EXTENDED EXAM PSAD
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
CAB
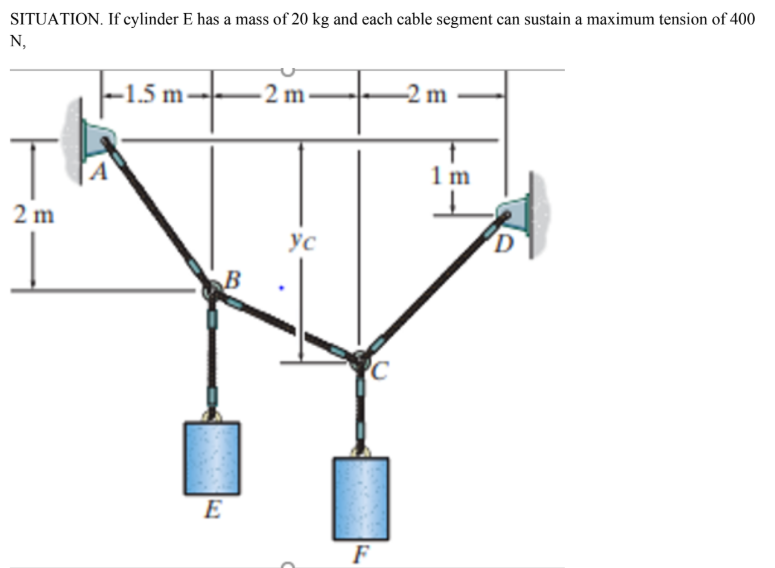
Determine the largest mass of cylinder F that can be supported.
A. 367.60
B. 376.60
C. 37.47
D. 73.74
Determine the tension on cable CD.
A. 342
B. 366
C. 355
D. 426
What is the sag Yc(ft)?
A. 3.03
B. 9.94
C. 4.03
D. 8.49
BCA
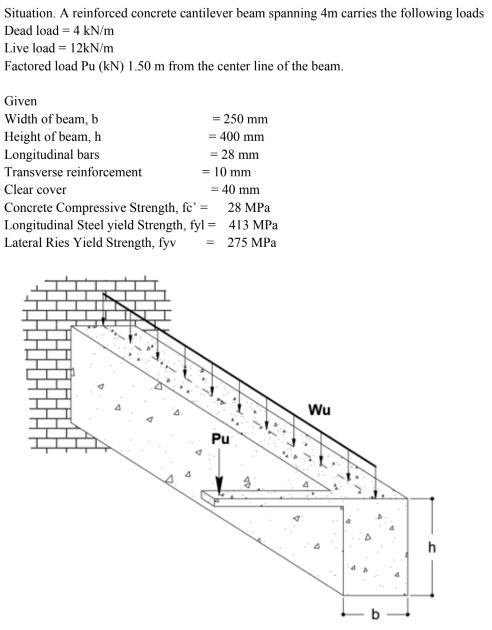
Determine the shear strength provided (kN) by the concrete.
73
76
94
64
If Pu = 10 kN, determine the spacing due to shear alone.
168
600
263
210
Determine the maximum value of Pu so that the effect of torsion can be neglected.
1.70
0.80
1.50
1.20
BDA
Situation. An 18 m long precast pile is to be lifted at two points from the casting bed. The weight of the pile is 4.86 kN/m.
At what equal distance (m) from the middle should the pile be lifted so that the maximum bending moment is theleast possible?
A. 2.95
B. 5.27
C. 2.25
D. 3.73
At what equal distance (m) from the ends should the pile be lifted so that the resulting shear stress is the smallest
A. 5.6
B. 3.4
C. 2.25
D. 3.73
As the pile is being moved, its left end is laid on the ground while being lifted through a hook attached 3 m. from the right end. What is the maximum positive moment (kN.m) due to its weight?
A. 126
B. 116
C. 108
D. 122
CBA
SITUATION. A cantilever beam 3.5 long, carries a concentrated load, P, at mid length. Given the following:
P = 200 kN E = 200 GPa I = 60.8 x 106 mm4
How much is the beam deflection (mm) at mid length?
A. 1.84
B. 23.50
C. 29.40
D. 14.70
What force (kN) should be applied at the free end to prevent deflection?
