Cell Bio FINAL - Various Assignment/Quiz Questions
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What would be useful criteria in determining whether or not unknown potential life-forms could be cells?
researchers should look for something that both alien and terrestrial cells would have in common— for example, the presence of catalytic molecules (possibly enzymes) arranged in an organized structure
a crucial feature required of all cells is the ability to catalyze chemical reactions in an organized fashion, allowing the use of chemical energy to perform cellular functions, especially replication
scientists would be less likely to look for the chemical composition of the molecules or presence of a nucleic acid genome (DNA, RNA, etc.), because they could be made out of something completely different on an alien world
What is cell theory?
that all cells are formed by the growth and division of existing cells— therefore, living things do not spontaneously arise, but must come from other living organisms
all organisms consist of one or more cells
cells are the basic fundamental units of all organisms
Which cellular features, unique to eukaryotes, might be focused on when studying the evolution of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
the mitochondria and the nucleus
Antibiotics tend to target features unique to bacterial cells and absent from eukaryotic cells. What is something that could be used as a target?
the cell wall — bacteria have cell walls made of a chemical polymer called peptidoglycan
human cells do NOT have cell walls at all, nor can they produce peptidoglycan
therefore, a great candidate would be an antibiotic that targets peptidoglycan cell walls, like penicillin does — selective toxicity
True or False: Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similar DNA
FALSE - the endosymbiotic origin theory suggests that these organelles arose from separate instances of the developing/evolving primitive eukaryotic cell engulfing a smaller bacteria cell
What property of a new, unknown organelle would support the endosymbiotic event hypothesis?
evidence of endosymbiosis would include properties that would be found in a formerly free-living prokaryote
multiple independent membranes; presence of independent DNA outside the nucleus
Which type of covalent bond allows for rotation about the bond axis?
single covalent bond — generally allows the rotation of one part of a molecule relative to the other around the bond axis
What is the melting point of an ionic solid?
the temperature at which the crystal separates into its constituent ions
What happens when an ionic solid is added to water?
highly polar liquids, such as water, are able to interact with the charged ions, shielding the charges from each other
this allows water to dissolve many ionic solids at temperatures much lower than their melting points
What can improve the water solubility of a compound?
adding a hydroxyl (-OH) and/or a carboxyl (-COOH) group— these functional groups contain polar oxygens that can form hydrogen bonds with water
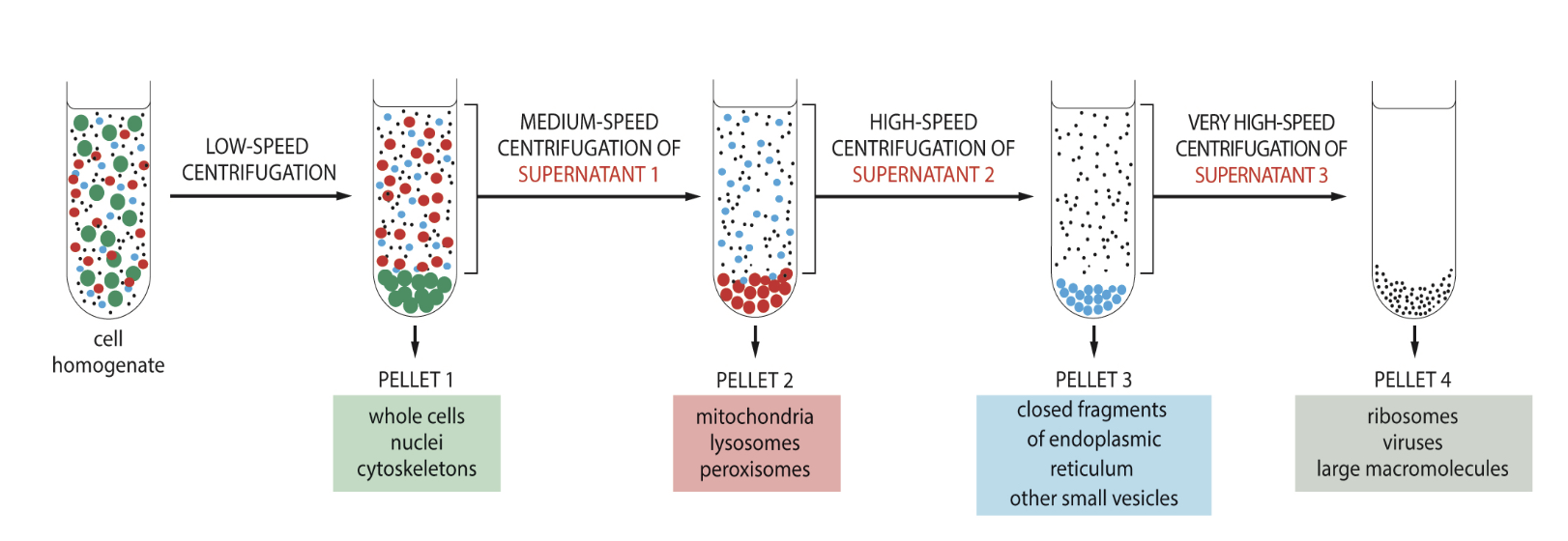
What is an ultracentrifuge used for?
separating different cellular organelles from each other
