Space
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What are the spectral classes in order? What is the mnemonic to remember them?
O be a fat guy kill me
O B A F G K M
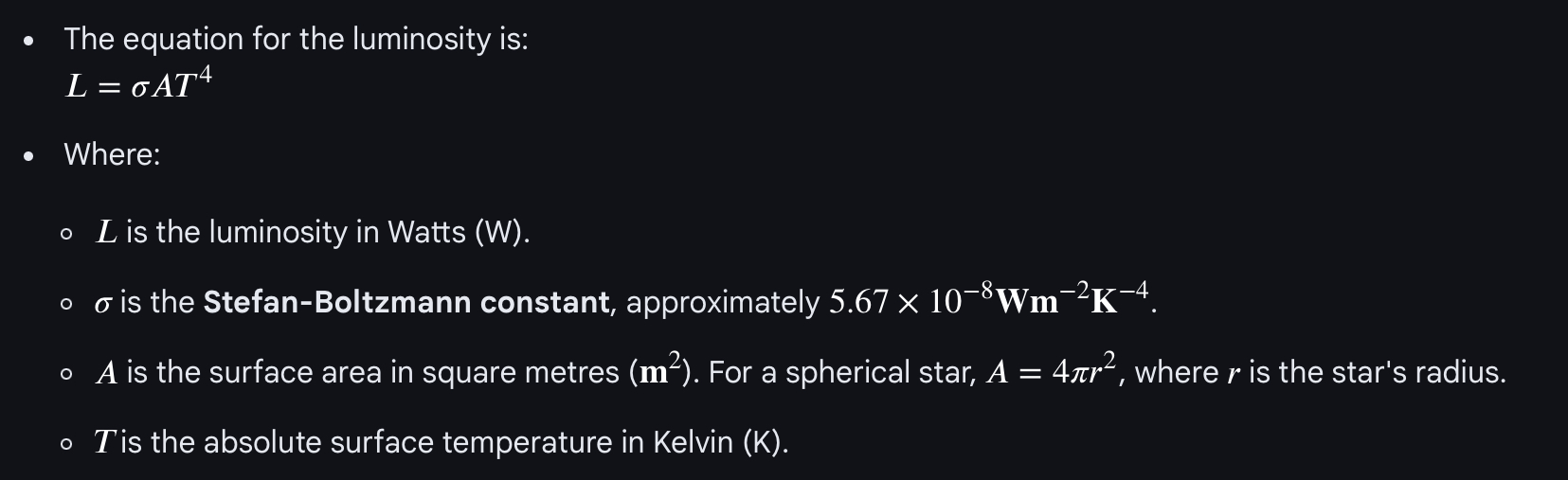
What can Stefan’s law equation be used to find?
The luminosity/power given off by a star
The heat loss/gain in insulating or cooling systems
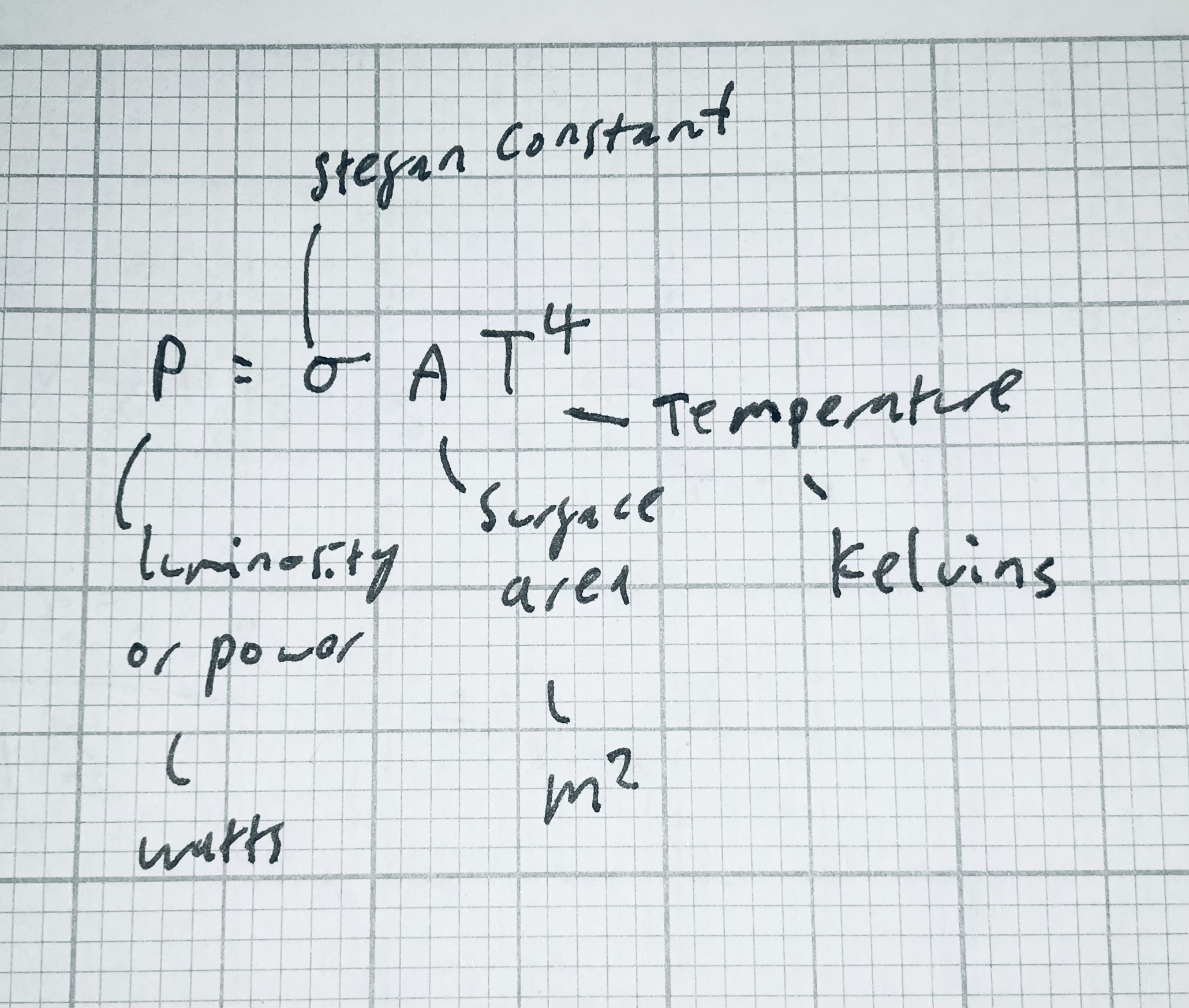
What do all the symbols represent in Stefan’s law? And their units
P=\sigma AT^4
What is the equation to find the surface area of a sphere/star?
4\pi r²
When using Stefan’s law to calculate the luminosity of a star what assumptions are you making? (4 marks)
The surface temperature is the same across the whole area of the star
The intensity is the same across the whole area of the star
The star is a perfect black body
The star is perfectly spherical
Suggest why can the spectrum of a star is useful?
The wavelengths of EM waves they release
Their velocity
Their Elemental composition
Their age
Their Surface area
Their Volume
Their Luminosity
What light is emitted when the temperature of a star is above the absolute temperature of -237K
Infrared light
State Wiens law
the peak wavelength of a star is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature.
The surface temperature of the sun is 5500K. Calculate its peak wavelength in nanometers
527nm
Define absorption (with the idea of atoms)
When atoms absorb photons to give them the energy to move to higher energy levels.
Define excitation
When an electron gains enough energy to move to higher energy levels and can leave if the energy is above the work function
Define ionization
When electrons are added or removed from atoms to produce ions
Explain the presence of black lines in a star spectrum
some photons from the light source is absorbed by electrons in a gas cloud before they’re not detected, so black lines appear
What elements would be expected to be found in the hottest stars?
