RUSVM Vet Prep: Microbiology
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
What is microbiology
The study of small life
What microbes are beneficial to humans?
Bread, cheese, yogurt, alcohol, wine, beer
Antibiotics
Vaccines, vitamins, enzymes
Which microbes are harmful to humans?
Diseases and food spoilage
What are some examples of prokaryotes?
Bacteria and archaea
What are some examples of eukaryotes?
Fungi
Protozoa
Helminths
What are some examples of acellular?
Virus
Prion
What is a microbiome or microbiota?
The aggregate of microorganisms associated with the human body. They have been described as having 10 times more bacterial cells than the human body
What are the 4 components of an ecosystem?
1) Cycling of important nutrients
2) Nitrogen fixers
3) Natural gas
4) Bioremediation
What is cycling of important nutrients?
Plants nutrition: carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur
What are nitrogen fixers?
Live in the soil where they convert vast quantities of nitrogen from air into a form that plants can use.
What is natural gas and give an example
A product of bacterial activity arising from the metabolism of methanogenic bacteria. Plays major role in energy production. Ex) Methane
What is bioremediation?
Introduction of microbes to restore stability to disturbed or polluted environments
What contribution did Zacharias Janssen have?
He created the first compound microscope
What contribution did Robert Hooke have?
Presented the first published depiction of microorganism, the micro-fungus Mucor
What contribution did Anton van Leeuwenhoek have?
Was the first to observed and described microscopic protozoa, red blood cells, sperm cells of animals, and bacteria
What are some different types of microscopes?
Light, Bright field and dark field, fluorescence, confocal (laser), transmission electron, and scanning electron.
What is a scanning electron microscope?
Scans the surface of the object. Makes the image 3D image.
What is a transmission electron microscope?
Transmits electron through an ultra thin section to show internal ultrastructural features such as nucleus.
Who introduced the belief that spontaneous generation of life form non living matter?
Aristotle
What is abiogenesis?
The theory that addresses the actual origins of life on Earth. It is the process by which life arises naturally from non-living matter.
What is a protocell?
A self-organized, endogenously ordered, spherical collection of lipids / molecules proposed as a stepping-stone to the origin of life.
What was Francesco Redi's experiment?
He used three flasks with meat. One uncovered, one sealed, and one covered with gauze. Unsealed meat had maggots. Sealed showed no maggots on meat. Gauze showed that maggots were on gauze but not on meat.
What was John Needham's experiment?
Used nutrient broth. Had it boiled leaving the flask open to cool where bacteria and mold appeared in broth.
What was Lazzaro Spallanzani's experiment?
Used Nutrient broth. Boiling 2 flasks for longer period of time, sealing one immediately and leaving one open. Bacteria and mold only appeared in the open flask.
What was Louis Pasteur's experiment?
Used nutrient broth. Boiling in flask with "S" shaped neck. Leaving flask open for weeks then breaking neck off flask. Bacteria and mold only appeared after neck had been removed from flask.
Father of Microbiology
Germ Theory
What did both Louis Pasteur & Charles Chamberland do to prevent diseases
Inoculation of an attenuated chicken cholera bacteria.
This concept established protection against disease by inoculating a weekend strain of the causative agent
What are some Louis Pasteur's notable contributions to microbiology?
Lactic acid fermentation
Pasteur Effect
Pasteurization (destroying bacteria)***
Developed a special vaccine for rabies (Pasteur treatment)
Vaccine for anthrax
Disproved theory of spontaneous generation
Proposed germ theory of disease
Yeasts are involved in alcoholic fermentation
Who was the first person to be inoculated against rabies by Louis Pasteur?
Joseph Meister
Who was the founder of modern microbiology and worked with anthrax, tuberculosis, and cholera?
