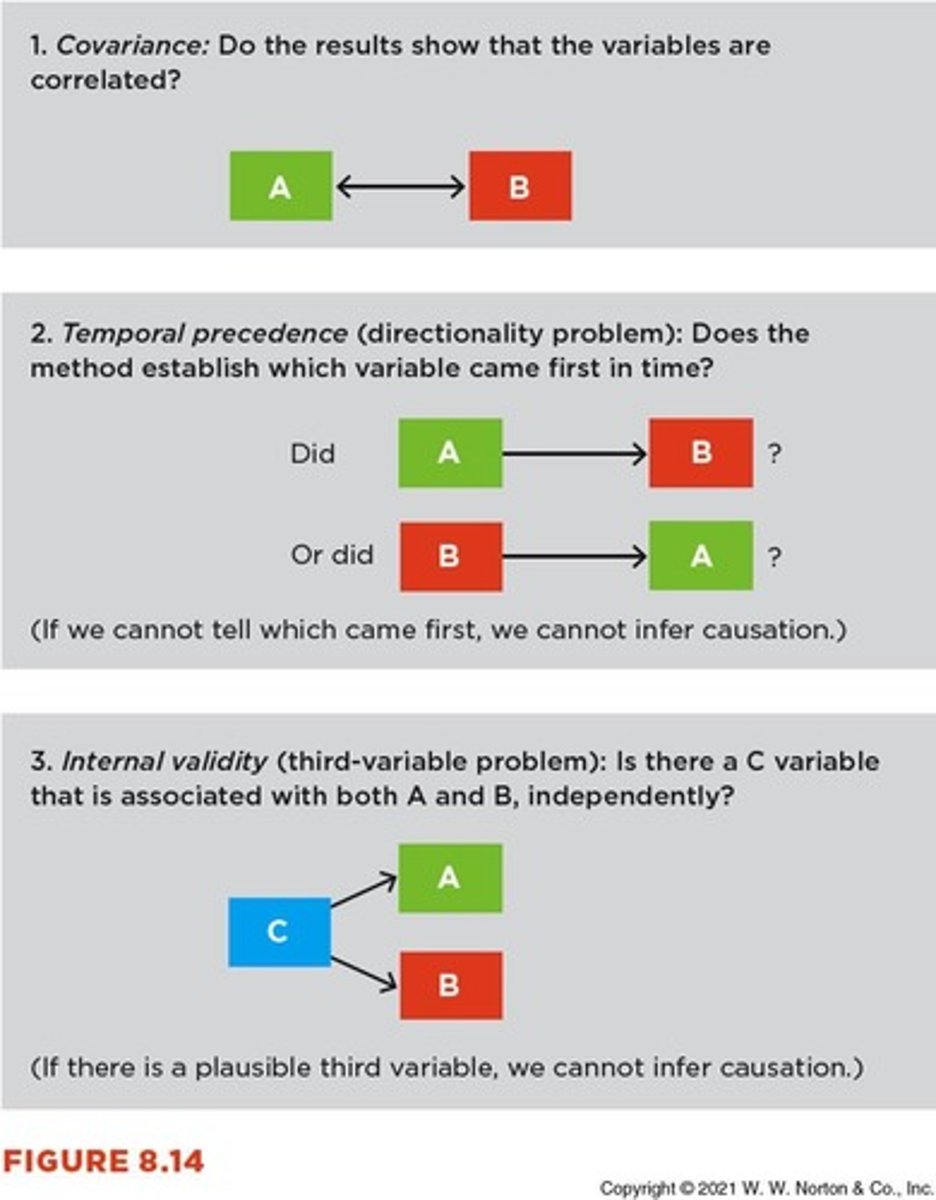
Covariance
Indicates whether variables are related.
Temporal Precedence
Establishes which variable occurs first.
Internal Validity
Assesses if a third variable explains the relationship.
