Lab Media
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
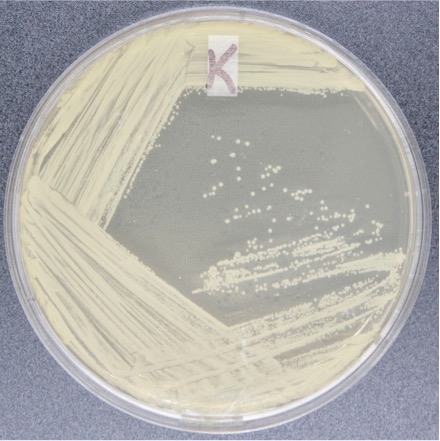
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA)
Selective only
— selective for G+, G- cannot grow
— phenylethyl alcohol inhibits the DNA synthesis of G-, making them unable to grow
useful for isolating, growing, and maintaining G+ organisms
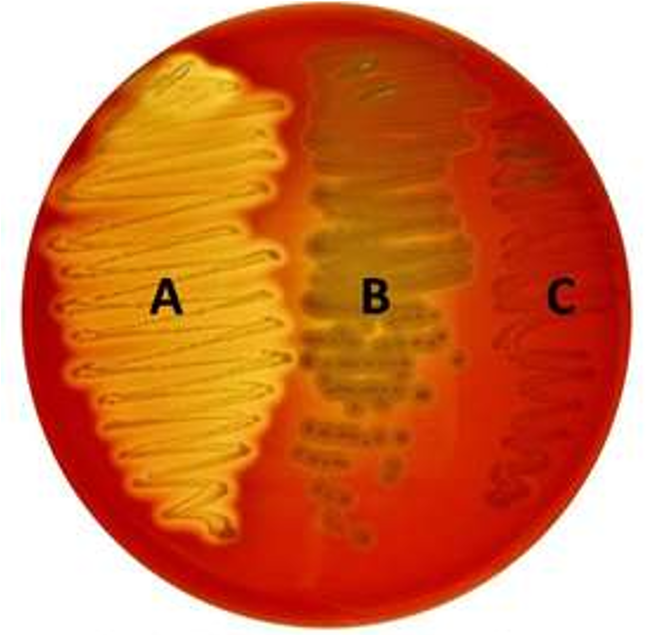
Blood Agar
Differential only; everything will grow
Based on hemolysis
— Alpha: incomplete hemolysis (greenish)
— Beta: complete hemolysis ( clear)
— Gamma: no hemolysis (no change)
Necessary for differentiating Streps
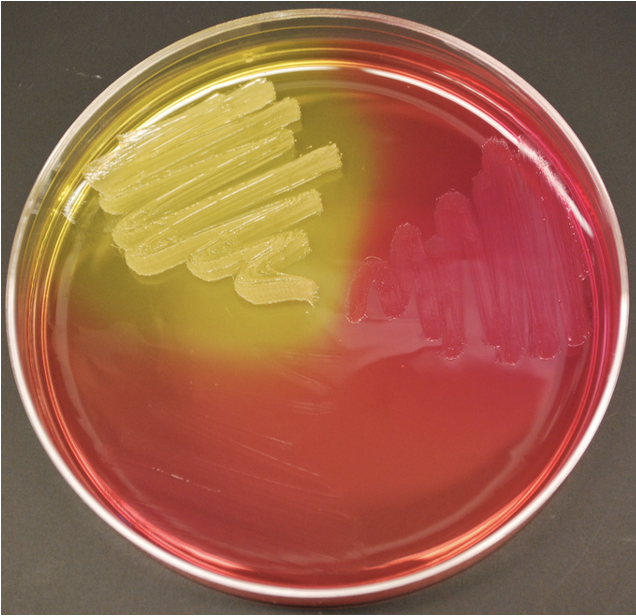
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
Selective & Differential
Selects for G+, against G-
— selecting agent: 7.5% NaCl
— G- can grow in high salt concentrations
— differential agent: mannitol and phenol red
mannitol fermentation produces acid which changes the phenol red to a yellow color
important for differentiating Straphs
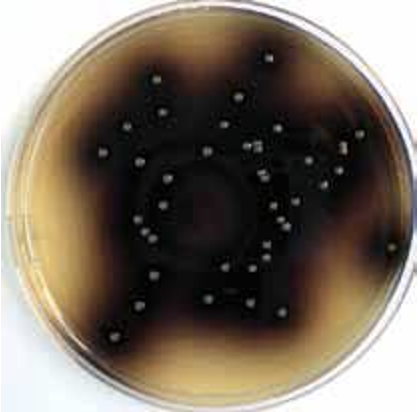
Bile Esculin Azide Agar