in differential centrifugation, larger organelles will form a pellet before smaller, lighter organelles do
What types of bonds link together the components of a ribosome?
both those those that involve the sharing of electrons between atoms (covalent bonds) and those that involve electrostatic interactions between atoms (noncovalent bonds)
What would be expected to happen if a protein folded in a hydrophobic environment?
the hydrophilic side chains would concentrate on the interior of the protein, and the hydrophobic side chains would be exposed to the surface
Why does an animal cell release heat?
the heat comes from the chemical bond energy present in the food molecules it metabolizes
What type of metabolic pathway is glycolysis?
it is a catabolic pathway— involves the generation of pyruvate (three-carbon sugar) from the breakdown of glucose (six-carbon sugar)
this results in the formation of the activated carrier ATP to be used by the cell to drive anabolic reactions
What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH?
NADH carries an extra proton and two high-energy electrons
NADH is reduced and NAD+ is oxidized
both NADH (electron donor) and NAD+ (electron acceptor) are involved in the oxidation of food molecules
What happens when NADH or NADPH transfers electrons to a recipient molecule?
the recipient molecule becomes reduced and the activated carriers are oxidized to NAD+ or NADP+, respectively— (redox reaction)
True or False: Feedback inhibition is difficult to reverse.
FALSE— it is very easy to reverse; feedback inhibition can work almost instantaneously and is rapidly reversed when product levels fall
If you wanted to purify the insulin receptor from a mixture of proteins, what methods could you use?
affinity chromatography is based on highly specific protein-protein interactions, such as the ligand-receptor and protein-antibody interactions.
You could (a)- use affinity chromatography with beads coated with anti-insulin receptor antibodies or (b)- use affinity chromatography with beads coated with insulin.
How do most motor proteins ensure their movements are unidirectional?
to achieve such directionality, one of the steps must be made irreversible —> therefore, they couple a conformational change to the hydrolysis of an ATP molecule
a great deal of free energy is released when ATP is hydrolyzed, making it very unlikely that the protein will move backward to undergo a reverse shape change
In cells that cannot carry out fermentation, which products derived from glycolysis will accumulate under anaerobic conditions?
Pyruvate and NADH — without oxygen, NADH would be unable to donate its electrons to the electron transport chain and the pyruvate produced by glycolysis would not be removed by fermentation
Researchers have studied factors that influence ethanol production in a specific yeast that uses metabolic reactions. To maximize ethanol yield, which environmental factor should be limiting?
Oxygen:
in the absence of oxygen, yeast cannot perform aerobic respiration and instead will switch to fermentation
fermentation products in yeast include CO2 and ethanol
What are the main processes of glycolysis?