Explain why
Iron cores
Heavier elements
Because elements have time to collide, So there is higher rate of fusion. More nuclei are fused together to form heavier elements
What would we expect to see in the absorption spectra of Hotter stars?
More black absorption lines
What elements would be expected to be found in cooler stars?
Lighter elements
What are nebula?
Collapsing clouds of gas and dust
Define what a nebula is
It is a collapsing cloud of gas and dust
Describe the life cycle of a low mass star
Nebula are giant clouds of gas and dust, which overtime collapse due to the attractive forces of gravity, this causes the dust particles to heat up from friction. Creating light.
Becoming a proto star, when temperature and pressure is high enough, nuclear fusion occurs in its core, causing lighter elements to form heavier elements,while release energy
Overtime it will grow in size and become a main sequence star
Gravity and radiation pressure is equal
When hydrogen runs out, nuclear fusion cannot occur and the forces of gravity become greater. And decreases in size
This allows the temperature to increase in the core, now helium can fuse together.
Star expands and becomes a red giant
Describe the lifecycle of a high mass star
Nebula are giant clouds of gas and dust, which overtime collapse due to the attractive forces of gravity, this causes the dust particles to heat up from friction. Creating light.
Becoming a proto star, when temperature and pressure is high enough, nuclear fusion occurs in its core, causing lighter elements to form heavier elements,while release energy
Overtime it will grow in size and become a main sequence star
Gravity and radiation pressure is equal
When hydrogen runs out, nuclear fusion cannot occur and the forces of gravity become greater. And decreases in size
This allows the temperature to increase in the core, now helium can fuse together.