A. 7.8
B. 62.5
C. 41.7
D. 100
To limit the deflection at mid-length to 9.5 mm, how much force (kN) should be applied at the free end?
A. 54.1
B. 129
C. 76.6
D. 64.7
ABD
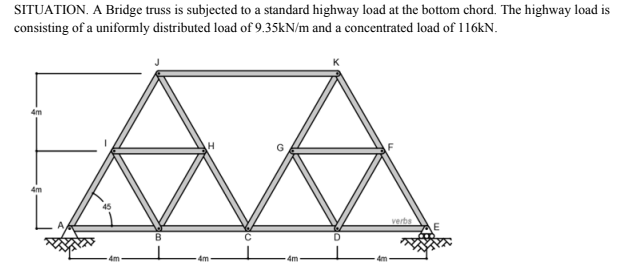
For the computation of design force, apply the moving concentrated load at the truss joint only. Find the maximum vertical reaction at A.
A. 190.8
B. 140.25
C. 160.5
D. 130.6
What is the maximum ordinate of the influence line for the force developed in member JK?
A. -1.0
B. -0.50
C. 1
D. 0.5
What is the maximum force developed in member JK.
A. 88
B. 140
C. 160
D. 94
ACA
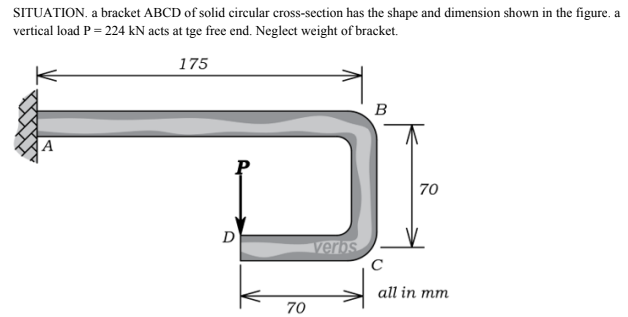
Determine the diameter (mm) of the bracket based on the allowable bending stress of 30 MPa.
A. 20
B. 30
C. 25
D. 35
Compute the max. shear stress for this diamter as required by bending.
A. 0.9
B. 0.85
C. 0.80
D. 0.95
If the diamter d = 15 mm, at what distance x from C should the force P = 224 N be applied so that it will not exceed the allowable bending stress of 30 MPa.
A. 130.62
B. 120.24
C. 138.24
D. 125.29
CDA
Find the maximum compressive stress (kPa) at the base of the wall if the water reaches the top of the wall.
A. 1426
B. 1638
C. 1128
D. 1536
If the maximum compressive stress at the base of the wall is not exceed 380 kPa, what is the allowable depth (m)
of the water?
A. 1.20
B. 1.50
C. 1.00
D. 2.00
If the allowable tensile stress at the base if the wall is zero, what is the maximum height of the water which the wall can retain?
A. 1.20
B. 1.50
C. 1.00
D. 2.00
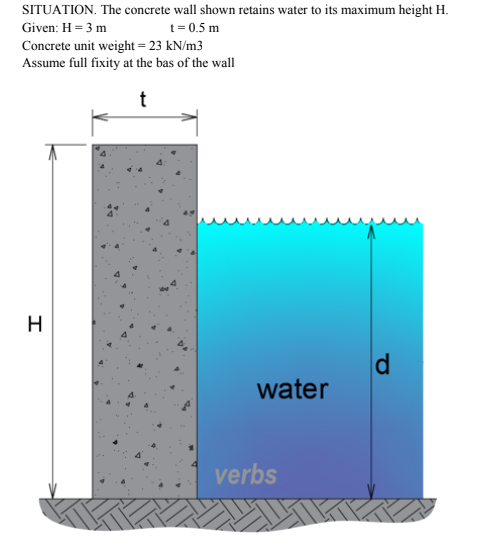
DDD
Situation – Roof trusses 6 m apart support purlins spaced at 1 m on centers. The purlins are simply
supported.
Given:
Roof slope = 15 degrees
Gravity loads acting at the top flange of the purlins (Total) = 900 Pa
Wind loads:
288 Pa pressure at the windward side
864 Pa suction at the leeway side
Properties of the Purlins
Section : 200 mm x 7 mm
Sx :6.19 x 104 mm3
Sy :1.60 x 104 mm3
Weight :79 N/m
Load Combination = D + W
Which of the following gives the bending stress about the x-axis, fbx (Mpa)?