Robert Koch
to link a specific microorganism with a specific disease, rejecting the idea of spontaneous generation and supporting the germ theory of disease
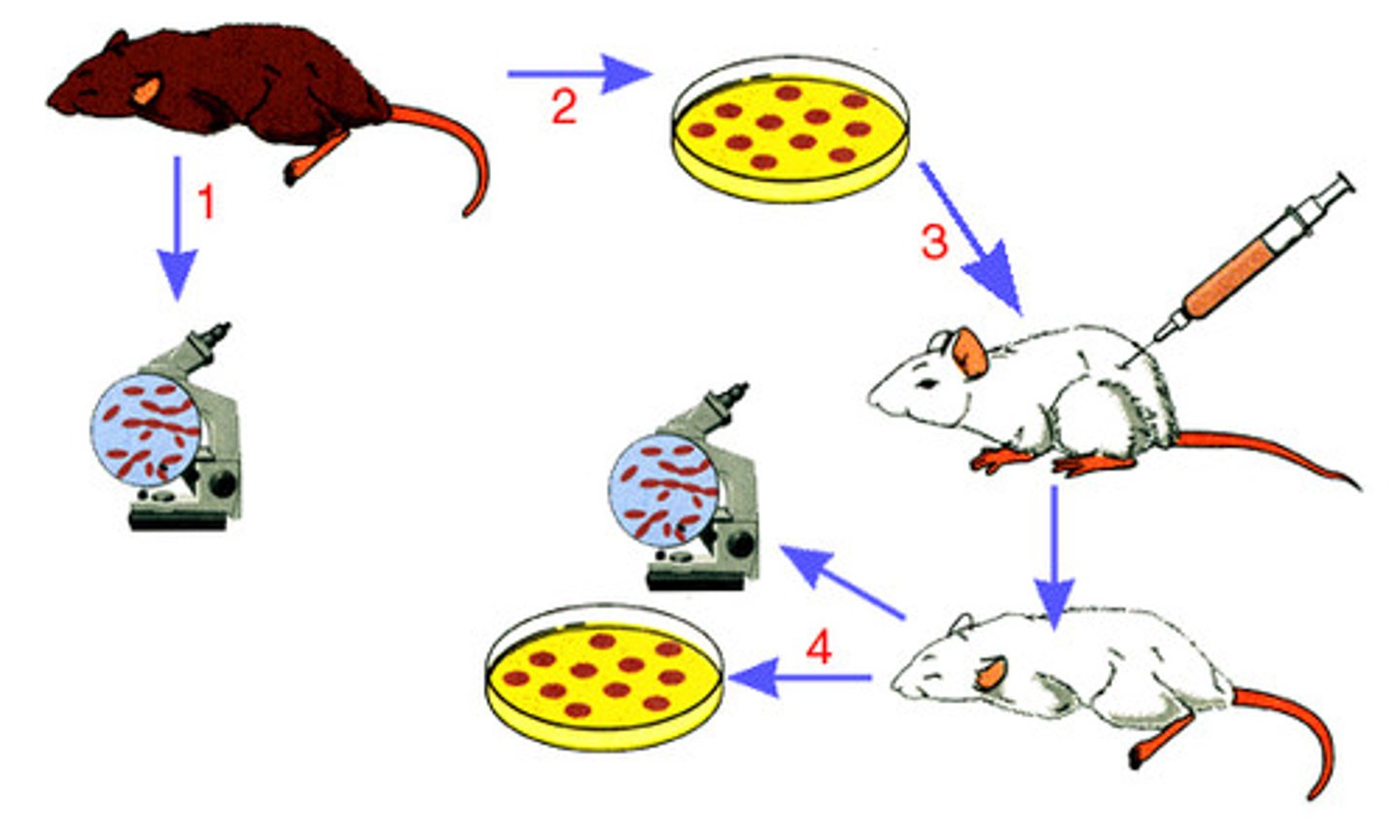
What are Robert Koch's 4 criteria to identify the causative agent of a particular disease?
(1) The microorganism must be found in diseased but not healthy individuals;
(2) The microorganism must be cultured from the diseased individual;
(3) Inoculation of a healthy individual with the cultured microorganism must recapitulated the disease; and finally
(4) The microorganism must be re-isolated from the inoculated, diseased individual and matched to the original microorganism.
Who is the father of antiseptic surgery (Sterile surgery using carbolic acid)?
Joseph Lister
What contributions did Joseph Lister bring to microbiology?
He used carbolic acid (phenol) to use as an antiseptic during surgeries. Introduced clean gowns and insisted on washing hands.
What is variolation?
Inoculation. This method used immunize an individual against smallpox (Variola) with material taken from patient in the hope that a mild but protective infection would result.
What contributions did Edward Jenner bring to microbiology?
Used cowpox vaccine against smallpox. Thought that a less pathogenic agent could confer protection against a more pathogenic one.
What contributions did Lady Mary Wortley Montagu bring to microbiology?
