Protecting and adapting to the environment (pg 100-103)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Protecting and adapting to the environment
Ecotourism
Tourism that minimises the impact on the environment to respect local cultures
Case study/Let’s get thinking
Where is a popular place that practices ecotourism? What details can you give me of the experience there as a tourist (what kind of place, what would tourist be able to do)?
An island in Asia called Borneo (Al lado de Malasya and Brunei)
Experience the unusual wildlife and super landscape.
Rainforest
Home to famous animal species like the Pygmy elephant and Bornean orangutan
It is also where the indigenous Dayak people live
Continuation of Let’s get thinking
As tourism increased, the country was concerned about protecting the rainforest so what did the country do? By doing this what do they protect?
What are examples of things they did to preserve the rainforest?
Ecotourism principles were introduced so that the environment is preserved but development can still take place (creation of jobs and income from tourists spending while protecting natural areas (that may act as carbon sinks)). Can protect biodiversity, endangered ecosystems, indigenous culture (preserving it).
Examples
Animals stay within a sanctuary that tourists pay to see
Locals are hired as tour guides
Craft sellers and tourists stay in lodges (cabañas) built from the local materials
Sustainable development can only occur successfully if action is taken on a local, national and international scale
What has the UN created in 1994 to adapt to the changing environment/tackle it? How many parties have signed up? What do these parties do annually and why?
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
197
They meet annually at conferences around the world to assess its progress
UNFCCC
Aim? Requirements?
Aim: To reduce the level of greenhouse gases globally
UNFCCC
Requires countries to provide reports on their climate change actions
States that developed countries should lead by example, and new funds should go to developing countries (e.g for wind turbines for renewable energy)
Helps developing countries to limit the greenhouse gas emissions in ways that don’t prevent their economic progress (sustainable development)
What is the Kyoto Protocol? What does it include? When was it developed?
It is an international treaty on climate change that was an extension of the UNFCCC
Includes target for 52 industrialised countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions
1997
What is the Paris Agreement? When was it developed?
It is an international treaty on climate change developed from the Kyoto protocol
In the COP 21 on 2016
Details of the Paris Agreement? However, why might it not be very effective?
It is the first global agreement to include both industrialised and developing countries
Instead of setting specific targets, it asks countries to determine, plan and report on their contributions to slow down climate change
Countries set their own targets and it is up to them if they want to achieve them
Difference between adapting and preventing
Adapting refers to adjusting to unavoidable changes or their effects
Prevention aims to stop something from happening in the first place
What are ways the world has innovated to adapt to the changing climate to address which issue?
Food insecurity in the future may be a problem so technology has been developed to secure food supplies.
Genetic modification develops new varieties by making them more resilient to climate change.
this can improve the quality and quantity of crops
For example Spain will become a more dry country and be at risk of drought, so plants would be modified to require less water
Water can also be provided more readily for farmers with modern irrigation systems
Extra: We can also help to slow climate change by reducing the amount of meat we eat. Since livestock farming needs a lot of land and releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
What would be the response to sea levels rising?
People moving (more migration)
Sea defences will have to be built to prevent flooding or the land being consumed by the sea
Real life example of a place in danger of floods? Details about the country (how easy is it for it to adapt)? How can it therefore help itself from being flooded in the future?
Tuvalu is an island nation that is just barely above sea level but cannot prevent sea level rises in its own because it has limited resources (small land area, remoteness, dependent on remittances and its fisheries) and it is dependent on aid.
However, as an independent state and member of the international community, it can join agreements on climate change, such as the UNFCCC which states that we funds should go to developing countries.
What countries are likely to be flooded in the future?
Bangladesh, the Netherlands, Vietnam, Myanmar
Natural disasters will also be more likely to happen due to climate change.
Which countries are more prone to them? However, why is it going to be difficult for them to deal with this?
Philippines, India, Haiti
Their resources which they are heavily reliant on are very sensitive to climate change, such as water and agriculture
Aprox half of Haiti’s population lives in rural areas and depend on farming
What are the consequences of natural disasters?
Destroy land and resources
Bring injury and death
Diseases (e.g waterborne infections like cholera)
Starvation
What has India done to its infrastructure like houses to adapt to the risk of flooding to save these communities?
Building houses on stilts in India keeps homes above rising water levels
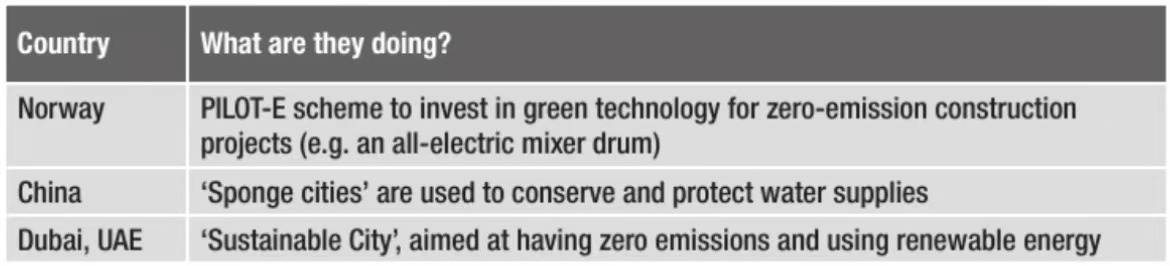
What are other real life examples of real life strategies to adapt and innovate?
Carbon footprint
The amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere due to the activities of an individual, organisation or community