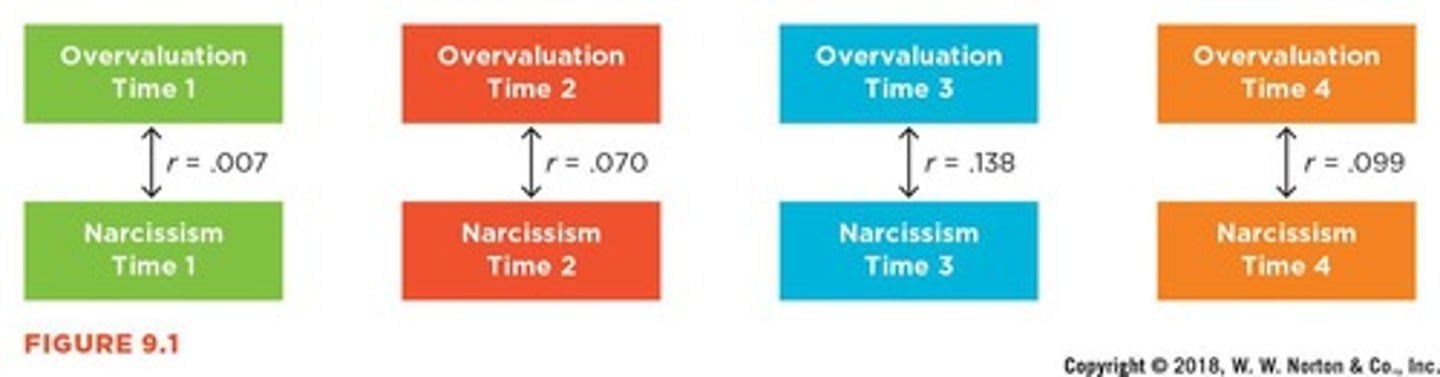
Longitudinal Designs
Measure same variables over multiple time points.
Multiple Regression
Analyzes relationships among multiple variables simultaneously.
Mediating Variables
Variables explaining the relationship between two others.
External Validity
Generalizability of study findings to other contexts.
Face Validity
Extent measure appears effective for its purpose.
Concurrent Validity
Measure correlates with established measures of the same construct.
Discriminant Validity
Measure does not correlate with unrelated constructs.
Convergent Validity
Measure correlates with similar constructs.
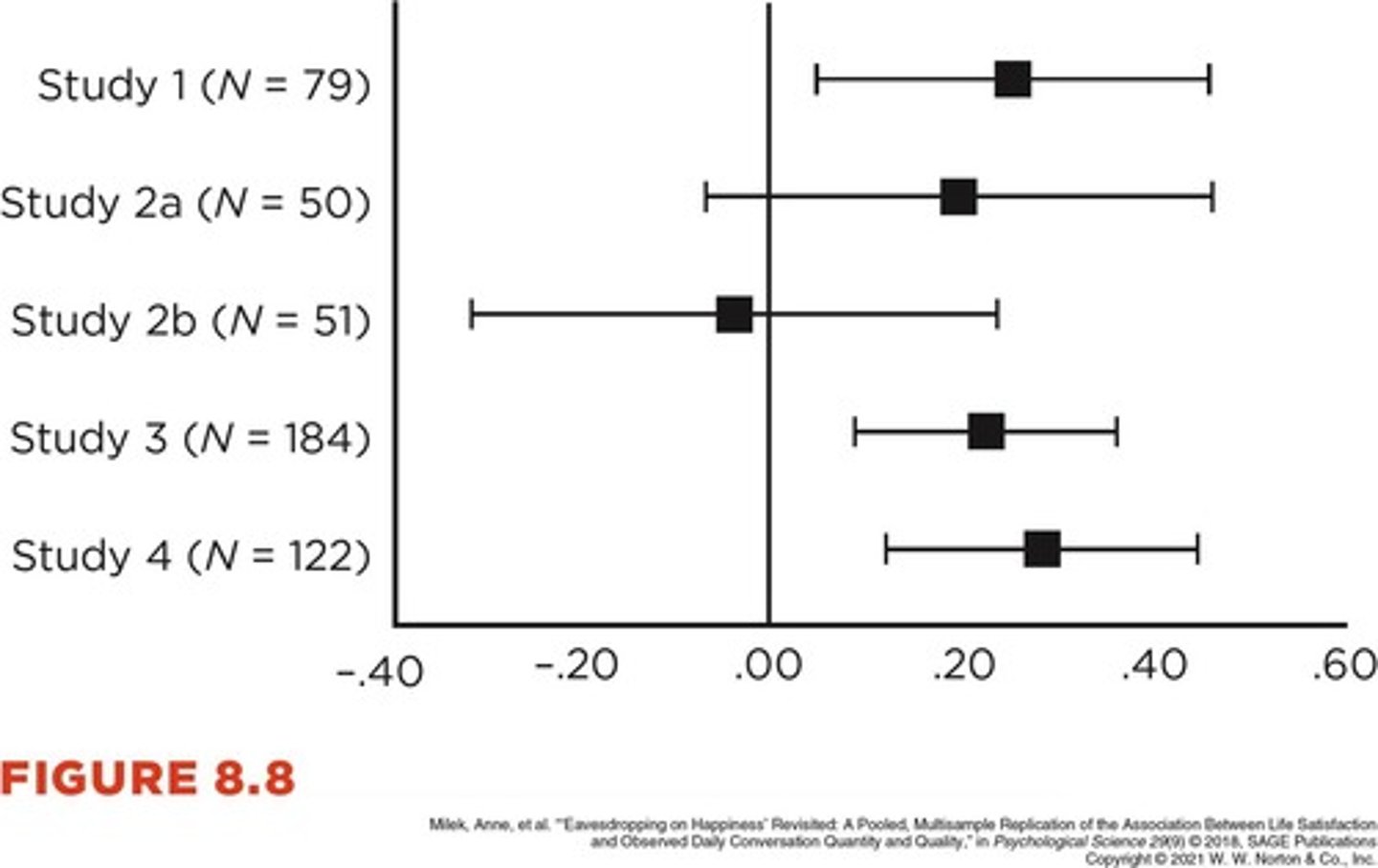
Replication
Repetition of study to confirm findings.