Variolation used live smallpox virus in the liquid taken from a smallpox blister in a mild case of the disease.
What contributions did Rudolf Virchow bring to microbiology?
Used cell theory (every cell stems from another cell)
Cellular Pathology.
Coined the term zoonosis
Often referred to as the "father of modern pathology"
Founder of social medicine and veterinary pathology
What contributions did Alexander Fleming bring to microbiology?
Discovered that lysozyme, enzyme found in tears, saliva and sweat, could kill bacteria. *first body secretion shown to have chemotherapeutic properties
Discovered penicillin for which he got the model prize in physiology and medicine.
What contributions did Ferdinand J. Cohn bring to microbiology?
Classified algae as plants
Classification of bacteria into 4 groups based on shape (spherical, short rods, threads, and spirals)
First to show Bacillus can change from vegetative state to an endospore state when subjected to an environment deleterious to the vegetative state.
What contributions did Edouard Chatton bring to microbiology?
Characterized the distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems of cellular organization based on presence or absence or nucleus.
True or False: Prokaryotes have no true nucleus?
True. Means before nucleus
True or False: Eukaryotes have no true nucleus?
False. Eukaryotes have a nucleus
What contributions did Elie Metchnikoff bring to microbiology?
Described phagocytosis.
What is phagocytosis?
Means eating of cells
A defensive process in which the body's white blood cells engulf and destroy microorganisms.
The body is protected form infection by leukocytes that engulf bacteria and other invading organism; cellular immunity.
What contributions did Giovanni Battista Grassi bring to microbiology?
Best known for his work on parasite life cycles including nematodes and malaria
What contributions did David Bruce bring to microbiology?
Investigated Malta Fever (brucellosis) and trypanosomes, identifying the cause of sleeping sickness.
Described Chagas disease or American trypanosomiasis, a tropical parasitic disease caused by a protozoan spread by insects
What contributions did Dmitri Ivanowski bring to microbiology?
Discovered Viruses
Filterability of an infectious agent which caused tobacco mosaic disease
What contributions did Martinus Beikerinck bring to microbiology?
Published results on the filtration experiments demonstrating that tobacco mosaic disease is caused by an infectious agent smaller than bacterium.
What are the 6 major elements found in biological macromolecules?
Carbon - Present in all biological macromolecules
Hydrogen - Present in all biological macromolecules
Oxygen - Present in all biological macromolecules
Nitrogen
Sulfur
Phosphorous
What do all living things have in common?
Have a plasma membrane
Use ATP for energy (replicating in viruses)
Genetic information in DNA
What is taxonomy?
Science of classification of living things
What are systematists?
Scientists who works on taxonomy
Who started taxonomy?
Aristotle came up with structural complexity. 500 organisms in 11 categories. Some of which are still maintained such as vertebrates and invertebrates.
Who was Carl Linnaeus?
Came up with two kingdoms and binomial nomenclature
What are the two kingdoms Carl Linnaeus came up with?
Vegetabilia and Animalia
What is binomial nomenclature?
Formal naming of a living organism
Ex. Genus species
1st letter of Genus - upper case
1st letter of species is lowercase
-Underline the words when handwritten
-Underline or italicize when typed
-can be abbreviated
ex. E. coli
What is a species for sexually reproducing organisms?
A population that can breed and produce fertile offspring
What is a post zygotic mechanisms?
The cross between donkey and horse produces mules.
However, these hybrid animals are sterile (two mules)
What is a species for asexually reproducing organisms?
Like bacteria, the species distinction is a little trickier.
What is the international code of Zoological Nomenclature?
"The Code"
Responsible for making a specific name for every animal
What are the 4 ways to give bacteria nomenclature?
1) Descriptive
- Staphylococcus aureus (grape-like cluster of spheres, golden in color)
2) Scientist's name
- Ehrlichia (Paul Ehrlich)
3) Geographic places
- Legionella longbeachiae (Long Beach, California),
4) Organizations
- Legionella (American Legion),
don't need to know examples
What is systematics or phylogeny?
Study of evolutionary history of living organism
What are the 3 domains?
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
by Carl Woese
Why 16s/18s ribosomal RNA?
Useful for inferring phylogenetic differences
DNA coding
conserved 3% difference
What does a rDNA sequence codes for?
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
Describe what a Prokaryotic cell is.
