exam 4 immunology, osmoregulation, sexual reproduction
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
What is the primary function of the immune system in multicellular organisms?
To protect against pathogenic organisms.
What percentage of microbes are pathogenic?
Only a small percentage.
What types of pathogens can the immune system fight?
Viruses, bacteria, protozoans, fungi, and parasitic animals.
What are the two main parts of the immune system?
Innate Immune System and Adaptive Immune System.
What are the characteristics of the Innate Immune System?
Nonspecific, no memory, and found throughout all animal and plant kingdoms.
What are the characteristics of the Adaptive Immune System?
Highly specific, has memory, and is found only in vertebrate animals.
What are some physical and chemical barriers of the Innate Immune System?
Skin, normal flora on skin, mucous and cilia in the respiratory tract, low pH of stomach, and antimicrobial peptides.
What is an antigen?
Anything that is foreign to the body and can trigger an immune response.
What are pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)?
Markers on microbes that are recognized by the immune system.
What is the inflammatory response?
A response characterized by pain, heat, redness, and swelling due to increased vascular permeability.
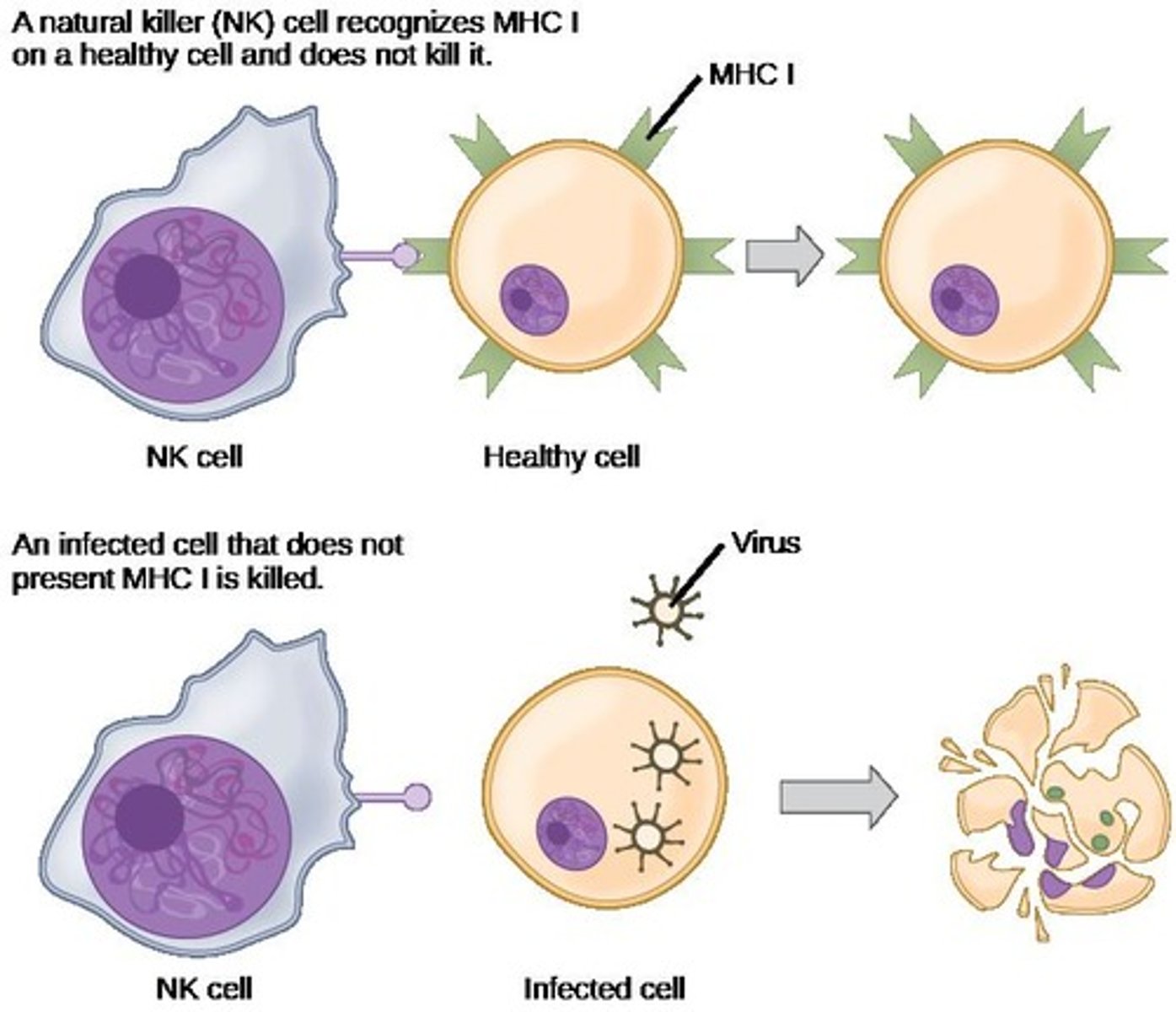
What role do Natural Killer Cells play in the immune system?
They kill virus-infected or altered self-cells, such as tumor cells.
What types of cells are involved in the Adaptive Immune Response?
B cells and T cells (lymphocytes).
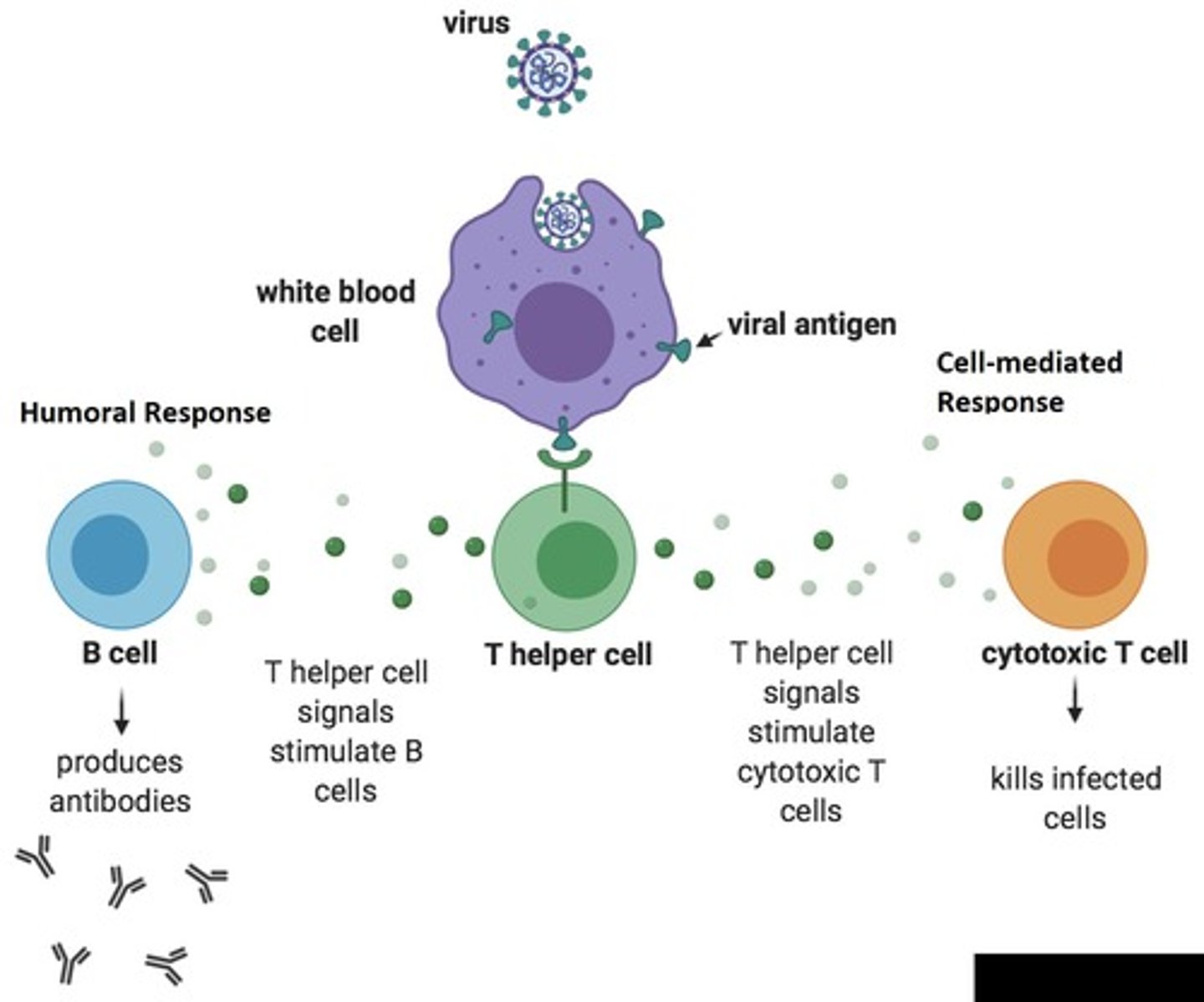
How long does it take for the Adaptive Immune Response to become upregulated?
Days to weeks.
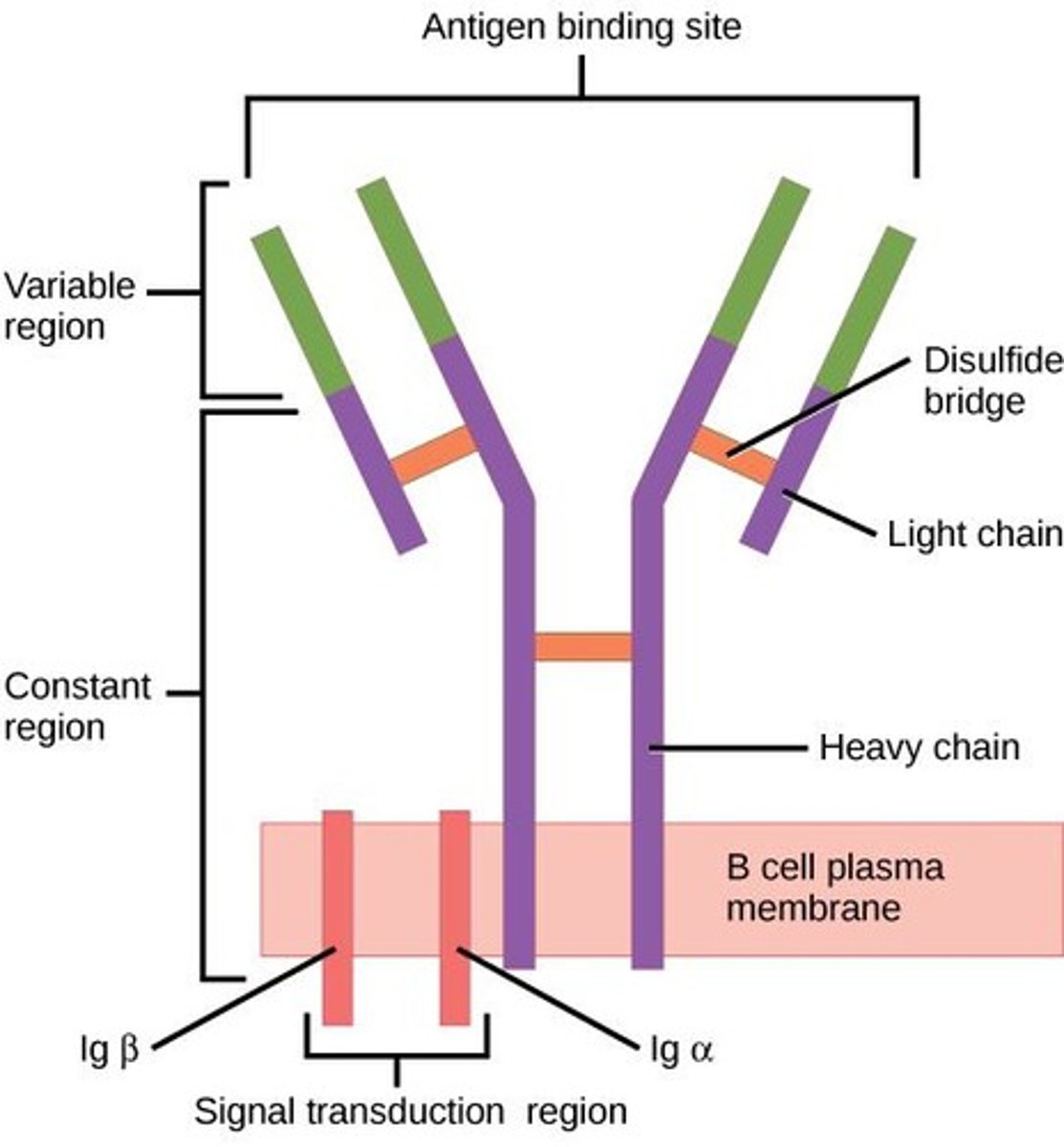
What are antibodies?