First, energy must be invested into the glucose molecule by using up some ATP.
The six-carbon sugar is split into two smaller molecules.
Energy is harvested from each as ATP and NADH.
Finally, two molecules of pyruvate are also generated.
If someone was on a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet, will they accumulate lipids?
yes, they will accumulate fats— cells can convert glycolytic metabolites into lipids
glycolysis and the citric acid cycle provide precursors to synthesize many organic molecules, including lipids
After an overnight fast what type of molecule is most of the acetyl CoA entering the citric acid cycle derived from?
fatty acids — after a fast, fats tend to be mobilized and converted to acetyl CoA
although glycogen is also used for carbohydrate storage, oxidation of glycogen provides only half as much energy as fatty acids
Which molecules are required for the citric acid cycle to full oxidize the carbons donated by acetyl CoA?
NAD+, oxaloacetate, O2, and GDP
What will occur when ATP and food molecules such as fatty acids are abundant?
Enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis will use energy to produce glucose
What does proton pumping entail?
Protons are pumped across the mitochondrial inner membrane as electrons are transferred through the mitochondrial electron transport chain:
The mitochondria use the protein gradient to synthesize ATP
The NADH dehydrogenase, cytochrome b-c1, and cytochrome oxidase complexes all pump protons across the membrane
The pH inside the mitochondrial matrix is higher than in the intermembrane space
What events are required for the synthesis of ATP?
the movement of protons down their gradient through ATP synthase
conformational changes of the F1 ATPase
rotation of the rotor in the membrane
Approximately how many molecules of ATP can be produced in mitochondria from the complete oxidation of a single glucose molecule?
30 molecules of ATP
Which of the components of ATP synthase rotate?
the passage of protons through the H+ carrier causes the carrier and the central stalk to spin rapidly
Which segment of a membrane phospholipid will always carry a negative charge?
the phosphate group — a typical membrane phospholipid molecule has a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails
Why must all living cells carefully regulate the fluidity of their membranes?
to allow membrane lipids and proteins to diffuse from their site of synthesis to other regions of the cell
to allow membranes, under appropriate conditions, to fuse with one another and mix their molecules
to ensure that membrane molecules are distributed evenly between daughter cells when a cell divides
Why are glycolipids found in the extracellular monolayer?
glycosylation of membrane glycolipids occurs in the Golgi lumen
membrane lipid orientation is maintained as the lipids are transported between membranes by transport vesicles
Why is phosphatidylethanolamine, a phospholipid, found in the cytoplasmic monolayer?
phospholipids are inserted into the cytosolic monolayer of the ER and then scramblase transfers the phospholipids randomly between the two leaflets
flippases specifically transfer the phosphatidylethanolamine to the cytoplasmic monolayer
What are the steps of the FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) technique?
The molecule of interest is fluorescently labeled
The relative mobility of the labeled molecule is measured
What could disrupt lipid bilayer formation?
The addition of a negatively-charged, hydrophilic phosphate to the hydrophobic lipid tail
How do transporters and channels select which solutes they help move across the membrane?
channels discriminate between solutes mainly on the basis of size and electric charge
transporters bind their solutes with great specificity in the same way an enzyme binds its substrate— it relies on shape
During exercise, carbohydrates replace glucose burned and salts replace those lost in sweat, as well as helping the small intestine absorb glucose. Which salt is most beneficial for glucose absorption?
NaCl, because Na+ is needed for glucose reentry
When a neuron is activated by a stimulus, its plasma membrane will change until it reaches a membrane potential of about +40 mV — what is special about this value?
It is approximately the membrane potential at which the electrochemical gradient for K+ is zero —> Na+ ions have no further tendency to enter or leave the cell, and are near their theoretical equilibrium potential
How does acetylcholine trigger muscle contraction?
It opens a ligand-gated Na+ channel, which leads to membrane depolarization and contraction of the muscle cell
muscle-relaxant drugs (like scopolamine) work by inhibiting the opening of acetylcholine-gated Na+ channels in the muscle cell membrane
Which membrane-enclosed organelles most likely evolved in a similar manner?
the nucleus and the ER —> most likely originated by invagination of the plasma membrane
In a typical human secretory cell, which membrane has the largest surface area?
