rad tech - lower extremity and knee
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
are AP toes a dorsoplantar or plantodorsal projection?
dorsoplantar
Dorsoplantar (AP) Axial Toes
Patient Position
Sitting or lying on X-ray table
Leg of interest on table
Part Position
Plantar surface of foot on IR
No rotation of foot
Metatarsal of interest centered to IR
CR
10-15◦ toward calcaneus
Centered to MTP of interest
Collimation
Include entire toe and at least ½ of metatarsal
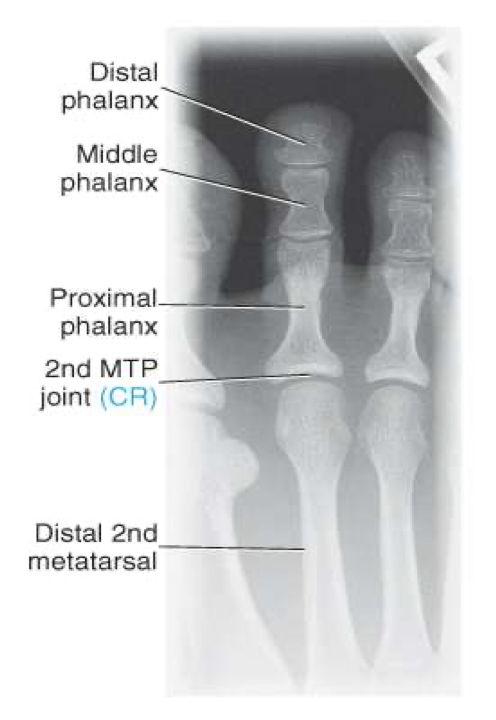
Evaluation Criteria of AP toes
Digits and minimum of distal ½ of metatarsal demonstrated
No overlap of soft tissues
IP and MTP joints appear open
No rotation of foot
Equal concavity of phalanges
Optimal exposure factors
Dorsoplantar (AP) Oblique Toes
Patient Position
Same as AP
Part Position
Foot is rotated 30-45◦ medially for 1st- 3rd & laterally for 4th & 5th
May need to pull other toes out of the way
Can use tape or rubber tubing etc
CR
CR is perpendicular to MTP of interest
Collimation
Same as AP
Evaluation Criteria for oblique toes
Digits and minimum of distal ½ of metatarsal demonstrated
IP and MTP joints appear open.
Increased concavity on one side of shaft
Heads of metatarsals with no or minimal overlap
Other toes do not obscure toe of interest
Optimal exposure factors

Lateral Toe
Patient Position
Same as AP & oblique
Part Position
1st ,2nd & 3rd rotated onto medial surface
Lateromedial projection
4th & 5th rotated onto lateral surface
Mediolateral projection
CR
CR perpendicular to PIP or IP ( 1st toe)
Collimation
Same as AP & oblique
Evaluation Criteria for lateral toes
Digits presented in true lateral position
Anterior surface is concave
IP and MTP joints appear open
Digit free of superimposition
Optimal exposure factors
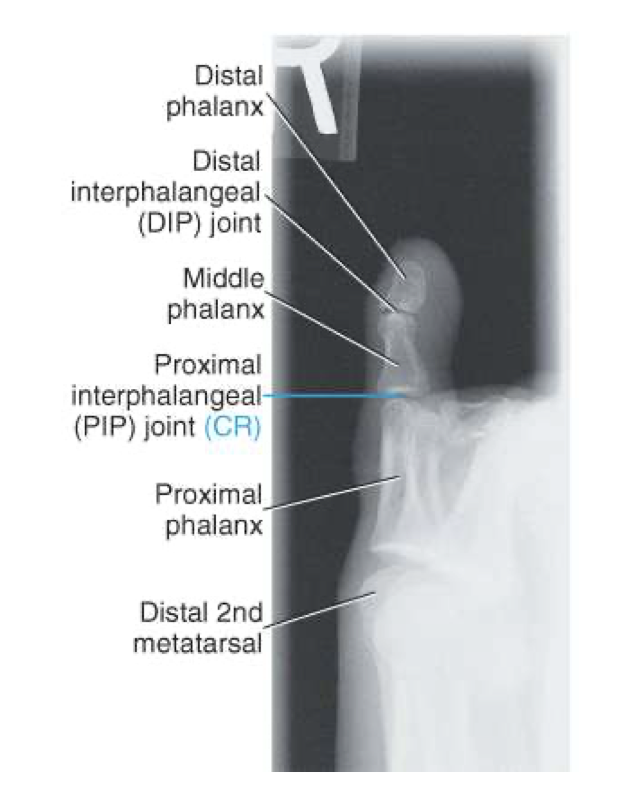
Dorsoplantar (AP) Axial Foot
Patient Position
Sitting or lying on table
Planter surface of foot on the table
May be performed with patient standing on IR*
NOTE: CR angle may need to be increased when patient is standing
Part Position
Plantar surface flat against IR
No rotation
CR
Angle approx. 10◦ toward heel; centered to base of 3rd metatarsal
Patients with a high longitudinal arch require a greater angle
o 15-degrees
A low longitudinal arch requires less angle
o 5-10 degrees
Collimation
Include entire foot
Evaluation Criteria for AP foot
Entire foot visualized
No rotation of metatarsals
MTP joints generally open
Bases of 1st & 2nd metatarsals separated