Proteins made by B cells that recognize specific antigens.
What is the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)?
Antigen presenting molecules that help T cells recognize antigens.
What is the difference between MHC Class I and Class II?
MHC Class I is found on all nucleated cells, while MHC Class II is found on antigen presenting cells like B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages.
What are the three populations of T cells?
Helper T cells (TH), cytotoxic T cells (Tc), and T regulatory cells.
What is the function of Helper T cells?
They release cytokines to upregulate B cells and other immune cells.
What is the process called that allows for the diversity of B and T cell receptors?
Gene rearrangement.
What is lymph and its role in the immune system?
Lymph is a watery fluid that travels through lymph vessels and contains white blood cells; it helps detect foreign substances.
What happens during the Primary Immune Response?
Initial exposure to an antigen takes days to weeks for B and T cells to respond, resulting in memory cells that last for decades.
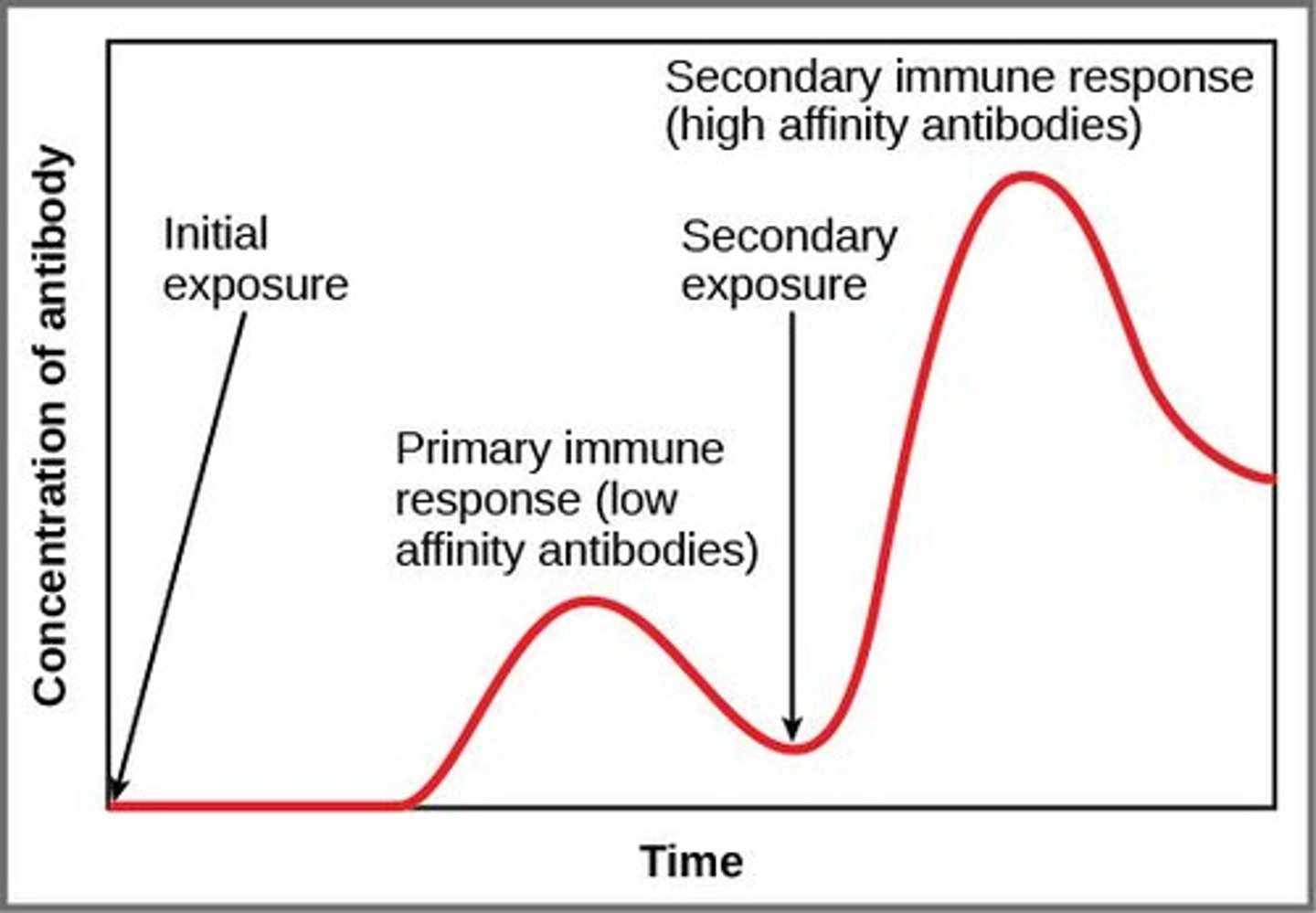
What is the Secondary Immune Response?
The faster response of memory cells upon re-exposure to the same antigen.
How does vaccination relate to the immune response?
Vaccination initiates a Primary Immune Response, allowing the body to create memory cells against a pathogen.
What are some potential issues with the immune system?
Chronic inflammation, allergies, autoimmunity, and immunodeficiency.