The rough ER:
folded up to form an extensive maze of interconnected spaces
this organelle can, in some cases, compose about half the total membrane present in the cell
What are the steps used to transport proteins into the mitochondria?
The mitochondrial protein is synthesized in the cytosol.
The receptor on the mitochondrial membrane binds the signal sequence on the protein.
The protein is delivered to the translocation apparatus on the mitochondria.
The protein is passed through the translocation apparatus.
The signal sequence is removed by signal peptidase and the protein folds into its final shape.
ATP is important for chaperone protein function. Why would protein import into the mitochondria be disrupted if ATP were depleted from inside the mitochondria?
the protein could slip back out of the mitochondria during transport
True or False: The ER produces proteins that are sent out of the ER to many areas of the cytosol.
FALSE— once proteins are in the ER, they do not reenter the cytosol
What would be a consequence of mutations that disrupt the interaction between cross-linking, stabilizing proteins, and keratin filaments?
Corneal damage caused by cell rupture from mechanical trauma
defects in keratin make cells vulnerable to rupture by mechanical stress, particularly in the skin and the cornea
Nocodazole is a microtubule-specific drug that binds free tubulin dimers and blocks microtubule polymerization. What might occur after nocodazole is added to cells growing in culture?
the cell cycle arrests in mitosis
the Golgi apparatus fails to organize at the normal site near the nucleus —> cell cycle progression through mitosis and localization of organelles require functional microtubules
What are the steps of muscle contraction?
Neuron stimulates a muscle cell
Action potential triggers opening of Ca2+ —release channel
Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Troponin moves tropomyosin protein
Myosin interacts with actin
What would increase the level of muscle contraction?
Both the addition of a leaky Ca2+ channel and blocking reuptake of Ca2+ by a Ca2+ pump would lead to increased cytosolic Ca2+, and therefore increase muscle contraction
Myosin is incubated with an ATP analog that can bind to it but cannot be hydrolyzed. What effect will this treatment have on the activity of myosin?
The myosin will be unable to bind to an actin filament — the ATP analog weakens myosin’s affinity for actin
At a cellular level, what is the mechanism behind rigor mortis?
After death, ATP production ceases. ATP is needed for myosin release from actin, and in its absence, muscles remain in a locked, contracted state.
If GTP hydrolysis occurs on a tubulin molecule at the plus end of a microtubule protofilament before another tubulin molecule is added, what typically happens?
The microtubule depolymerizes — because GDP-bound tubulin subunits associate less tightly, hydrolysis of GTP generally causes a microtubule to disassemble
RTKs can activate the enzyme phosphoinositide 3-kinase, which phosphorylates inositol phospholipids. These phospholipids then do what?
Serve as docking sites that recruit specific intracellular signaling proteins to the plasma membrane
The drug Viagra promotes blood vessel dilation by prolonging signaling through nitric oxide (NO). How does Viagra boost NO?
It blocks the enzyme that degrades cyclic GMP
What is true about the phosphorylation of condensins by M-Cdk?
it triggers their assembly onto DNA, compressing chromosomes into a more compact form
this chromosomal condensation occurs at the start of M-phase
makes chromosomes easier to segregate into the two daughter cells that will form as a result of mitosis
The anaphase-promoting complex, or cyclosome (APC/C), triggers the onset of anaphase by doing what?
triggering the destruction of the cohesions that hold the sister chromatids together —> this release allows the chromatids to be pulled toward the opposite poles of the dividing cell
When is kinesin-5 active and how does it affect the spindle?
During anaphase B, kinesin-5 slides the microtubules past one another toward the spindle poles, pushing the poles apart and lengthening the spindle
What are the main functions of kinetochores?
attaching the sister chromatids to the dynamically growing and shrinking microtubules
sensing tension when sister chromatids are attached to opposite poles of the spindle
What could cause the cell to prematurely enter anaphase and the sister chromatids to separate?