Bases of 3rd- 5th overlap
Joint space between 1st & 2nd cuneiform is open
Distal phalanges not overexposed
o May need to use a compensating filter to maintain an uniform image exposure

Dorsoplantar (AP) Oblique Foot
Patient Position
Same as AP axial
Part Position
Foot is rotated medially 30-40 degrees
Dorsum of foot near parallel to IR
Low arch= less rotation; high arch= more rotation
CR
Perpendicular to base of 3rd metatarsal
Collimation
Include entire foot and ankle joint

Evaluation Criteria for oblique foot
Entire foot visualized
Third through fifth metatarsal bases free of superimposition
Bases of 1st – 2nd are overlapped
Tuberosity demonstrated at base of fifth metatarsal
Sinus tarsi visualized
Cuboid-cuneiform joint space is open
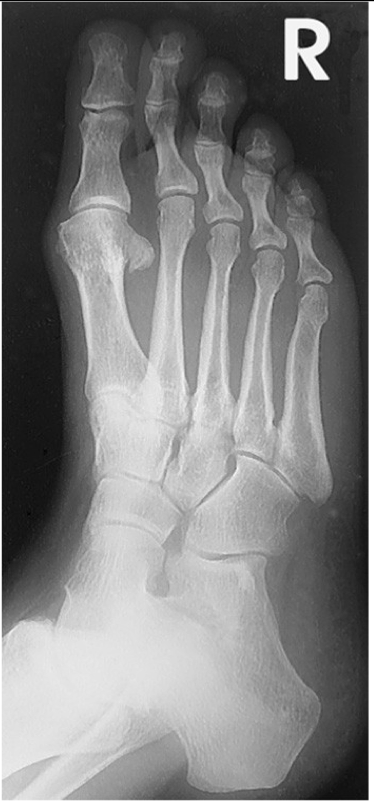
is a lateral foot mediolateral or lateromedial
mediolateral
Lateral Foot
Patient Position
Patient lies on affected side or standing at upright IR
If recumbent: Flex affected knee 45-degrees
Other leg is placed behind
Part Position
Foot in a lateral position with lateral surface against IR
Dorsiflex foot and place plantar surface perpendicular to IR
CR
perpendicular to medial cuneiform
Collimation
to include at least 2.5 cm of the ankle
Evaluation Criteria for lateral foot
Entire foot visualized
Talar domes are superimposed and tibiotalar joint demonstrated
Metatarsals are nearly superimposed
Base of the fifth metatarsal visible
Distal fibula superimposed on posterior tibia
Long axis of foot forms a 90 degree angle with the tib/fib

AP Ankle
Patient Position
Sitting or lying on table
o Can be standing
Affected leg extended on table
Part Position
Foot is dorsiflexed to form a right angle to tib/fib
Note: we don’t force this if there is an injury
Intermalleolar line forms a 15-20 degree angle to the IR
CR
Perpendicular to a point midway between malleoli
Collimation
Include approx of 1/3 tib/fib, talus and proximal metatarsals
Must include base of 5th metatarsal

Evaluation Criteria of AP ankle
Distal ⅓ of tibia and fibula demonstrated
Proximal ½ of metatarsals included
Medial and superior aspect of Mortise joint open
Lateral distal tibia+ lateral talus superimposed over fibula
Closed lateral Mortise joint
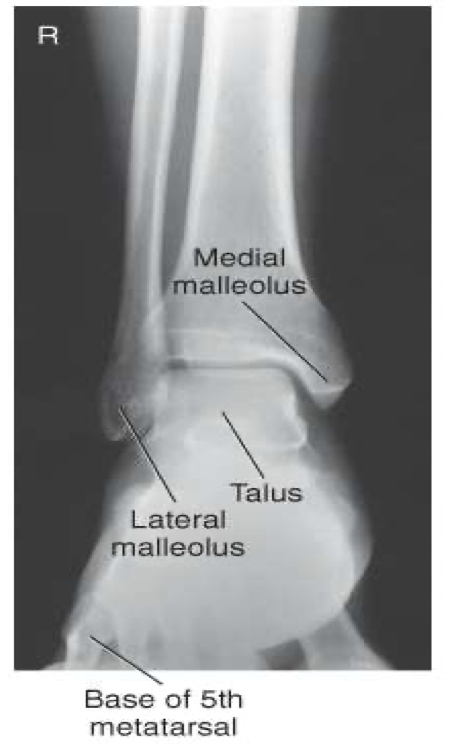
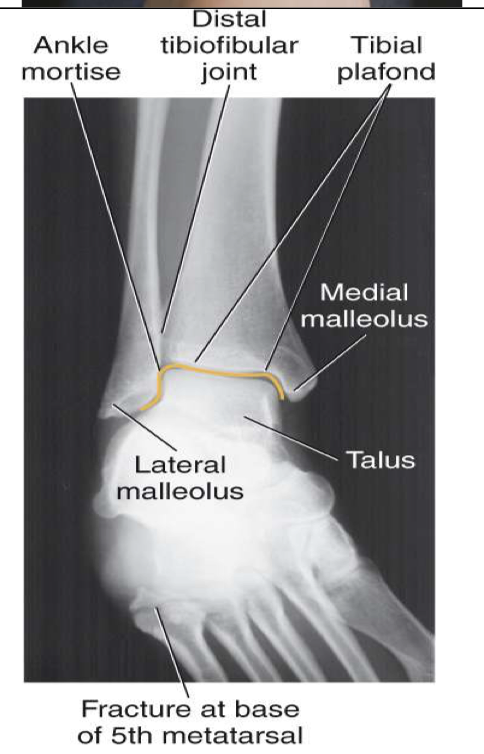
AP Oblique ( Mortise) Ankle
Patient Position
Same as AP
Part Position
Foot is not dorsiflexed, allow it to remain extended (visualize the base of the 5th MT).