What is autoimmunity?
When the immune system mistakenly recognizes self-antigens as foreign, leading to tissue damage.
What is an example of a primary immunodeficiency?
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID).
What is an example of an acquired immunodeficiency?
AIDS, resulting from HIV infection.
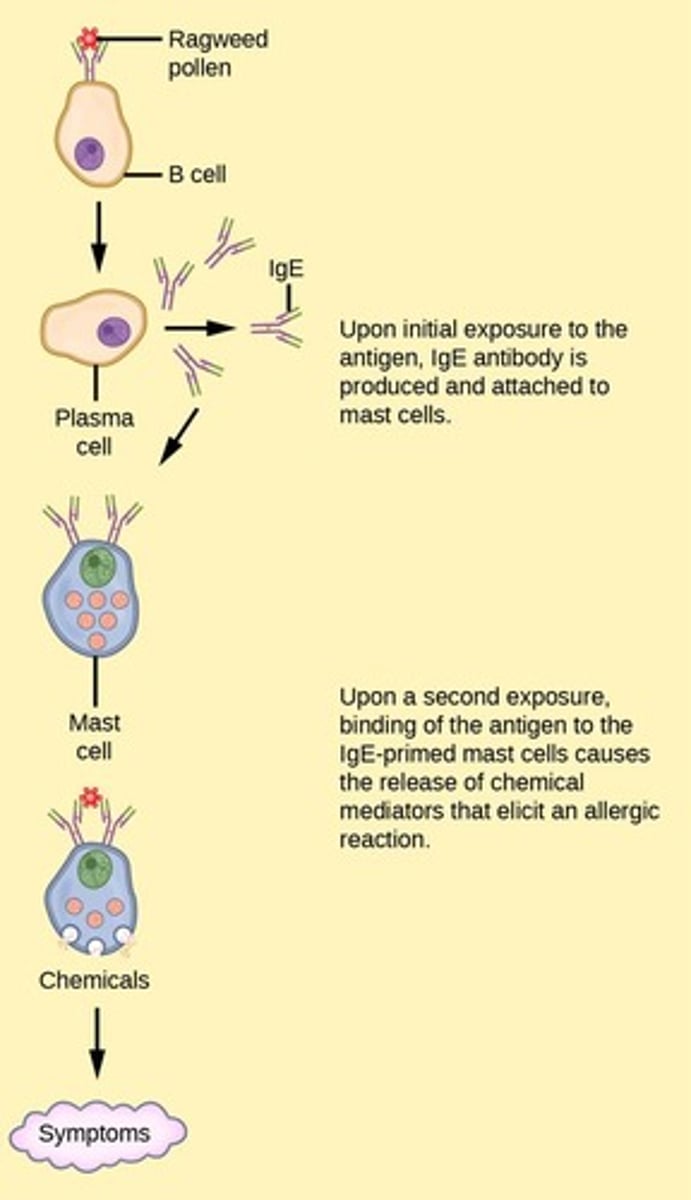
What triggers an allergic reaction?
An overreaction of the immune system to innocuous foreign substances.
Osmoregulation
process of maintenance of salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body's fluids
Both _____________and _______________contribute to the osmotic balance
electrolytes,
non-electrolytes
Important Cations
sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium
important Anions
chloride, carbonate, bicarbonate, phosphate
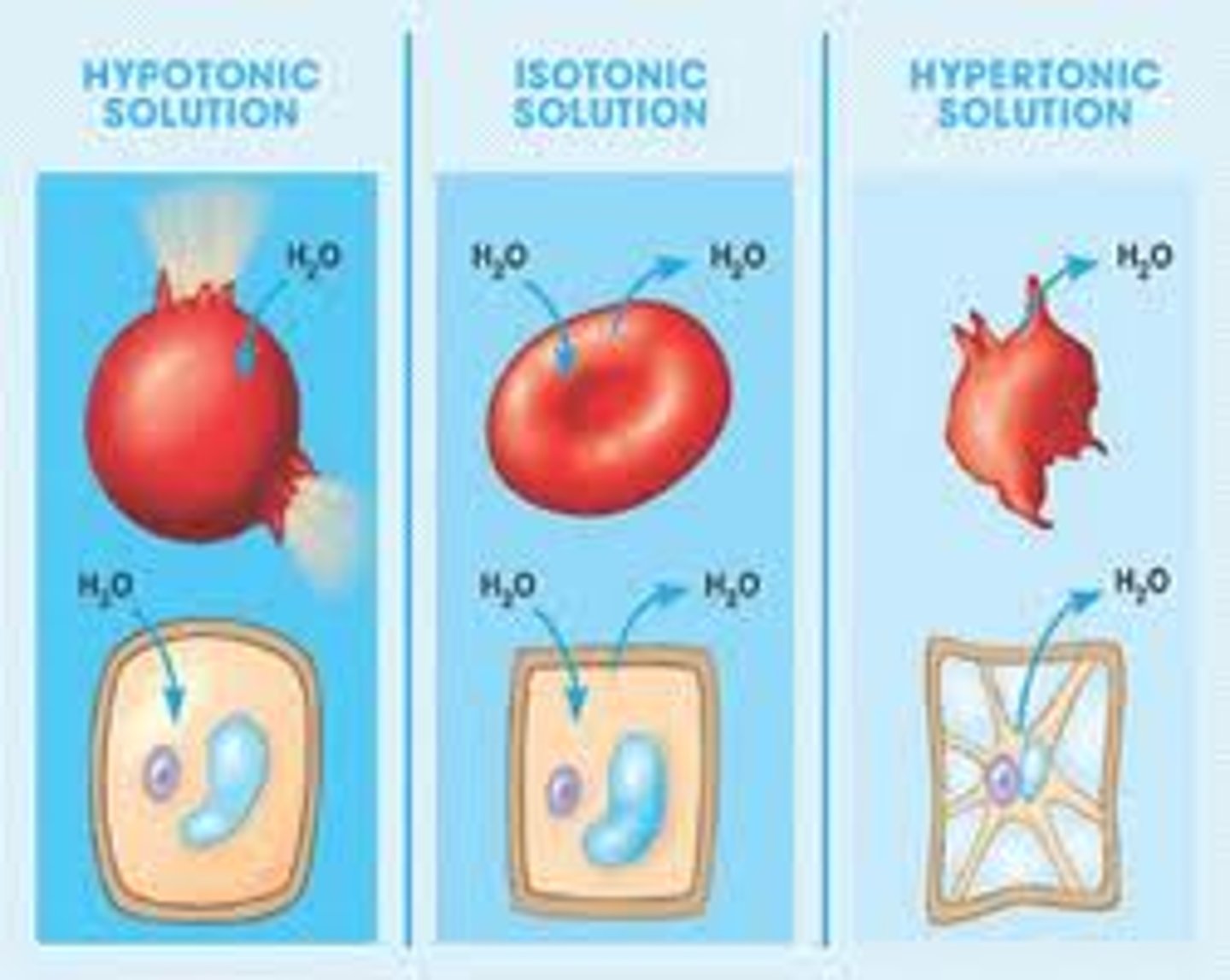
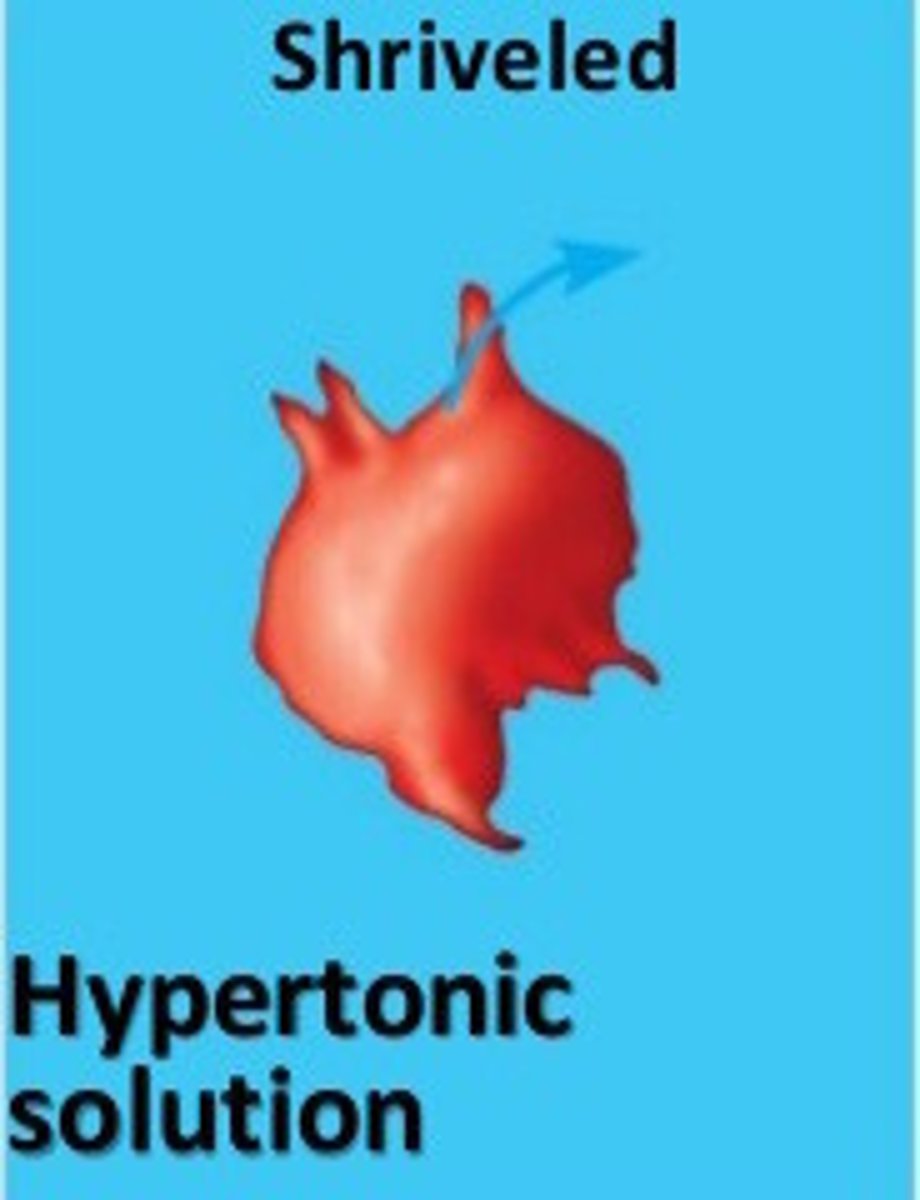
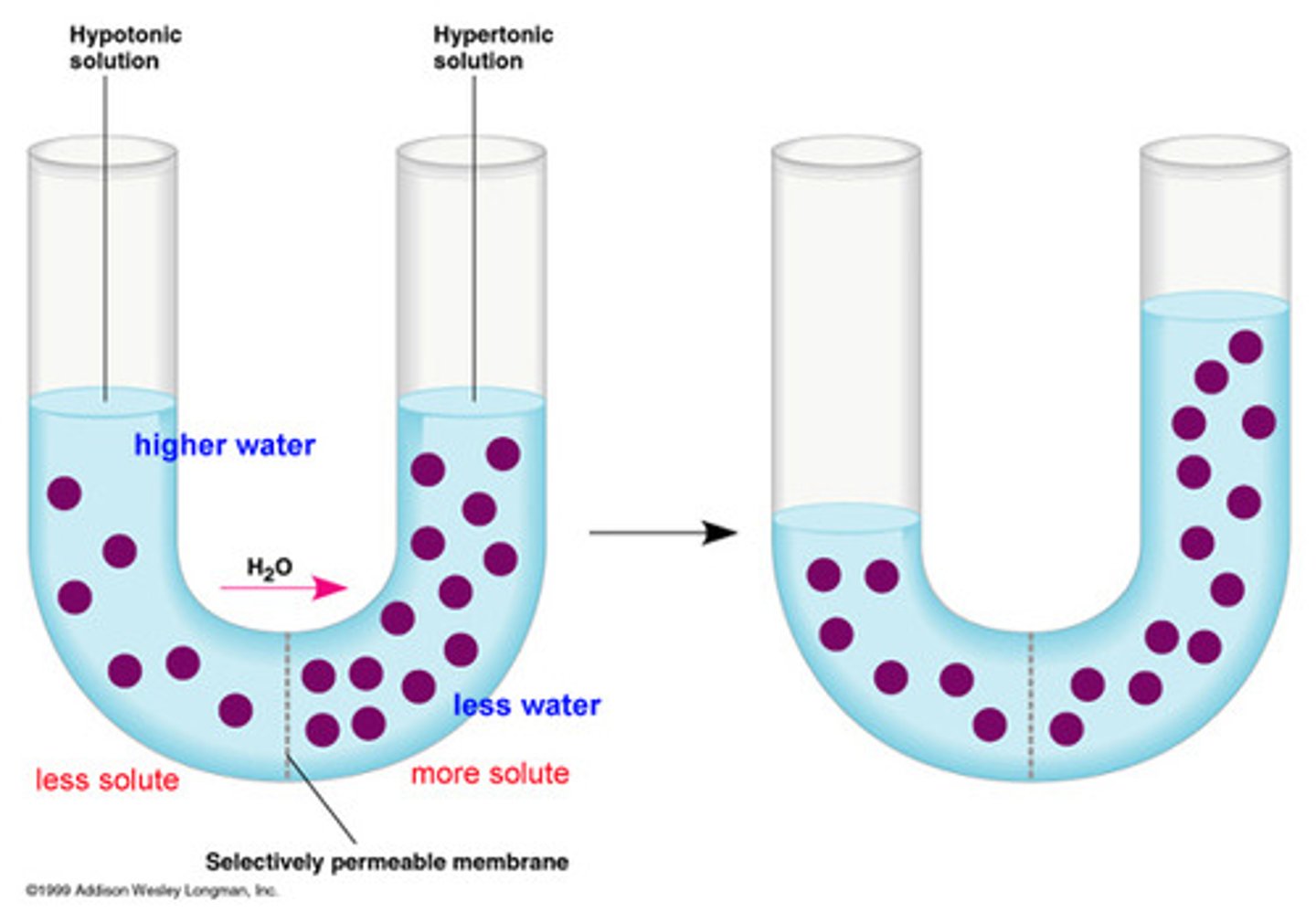
Hypertonic solution
Water comes out of the cell without being replenished causing it to shrink
no enough water
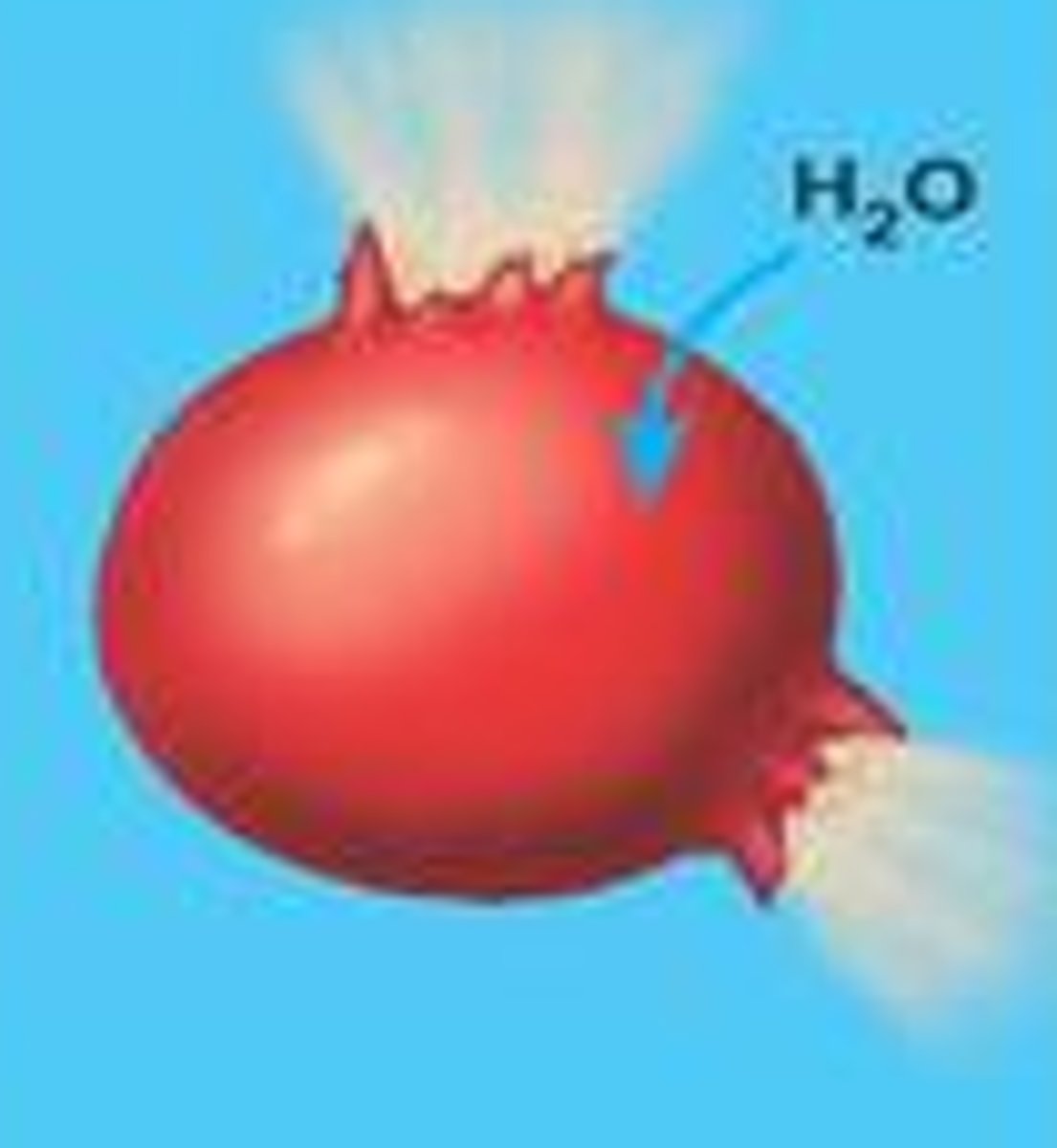
Hypotonic solution
Water overflows into the cell without having a way coming out busting the cells
not nought solutes

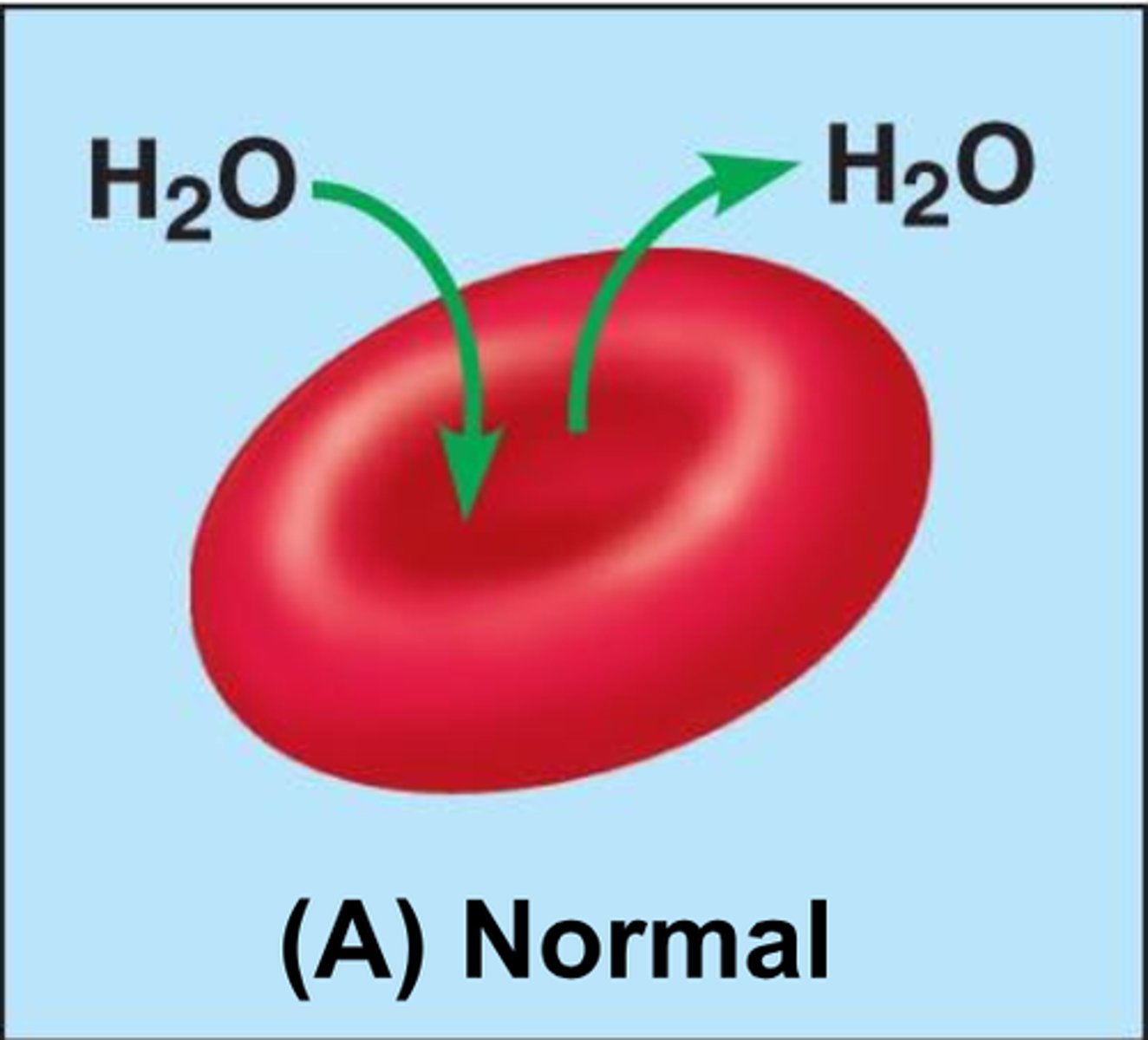
Isotonic solutions
cells retain their normal size and shape in isotonic solutions
better balance of both water and solutes
Osmoregulators
mechanisms to adapt to a variety of environments
Osmoconformers
Internal environment is osmotic (same
osmotic pressure) relation to the external environment.
