DCAP Final Exam Review
1/220
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
221 Terms
What is the process by which water molecules stick to each other called?
Cohesion
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose
Disaccharides
maltose, lactose
Polysaccharides
glycogen, starch
Homeostasis
balance in the body
Which of the following terms describes molecules that do not dissolve in water?
Hydrophobic
Protein
A macromolecule composed of amino acids
Lipid
A macromolecule that serves as a long-term energy storage and structural component of cell membranes.
Carbohydrate
A macromolecule that provides a rapid energy source for the body.
Nucleic acid
A macromolecule responsible for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
What is the name for the study of cells?
Cytology
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment or origin
Superficial
Near the surface
Dorsal
Toward the back
Distal
Away from the point of attachment or origin
Covalent bond
Involves sharing electrons between atoms
Ionic bond
Involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another
Polar molecule
A molecule that has a partial positive and a partial negative charge
Nonpolar molecule
A molecule that has a symmetrical electron distribution
PH of lower numbers
are more acidic
PH of higher numbers
are less acidic
Which of the following is an example of positive feedback mechanism in the human body?
Blood clotting
A podiatrist (foot doctor) is an example of which subdiscipline of anatomy?
Regional anatomy
What is the role of enzymes in metabolic reactions?
To act as catalysts and speed up the reactions
Sagittal plane
Divides the body into left and right halves
Frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back halves
Transverse plane
Divides the body into upper and lower halves
The nucleus of an atom is made up of ______ and ______ .
Protons and Neutrons
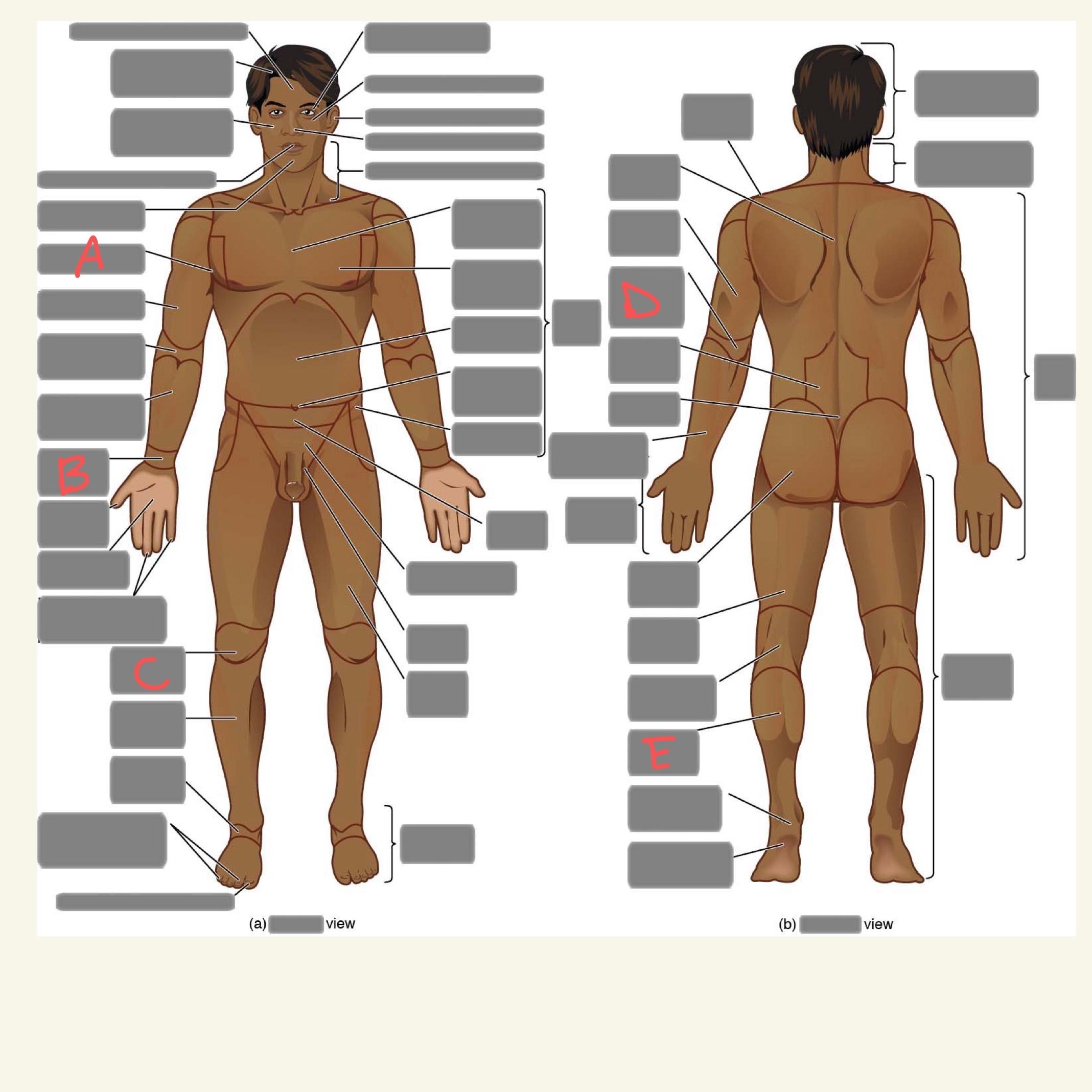
A
axillary
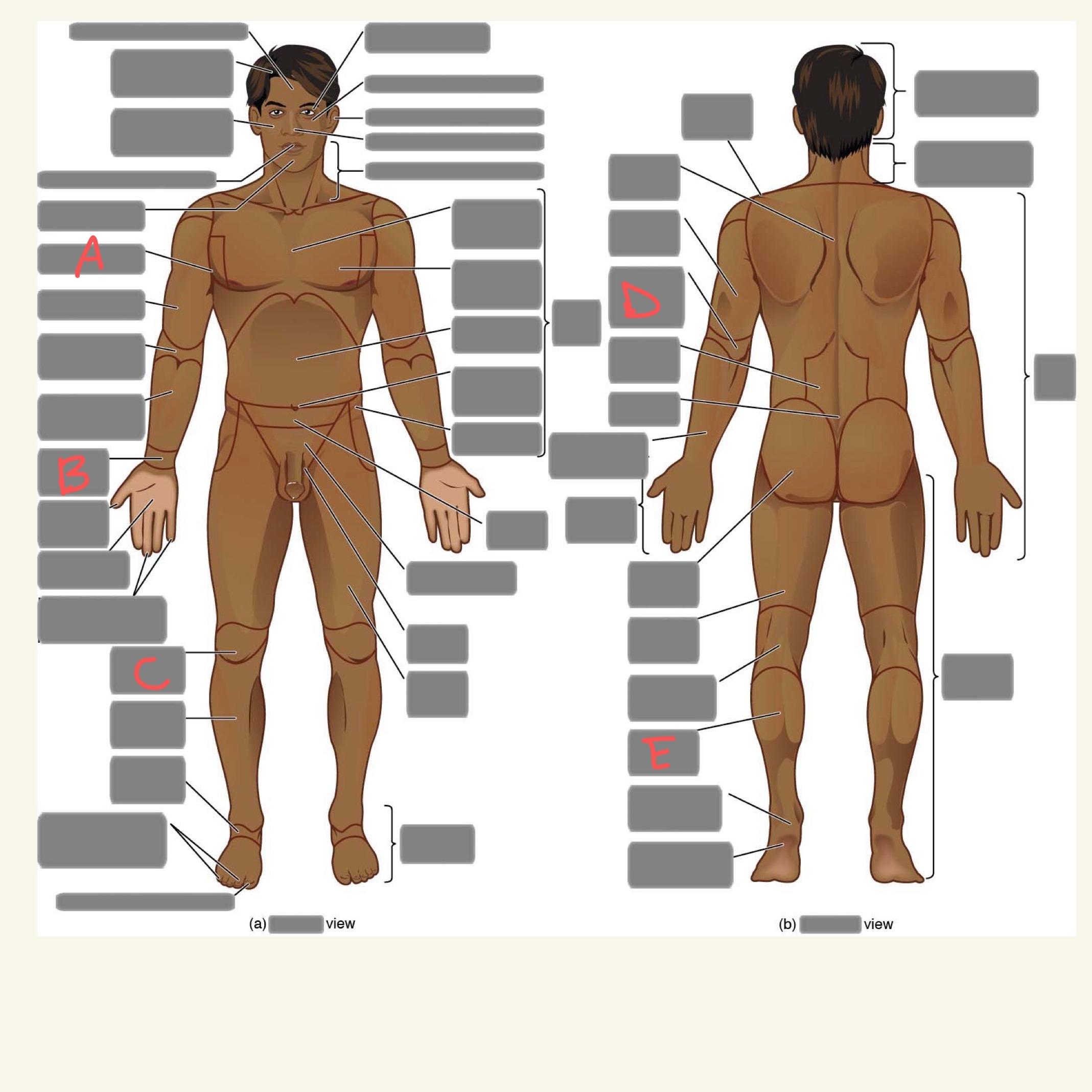
B
carpal
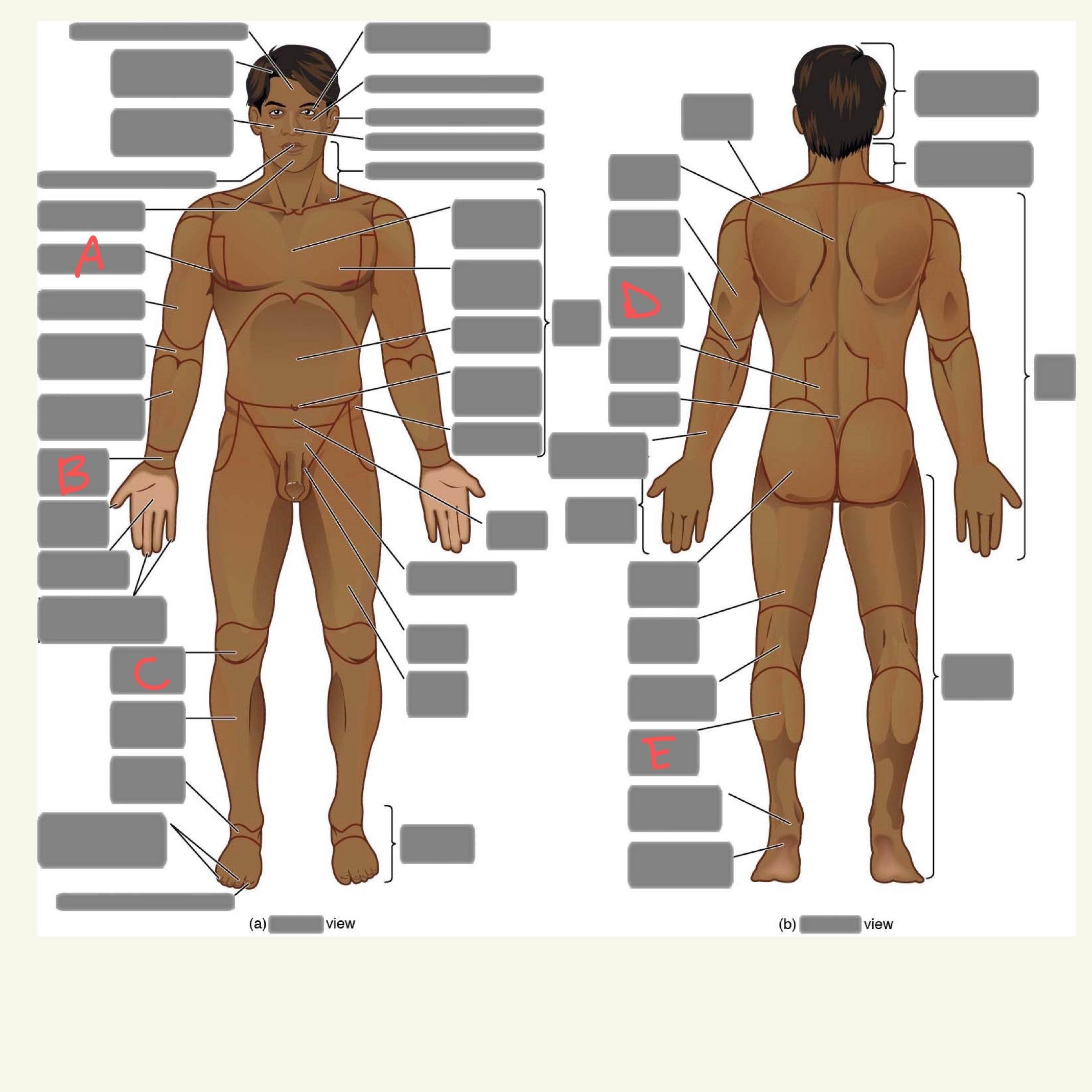
C
patellar
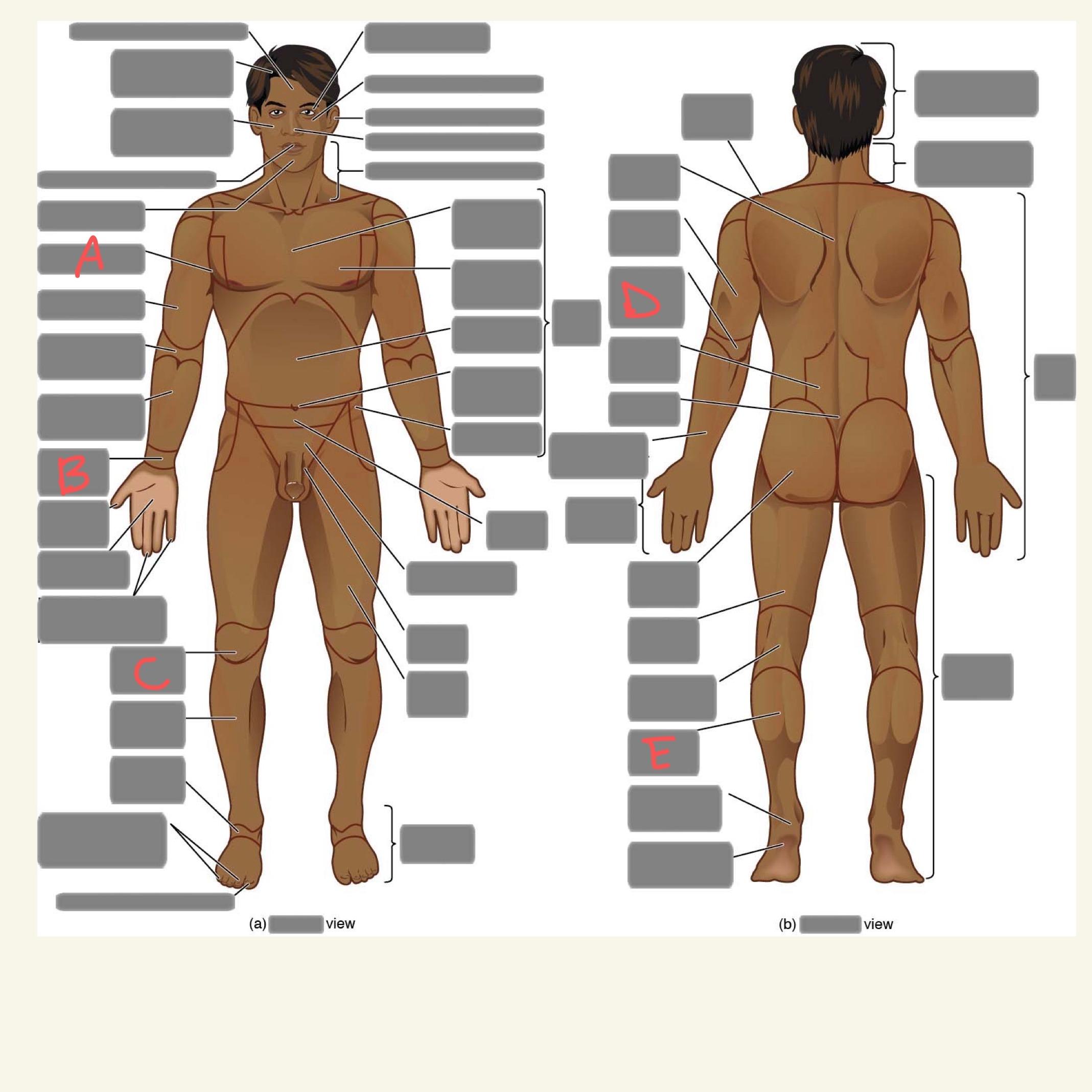
D
olecranal
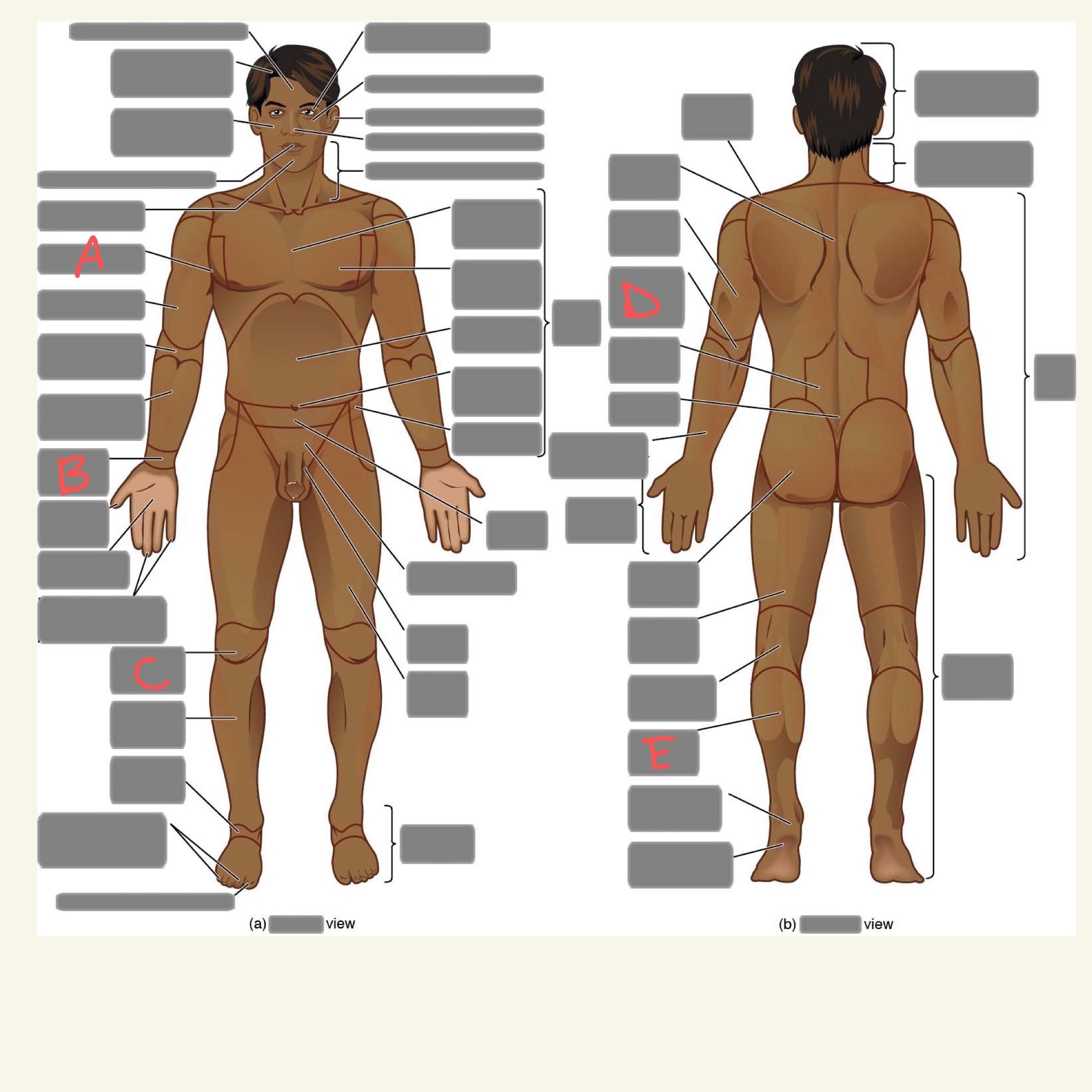
E
sural
Exothermic Reaction
Needs less energy than it creates. Net Gain.
Endothermic Reaction
Needs more energy than it creates. Net Loss.