Entire lower limb is rotated 15-20◦ to place intermalleolar line parallel to IR
CR
Perpendicular to midway b/w malleoli
Collimation
Include distal tib/fib (⅓ ) and proximal metatarsals, especially the base of the 5th medially
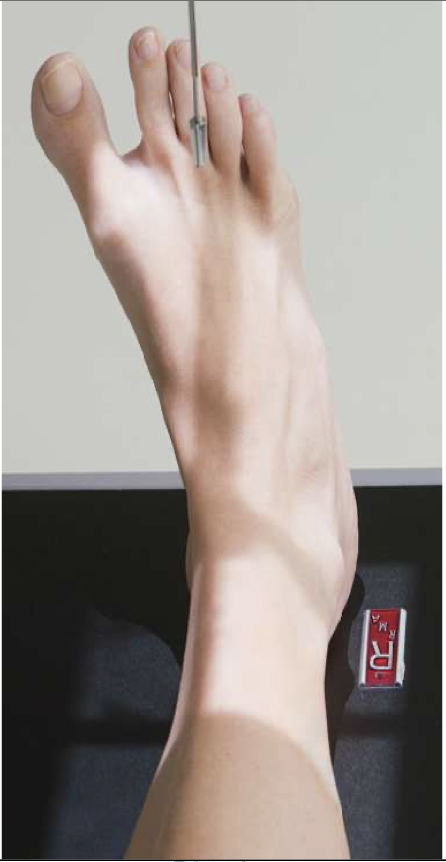
Evaluation Criteria for AP mortise ankle
• Entire ankle mortise open
Medial , lateral & superior aspects
• Distal ⅓ of tibia and fibula demonstrated
Little, if any, overlap of distal tib/fib
• Proximal ½ of metatarsals included
• Optimal exposure factors
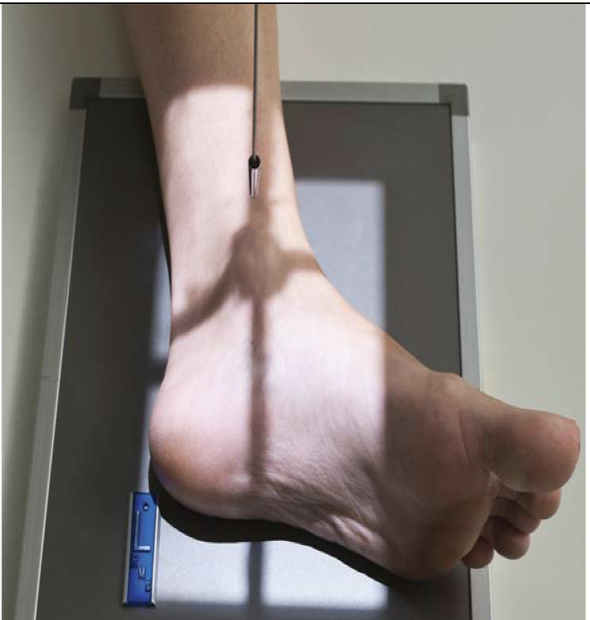
Lateral Ankle
Patient Position
Lying on affected side with lateral ankle against IR
o Can be standing
Part Position
Foot dorsiflexed to place foot at right angle to tib/fib
Affected ankle in a true lateral
Lateral malleolus located 1 cm posterior to the medial malleolus
CR
perpendicular to medial malleolus
Collimation
to include entire ankle joint, distal tib/fib and base of 5th metatarsal
especially the base of the 5th
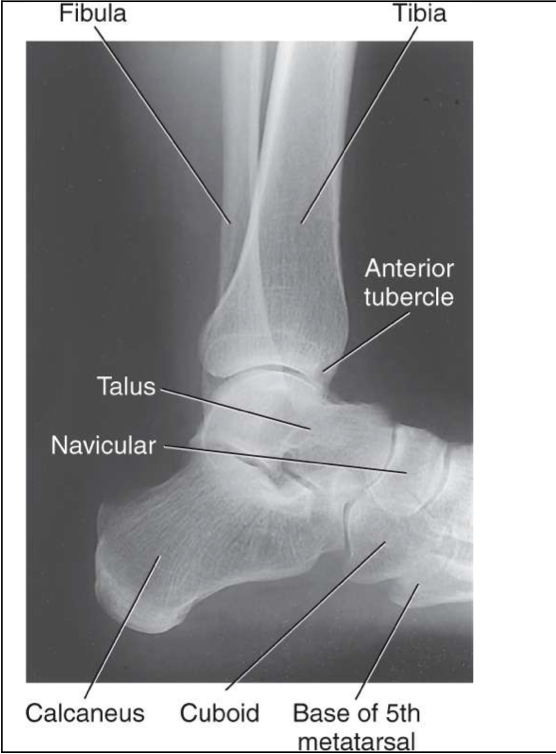
Evaluation Criteria of lateral ankle
Entire talus and calcaneus visualized
Base of 5th metatarsal demonstrated
Lateral malleolus superimposed over posterior half of tibia
Talar domes superimposed & tibiotalar joint is open
Optimal exposure factors – visualize the distal fibula through the talus.