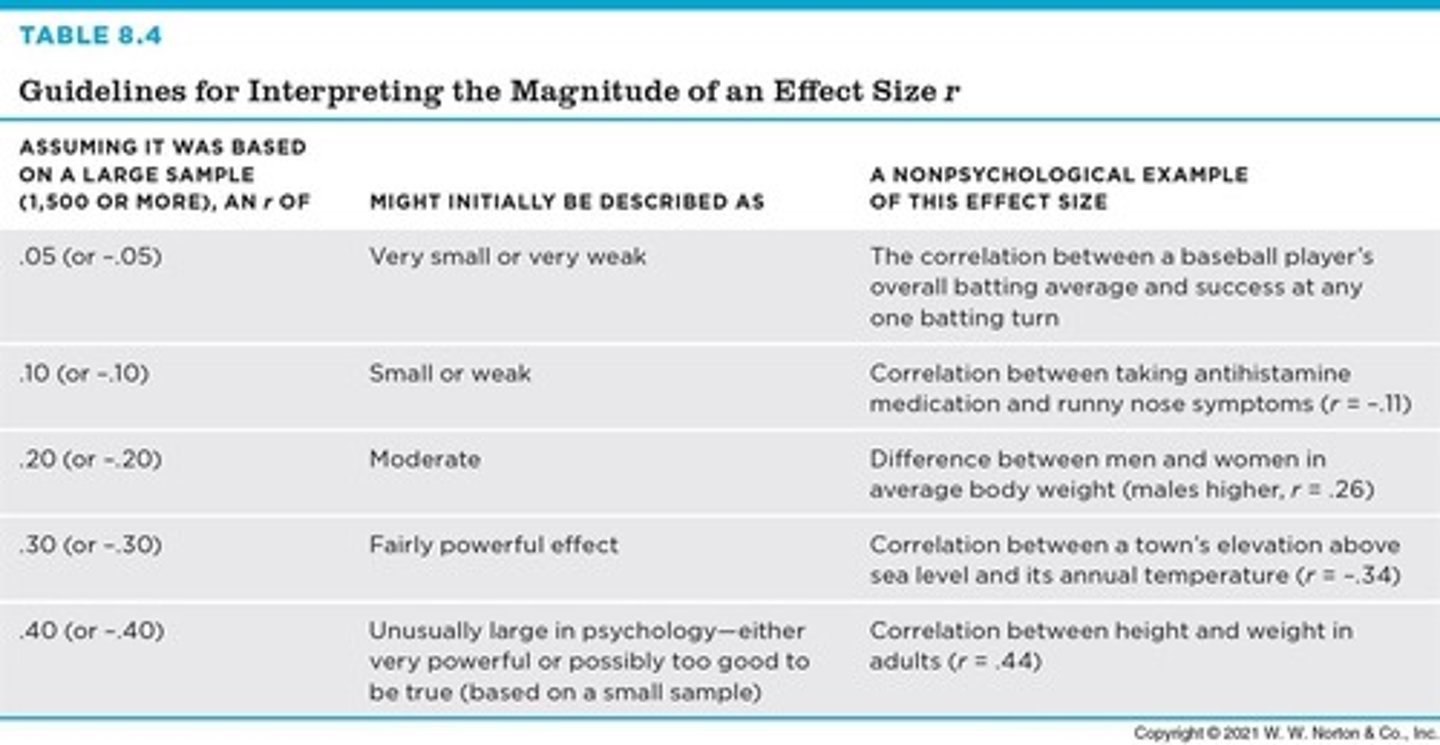
Benchmarks
Standards for comparing effect sizes.