Star expands and becomes a red super giant
What is the most stable type of star?
Main sequence star
Why is it that iron is only present in the star’s core?
iron is the most stable element, so fusion no longer happens
What happens after a red super giant?
The temperature decreases and fusion stops so the star collapses rapidly, and all the matter rebounds off the iron core.
Core becomes very dense and electrons become neutrons.
If it was a large mass star, it would become a black hole
If it was a lesser mass star it would become a neutron star
Define a black hole
When all the stars mass condenses to a singularity
What causes the radiation pressure in stars?
Nuclear Fusion
Explain why the binding energy per nucleon for fission has a steeper gradient, then for fission
Cause more energy is produced from fusion than fission
Define a light year
The distance light travels in one year
What is the distance for one light year in meters?
365×24×60×60= 31536000
\left(3\times10^8\right)\times31536000=9.46\times10^{15}
What is the standard unit for the measurement of distance in space?
Astronomical unit (Au or au)
What Does one astronomical unit represent?
The main radius of the Earth orbit around the sun, which is 1.5\times10^{11}m
How many Au is voyager which is 2.6\times10^{13}m away from earth?
\frac{2.6\times10^{13}}{1.5\times10^{11}}=173 Au
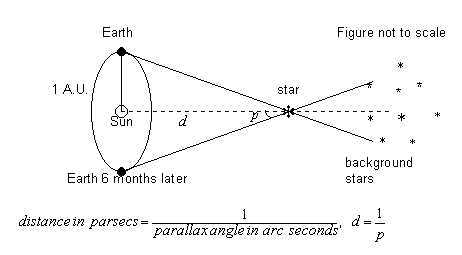
What is the unit for a parallax angle?
Arc seconds
What is one arc second worth?
\frac{1\degree}{3600}
If the parallax angle is 1 arc second the d is…
1 parsec
