Exam 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Dressing Percentage
The percentage of the live animal's weight that becomes the carcass after slaughter. Average is different for different species
Humane Method of Slaughter Act of 1978
Legislation requiring humane treatment of food animals during slaughter, ensuring freedom from fear, stress, and pain.
Mandates a quick and effective death for these animals
act applies to all livestock except poultry
Stunning Methods
Mechanical, chemical, and electrical stunning techniques used in slaughter to render animals unconscious before slaughter.
Specific Risk Materials (SRM)
Tissues in cattle prone to prion contamination, such as tonsils and distal ileum, requiring removal to prevent disease spread.
By-products
Secondary products from slaughter, including edible (e.g., kidneys, heart) and inedible parts (e.g., hides), processed in rendering industry.
Curing
Process involving the use of ingredients like salt, sugar, and nitrate to preserve and flavor meat through dry, injection, or combination methods.
Sausage Manufacturing
Process of creating uniform meat products through emulsion of fat particles in water using salt-soluble heat coagulable proteins.
Meat Tenderness
Quality influenced by factors like species, breed, fat content, age, and water holding capacity, measured by Warner Bratzler shear force.
Why are values so different for dressing percentage?
Weight of hide
Head and skin left (hogs)
Weight/volume of intestinal content
Muscle mass of different species
Pre slaughter management
freedom from fear/stress and freedom from pain
12-24 hour fast
makes evisceration easier
food safety- less bacteria from GI tract to meat
free access to water
helps with blood and pelt/hide removal
Mechanical stunning
concussion or penetration of the head used in cattle or sheep to render unconcious
Chemical stunning
uses CO2, used for hogs and poutry, essentailly puts them to sleep
electrical stunning
varies in voltage, amperage and time parameters, used for hogs and poultry (sometimes does not work fully)
Pros/cons of stunning methods
stun to bleeding time varies with each method
some dont always work
slower per animal (electrical)
Injuries to workers can happen
What are the steps to the slaughter process after stunning?
exsanguination → scalding/skinning → evisceration → carcass manipulation → antimicrobial intervention → electrical stimulation
exsanguination
bleeding the animal/removing the blood
scalding/skinning
removing feathers/hair/hides from specific animals (poultry, hogs, cattle, sheep)
evisceration
removal of internal organs (GI, heart, lungs, liver, etc) (for by product use)
Carcass manipulation
removal of head, foreshanks, hind shanks, bruising etc.
what is SRM
Specific risk materials
Why remove SRM’s
to prevent prion contamination that may cause TSE or BSE. Getting to the problem areas before they cause problems.
What are SRM’s
tissues in cattle that are considered high risk for prion contamination (TSE and BSE) areas are mostly the tonsils and distal ileum
after 30 mo of age other SRM’s are removed
How do you determine if a cow is older than 30 mo?
one of the 2nd set of permenant incisors have erupted
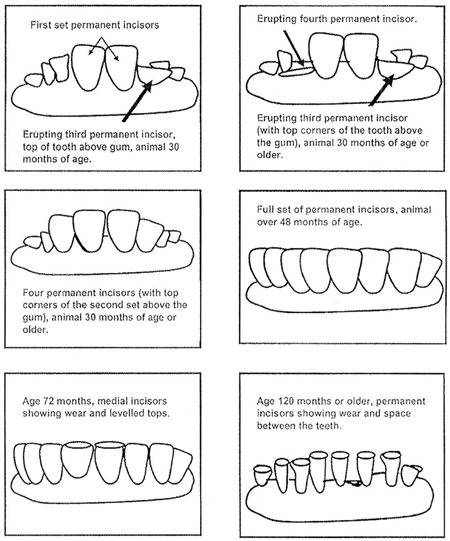
30 months and older tooth age determination
younger than 30 months
What are variety meats of a beef carcass?
kidneys, heart, liver, tongue, etc.
what is the most valuable byproduct of a cattle carcass?
the hide
what is further processing?
converts waste animal products/tissues into stable, value added materials
what are some primary byproducts
hides, fat, bones, internal organs
In what ways can you further process
rendering, drying, freezing, salting, smoking, curing
what is the curing reaction?
myoglobin + nitric oxide = nitric oxide myoglobin + heat = nitrosylhemochromagen
what does salt do for curing
gives product flavor, preserves, dehydrates meat
what does sugar do for curing
adds flavor, counteracts the salt, provides energy for bacterial conversion, lowers acidity
what does nitrate do for curing
adds flavor, prevents “warmed over” flavors, slows rancidity, slows growth of clostridium botulinum, contributes pink color
dry curing
rubbed into meats surface, good flavor/texture minimal equipment, no refrigeration of curing products, controlled bacteria, slow process, can go rancid, storage is costly, increased shrinkage, salty
injection curing
curing solution goes directly into meat (Stitch pumping, artery or machine), rapid penetration, reduces spoilage, adds alkaline phosphates, low salinity, flavor profile is diminished, texture is different
combination curing
both dry and injection methods (injection with dry cure or injection with low salt liquid and high salt pickle)
what is sausage?
any meat chopped, seasoned and formed into a uniform shape
what is emulsion?
a dispersion of fat particles in water held by the actions of salt soluble heat coagulable proteins (SSHCP)
what are the SSHCP protiens
actin, myosin, actomyosin
why are the SSHCP proteins salt soluble?
its released within muscle during emulsion by salt solution being added to mixture
why are the SSHCP’s heat coagulable
they have the ability to harden during the cooking cycle
What do the SSHCP’s do
during emulsion they coat the fat, by doing so they prevent fatting out
What is tenderness and how is it measured?
measured on a grading scale (beef and lamb) and is measured by palatability (tenderness, flavor, juiciness, collagen content etc.)
Warner Bratzler Sheer force
the pounds of force it takes to cut a ½ in core from cooked steaks and roasts
how many pounds of sheer force does it take for tough meat
12+ lbs (unacceptable)
how many pounds of sheer force does it take for marginal meat
8-12 lbs
how many pounds of sheer force does it take for tender meat
less than 8 lbs
what factors contribute to tenderness?
species, breed, fat, type of muscle (support/locomotive), age, water holding capacity,
how do you determine a carcass’s sex class
determining if the carcass has a pizzle eye (male) or a different semimembranosus
what are the 8 quality grades?
prime, choice, select, standard, commercial, utility, cutter, canner
What are the maturity groups and what are the chronological ages related to the maturity groups?
A, B, C, D, E (A being the youngest and E being the oldest)
What part of the carcass is marbling measured?
ribeye area
What degree of marbling classifies a carcass as prime, choice, or select?
Chronological age of cattle (A B C D E) Feedlot cattle (30 42 72 96) Younger cows Older cows Step-wise procedure for Quality Grading Beef Carcasses
What are the steps to quality grading?
1- determine sex class of carcass
2- determine carcass maturity
3- evaluate marbling
4- combine marbling and maturity to defermine USDA QG
How do you determine carcass maturity?
Degree of skeletal ossification in the thoracic, sacral and lumbar vertebrae
color and shape of ribs
What are the yeild grades of beef cattle
range from 1-5