excretory system
Regulates body fluid concentrations
Concentration of mineral ions depend on what two ions
Sodium and potassium
Water can enter the body through:
drinking, food, metabolism
Where does water go:
it moves to the region with the lowest water concentration
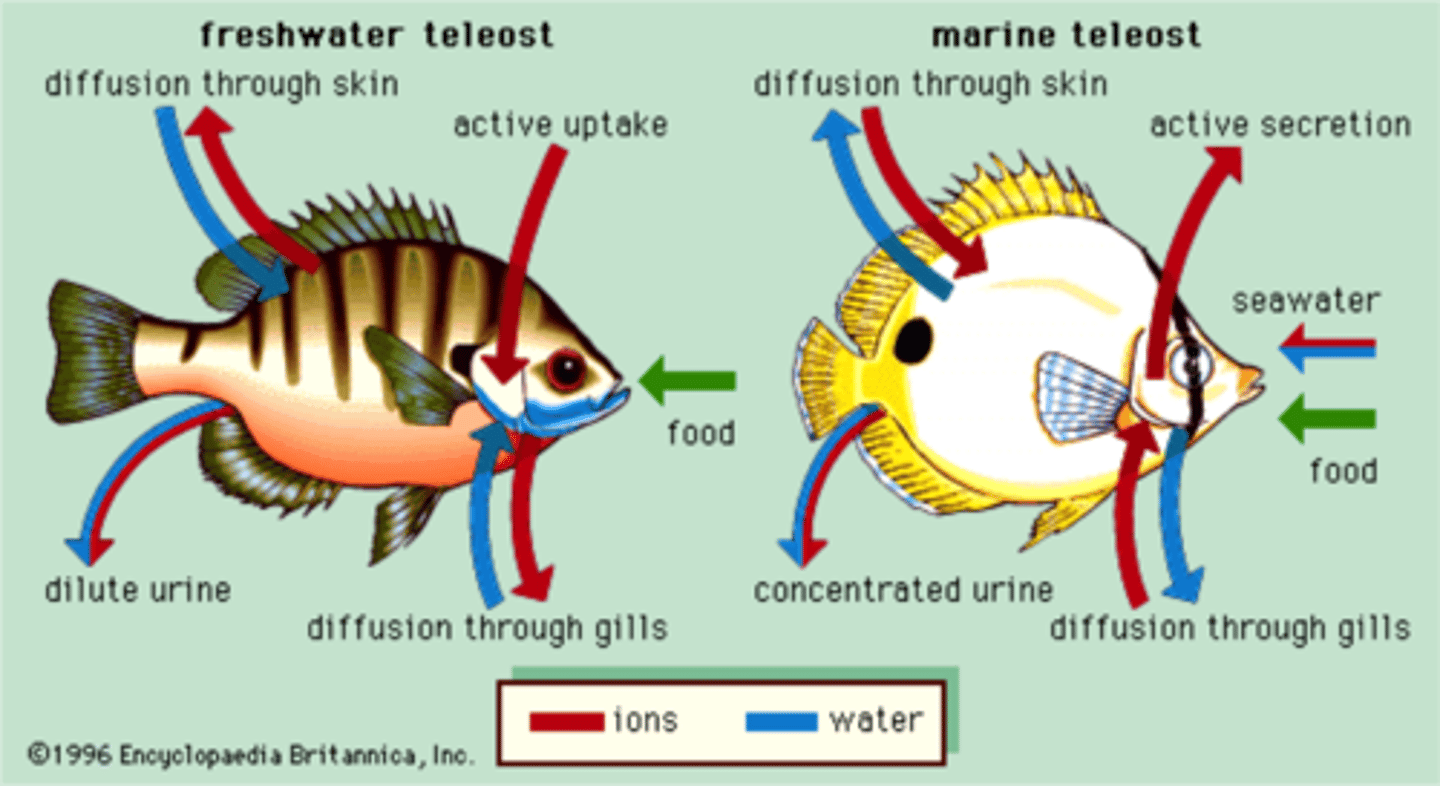
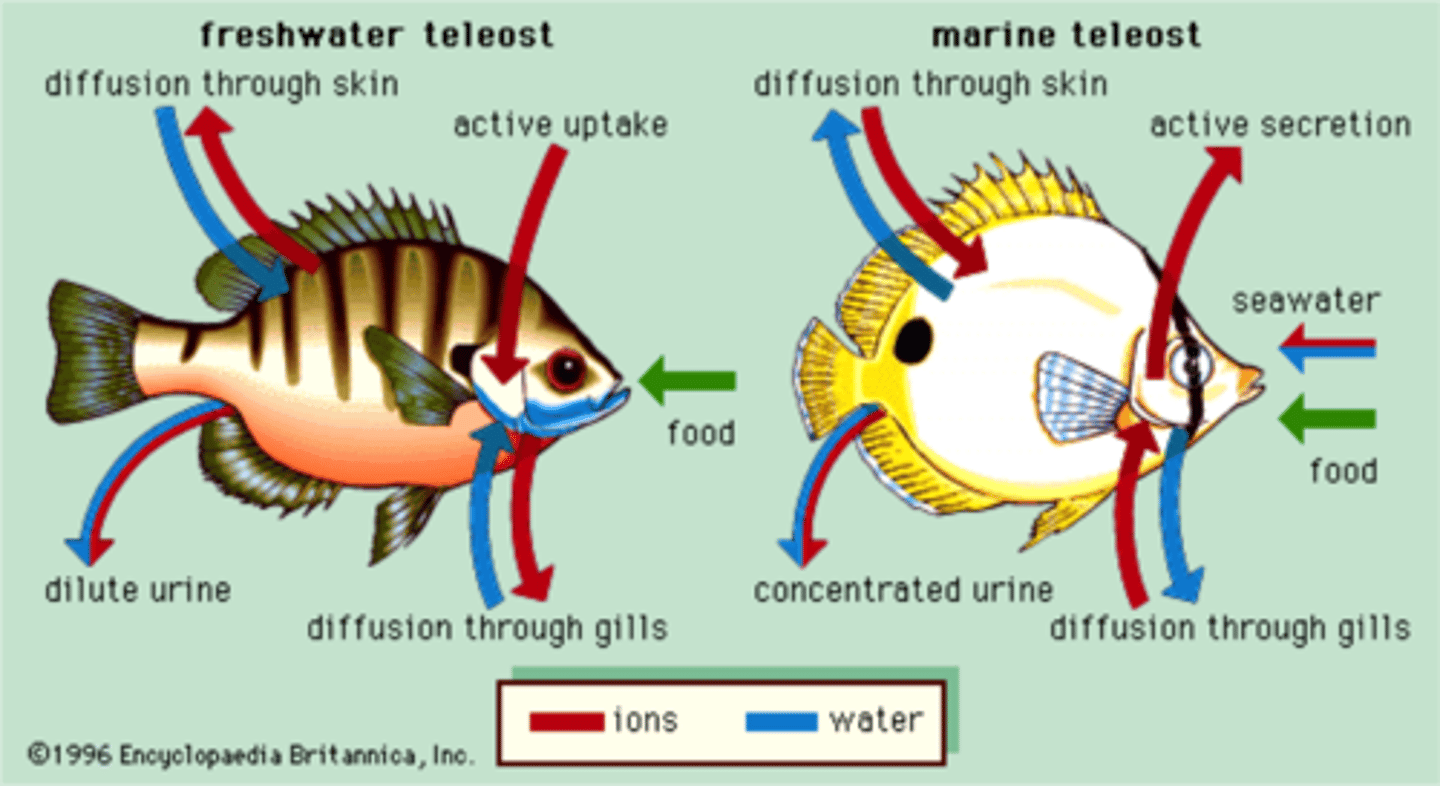
Marine environment
• High concentration of dissolved salts
• Tends to promote the osmotic loss of water, and
• The gain of ions by drinking water
• Marine invertebrates nearly isotonic to seawater
• Blood of cartilaginous fishes contains enough urea to match the
tonicity of sea water
Freshwater environment
• Tends to promote a gain of water by osmosis, and
• A loss of ions as excess water is excreted
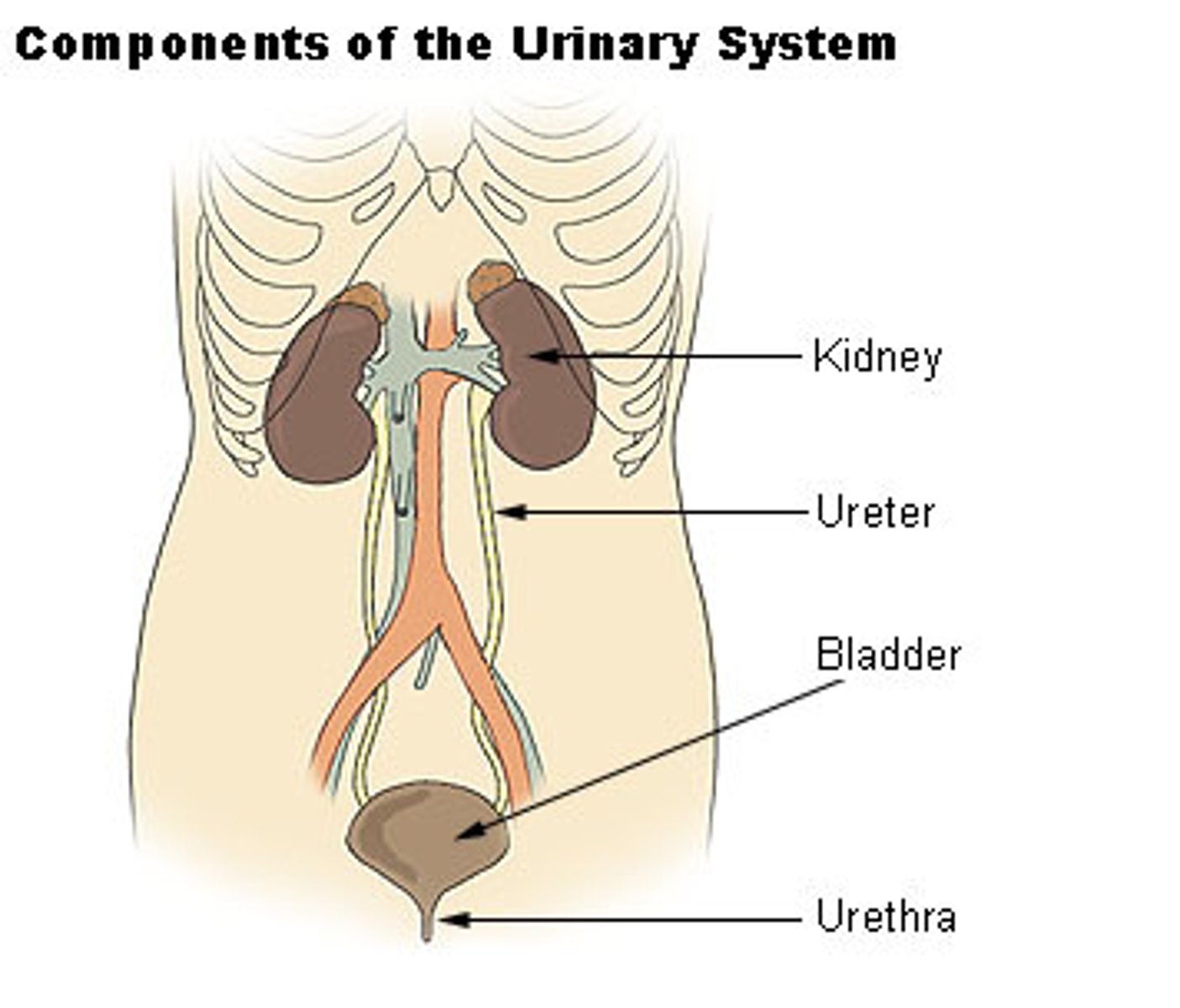
Where are the kidneys located?
