Sexually Transmitted Infections
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
how do we manage STIs?
-sexual history taking
-screen and test
taking a sexual history
-CDC 5P’s:
-partners
-practices
-protection from STIs
-past history of STIs
-pregnancy intention
STI strategy- GOALS framework
-universal opt-out screening more beneficial and cost-effective than risk-based screening
-emphasizing benefits, rather than risks, more successful in motivating patients
-positive interactions with healthcare providers promote engagement in prevention and care
-patients want their healthcare providers to talk with them about sexual health
screening v diagnostic testing
-screening tests: testing for disease in people who do not have symptoms
-diagnostic testing: testing for disease in people who have symptoms
who do we screen for gonorrhea and chlamydia?
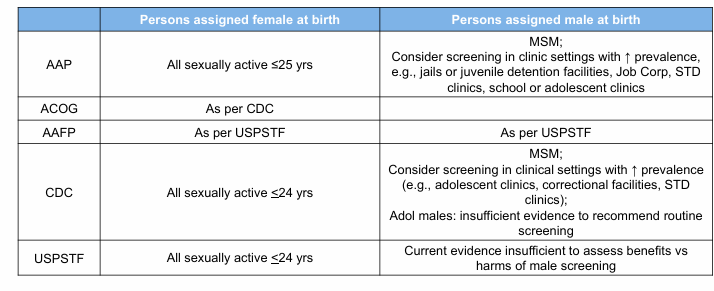
chlamydia and gonorrhea screening recommendations