Should see anterior pretalar and posterior pericapsular fat pads
Note: Foot must be dorsiflexed 90° for anterior pretalar fat pad to properly demonstrated
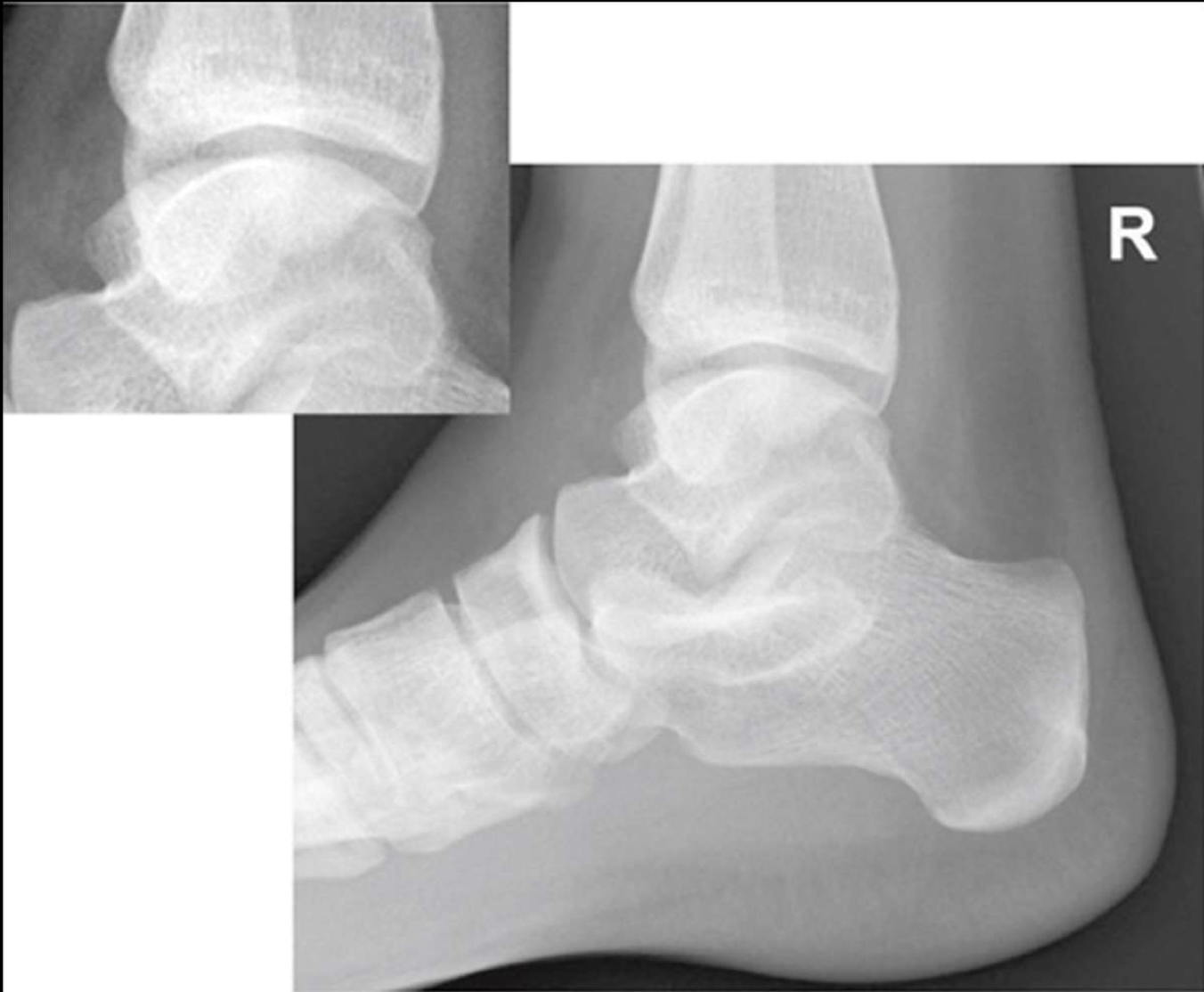
is this lateral ankle over or under rotated
under
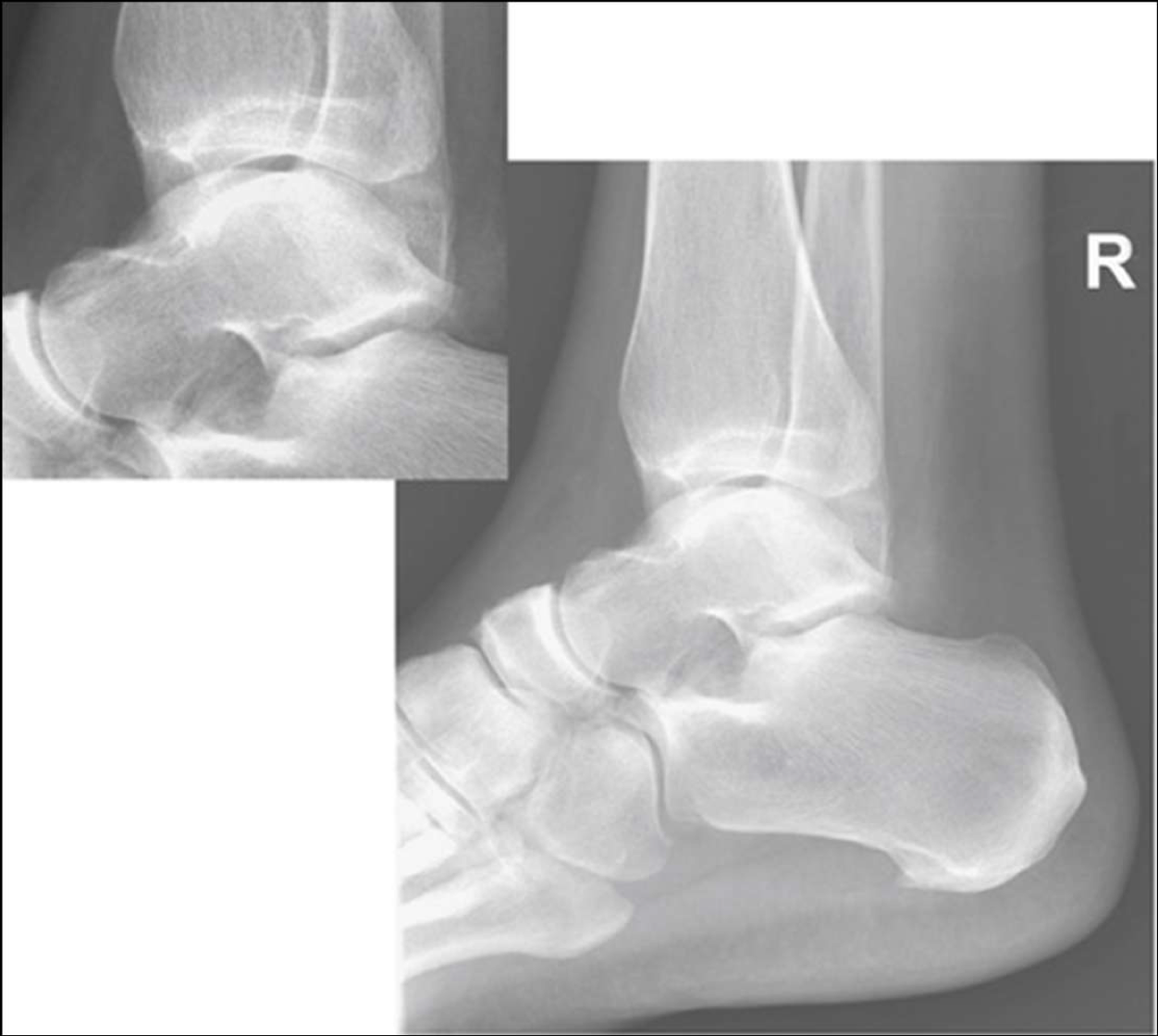
is this lateral ankle over or under rotated
over rotated
AP Tibia & Fibula
Patient Position
• Lying on x-ray table
• Affected leg extended
Part Position
• Entire affected limb is in a true AP
• Affected foot is dorsiflexed 90o
CR
• perpendicular to the IR; centered to midshaft region of tib/fib
Collimation
• Knee to ankle must be included
Usually requires the IR to be placed diagonally
May also require increase SID
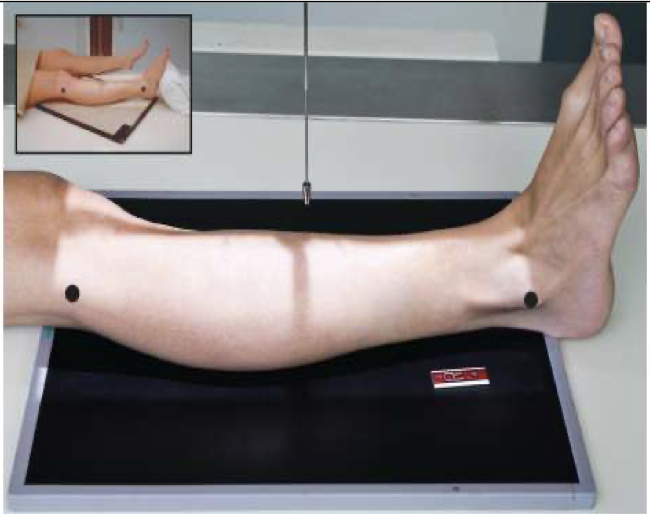
Evaluation Criteria for AP Tib/Fib
• Entire tibia and fibula demonstrated
• Knee and ankle joints demonstrated
• Partial superimposition of fibula and tibia at proximal and distal ends
Due to divergence of the beam, neither knee nor ankle joint is fully open
• Optimal exposure factors
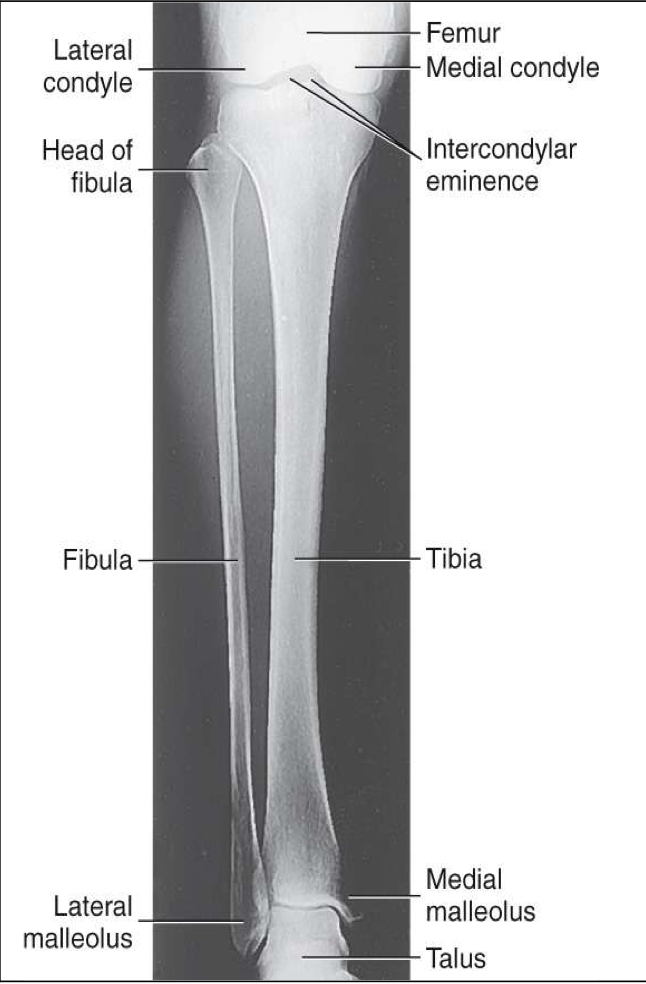
Lateral Tibia & Fibula
Patient Position
• Lying on affected side
Part Position
• Both knee and ankle are in a true lateral position