either side of
vertebral column, just
below the diaphragm
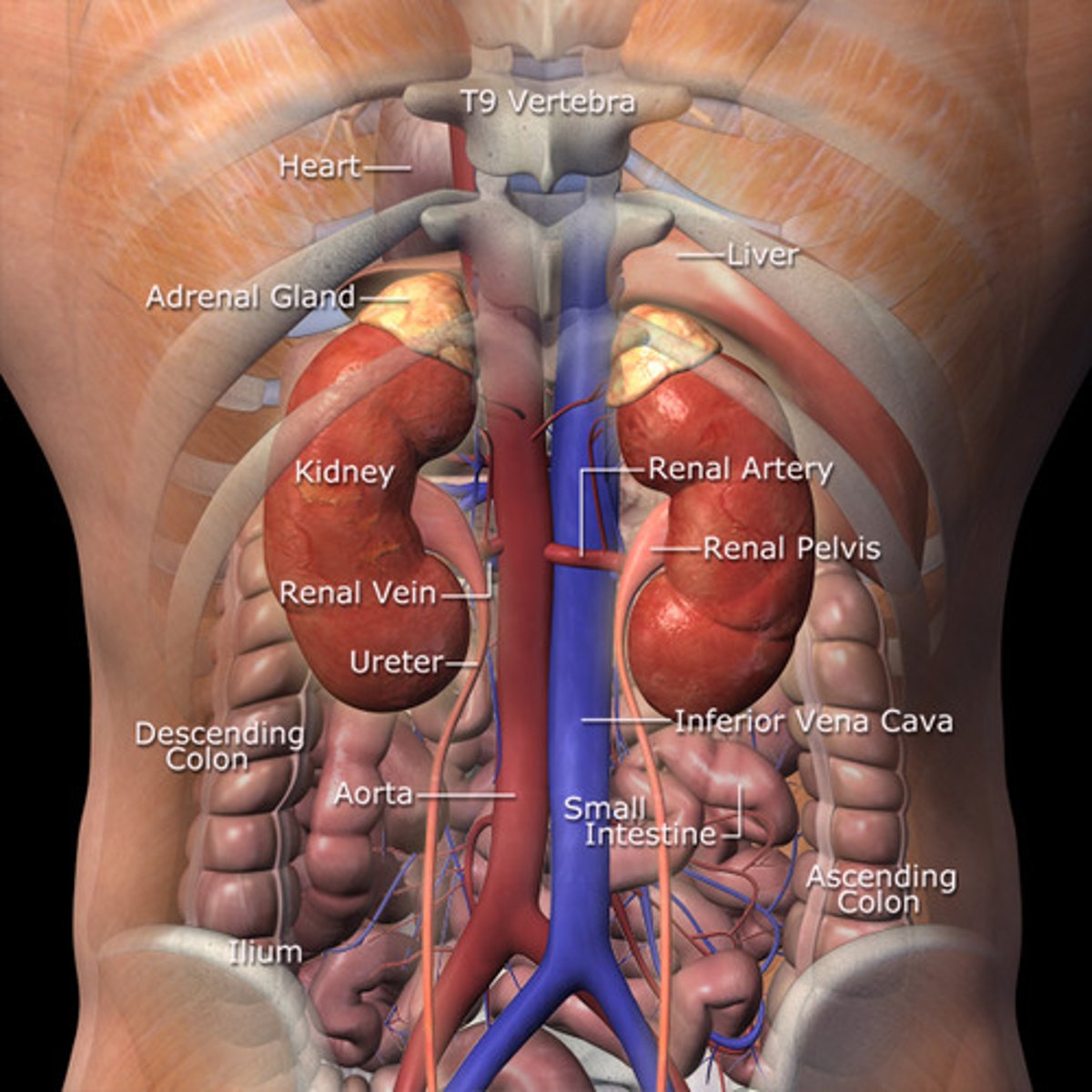
what is the tube like structure that carries the urine from the kidneys to the bladder
ureter
Collects urine from the kidney to the
urinary bladder
Urine voided through
urethra (tube between bladder and exit)
Each kidney composed of
millions of tubular nephrons
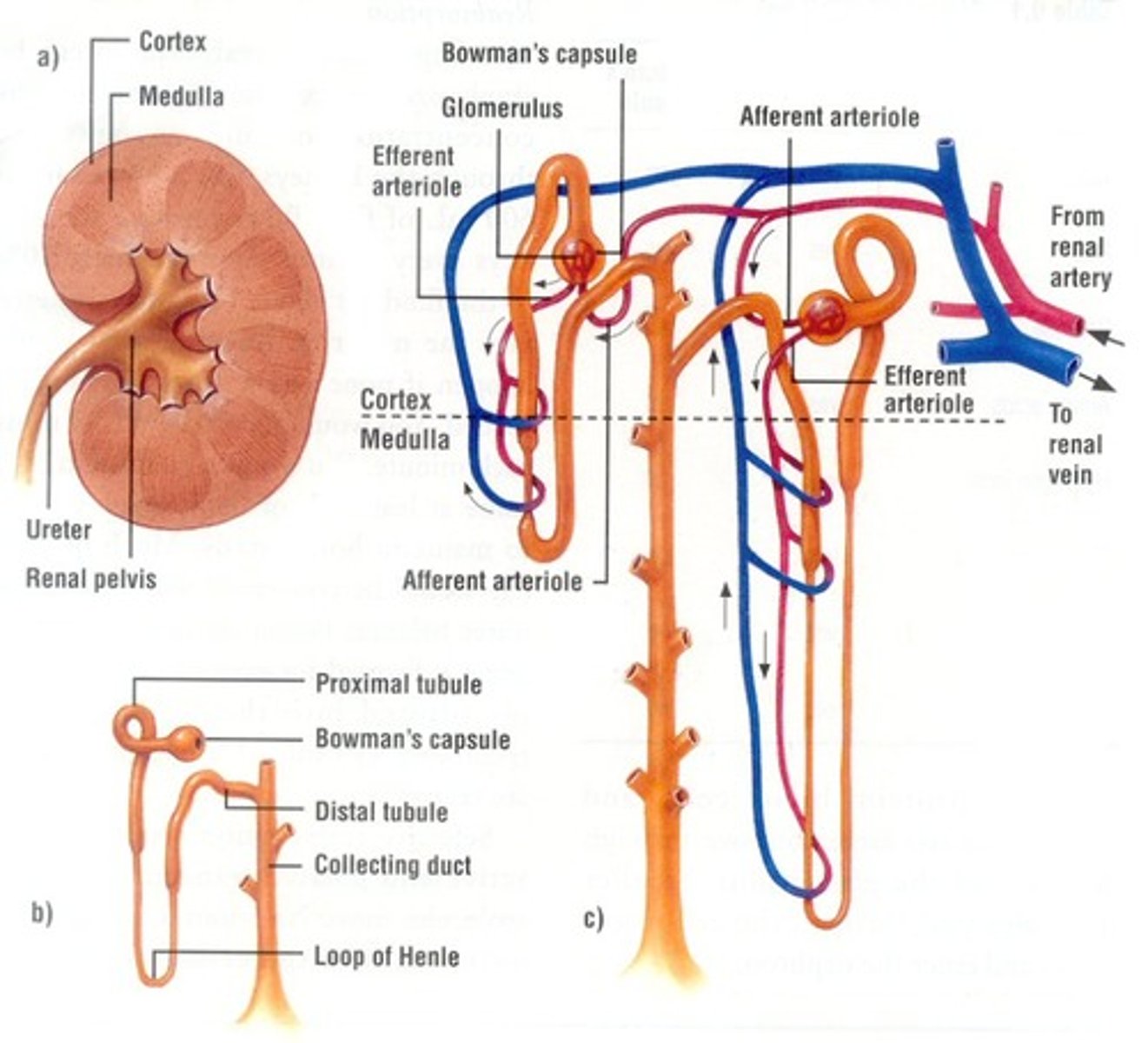
Each nephron composed of several parts:
• Glomerular capsule
• Glomerulus
• Proximal convoluted tubule
• Loop of the nephron
• Distal convoluted tube
• Collecting duct
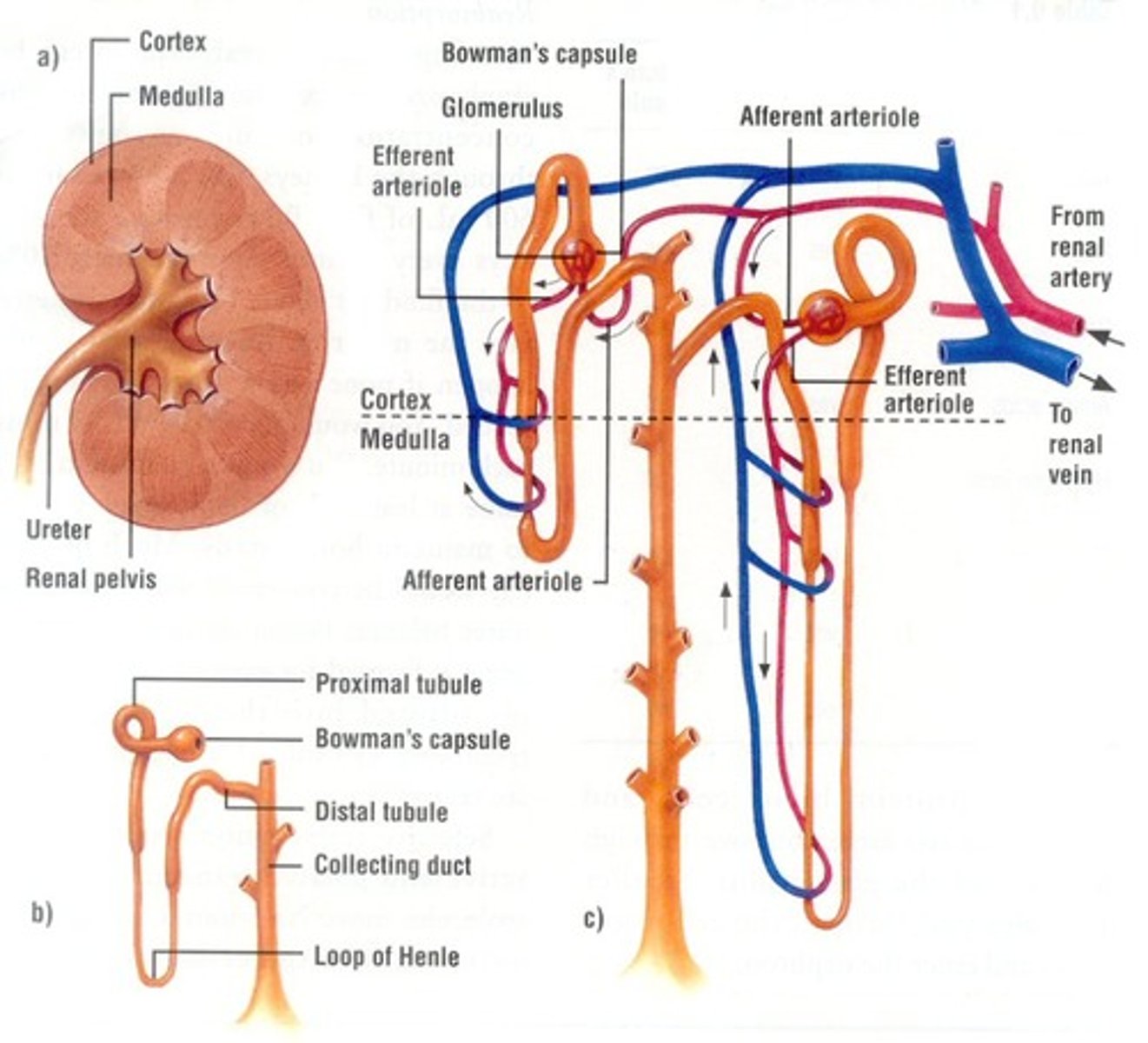
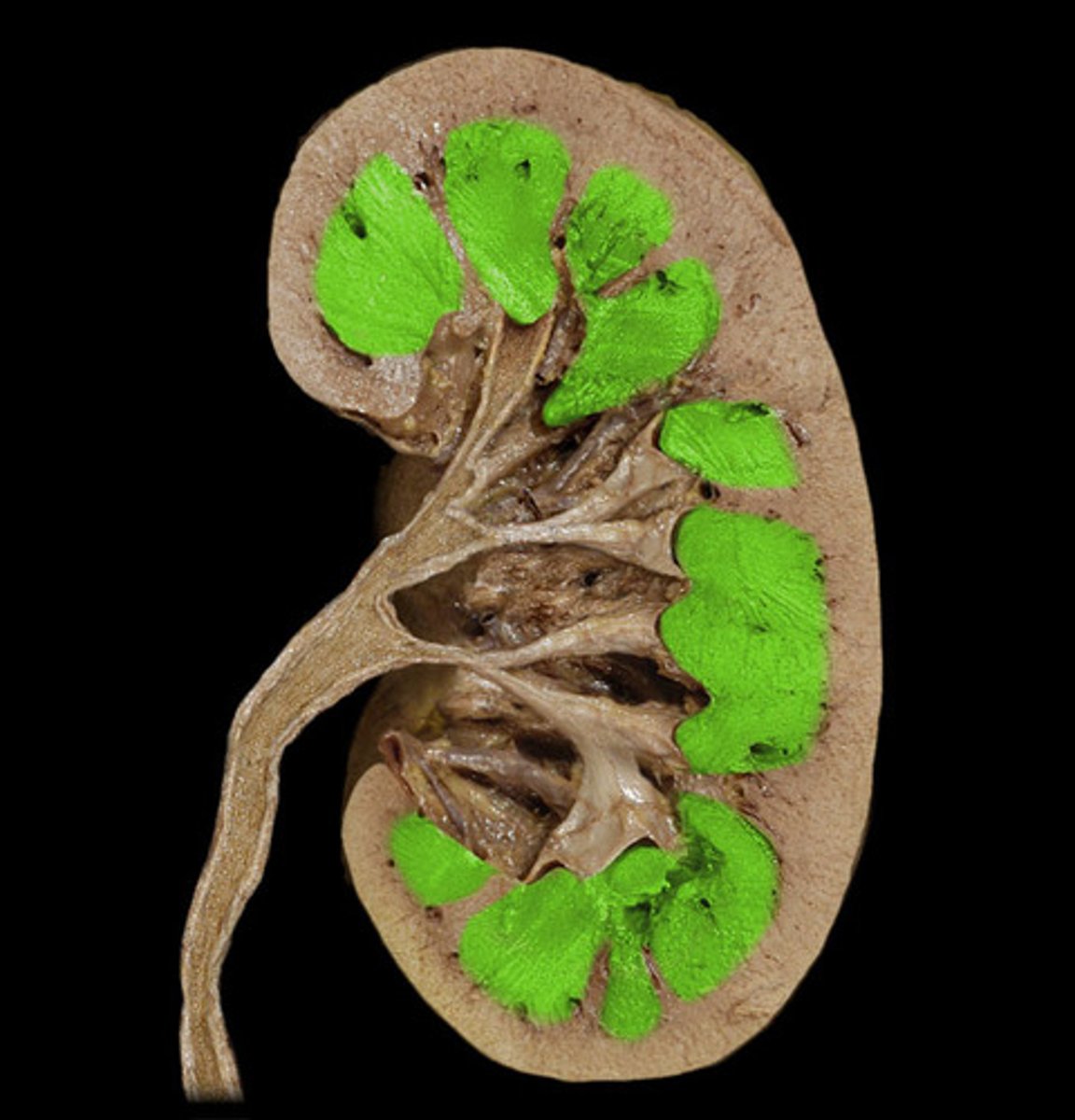
renal cortex
• Outer region
