12.5 (4.1.1) Non-specific animal defences against pathogens
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
immune system
a group of cells, tissues, organs and mechanisms that defend an organism against pathogens and other foreign substances
immune response
a complex series of specific and nonspecific processes involving a range of cells and chemicals
skin as a physical barrier
prevents entry of bacteria
produces sebum which inhibits pathogen growth (antiseptic)
skin flora as a physical barrier
large population of natural healthy bacteria that outcompete pathogens for surface space
mucous membranes as a physical barrier
traps pathogens
contains lysosomes that destroy pathogens
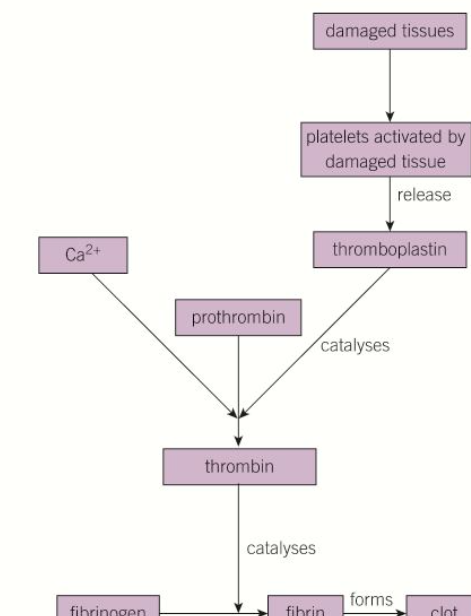
steps of blood clotting
1) platelets rush to site releasing thromboplastin and serotonin
2) thromboplastin catalyses the conversion of prothrombin into thrombin (in the presence of Ca2+ ions)
3) thrombin catalyses the conversion of fibrinogen to form fibrin
4) fibrin forms a clot
5) clot dries out, forming a tough scab that keeps pathogens out
thromboplastin
enzyme that triggers the conversion of prothrombin into thrombin (in the presence of Ca2+ ions) resulting in the formation of a blood clot
serotonin
makes smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessel contract so they narrow and reduce supply of blood to the damaged area to reduce blood loss and promotes platelet formation
blood clotting cascade diagram
inflammation
the swelling of skin
what doe mast cells release
histamines and cytokines
histamines
make blood vessels dilate causing localised heat and redness preventing pathogens reproducing
increase permeability of the blood vessel walls, causing more tissue fluid to escape causing swelling and pain
cytokines
attract white blood cells to the site, disposing of the pathogens by phagocytosis
how do fevers protect against pathogens
cytokines stimulate hypothalamus to increasing the body’s setpoint for temperature
body temp increases
higher temps inhibit pathogen reproduction
specific immune system works faster at a higher temp
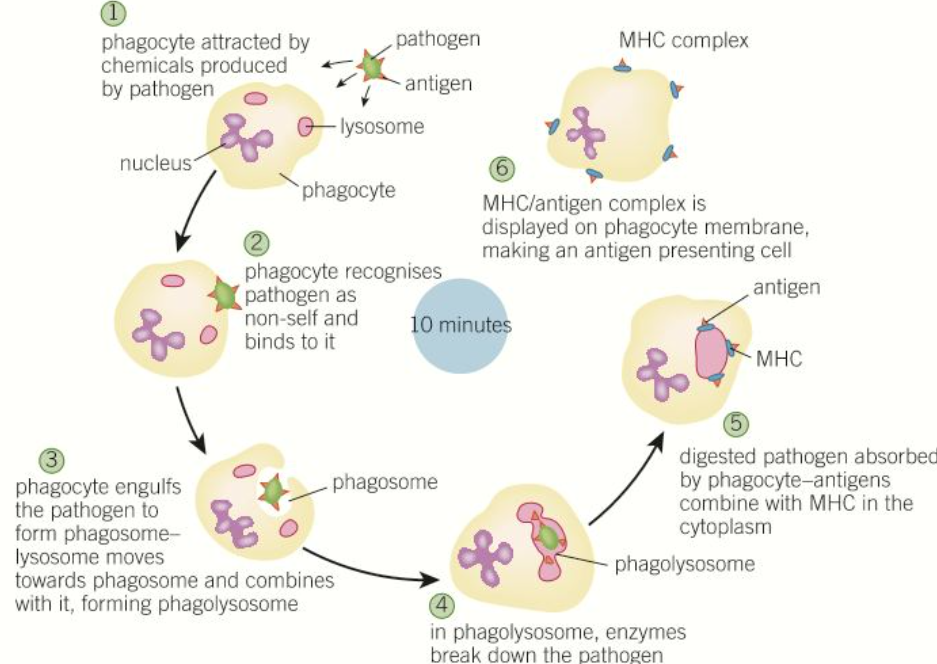
steps of phagocytosis
1) pathogens release chemicals that attract phagocytes
2) phagocytes recognise non-human proteins on pathogen
3) phagocyte engulfs pathogen and encloses it a vacuole called a phagosome
4) phagosome combines with a lysosome to form a phagolysosome
5) enzymes from the lysosome digest and destroy the pathogen
6) antigens from the digested pathogen combine with MHC in the cytoplasm
7) MHC/antigen complex is displayed on phagocyte plasma membrane, making an antigen-presenting cell
diagram of steps of phagocytosis
major histocompatibility complex MHC
special glycoproteins in the cytoplasm which combine with antigens from the pathogen during phagocytosis
moves the pathogen antigens to the macrophages own CSM becoming an antigen-presenting cell
macrophage
specialised phagocytes
take longer to break pathogens down than normal phagocytosis
form MHC
how to make a blood smear
spread a drop of blood very thinly across a slide
opsonins
chemicals that bind to pathogens and ‘tag’ them so they can be more easily recognised by pathogens