who receives diagnostic testing?
-everyone with symptoms
extragenital STIs
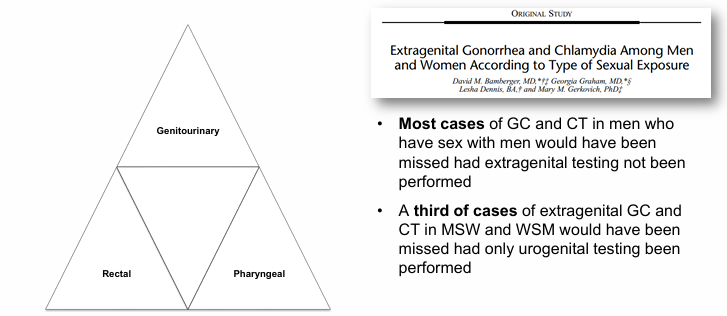
STI presentation- dysuria
-sensation of pain and/or burning, stinging, or itching of the urethra or urethral meatus with urination
-caused by urethritis urethral inflammation: urine comes in contact with the inflamed or irritated urethral mucosal lining causing pain
-diagnosis: presence of mucopurulent or purulent discharge, gram stain of urethral secretions, >/=2 WBC/HPF v >/=5 WBC/HPF
-positive leukocyte esterase or >10 WBCs/hpf on first void urine
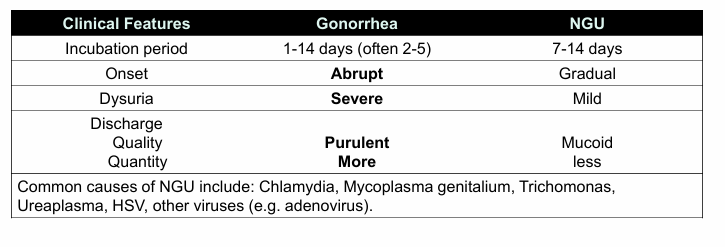
STI differential- dysuria
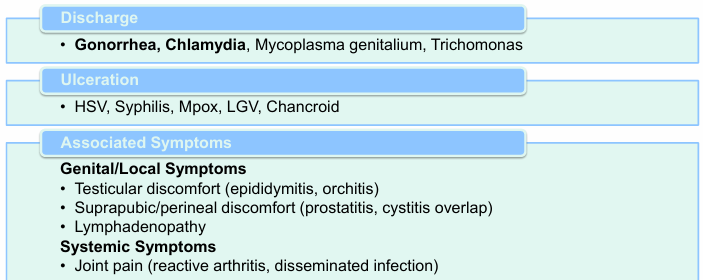
gonorrhea v. non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU)
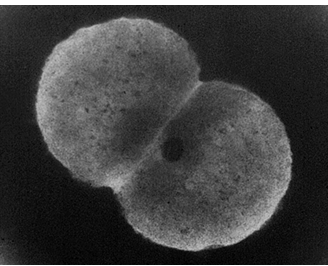
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (GC) epidemiology
-second most common notifiable sexually transmitted infection in the US
-transmitted by sexual contact from: urethral, cervical, rectal, adn pharyngeal contact; perinatally
-re-infection is common
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (GC)
-gram negative intracellular diplococci
-fastidious organisms requiring complex media and CO2-enriched atmosphere for optimal growth
-oxidase positive
-ferments glucose only v. N. meningitidis which ferments glucose and maltose
-infects mucus-secreting epithelial cells and evades host response through alteration of surface structures