Defect in the spindle assembly checkpoint —> cell will not be held in metaphase until proper attachment to both spindle poles occurs, allowing the sister chromatids to separate prematurely and enter anaphase
What is the difference between apoptosis and necrosis?
Apoptotic cells will die neatly, without damaging their neighbors. They tend to shrink and condense as they consume themselves from the inside —> it is a form of programmed cell death.
Necrotic cells will typically swell and burst, spilling their contents over their neighbors. Necrosis is not programmed, and results from an infection that kills the cell.
How many kinetochores are present in a human cell during mitosis?
92 kinetochores — human cells have 46 total diploid chromosomes, each of which has two kinetochores after duplication
True or False: Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells present organelles.
FALSE— prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles
What are two parameters that explain how macromolecular diversity is generated among nucleic acids as a result of the polymerization process?
Types of sugars
Sequence of nucleotides
A polypeptide is a polymer made up of which kind of monomers?
Amino acids
What are the four different structure levels of proteins?
Primary structure — the sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure — composed by alpha-helices and beta-sheets
Tertiary structure — maintained by non-covalent and covalent interactions
Quaternary structure — composed of different polypeptides
True or False: In order to perform a Western blot (immunoblot) analysis, we have to transfer the proteins from the gel into a nitrocellulose membrane. Protein transfer is done by electrophoresis.
TRUE
What are house-keeping genes?
genes that code for proteins involved in metabolic pathways, DNA replication, and gene expression
genes that are required for all cells to live
Which type of cytoskeletal network lacks polarity?
Intermediate filaments
What chemical will bind and stabilize MTs, allowing them to grow but not shrink?
Taxol
Dynamic instability causes microtubules to either grow or shrink rapidly. Consider an individual MT that is in its shrinking phase. What must happen for the MT to stop shrinking and to start growing again?
A GTP cap must be established at the MT plus(+) end
What happens during endocrine signaling?
A hormone is released into the bloodstream; it is a long-range signal
The target cell of a steroid hormone like cortisol is able to specifically respond to it because…?
Only the target cell has appropriate cytosolic receptors
True or False: Different target cells can respond to the same signal differently.
TRUE
What is true about G-protein-coupled receptors?
they have an extracellular ligand binding domain
they have a seven-pass transmembrane protein
they have an intrinsic GEF domain
What happens when the Maturation-Promoting Factor (MPF) from dividing cells was extracted and introduced in a non-dividing receptor cell?
The receptor cell activates M-cyclins that induce mitosis
What are the electron acceptors for catabolic vs. anabolic pathways?
NAD+ is used as an electron acceptor in catabolic pathways, where the ratio of oxidized (NAD+) to the reduced (NADH) forms must be maintained very high (»1)
NADP+ is used as an electron acceptor in anabolic pathways, where the ratio of oxidized (NADP+) to reduced (NADPH) forms must be maintained very low («1)
What is cell fractionation?
The process of using centrifugation to separate various cellular components based on their size
What types of non-covalent bonds can form between a nitrogen atom and a hydrogen bond to an oxygen atom?
Hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces (attractions)
What are some mechanisms that cells can use to regulate enzyme activities?
phosphorylation
binding of small molecules
changing the concentration of substrates
using GTP-binding proteins
What are the parameters that explain how macromolecular diversity is generated among polysaccharides as a result of the polymerization process?
Different types of sugar monomer building blocks
Sequence of sugar monomers
Different types of linkages/bonds
Number of monomers/length of polysaccharide
Why are alpha-helices and beta-sheets commonly-occurring folding patterns in proteins?
These structures are stabilized by H-bonds in peptide backbone — therefore, several different (but not all) sequences can form an alpha-helix or beta-sheet.