No nuclear membrane or nuceoli
Cell wall includes peptidoglycan
Binary fission when going through cell division
No meiosis but transfers DNA fragments
Describe what a Eukaryotic cell is.
True Nucleus consisting of nuclear membrane and nucleoli
When cell wall is present its chemically simple
Cell division through mitosis
Sexual reproduction involves meiosis
What are three types of Archaea?
Methanogens
Extreme halophiles (salt)
Extreme thermophiles (Heat)
Describe the characteristics of being in a Archaea domain.
Prokaryotic
Lack peptidoglycan
Binary Fission
Many live in extreme environments
A pathogenetic one yet to be identified
Describe the characteristics of being in a Eubacteria domain.
Prokaryotes Unicellular
Ubiquitous
*Have peptidoglycan in the cell wall*
Binary Fission
Pathogens, opportunistic pathogens, harmless and beneficial
Describe the characteristics of being in a Eukaryota domain.
Protozoans
Fungi
Helminths (nematodes, cestodes, trematodes)
Algae
Slime and water molds
Animals
Plants
What are the three major groups of alveolate?
Predatory
Photosynthetic
Parasitic
What are the methods of identifying Bacteria?
1) Culture and analysis of morphological characteristics, staining
2) Biochemical tests "ELISA"
3) Serology "host response to infection"
4) Phage typing
5) Fatty acid profiles
6) Nucleic acid base testing
7) Mass spectrometry
What are two ways to classify parasites?
Protozoan (single cell)
Metazoan (more complex multicellular)
How to identify a type of parasite?
-Morphology
-Molecular techniques (DNA sequence)
-Host specificity
-Geographical location
-Tissue tropism (where are they in the host
What is serendipity?
Accidental discovery of something useful or valuable.
"In the fields of observation chance favors only the prepared mind"
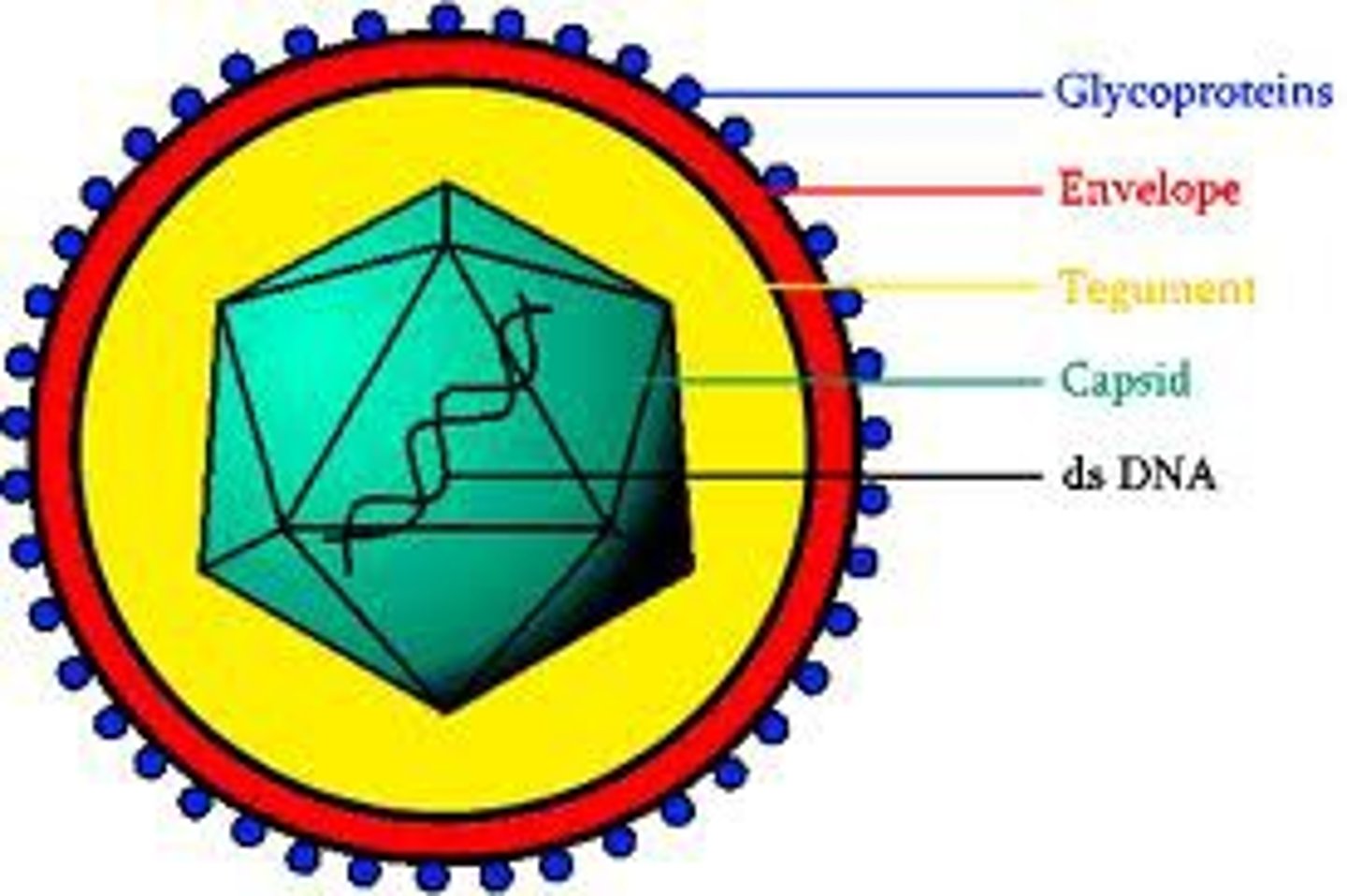
What is a Virus?
A small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms.
What are the three parts to a virus particle (virions)?
1) The genetic material is either DNA or RNA
2) A protein coat that protects these genes
3) An envelope (phospholipids and proteins)
What are the 7 ways one can identify bacteria?
1) Culture and analysis of morphologic characteristics and differential staining
2) Biochemical tests (ELISA)
3) Serology
4) Phage typing
5) Fatty acid profiles
6) Nucleic acid based testing
7) Mass spectrometry
What are the two ways of classifying parasites?
1) Protozoan (single cell)
2) Metazoan (more complex multicellular organisms
What are the 5 ways of identifying parasites?
1) Morphology
2) Molecular techniques
3) Host specificity
4) Geographical location
5) Tissue tropism
What are the 5 ways of identifying viruses?
1) Direct observation from clinical samples using transmission electron microscope