Selective & Differential
Selects for certain G+, against all G-
— selecting agent: sodium azide inhibitory for G- bile inhibitory to some G+
— differential agent: esculin and ferric citrate
Turns a dark brown/black pigment
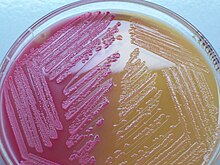
MacConkey Agar (MAC)
Selective = G- bacteria, bile salts & crystal violet
Differential = lactose fermentation, lactose & neutral red
Pink color change if the bacteria can ferment sugar
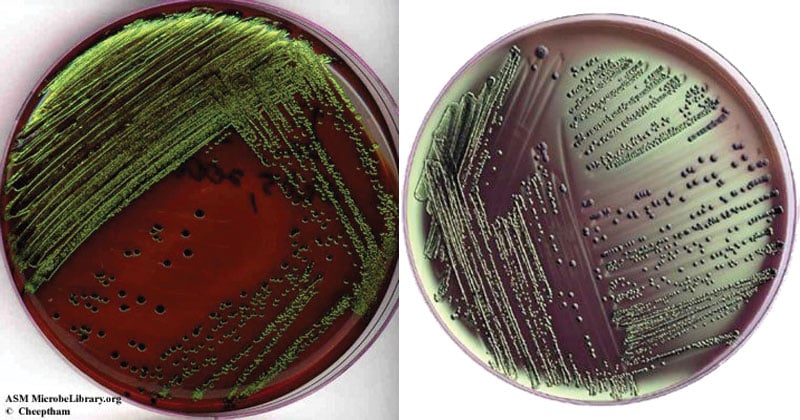
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB)
Selective = G-, Eosin Y & Methylene Blue
Differential = Rate of lactose Fermentation, lactose & dyes
Vigorous fermenter = metallic green sheen
Slow fermenter = grow pink
No fermentation = no color change
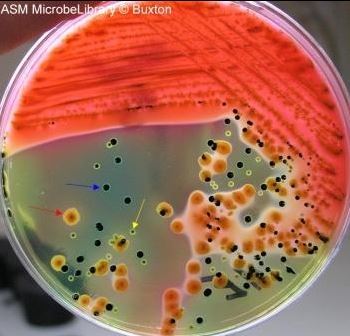
Hektoen Enteric Agar (HeK)
Selective = G-, bile salts
Differential:
lactose fermentation, bromothymol blue & acid fuchsin
— orange color change
Hydrogen sulfide gas production, sodium thiosulfate & ferric citrate
— black color change
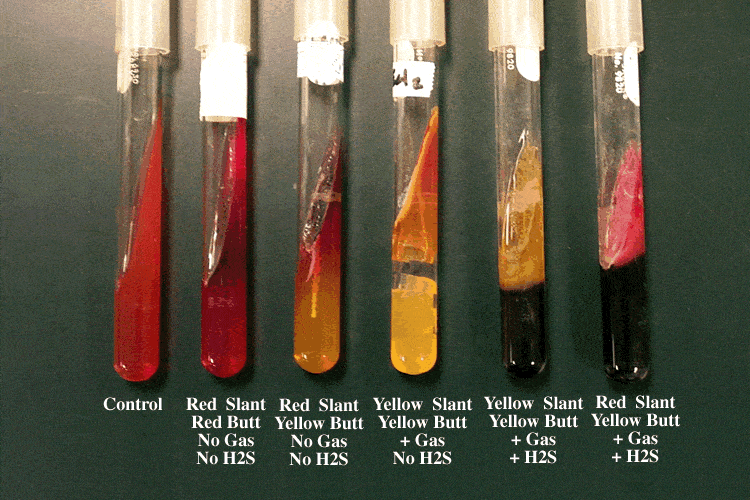
Triple Sugar Iron Agar (TSI)
