Cell Bio Unit 2 (1/23/2025)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cell structure consists of:
cell membrane
cytoplasm
cytoplasmic organelles
nucleus
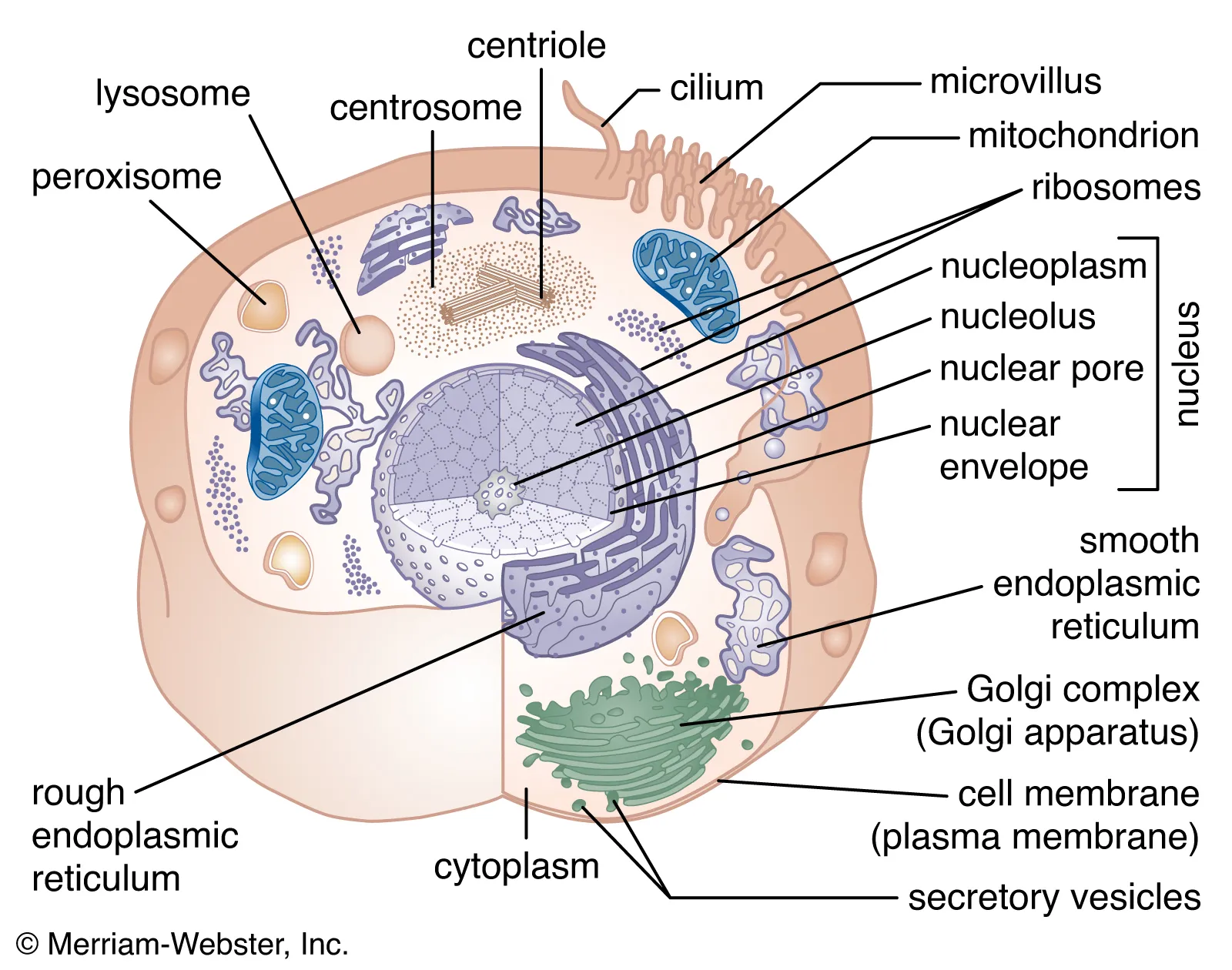
Explain the structure and function of the cell membrane
frail, semipermeable, flexible structure that encases and surrounds the cell
made of lipids and proteins
functions as a barrier to protect contents from the outside environment and controls passage of water and materials into and out of the cell
plays primary role in cell’s transport system
Explain the structure and function of the cytoplasm
the protoplasm that exists outside the cell’s nucleus
is everything but the nucleus
makes up the majority of the cell
primarily water, but contains proteins, carbs, lipids, salts, and minerals
all cellular metabolic functions occur in the cytoplasm
What are the 4 major functions of the cytoplasm?
accepts unrefined material and assembles them into new substances (i.e. proteins)
breaks down organic materials to produce energy
packaging substances for distribution to other areas of the cell or to various sites in the body through the circulation
eliminating waste products
What are cytoplasmic organelles?
tiny “organs”, tubules, vesicles, granules, and fibrils
perform various functions of the cell
How do DNA and mRNA affect the cytoplasmic organelles?