A. 93
B. 96
C. 99
D. 90
Which of the following gives the bending stress about the y-axis, fby (Mpa)?
A. 92
B. 144
C. 167
D. 136
What should be the maximum purlin spacing (m) to prevent overstressing? Fbx = Fby = 207MPa
A. 0.50
B. 0.75
C. 0.30
D. 0.90
BBC
Based on bolt capacity in shear.
A. 75
B. 82
C. 41
D. 150
Based on bolt bearing capacity.
A. 184
B. 123
C. 61
D. 207
Based on block shear strength of the double angle.
A. 173
B. 74
C. 272
D. 136
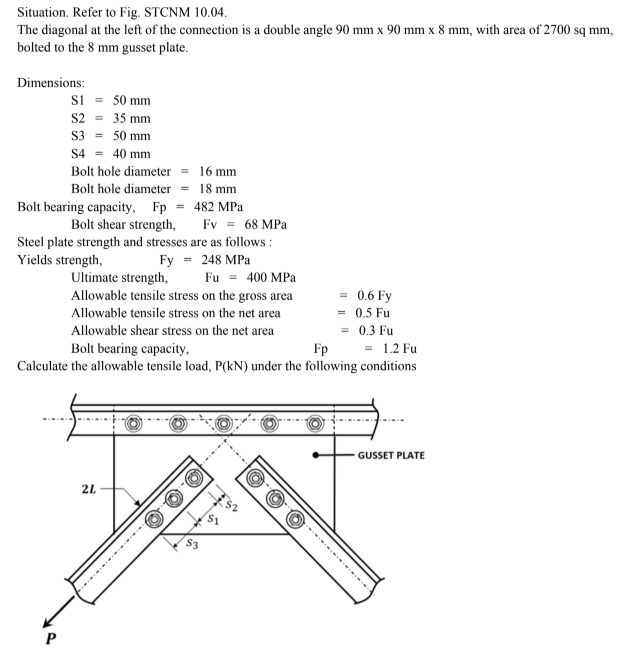
DBA
SITUATION. A 12 mm thick steel tire has a width of 110 mm and has an internal diameter of 800 mm. The tire is heated and shrunk to a steel wheel 800.5 mm diameter. Take the modulus of Elasticity, E = 200 GPa.
Determine the compressive pressure (MPa) between the tire and the wheel.
A. 7.50
B. 5.25
C. 10.50
D. 3.75
Determine the tensile stress (MPa) in the tire.
A. 175
B. 125
C. 250
D. 350
Determine the thickness (mm) of the tire to resist pressure of 1.5 MPa if it has an allowable stress of 124 MPa.
A. 4.84
B. 8.44
C. 2.12
D. 6.32
BCA
SITUATION. A parabolic cable carries a horizontally distributed load of 20 kN/m. The horizontal span between the supports A and C is 60 m. The lowest point B has a vertical distance of 6 m below the support at A and 12 m below the support at C.
Determine the horizontal distance (m) between the lowest point and the support at A.
A. 21.67
B. 24.85
C. 25.35
D. 26.45
Determine the tension (kN) at cable A?
A. 1029
B. 703
C. 1143
D. 1247
Determine the tension (kN) at cable C.
A. 1247
B. 1143
C. 1029
D. 703
BDB
What is the critical effective slenderness ratio of the column?
A. 38
B. 83
C. 54
D. 58
Calculate the critical load Pc in kN?
A. 11210
B. 4733
C. 5493
D. 2319
Determine the minimum length of the column for which the Euler’s formula is valid if the proportional limit of the steel used is 320 MPa.
A. 11.70
B. 7.60
C. 3.80
D. 10.80

DBB
Calculate the maximum bending stress (MPa) in the beam due to dead load.
A. 123
B. 92
C. 107
D. 98
Determine the maximum moment due to live load plus impact.
A. 524.47
B. 651.35
C. 681.81
D. NOTA
Calculate the maximum bending stress (MPa) in the beam due to live load plus impact.
A. 79
B. 68
C. 62
D. 56

DCC
Determine the tensile force (kN) in the cable if W = 36 kN.