What are true statements about the electron transport chain (ETC)?
oxygen is the final electron acceptor
electron transport within the complexes represents coupled oxidation-reduction reactions
activated carriers donate electrons to proteins within the ETC complexes
protons are move into the intermembrane space by ETC
ETC complexes generate the proton gradient (PMF), which is harnessed to synthesize ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
What are the ways in which cells can restrict membrane-associated proteins to specific regions of the plasma membrane?
anchor the proteins from the outside (to the extracellular matrix)
anchor the proteins from the inside (to the cell cortex or cytoskeleton)
anchor the proteins by linking across two cells (cell-cell adhesion)
maintain physical barriers (using cell adhesion junctions) that restrict proteins to different membrane regions on cell
Which membrane would show a more rapid recovery of fluorescence in a FRAP study?
A membrane containing a larger proportion of unsaturated fatty acids.
Why are there NO known motor proteins that move on intermediate filaments?
Intermediate filaments have no polarity.
their ends are chemically indistinguishable
therefore, a hypothetical motor protein bound to an intermediate filament will not be able to sense a defined direction, and move its cargo toward a specific location
Can a vesicle move in any direction along an actin filament?
NO- they can only move in one direction; this is because myosin motor proteins can only move toward the plus end of actin filaments
What are the parameters that explain how macromolecular diversity is generated among phospholipids?
Length of fatty acid chains (number of carbons in fatty acid backbone).
Saturation of fatty acid chains (double bonds on backbone).
Type of polar head group.
What are the similarities and differences between hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces?
Similarities:
both are short-range forces
both involve weak electrostatic interactions
both are non-covalent forces
Differences:
hydrogen bonding will take place only between an H attached to an electronegative atom and other specific atoms
van der Waals attractions will occur between any two atoms
What are the features of a protein domain?
it is a compact and stable structure composed of alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
it can fold into a compact shape independently of the rest of the polypeptide
it can possess specific functions
What is the role of a carrier molecule?
trap energy released from catabolic/exothermic reactions and provide energy for the completion of anabolic/biosynthetic/endothermic reactions
without carrier molecules, a cell has no energy currency, and cannot perform any of its functions
What are the similarities and differences between messenger RNA (mRNA) and micro RNA (miRNA)?
Similarities:
both are transcribed in the nucleus, then processed and exported to the cytosol
miRNA binds to mRNAs to function; mRNAs bind to tRNAs to function
Differences:
mRNA is translated into a protein; miRNA is not translated
mRNA controls the expression of a single protein; miRNA controls the expression of several proteins
In a motility assay, investigators attach myosin motor proteins to a glass slide and then add actin filaments. Once the filaments have bound to the myosin, what can be expected to occur?
In the presence of ATP, the filaments will glide toward their minus ends.
If GTP hydrolysis occurs on a tubulin molecule at the plus end of a microtubule protofilament before another tubulin molecule is added, what typically happens?
The microtubule depolymerizes
What statements can describe intermediate filaments?
they have the highest tensile strength of all the cytoskeletal filaments
they are wider than actin filaments
they deform under stress, but they do not rupture
nonpolar - distribute the effects of locally applied forces, allowing membranes to retain their structural integrity
are not embedded in the centrosome, and don’t exhibit dynamic instability
Consider an individual microtubule (MT) in its shrinking phase. What would happen if only GTPgammaS, but no GTP, were present in the solution?
The MT would stop shrinking, and start growing continuously without collapse.
True or False: Without actin, cells can form a functional mitotic spindle and pull their chromosomes apart, but cannot divide.
TRUE— actin microfilaments generate the contractile ring that is required to pinch off daughter cells during cytokinesis; mitotic spindle formation and chromosome movement require microtubule function, which will not be affected by absence of actin
What makes it possible for a combination of signal molecules to evoke a response that differs from the sum of the effects that each signal could trigger on its own?
The ability of different intracellular relay systems to interact
How is Protein Kinase C activated?
By binding to DAG and calcium ions
What is a proto-oncogene?
A wild-type gene that encodes a signaling pathway component that, when mutated, can cause cancer