• Patellar surface perpendicular to IR
CR
• perpendicular to IR & centered to mid tib/fib
Collimation
• to include both joints
Evaluation Criteria for lateral tib/fib
• Entire tibia and fibula demonstrated
• Knee and ankle joints demonstrated
• Proximal head of fibula superimposed by tibia
• Distal fibula superimposed over posterior half of tibia
• Optimal exposure factors
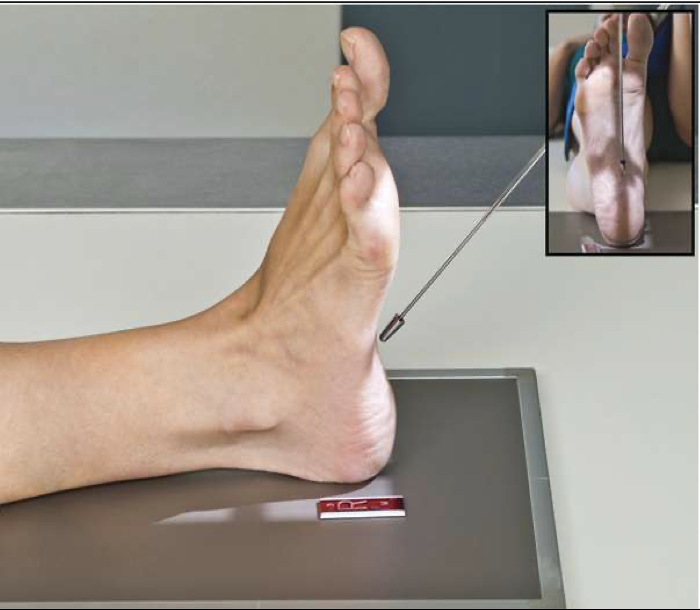
Plantodorsal Axial Calcaneus
Patient Position
• Sitting or lying on table
• Affected leg extended
Foot is dorsiflexion
Part Position
• Plantar surface of foot should be 90o to the IR
• Patient may hold foot in place with “strap”
CR
angled 40o toward the plantar surface (cephalad)
• Centered to the base of the third metatarsal
Collimation
include entire calcaneus + ankle joint
Tip: Imagine a line between the base of the fifth metatarsal and the lateral malleolus ;CR should be parallel to this line (Angle less if foot is flexed more, angle more if not flexed enough)
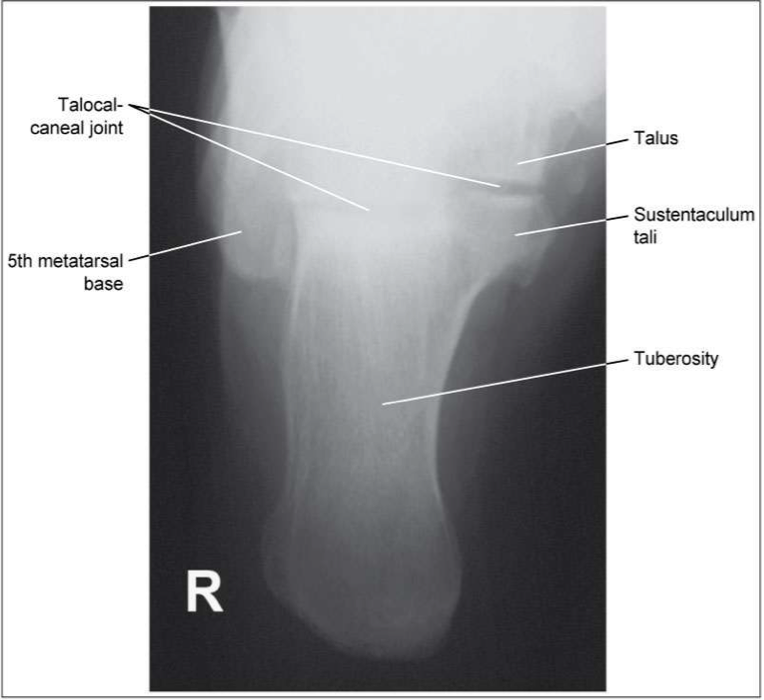
Evaluation Criteria of plantodorsal axial calcaneous
• Entire calcaneous visualized
• Including open talocalcaneal joint space
• No rotation