-peak incidence 20-24 years of age
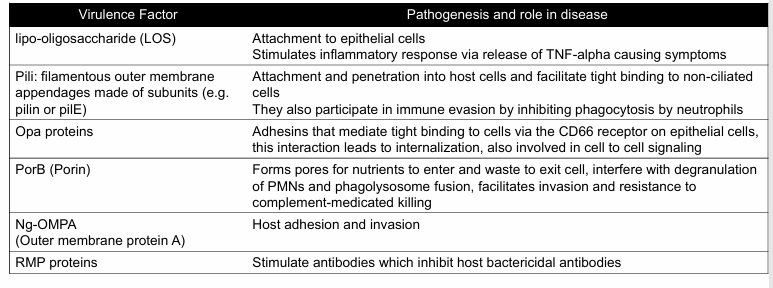
Gonorrhea pathophysiology
-infects columnar or cuboidal epithelium
-uses virulence factors to adhere, invade, and multiply
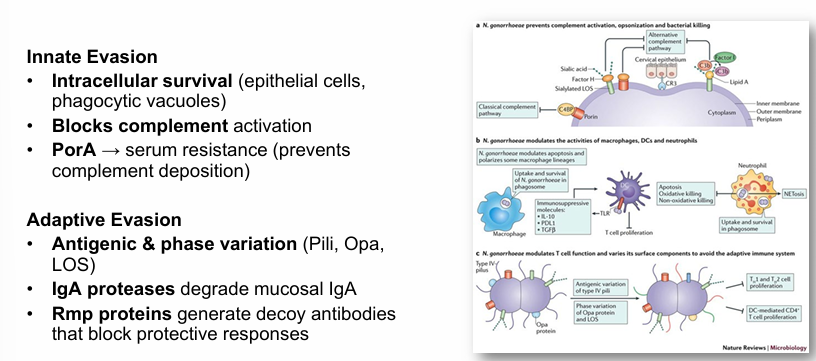
-immune evasion through antigenic and phase variation
-sRNA networks help adapt to stress and enhance survival
gonorrhea pathophysiology steps
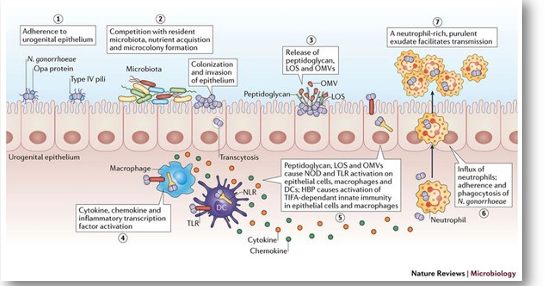
gonorrhea pathophysiology- evasion
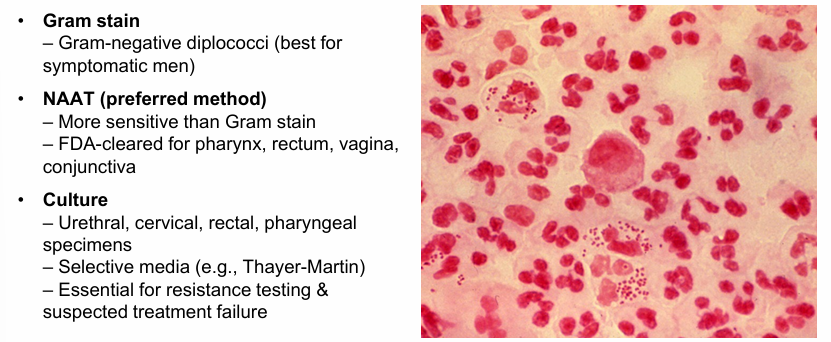
gonorrhea diagnosis
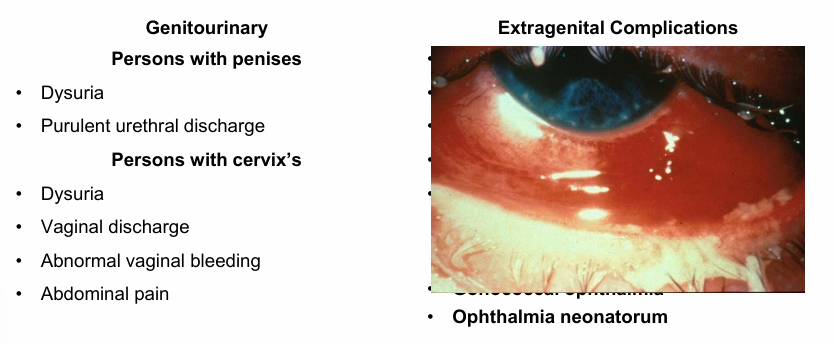
gonorrhea clinical presentations
disseminated gonococcal infection
-1-3% of infected patients
-associated with female sex and menstruation
-deficiency in C5-C8 may increase susceptibility
-symptoms: fever, pustular skin lesions, tenosynovitis, migratory polyarthralgia (septic arthritis in one or two joints), asymmetric arthralgia and hepatitis, endocarditis, meningitis rarely occurs
-diagnosis: gram stain, culture, nucleic acid amplification
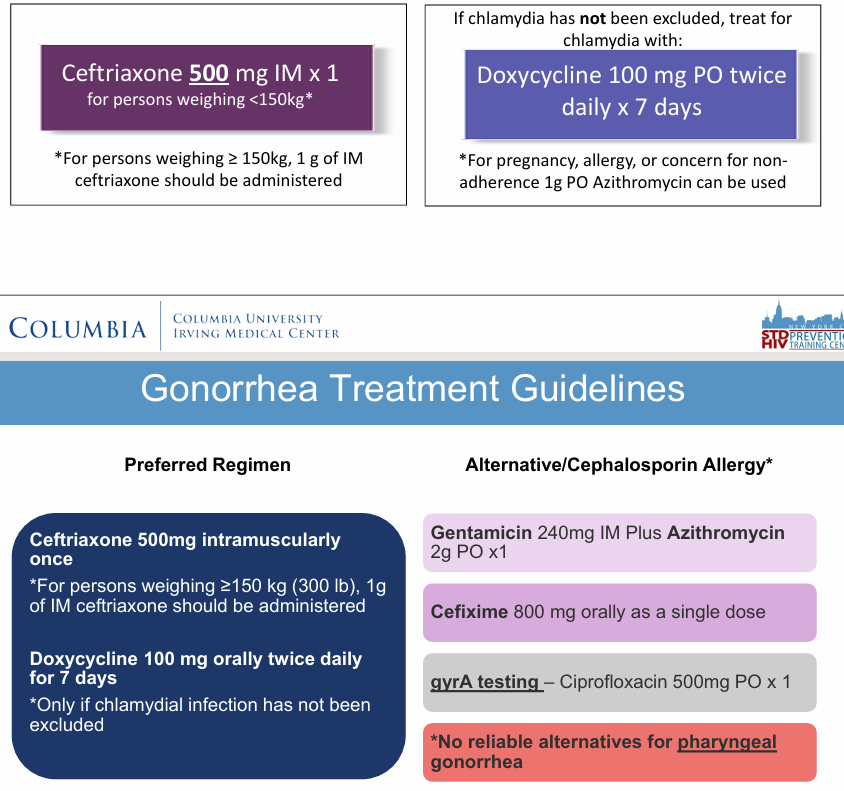
gonorrhea treatment guidelines
gonorrhea mechanisms of resistance
-PBP2 mutations (penA) → beta-lactam resistance
-Efflux pumps (MtrCDE, MtrR) → expel antibiotics
-porB variations → decrease permeability, beta-lactam resistance
-plasmid-mediated resistance → bIaTEM-1 (beta-lactamase), tetM (tetracycline); transferable from commensal Neisseria
near future alternative gonorrhea treatments