Which of the following is an example of negative feedback mechanism in the human body?
Regulation of body temperature
Which of the following statements correctly describes anatomy and physiology?
Anatomy studies the form and structure of the body, while physiology examines how the body functions.
Which body system is responsible for transporting nutrients, waste products, gases, and hormones throughout the body?
Cardiovascular system
A solution with a pH of _____ is considered neutral.
7
Which of the following is NOT a function of lipids?
Acting as catalysts in metabolic reactions
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
To control what enters and exits the cell
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells; found in alveoli or lining of body cavities
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Designed for absorption and secretion in small glands; found in walls of kidney tubules
Simple columnar epithelium
Contain goblet cells; lines digestive tract
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Have cilia for protection against inhaled debris; located in large passageways of the respiratory system
Stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple layers of cells used for protection; located in epidermis
Transitional epithelium
Cells that are able to stretch; line the bladder
smooth muscle is controlled
involuntarily
skeletal muscle is controlled
voluntary
Epithelial Tissue
Covering body surfaces and lining body cavities
Connective Tissue
Supporting and protecting the body's structures
Muscle Tissue
Generating force and producing motion
Nervous Tissue
Mediating perception and response
Phagocytosis
cellular 'eating'
Pinocytosis
cellular 'drinking'
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
uses receptors on plasma membrane to bind to specific molecules and bring them into the cell
Exocytosis
large substances secreted from cell
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
Modification and packaging of proteins
Mucous membranes
line the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
Serous membranes
lines body cavities
Cutaneous membrane
skin
Synovial membranes
line joint cavities
Hypertonic solution
A solution with a higher solute concentration compared to the cell.