• Granular appearance
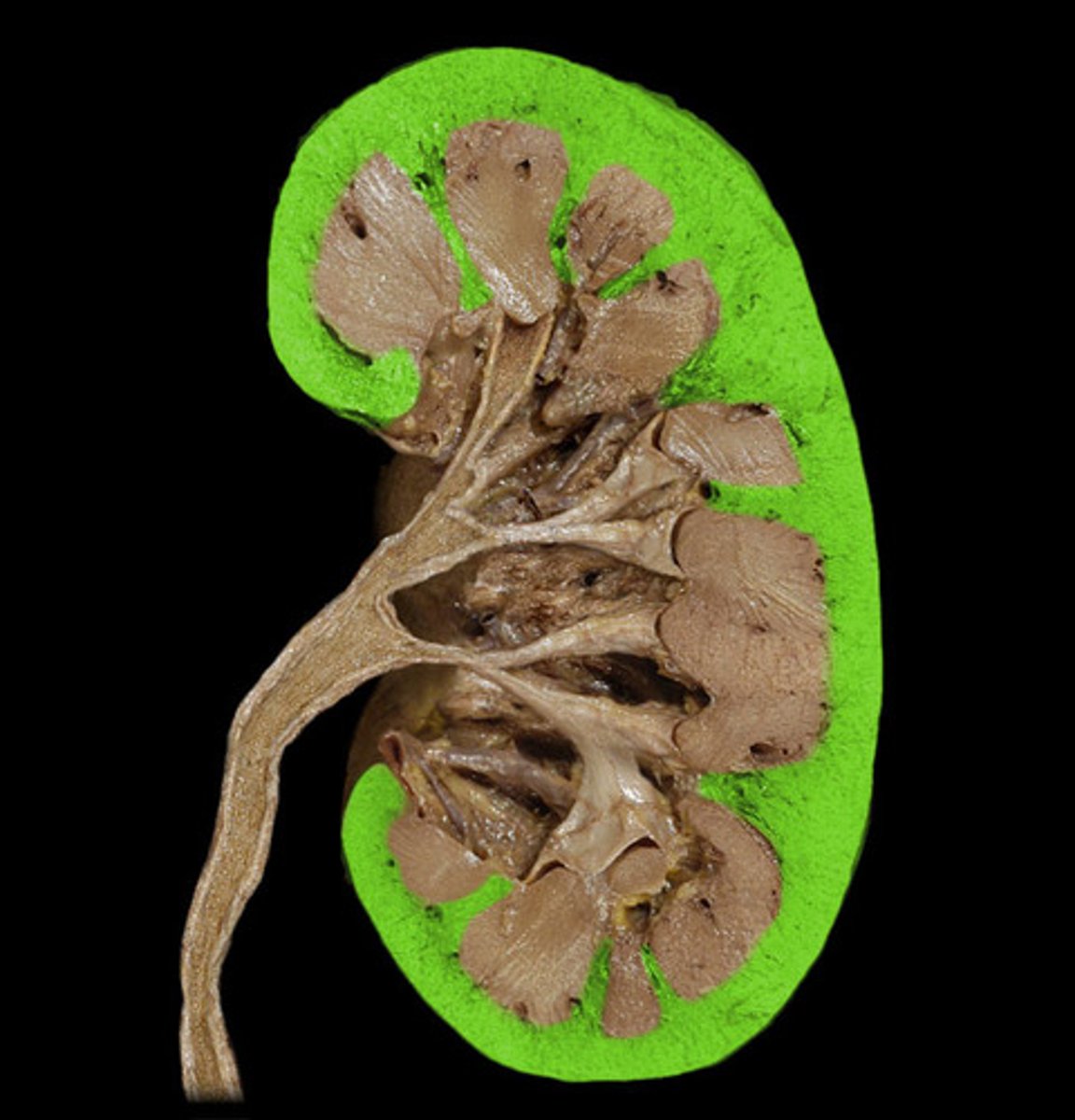
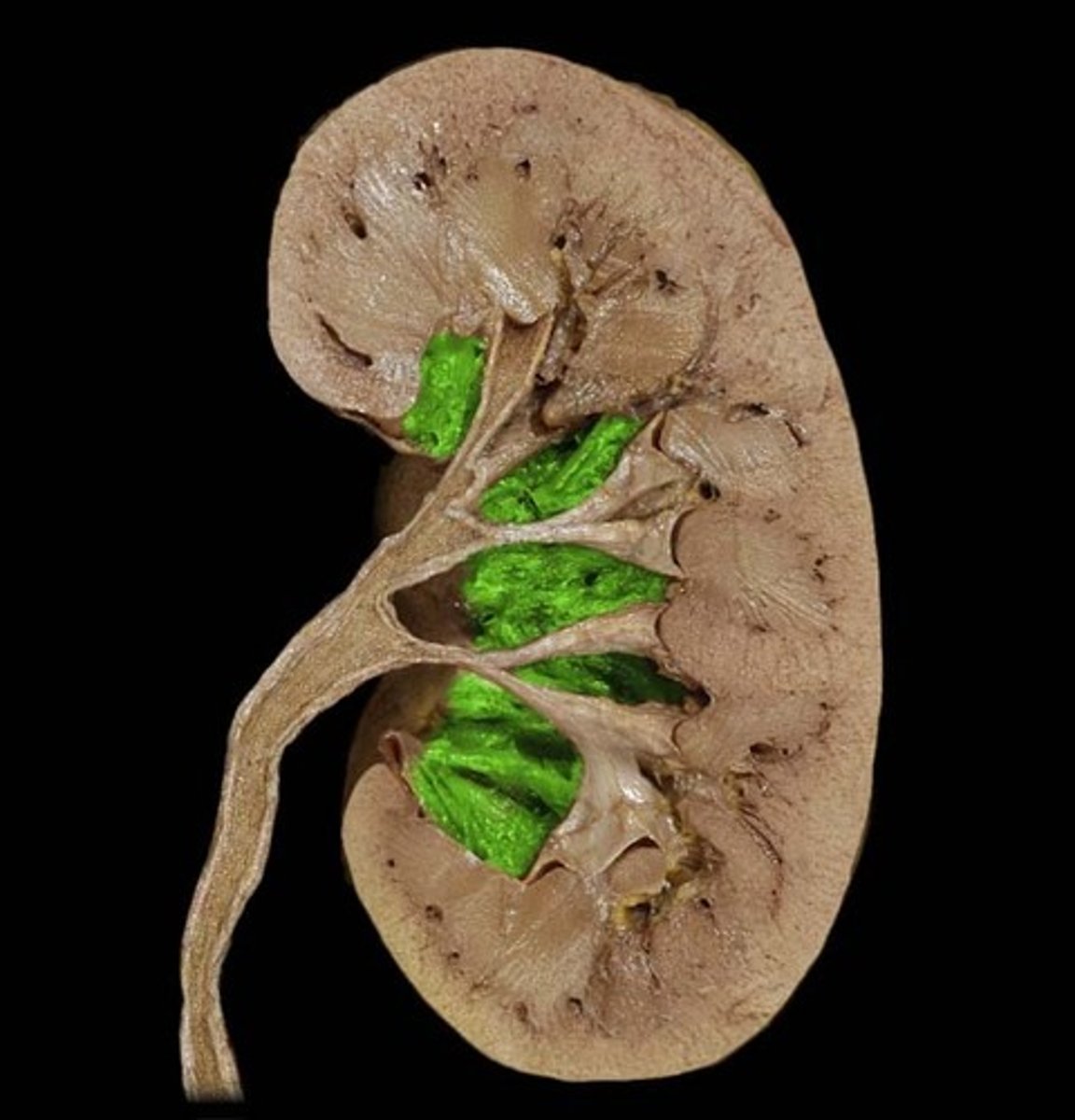
Renal medulla
• Cone-shaped renal pyramids
Renal pelvis
• Hollow-chambered innermost part of the kidney
Urine production requires three distinct processes:
• Glomerular filtration in glomerular capsule
• Tubular reabsorption at the proximal convoluted tubule
• Tubular secretion at the distal convoluted tubule
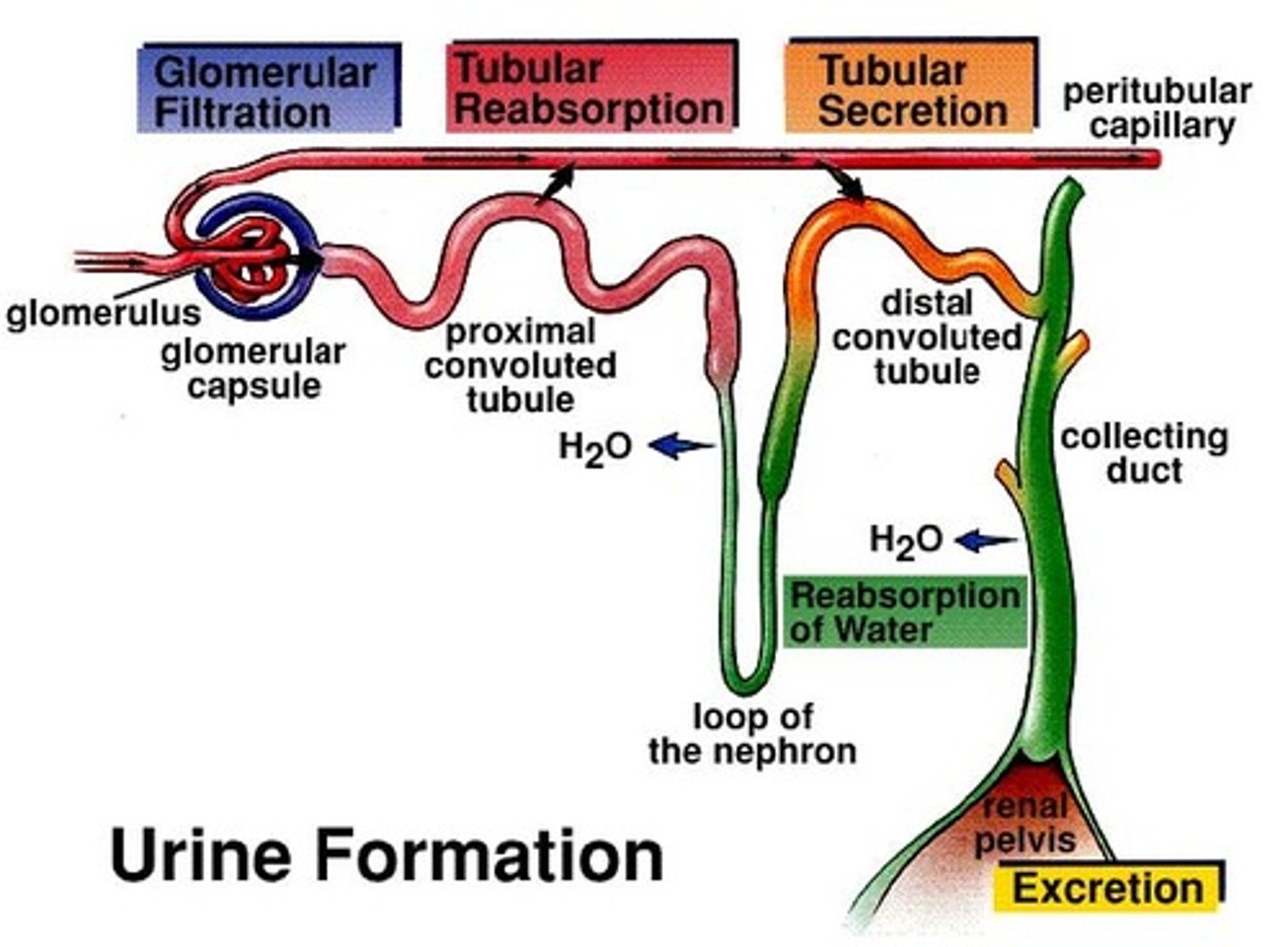
Most absorption occurs at the ____________________ ________________ in the Kidney
Proximal tubule
Excretion of hypertonic urine:
• Dependent upon the reabsorption of water
• Absorbed from
• Loop of the Henle