gonorrhea follow-up

non-gonococcal urethritis
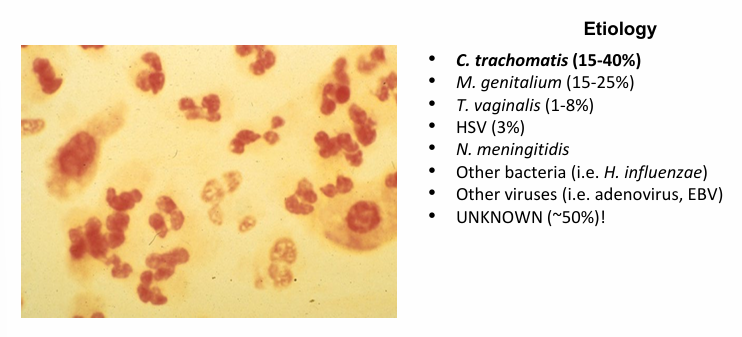
chlamydia epidemiology
-most frequently reportable bacterial STI in the US
-highest prevalence </=25 year olds
-most cases are ASYMPTOMATIC
-screening for women is routine but there is insufficient evidence to screen for all sexually active men
-screening for men based on clinical settings of increased rates and increased risk factors
chlamydia pathophysiology

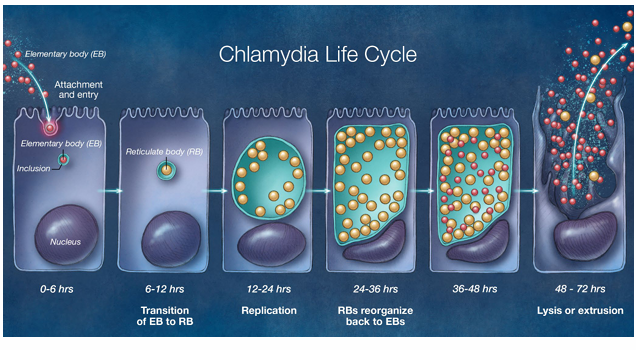
chlamydia life cycle
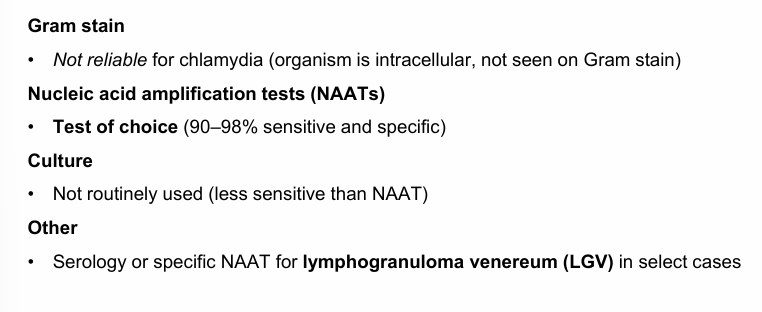
chlamydia diagnosis
chlamydia clinical presentations

chlamydia clinical presentations (LGV)

uncomplicated chlamydia treatment
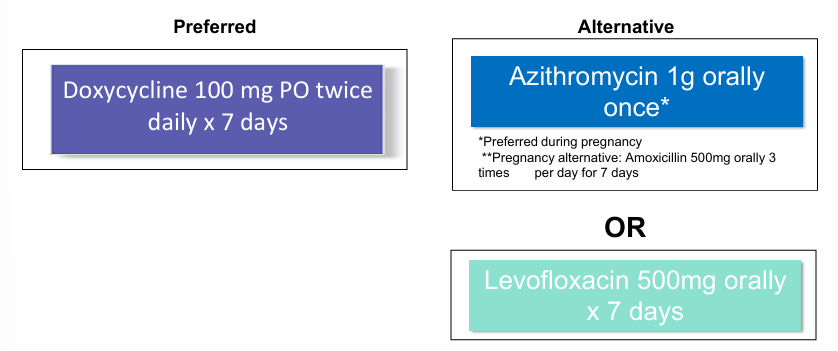
LGV rectal treatment (proctitis with CT)
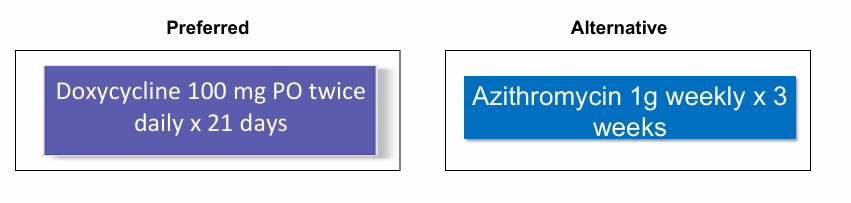
why doxycycline and not azithromycin for chlamydia tx?
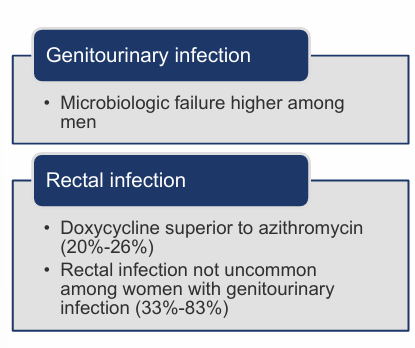
chlamydia follow-up