Isotonic solution
A solution with the same concentration of solutes as the cell.
Hypotonic solution
A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to the cell.
The correct order of the phases of mitosis is
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
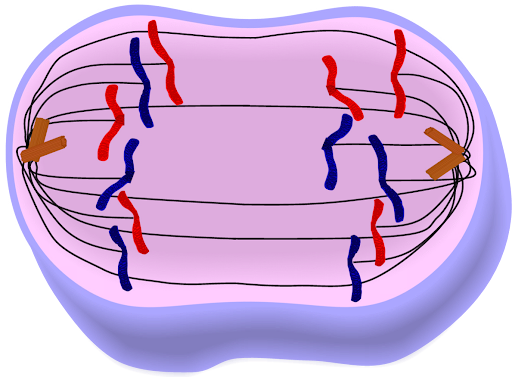
Identify the phase of mitosis shown here:
Anaphase
Which type of cell secretes mucus?
Goblet cell
what is responsible for protein synthesis
The Ribosome
Which type of cartilage is found in the external ear?
Elastic cartilage
What type of tissue makes up the brain and spinal cord?
nervous tissue
These are cellular extensions that move substances along the outside of the cell.
cilia
Epithelial tissue
Tightly packed cells arranged in continuous sheets
Connective
Relatively few cells embedded in an extracellular matrix
Muscle
Types include smooth, cardiac, and skeletal
Nervous
Specialized cells called neurons and supportive cells called neuroglia
These increase the surface area of the plasma membrane for absorption
microvilli
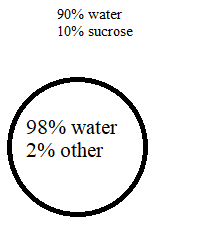
A cell is placed in a solution as shown in the picture. The membrane is permeable to water but impermeable to sucrose.
Out of the cell
Which organelle is responsible for breaking down waste materials?
Lysosomes
A ligand is a molecule that
binds to and activates a receptor
Glycocalyx acts as a