2) Cultivation in cell cultures
3) Fluorescent antibody staining technique from infected cells or cell cultures
4) ELISA to detect viral antigens
5) Molecular methods (PCR)
What is molecular biology?
The study of molecular foundation of the process of replication, transcription, translation, and cell function.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
Where genetic material is transcribed into RNA and then translated into protein, despite being an oversimplified picture of molecular biology.
Who came up with the idea of the central dogma of molecular biology?
Francis Crick
What must DNA, RNA and protein (Genetic material) be able to do?
1) Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism
2) Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division
3) Be accurately copied
4) Account for the known variation within and between species
What did Frederick Griffith do?
Use 2 strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae in mice to see find if genetic material from the heat-killed type S bacteria had been transferred to the living type R bacteria.
What are the two types of S. pneumoniae
One strain secreted capsules that look smooth and cause fatal infections in mice, which prevented immune system from killing bacteria. Living bacteria found in blood
Another strain secreted capsules that look rough and infections are non fatal in mice. No bacteria found in blood.
What three scientists used purification methods to reveal that DNA is the genetic material?
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty
Who proposed the structure of the DNA double helix?
Watson, Crick, with Wilkins
What is a nucleic acid?
A polymer that consists of a chain of nucleotides
What are the 3 building blocks in a nucleotide?
Phosphate group, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base
What is DNA?
Double stranded, helical, sugar phosphate backbone, stabilized by hydrogen bonding, and base pairs with specific pairing.
What are the 3 components of DNA?
Phosphate group
Pentose Sugar (deoxyribose)
Nitrogenous base (Purines and Pyrimidines)
What are the 2 components in purines involved with DNA?
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
What are the 2 components in pyrimidines involved with DNA?
Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T)
What are the 3 components of RNA?
Phosphate group
Pentose Sugar (ribose)
Nitrogenous base (Purines and Pyrimidines)
What are the 2 components in pyrimidines involved with RNA?
Cytosine (C) and Uracil (U)
What is a phosphodiester bond?
A phosphate group which links two sugars
What is a nitrogenous base?
A type of organic molecule that consists of one or two ring structures (Purines A & G)
In RNA what is thymine replaced by?
Uracil (U)