DNA determines the function of each organelle
mRNA carries the instructions into the cytoplasm
What are the 6 major organelles?
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi complex
mitochondria
lysosomes
ribosomes
centrosomes
Explain the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
highway system of the cell
food transfer
passageway for mRNA
network of tubules that spread in all directions throughout the cytoplasm
enables cell to communicate with extracellular environment
2 types:
rough surfaced
smooth surfaced
Explain the golgi complex/apparatus
hauls “freight” into and out of the cell
located near the nucleus and extends to the cell membrane
unites large carbohydrate molecules and combines them with proteins to form glycoproteins
(if a cell manufactures enzymes or hormones, the golgi complex concentrates, packages, and transports them through the cell membrane into the blood stream)
Explain the mitochondria
“power generating station” of the cell
large, bean-like structures
number varies greatly between cells
greatest number is found in cells exhibiting the greatest activity
produce energy for cellular activity by breaking down nutrients through oxidation
some enzymes contained in the mitochondria are essential in the production of ATP
What does ATP stand for?
adenosine triphosphate
Explain mitochondrial ATP
the prime energy containing molecule in the cell
essential for sustaining life
plays a major role in active transport within the cell
Explain lysosomes
“garbage bags with poison pills”
small, pea-like sacs containing digestive enzymes
digestive organs of the cells
help control intracellular contaminants
dispose of bacteria and food
etc.
failure results in accumulation of “stuff” that may be toxic
Why are lysosomes termed “suicide bags”?
the enzymes they contain can break down and digest the cell itself when lysosome’s membrane breaks
What can happen to lysosomes with exposure to radiation?
can rupture (this causes the cell to die)
Explain ribosomes
“manufacturing facilities of the cell”
small spherical organelles that attach to endoplasmic reticulum
consists of 2/3 RNA and 1/3 protein
job is to manufacture the various proteins that the cell requires
the site of protein synthesis
Explain centrosomes
“weavers of the spindle”
located in the center of the cell near the nucleus
contain centrioles
What are centrioles?
pairs of small, hollow, cylindrical structures that are believed to play a part in the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division
Explain the nucleus
“information processing and administrative center”
separated from other parts of the cell by a double walled membrane with pores, called the nuclear envelope
contains the DNA
contains rounded body called the nucleolus
What is the nucleolus?
the RNA copy center
What is cell division?
the multiplication process whereby one cell divides to form 2 or more cells
(AKA cell proliferation)
What are the 2 types of cell division?
mitosis (for all somatic cells)
meiosis (for all primary germ cells)
What are female germ cells called?
ovum, oocytes, ootid, or ova
What are male germ cells called?
spermatid or spermatozoa
What are the 2 reasons for somatic cell division?
repair of damage
growth of new tissue
What is mitosis?
the formation of 2 daughter cells identical to the parent (approximately equal distribution of all cellular material between the 2 daughter cells)
46 chromosomes each
What are the 4 distinct phases of the cell life cycle?
M - mitosis
G1 - gap in cell growth (pre mRNA synthesis)
S - DNA synthesis phase
G2 - post DNA synthesis
interphase is made up of the G1, S, and G2 phases
Which phase of the cell life cycle is most radiosensitive?
Which phase of the cell life cycle is most radioresistant?
most radiosensitive: mitosis
most radioresistant: synthesis
What is interphase?
the period of cell growth between divisions (the bulk of the cell’s lifetime)
What are the 4 phases of mitosis?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
Explain prophase as 1 of the 4 stages of mitosis
nucleus swells, DNA begins to take form
Explain metaphase as 1 of the 4 stages of mitosis
chromosomes appear and line up in the middle of the nucleus
Explain anaphase as 1 of the 4 stages of mitosis
chromosomes split
Explain telophase as 1 of the 4 stages of mitosis
split chromosomes disappear into its own DNA mass, nuclear membrane closes off
What is cell time?
“generation time”
the average time from one mitosis to another
most human cells have a generation time of 10-20 hours
some specialized cells have a cell time of several hundred hours
some cells, such as nerve cells, do not reproduce
What is meiosis?
special type of division that reduces the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell to ½ the number of chromosomes in the parent cell
What are the 2 separate steps in meiosis?
replication - cell proceeds through the same phase of mitosis like somatic cells
reduction - the 2 daughter cells from the first step undergo another division but WITHOUT THE S PHASE (there is no duplication of chromosomes)
What is the end result of meiosis?
4 cells with 23 chromosomes each (when combined with another germ cell, the result will be a cell with 46 chromosomes)