• The collecting duct
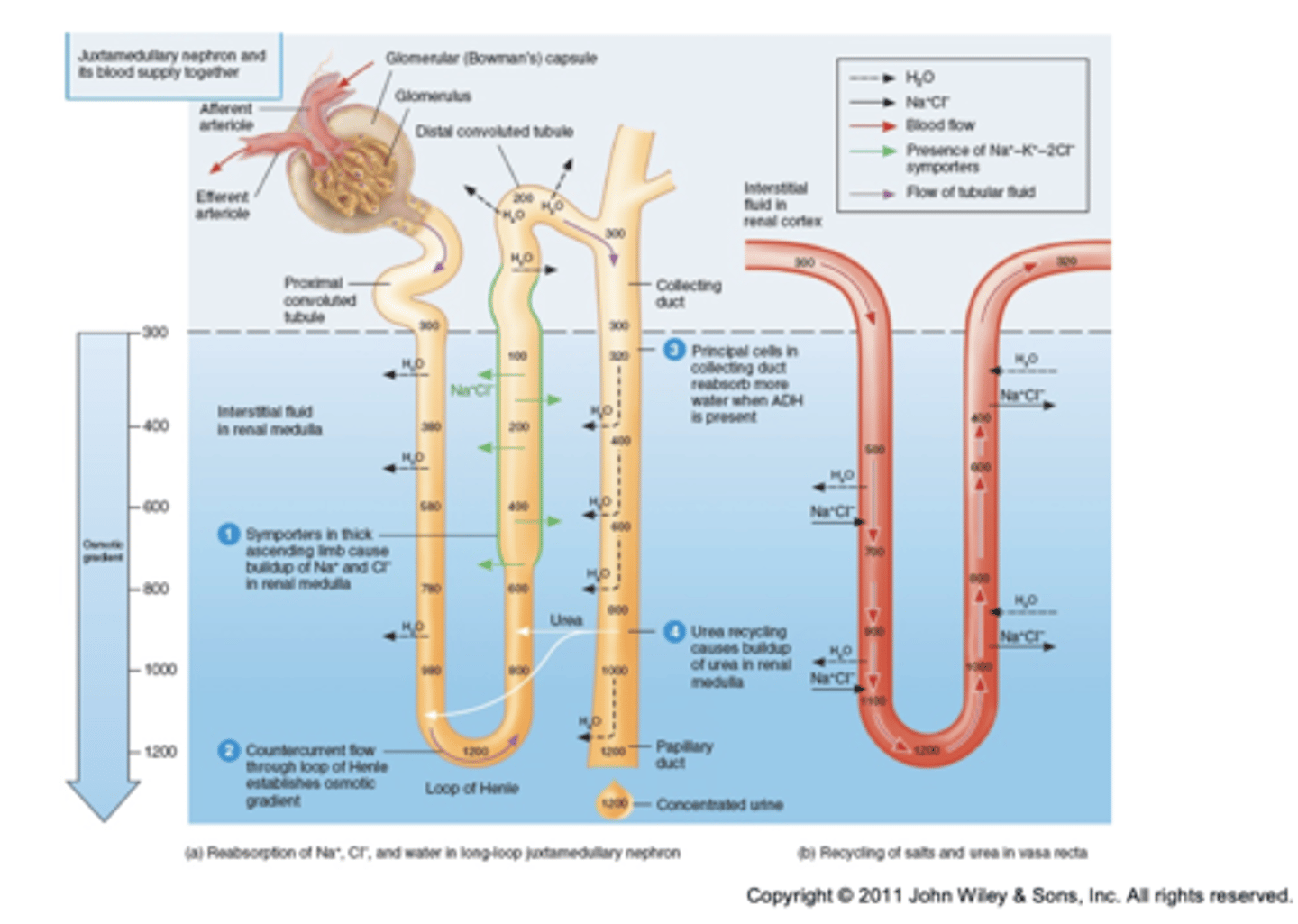
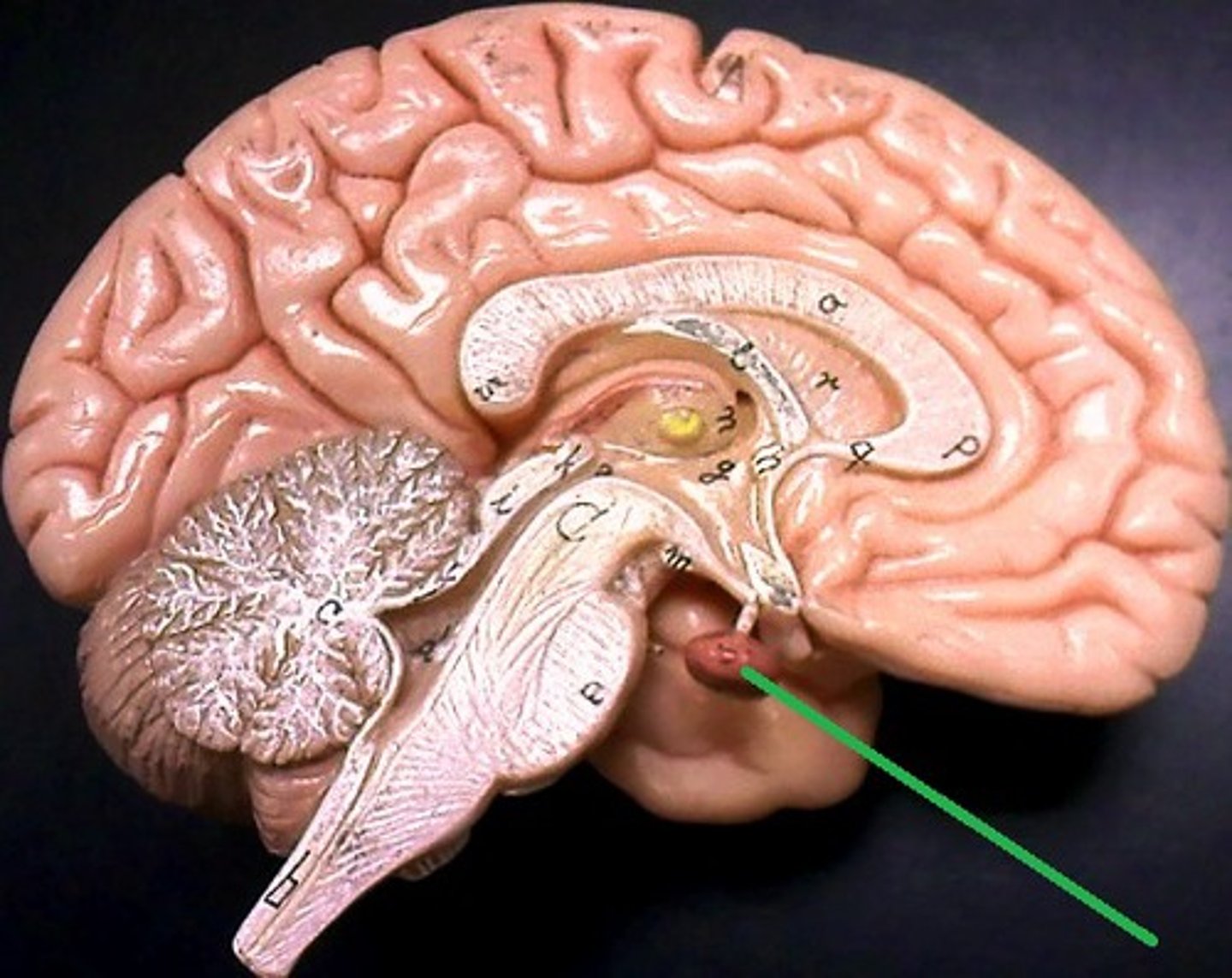
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, vasopressin)
• Plays a role in water reabsorption
• Released by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland (brain)
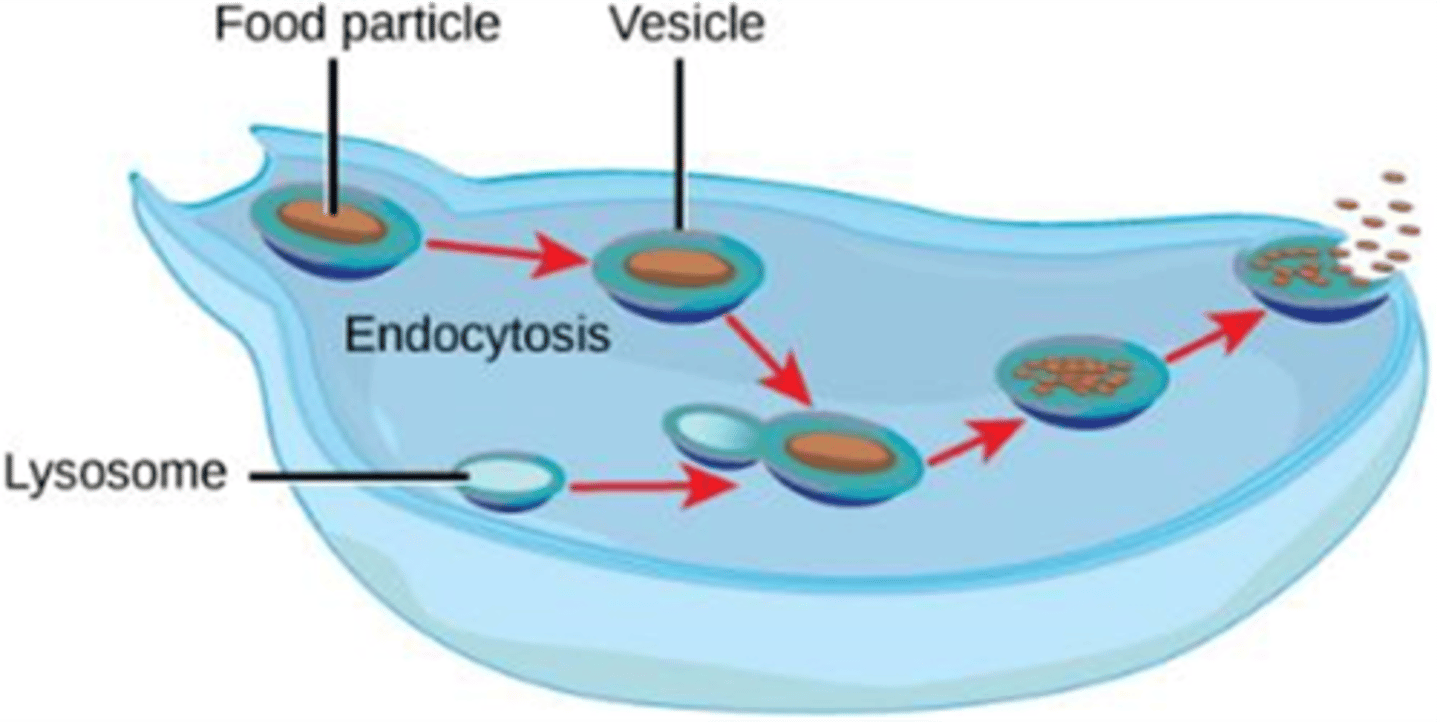
Some unicellular (invertebrates) organisms excrete wastes by
Exocytosis
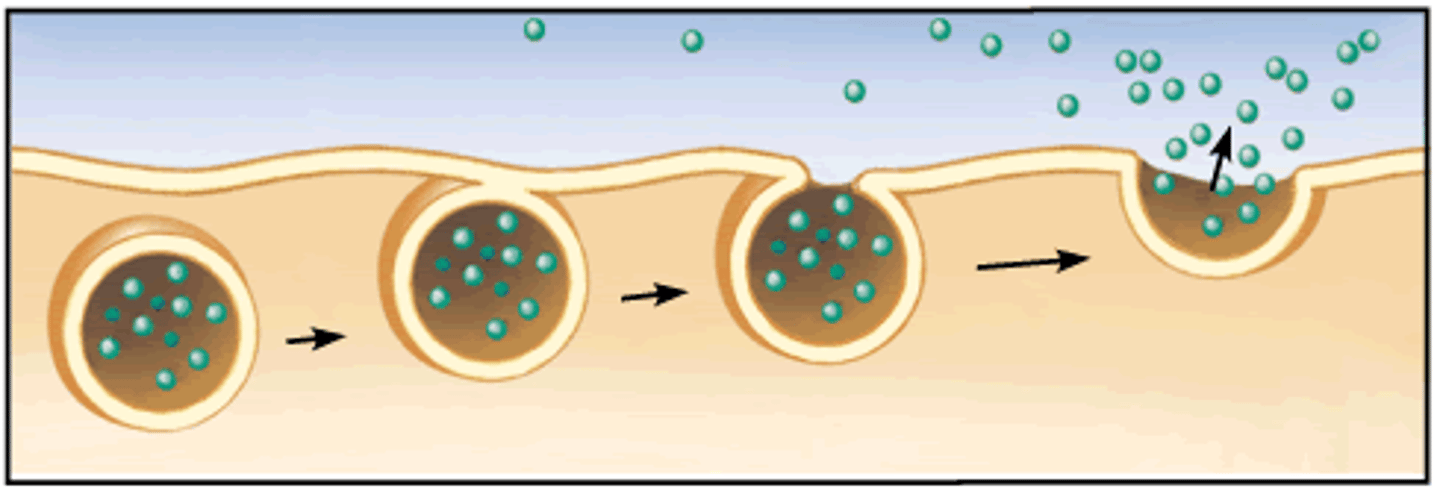
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane.
Most animals (invertebrates) have
tubular excretory organs

What do excretory organs do?
• Regulate the water-salt balance of the body
• Excrete metabolic wastes into the environment