• Base of the 5th MT seen laterally
• Sustentaculum tali visible in profile medially
Lateral Calcaneus
Patient Position
• Lying on affected side
Part Position
• Affected foot/ankle in a true lateral position
• Lateral malleolus is slightly (1 cm) posterior to medial malleolus
• Foot dorsiflexed 90o
CR
• is perpendicular to IR; centered 2.5cm (1″) inferior to medial malleolus
Collimation
• to include ankle joint and entire calcaneus
• Note: if lateral calcaneus is performed only to rule out heel spurs, collimation may be closer
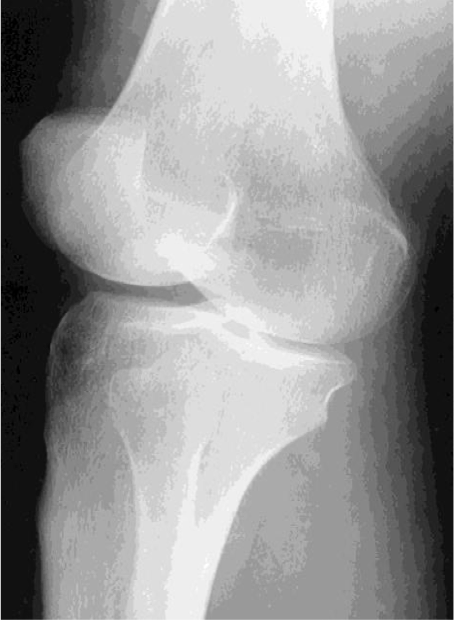
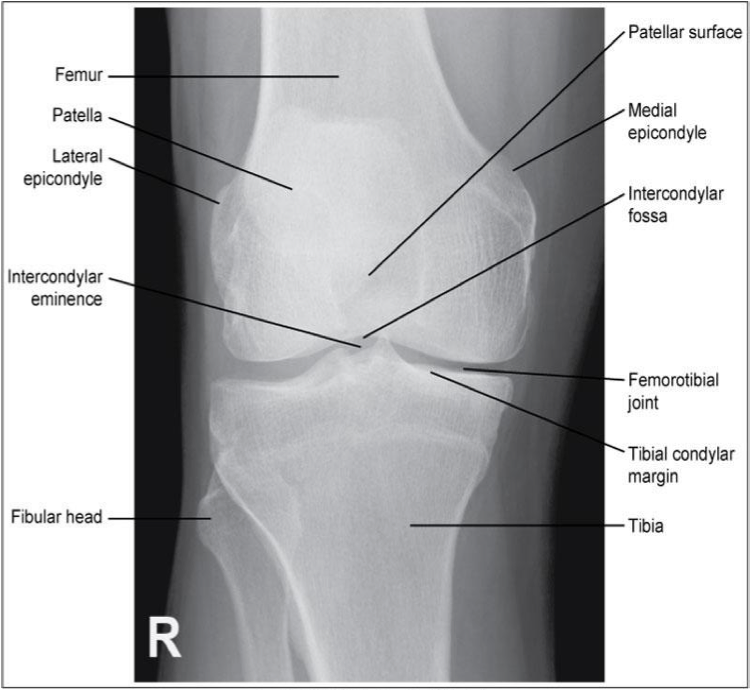
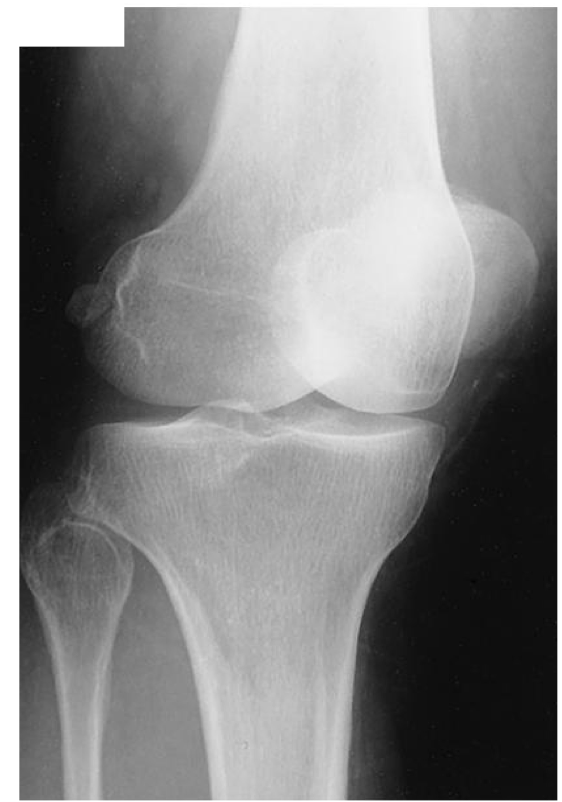
AP Knee
Patient Position
• Supine with no rotation
• Affected knee extended ( can be standing)
Part Position
• Knee is in a true AP position
• Femoral epicondyles are in profile
A line drawn between the epicondyles is parallel to the IR
• Leg internally rotated ≈ 3-5°
CR
• CR is parallel to the tibial plateau
Amount of CR angle required depends on thickness of patient’s thighs (See below)
• CR is centered 1.25 cm inferior to the apex of the patella
Collimation
Include about ¼ of distal femur + proximal tib/fib
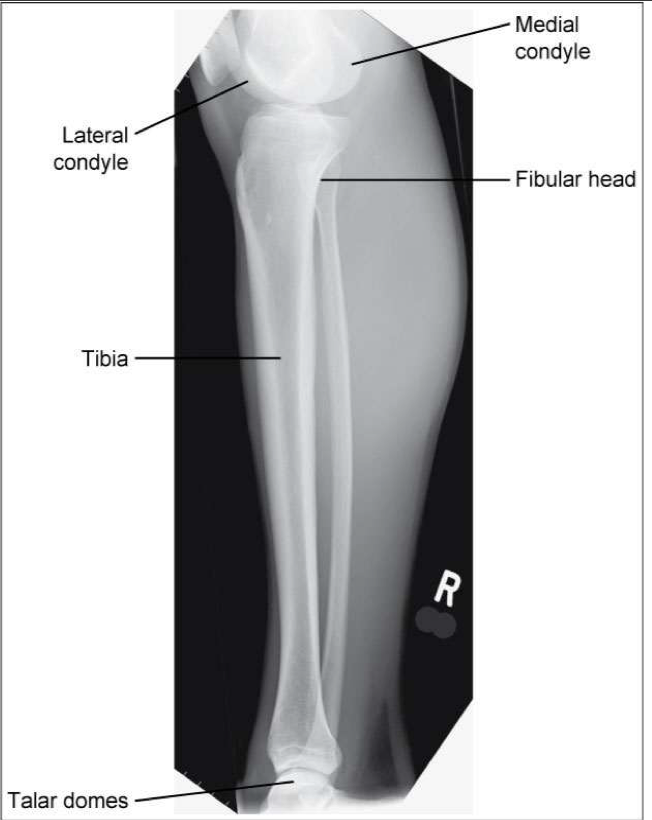