A. 66
B. 80
C. 40
D. 33
Determine the vertical reaction (kN) at B if W = 36kN.
A. 56
B. 48
C. 64
D. 39
If the allowable tensile force in the cable AC is 45kN, what is the maximum load W (kN) that can be lifted.
A. 56
B. 48
C. 50
D. 39
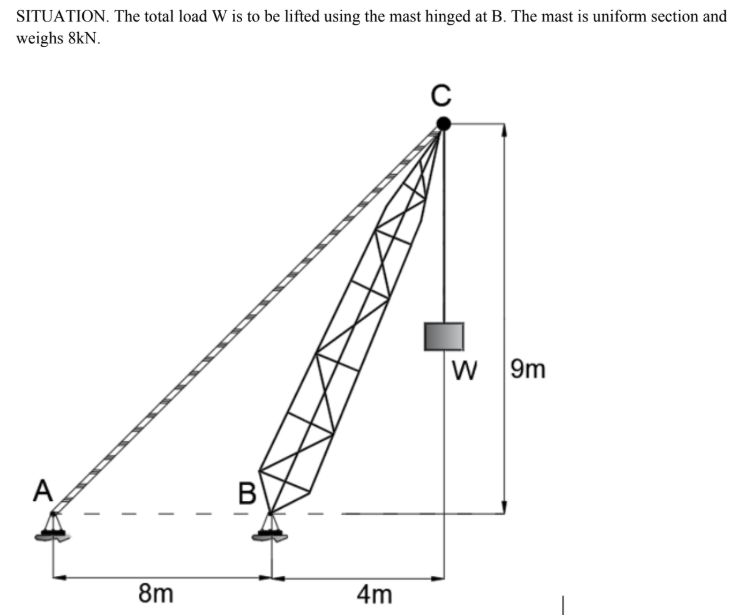
CBC
SITUATION. The rigid bar AB has a hinged at A and supported by steel plate hanger, designated at D. The
hanger is fixed at D with two plates.
L1 = 2.0m
L2 = 1.2m
H = 3.0m
Thickness of plate hanger = 10mm
Width of plate hanger = 40mm
Bolt diameter = 20mm
Allowable bolt bearing stress = 240 MPa
Allowable bolt shear stress = 68 MPa
What is the allowable stress (MPa) in the hanger based on bolt capacity in double shear at D.
A. 53.4
B. 86.6
C. 106.8
D. 43.3
If the maximum tensile stress in the hanger is 138 MPa, find the allowable load W (kN).
A. 55.2
B. 34.5
C. 69.0
D. 138.5
If the load W = 60kN, what is the vertical displacement (mm) at B?
A. 3.6
B. 9.22
C. 5.76
D. 6.0
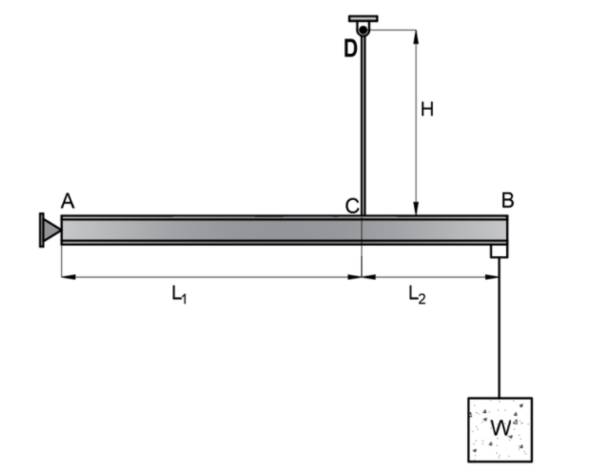
CAD
SITUATION.
Given:
b= 350 mm h1= 100 mm h2= 500 mm
Tension steel, As = 6 of 28 mm diameter bars
Compression steel, As’ = 4 of 28 mm diameter bars
Lateral ties = 12 mm
Clear concrete cover = 40 mm
Concrete: fc’ = 28MPa
Steel: fyt = 415MPa (main bars)
fyv = 275MPa (ties)
Allowable concrete shear stress at factored load, 0.88 MPa
Which of the following gives the minimum spacing, a (mm)?
A. 56
B. 28
C. 53
D. 38
Which of the following gives the nominal shear strength (kN) provided by the concrete?