Test Tube
Differential:
Sugar fermentation = lactose, sucrose, glucose, phenol red
— all yellow multiple sugar, yellow just at the bottom only glucose
H2S gas Production = sodium thiosulfate and ferric citrate
— black color change
Oxygen tolerance
— Slant is full of oxygen = strict aerobes grow
— Butt has lower oxygen = facultative anaerobes grow

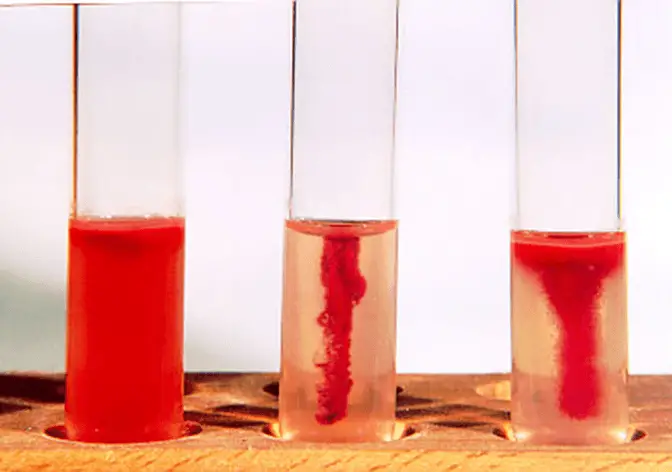
Motility Test
Determination of Presence of Flagella for motility
— motility agar = lower agar concentration
— tetrazolium salt = makes red growth
° fuzzy growth around the line of inoculation means motility

Citrate Test
Tests if organisms can utilize citrate as a carbon source
— citrate as the sole carbon source
— bromothymol blue as a pH indicator
— green changes to blue
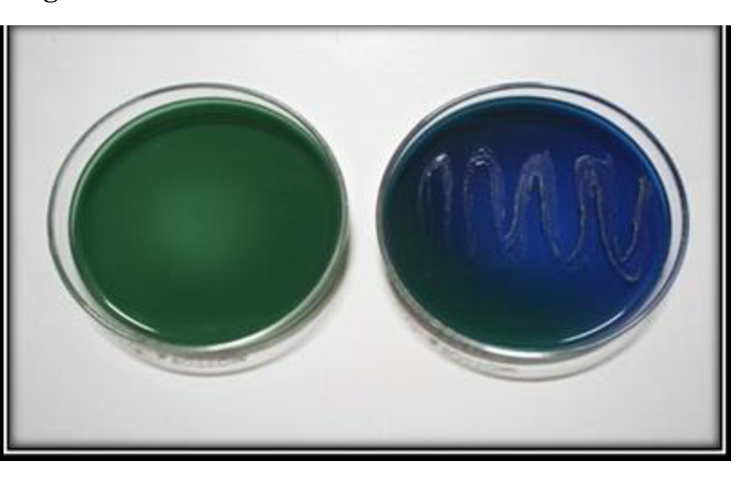
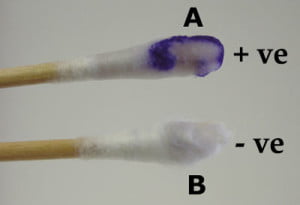
Oxidase Test
looks for the presence of cytochrome oxidase: protein used as part of the ETC
Oxidase Reagent = chromogenic reducing agent
— changes color to dark purple (positive - indicating cytochrome oxidase)