PID diagnosis
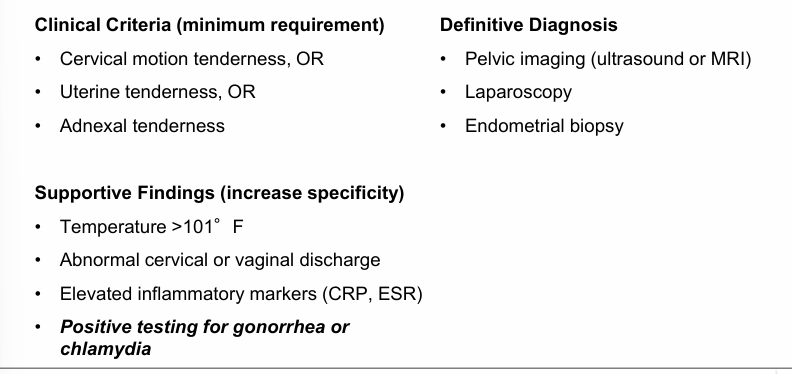
PID pathophysiology

fertility associated complications of PID
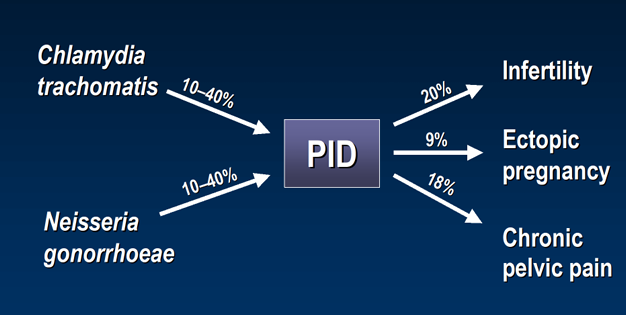
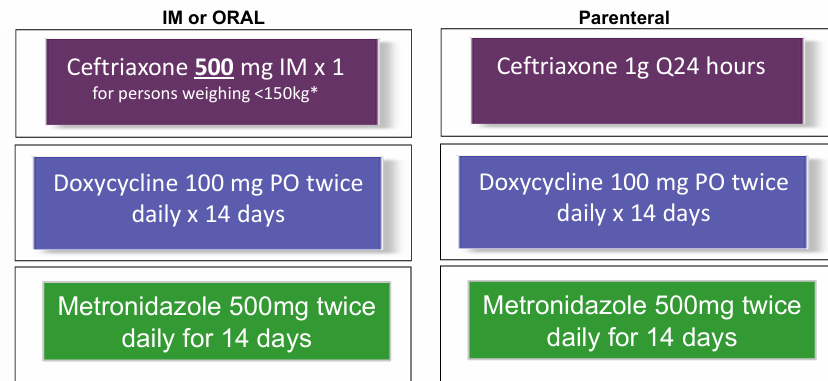
PID treatment
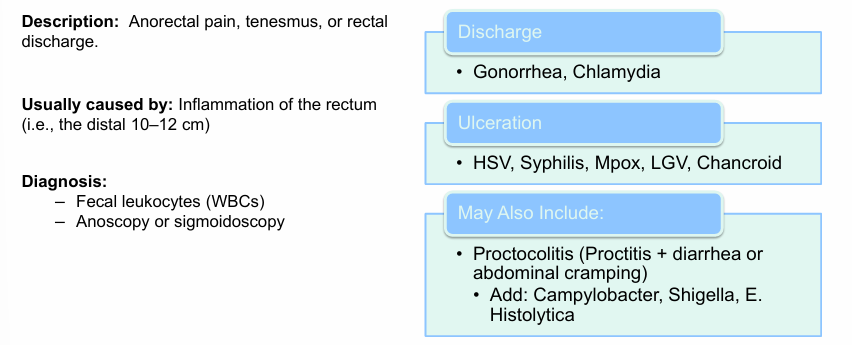
proctitis presentation
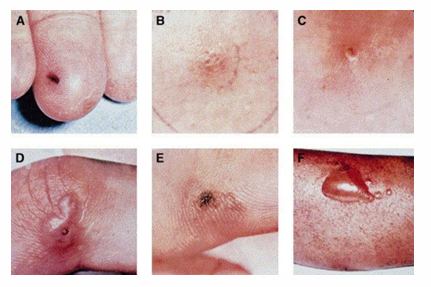
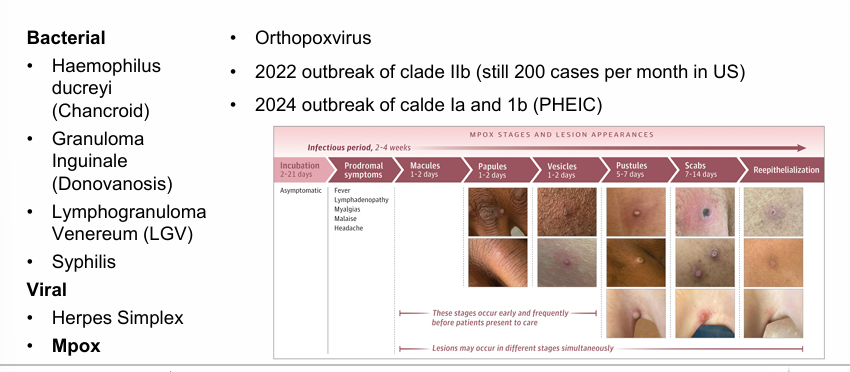
STI presentation- ulcers