A. 159
B. 285
C. 158.7
D. 362
Which of the following gives the nominal shear strength (kN) of the section if the lateral ties are spaced at 125 mm on center?
A. 257
B. 415.7
C. 256.5
D. 416

BCC
SITUATION. A 12m simply supported beam is provided by an additional support at midspan. The beam has a width of b = 300mm and a total depth h = 450mm. It is reinforced with 4-25mmφ at the tension side and 2-25mmφ at the compression side with 70mm cover to centroid of reinforcements. fc’ = 30 MPa, fy = 415 MPa.
Determine the depth of compression block (mm).
A. 142.24
B. 106.52
C. 159.77
D. 53.26
Determine the nominal bending moment. (kN-m)
A. 336.1
B. 244.92
C. 266.2
D. 119.5
Determine the total factored uniform load (kN/m) including the beam’s weight.
A. 84.025
B. 65.07
C. 53.24
D. 71.84
A
The material has the same composition at every point but the elastic properties may not be the same in all directions.
A. Isotropic
B. Orthotropic
C. Prismatic
D. Homogeneous
A
The composite material exhibits elastic properties in one direction different from that in the perpendicular
direction.
A. Orthotropic
B. Isotropic
C. Homogeneous
D. Prismatic
C
The material with the same elastic properties at all points.
A. Prismatic
B. Isotropic
C. Homogeneous
D. Orthotropic
CAD
SITUATION. A combined footing as shown carries ultimate column loads:
Pu1 = 928 kN
Pu2 = 1484 kN
Dimension = 6m x 4m
Distance between columns = 3.9m
Effective depth of footing = 500mm
Reduction factor for shear, Ø = 0.75
Reduction factor for moment, Ø = 0.90
fc’= 27.7 MPa
fy = 413 MPa
Determine the maximum punching shear stress (MPa).
A. 1.96
B. 0.77
C. 0.98
D. 1.74
Determine the wide beam shear stress (MPa).
A. 0.39
B. 1.73
C. 0.41
D. 0.87
Determine the number of 20mm Ø bars parallel to the longer side at the right overhang.
A. 12
B. 10
C. 20
D. 22
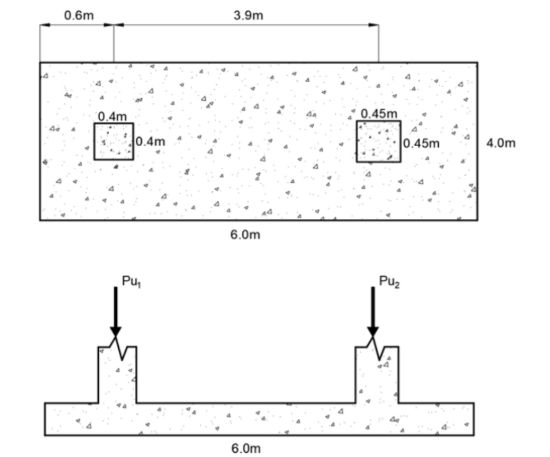
BAD
SITUATION. The weight of the cylindrical tank is negligible in comparison with the weight of water it contains (water weighs 9.81kN/m3). The coefficient of friction between the tank and the horizontal surface is u (sub) s.
Assuming a full tank, find the smallest force P (kN)required to tip the tank.
A. 11.81
B. 14.35
C. 5.91
D. 7.18
Find the smallest coefficient of static friction u (sub) s
A. 0.17
B. 0.13
C. 0.23
D. 0.31
If force P = 6.5 kN initiates tipping determine the depth (m) of water in the tank.
A. 1.67
B. 0.85
C. 1.32
D. 1.45
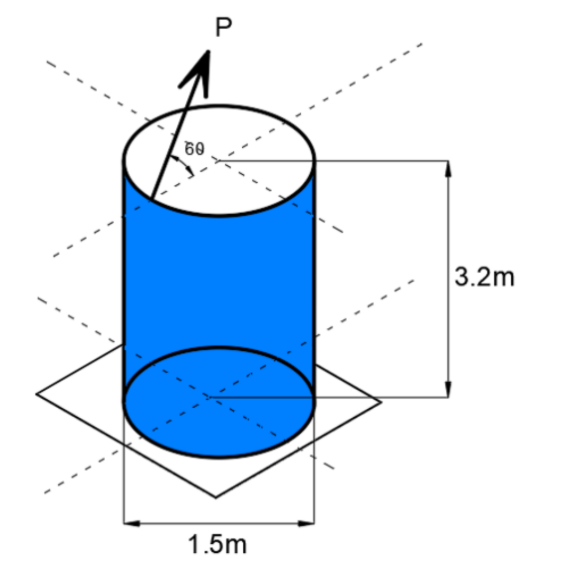
BDB
SITUATION. A spiral column 600 mm in diameter has an unsupported height of 3m. The column is bent in single curvature and is braced against sidesway.