Third-Variable Problem
Unaccounted variable affecting relationship between two variables.
Causal Claims
Hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships.
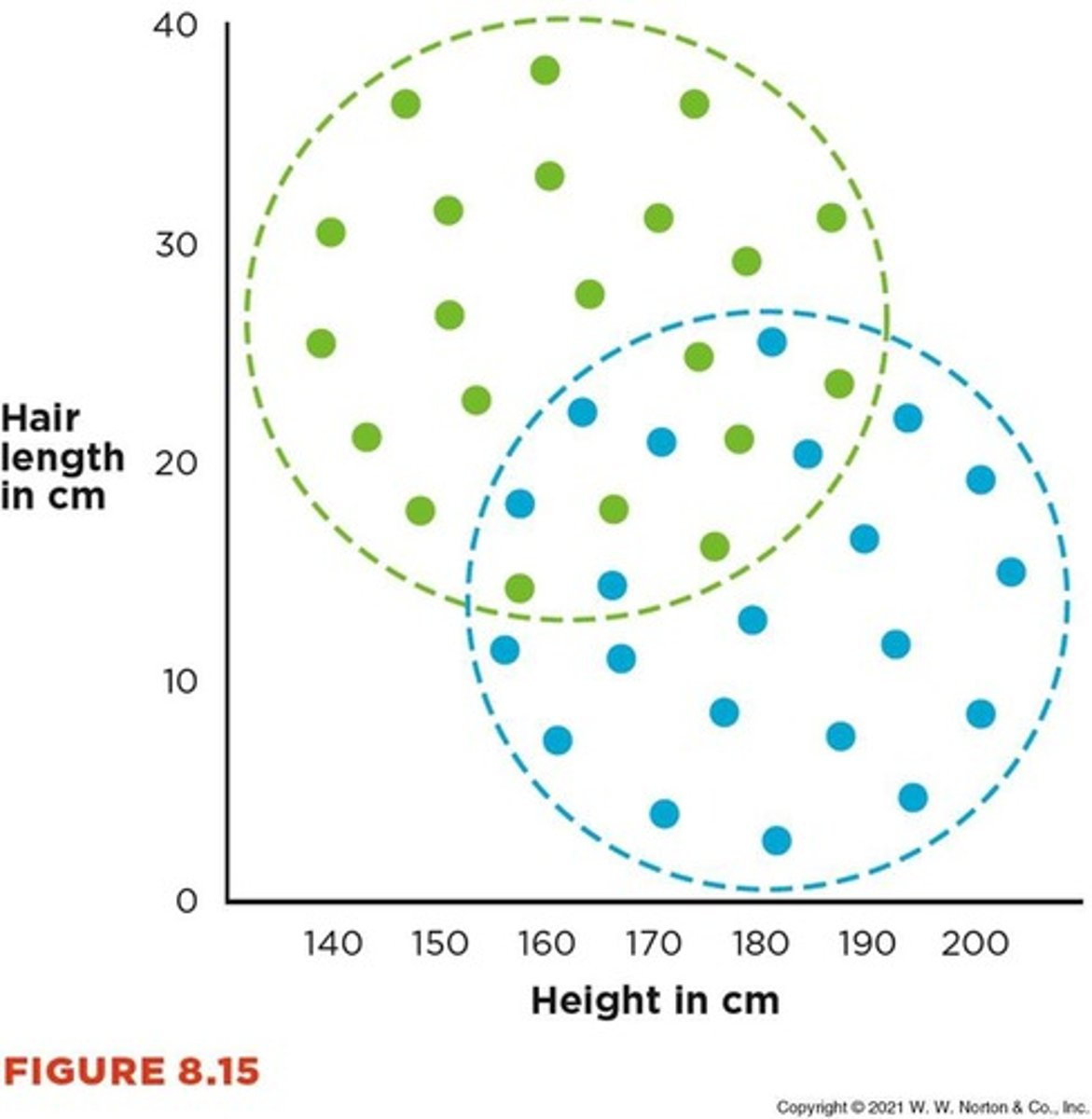
Cross-Sectional Correlations
Correlations between variables measured simultaneously.