herpes simplex

HSV-1 v. HSV-2

herpes simplex testing

herpes simplex treatment and prevention

Mpox
STI primary and secondary prevention

STI routine screening
-HIV testing
-offer GC/CT, RPR testing broadly
STI syndromic testing/treatment and presumptive treatment
-treat symptomatic and exposed patients
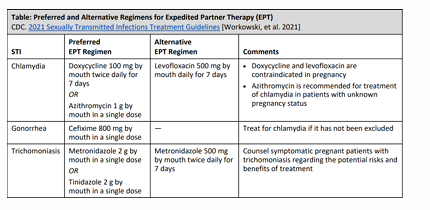
expedited partner therapy- treatment
STI vaccination
-HPV
-hepatitis A
-hepatitis B
-Mpox
-Men B?
STI medication prophylaxis
-HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
-doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis: 200mg doxycycline taken 24-72 hours after sex, effective against: chlamydia, syphilis, possibly gonorrhea
summary

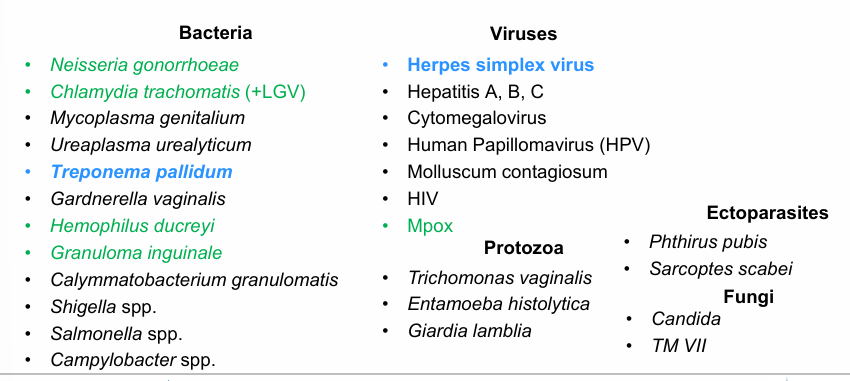
STI categories (bacteria, viruses, protozoa, ectoparasites, fungi)