The parallax angle does Alpha Centuri found the angle measures after six months was 1.5 to Arc seconds1.52 different from that measured at first how far is Alpha Centuri from earth in parsec?
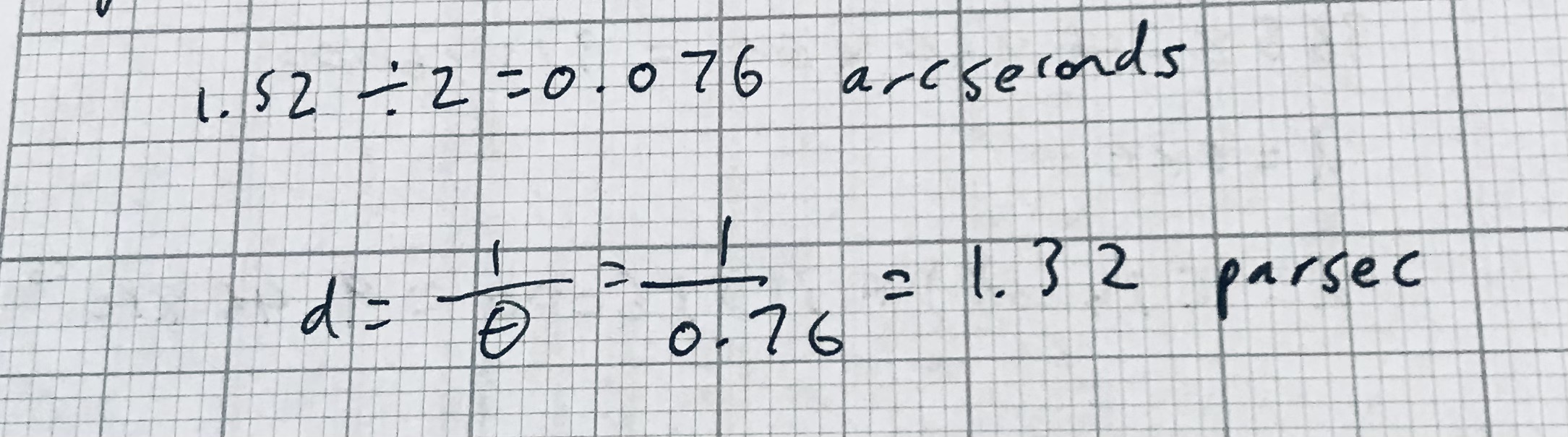
Describe the controls used in the method to test the inverse square law for intensity
Keep the 2 objects at the same height to the oil drop
Keep the surrounding dark
Measure from the centers of the object when measuring the distance
What is the formula used in the method for testing the inverse square law for intensity of an object
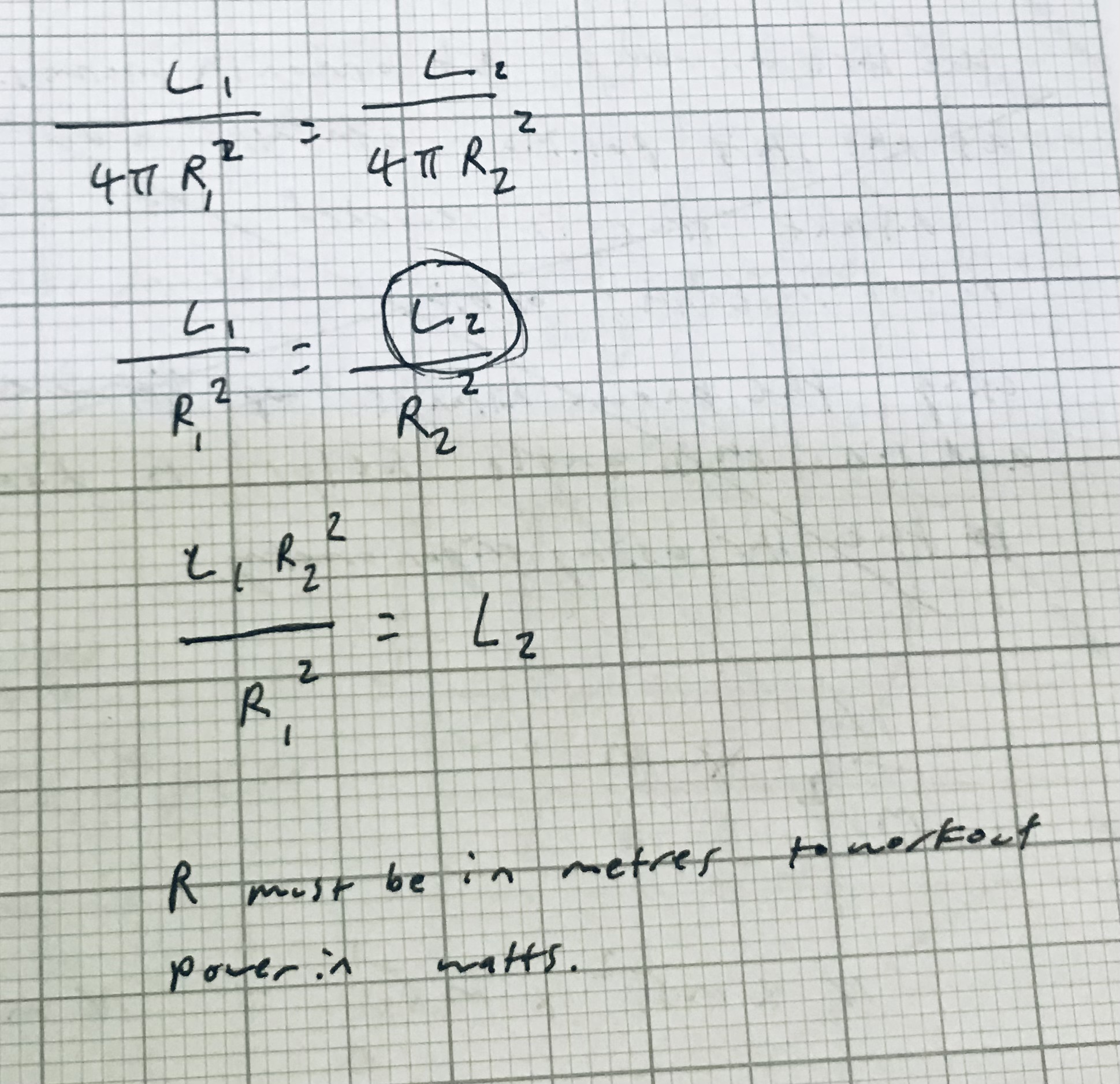
If the distance are doubled, What would happen to the brightness of the image?
It would quartered
Explain how we can use the parallax method to determine the distance between the probes and the angles to the vertical to find the distance of a star to the Earth, using trigonometry
observe the start over six months period
Measure the angle of the star against the background of stars
Use trigonometry to find the distance between a star and the sun
Define standard candles
They are a class of stellar objects which have a known luminosity,
and whose distance can be determined by measuring the radiant flux density
What is one example of standard candles?
Cepheid variables
What are Cepheid variables?
Stars that vary that luminosity from a maximum to a minimum in a regular time. Because they’re radius varies, which causes it’s temperature to also vary
What is the formula to work out the luminosity of a Cepheid variable star? And what are the units for each symbol?
Red shift