Temporal Precedence
Establishing which variable precedes the other.
Covariance
Significant correlation indicates variable relationship.
Longitudinal Studies
Research designs assessing variables over time.
Internal Validity
Degree to which results are attributable to the study.
Multiple Regression
Statistical method analyzing relationships among multiple variables.
Criterion Variable
Outcome variable being predicted in regression analysis.
Predictor Variable
Variable used to predict the criterion variable.
Beta
Coefficient indicating strength and direction of relationships.
Statistical Significance
Probability that results are not due to chance.
Confidence Interval (CI)
Range estimating the true value of a parameter.
Design Confounds
Variables that unintentionally vary with independent variable.
Mediators
Variables explaining the relationship between two others.
Third Variables
External factors affecting the correlation between two variables.
Regression Analysis
Technique to determine relationships among variables.
Control Variables
Variables held constant to prevent confounding effects.
Experimental Variables
Includes manipulated and measured variables in experiments.
Independent Variable (IV)
Variable manipulated by the researcher.
Dependent Variable (DV)
Variable measured to assess effect of IV.
Significance Level
Threshold (e.g., p < .05) for determining statistical significance.
Longitudinal Design Criteria
Covariance, temporal precedence, and internal validity.
Regression Predictors
Variables added to improve prediction accuracy.
Systematic variability
Consistent differences affecting study outcomes.
Unsystematic variability
Random differences not affecting study outcomes.
Selection effect
Differences in participant characteristics across groups.
Random assignment
Participants randomly allocated to groups.
Matched groups
Participants paired based on similar characteristics.
Pretest/Posttest Design
Measures participants before and after treatment.
Order effects
Previous conditions influence responses to subsequent conditions.
Practice effects
Improvement due to repeated exposure to tasks.
Carryover effects
Impact of one condition persists into another.
Counterbalancing
Method to control order effects in experiments.
Full counterbalancing
All possible orders of conditions are used.
Partial counterbalancing
Only some orders of conditions are used.
Design confound
Unintentional variable affecting independent variable outcomes.
Observer bias
Researcher expectations influence participant behavior.
Demand characteristics
Participants alter behavior based on perceived study aims.
Placebo effects
Participant's belief affects their response to treatment.
History threat
External events influence study outcomes over time.
Regression threat
Extreme scores move closer to the mean over time.
Testing threat
Repeated testing affects participant performance.
Instrumentation threat
Changes in measurement tools affect study results.
Selection-history threat
External factors affect only one experimental group.
Selection-attrition threat
Loss of participants affects only one group.
Comparison group
Group with equal exposure, no treatment given.
Regression to the mean
Extreme scores move closer to average over time.
Attrition
Dropout of extreme cases affects group averages.
Testing
Repeated testing influences participants' performance.
Instrumentation
Changes in measurement tools affect results.
Design confound
Unintentional variable varies with independent variable.
Selection effect
Systematic differences in participant groups.
Observer bias
Researcher expectations influence ratings of behavior.
Order effect
Previous conditions affect responses in repeated measures.
Demand characteristic
Participants alter behavior based on study expectations.
Practice effects
Improvement due to familiarity with the test.
Fatigue effects
Decline in performance due to tiredness.
Control variables
Variables kept constant to isolate independent variable.
Random assignment
Participants randomly placed in different groups.
Posttest
Assessment after treatment to measure effects.
Pretest
Assessment before treatment to establish baseline.
Extreme scores
Scores significantly higher or lower than average.
Leniency in coding
Coders become less strict over time.
Independent variable
Variable manipulated to observe effects on dependent variable.
Dependent variable
Variable measured to assess impact of independent variable.
Systematic variation
Consistent differences that affect experimental outcomes.
Experimental group
Group receiving treatment in an experiment.
Maturation
Natural development affecting experimental group outcomes.
Purpose of the Study
Research aim influencing design and participant guessing.
Comparison Group
Group with equal maturation, no treatment received.
History
External factors altering experimental group over time.
Placebo Effect
Improvement due to belief in treatment efficacy.
Regression to the Mean
Extreme scores normalize over time due to chance.
Attrition
Changes due to extreme cases dropping out systematically.
Null Effects
Lack of difference from independent variable manipulation.
Between-Groups Difference
Insufficient difference between experimental groups.
Within-Groups Variability
Variability obscuring differences between groups.
Weak Manipulations
Ineffective treatment leading to null effects.
Insensitive Measures
Tools failing to detect group differences.