Given:
Concrete compressive strength, fc’=20.7 MPa
Steel yield strength, fy=413 MPa
Effective length factor, K=1.0
If the required steel ratio is 2%, find the number of 28 mm diameter bars.
A. 8
B. 10
C. 12
D. 14
If Pu=6400 kN, determine the number of 32 mm bars.
A. 24
B. 20
C. 22
D. 16
What is the slenderness ratio of the column?
A. 40
B. 20
C. 22
D. 46
BAB
Determine the reaction at G.
A. 17.9
B. 11.2
C. 12.45
D. 4.15
Determine the stress (kN) in member AB.
A. 3.1(tension)
B. 3.1(compression)
C. 3.6(tension)
D. 3.6(compression)
Determine the stress (kN) in member BE.
A. 3.25(tension)
B. 0
C. 3.75 (tension)
D. 4.15(tension)
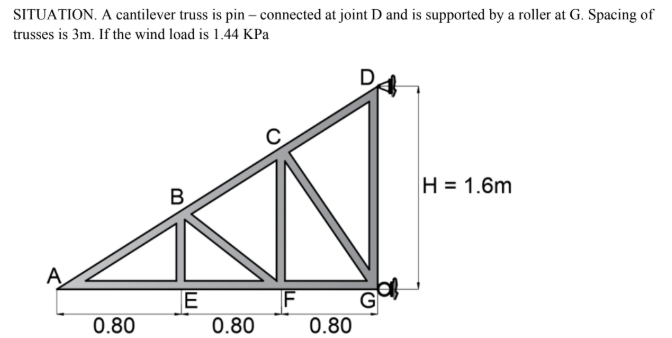
CAD
SITUATION. A rectangular section 300 x 650 is simply supported on a span of 12m. It carries a dead load equal to self-weight and a live load of 6kN/m. An initial prestress force P = 1500kN is applied at an eccentricity of 100mm. Using 24kN/m3 as unit weight of concrete. Assume 20% loss at service loads.
Determine the stress at the bottom fiber at midspan due to final prestressing force alone.
A. -0.59
B. -0.47
C. -11.83
D. -14.79
Determine the stress at the top fiber at midspan due to self-weight and initial prestress force.
A. -4.58
B. -4.46
C. -10.81
D. -7.85
Determine the stress at the bottom fiber at midspan due to service loads and final prestress force.
A. -5.70
B. -9.57
C. -9.69
D. -2.73
BCB
SITUATION. The bolt shown in the figure is subjected to a total tensile force of 100 kN.
Determine the tensile stress in the body of the bolt in MPa.
A. 141.47
B. 93.06
C. 132.49
D. 79.36
Determine the tensile stress at the root of the bolt in MPa.
A. 141.47
B. 93.06
C. 132.49
D. 79.36
Determine the compressive stress at the head as the bolt bears on the surface to resist the tensile load.
A. 32.08
B. 48.96
C. 57.07
D. 35.37

ABA
SITUATION. A solid steel post that is free from one end and fixed from the other end is subjected to pure torsion
Given: Post diameter = 80 mm
Length = 3 m
Shear Modulus = 70 GPa
What is the torsional rigidity of the post (kN-m2)
A. 281.49 kN-m2
B. 235.15 kN-m2
C. 266.91 kN-m2
D. 224.67 kN-m2
Determine the torsional stiffness of the post.
A. 99.6 kN-m
B. 93.83 kN-m
C. 69.9 kN-m
D. 96.9 kN-m
Determine the maximum shear stress (MPa) in the post if it is subjected to a torque of 540 N.m.
A. 5.37 MPa
B. 6.15 MPa
C. 6.25 MPa
D. 5.61 MPa