Evaluation Criteria for AP knee
• Femorotibial joint space open
• Femoral condyles are symmetrical
• Femoral epicondyles in profile
• Knee joint centered to collimation field
• Articular facets of tibia on end
• Intercondylar eminence centered within the fossa
• Intercondylar fossa is barely seen
• Approx ½ of fibular head superimposed by tibia
• Head of fibula approx 1.25 cm from tibial plateau
• Patella sits slightly lateral to midline
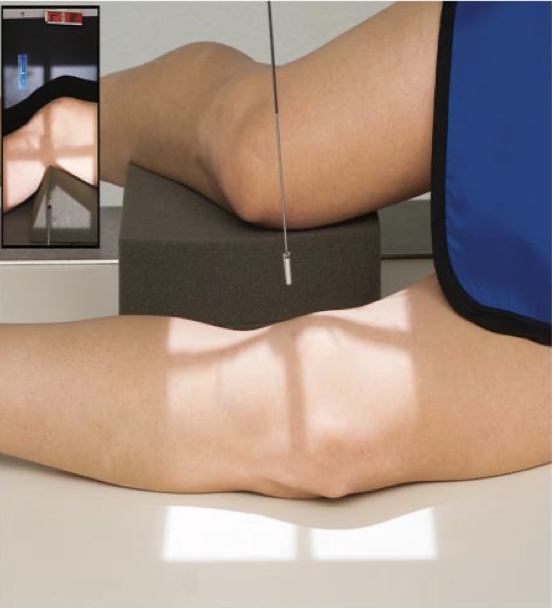
Lateral Knee ( mediolateral)
Patient Position
• Lying on affected side
• Unaffected leg either behind or in front of affected leg
• (can be standing)
Part Position
• Affected knee is flexed 20-30°
Some texts suggest only 10- 15 °
• Use caution if flexing injured knee; may leave knee extended or partially flexed
• Knee in a true lateral
Femoral epicondyles are superimposed
Patellar surface is perpendicular to IR
CR
• CR is angled 5-7° cephalad; centered 2.5 cm inferior to medial epicondyle of femur
≤ 5° for taller, thinner patients
≥ 7 ° for shorter patients with wider pelvis
• Tip: rotate collimator so CR is directed across the femoral condyles
Collimation
Include distal femur/proximal tib/fib