cell fingerprint
Phospholipids with attached carbohydrates are called
glycolipids
Proteins that regulate movement of substances across the membrane are called
transport proteins
Structure of the Nucleus
surrounded by a membrane, contains DNA, contains nucleolus
Function of the Nucleus
protect and store genetic material, control cell activities
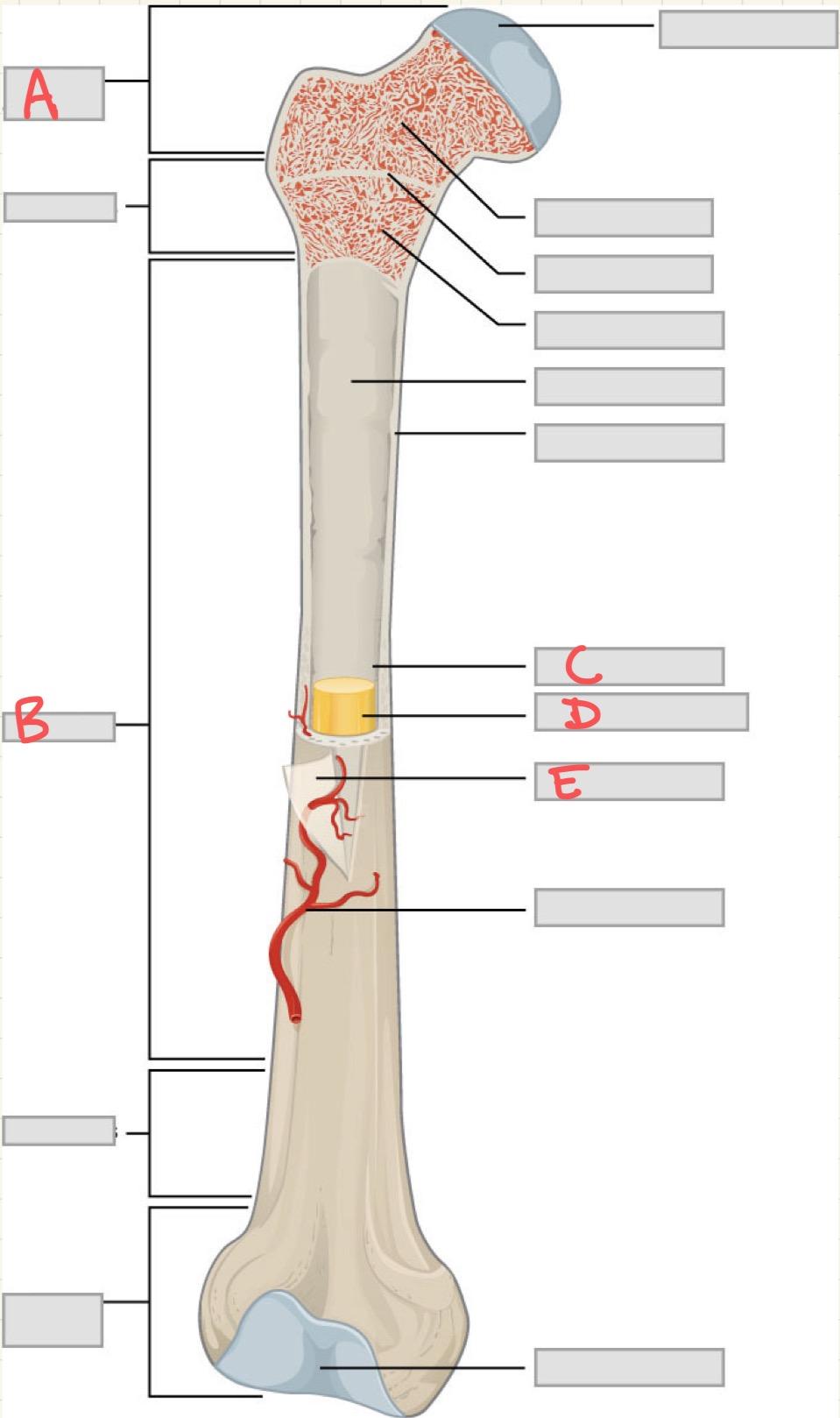
A
Epiphysis
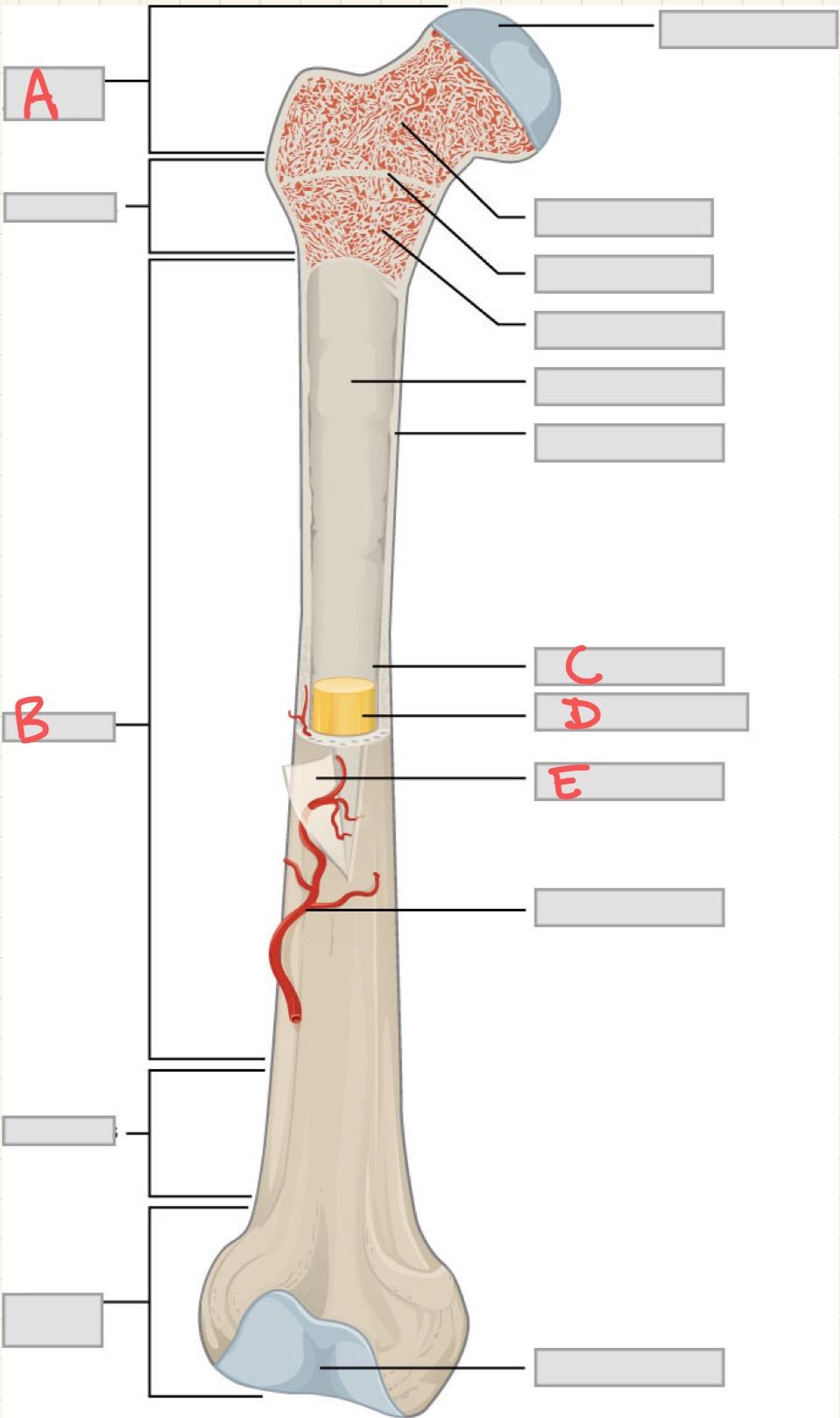
B
Diaphysis
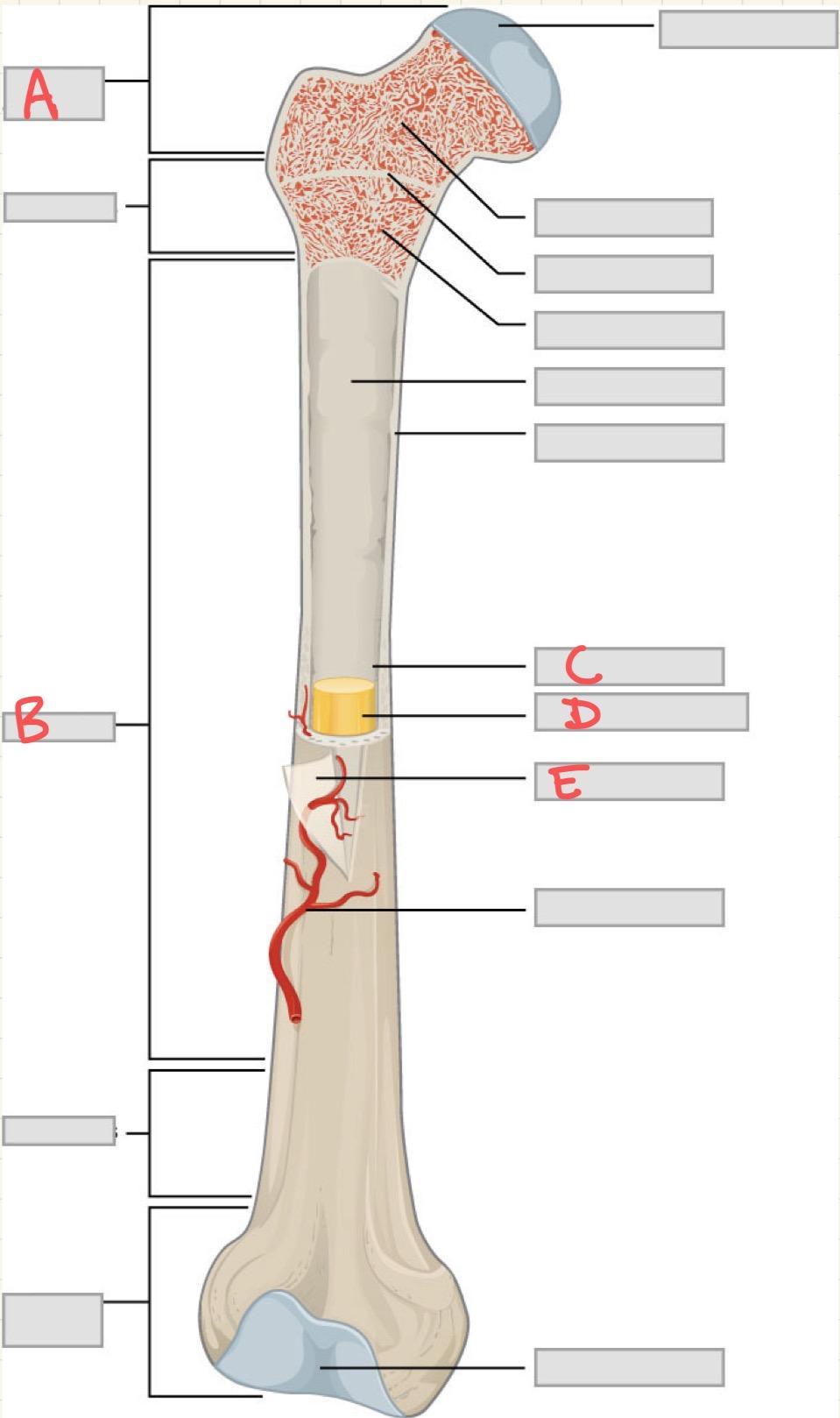
C
Medullary cavity
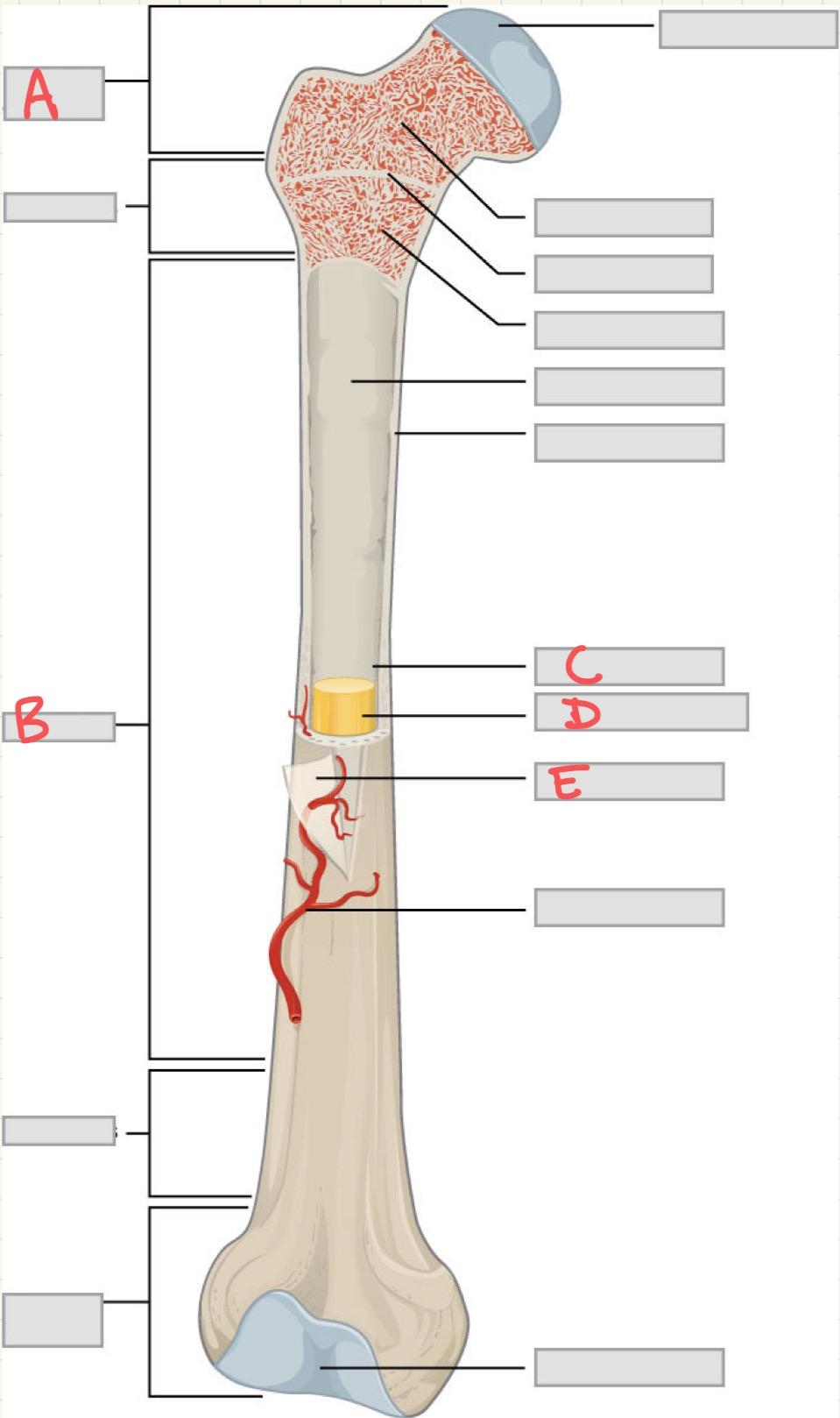
D
Yellow bone marrow
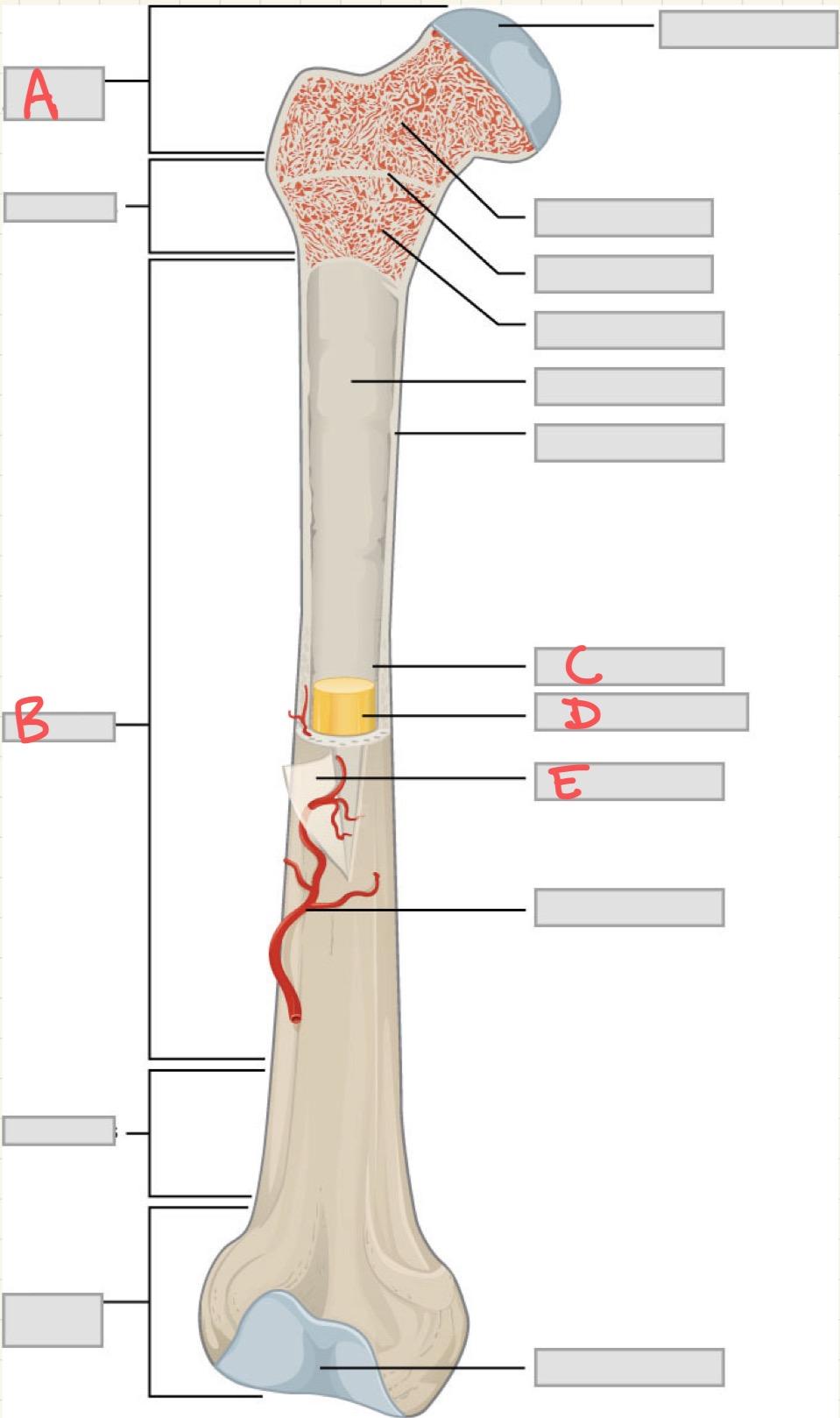
E
Periosteum
Which structure in a long bone is responsible for growth in length during childhood and adolescence?
Epiphyseal plate
What is the primary function of the periosteum?
To cover the outer surface of bone
Which hormone is released in response to increased blood calcium levels?
Calcitonin
What is the correct sequence of cell differentiation in bone tissue?
Osteogenic cells → Osteoblasts → Osteocytes
Which of the following best describes the process of intramembranous ossification?
It forms bone directly from mesenchymal connective tissue
osteogenic cells
stem cells that divide
osteoblasts
immature bone cells that synthesis and secrete collagen
osteoclasts
large phagocytic cells that break down bone
chondroblasts
immature cells that produce cartilage