NOTE: May use “boomerang” filter for better soft tissue demonstration
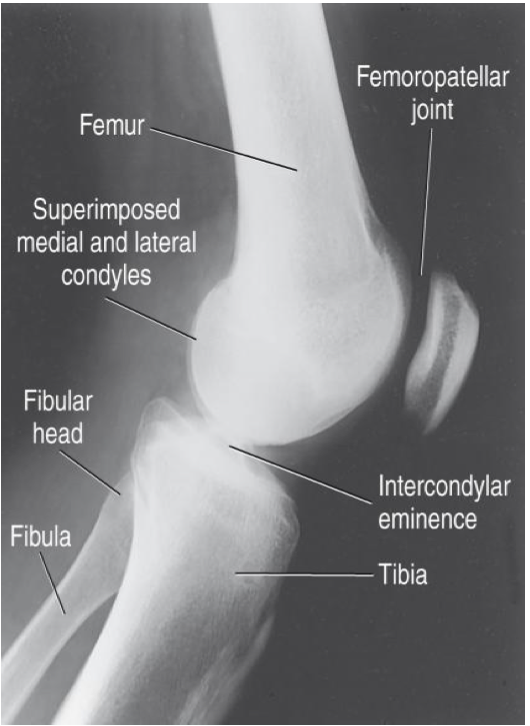
Evaluation Criteria for lateral knee
• Femoral condyles superimposed
Determined by rotation
Use abductor tubercle to determine if medial condyle is anterior/posterior
• Distal articular surfaces of femoral condyles superimposed
Determined by adequate CR angle
• Patella in profile (indicates no rotation)
• Patellofemoral joint space open
• Fibular head is partially superimposed by tibia
• Soft tissues well demonstrated
• Filter used
Medial & Lateral Oblique Knee
@ QEH not part of knee protocol; only performed if specifically requested
• Knee is rotated 45° medially & then 45° laterally
• Both obliques acquired
• Centering, CR angle & Collimation are the same as an AP Knee
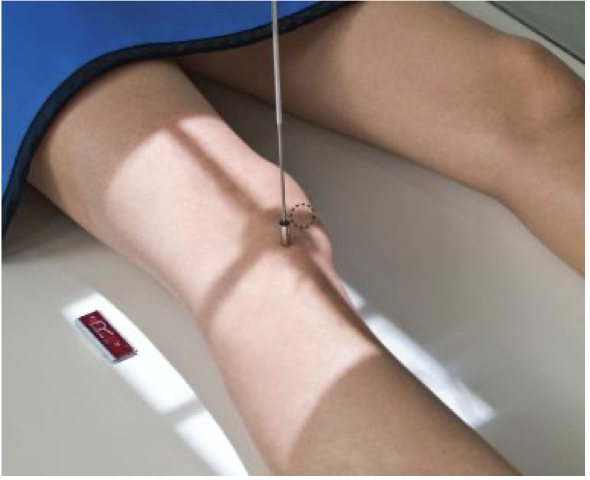
Medial Oblique knee evaluation criteria
• Proximal tibiofibular joint open
• Demonstrates lateral femoral and tibial condyles
• Half of patella superimposed over medial femoral condyle
Lateral Oblique knee evaluation criteria
• Fibula superimposed over mid tibia
• Demonstrates medial femoral and tibial condyles
• Half of patella superimposed over lateral femoral condyle