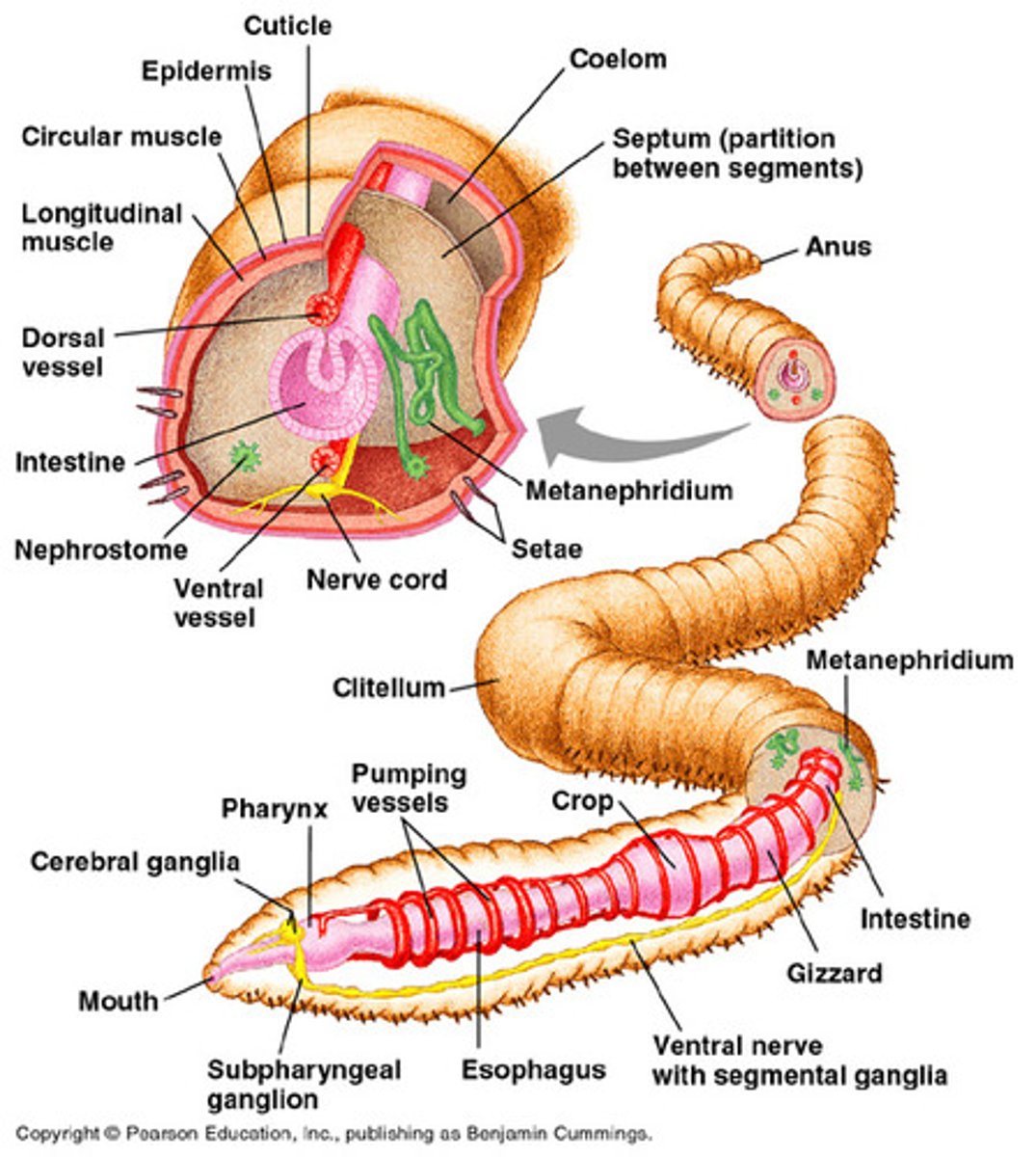
• Flame Cells
• Nephridia
• Malpighian Tubules
Planarians
Earthworms
Insects
Invertebrates
• Most are isotonic with water they live in
• Osmoconformers

Bony Fishes
• Body fluids of bony fishes with only moderate amount of salt
• Osmoregulators
• Some manage to adjust to both, salt and fresh water
(salmons), most cannot.

Cartilaginous fishes (sharks, rays...)
• Achieve isotonicity by having high concentrations of organic
compounds (urea in blood)

Terrestrial (land) animals lose water through
excretion and
respiration

Where is sodium filtered?
filtered at glomerulus is returned to blood at the distal convoluted tubule
more than 99%
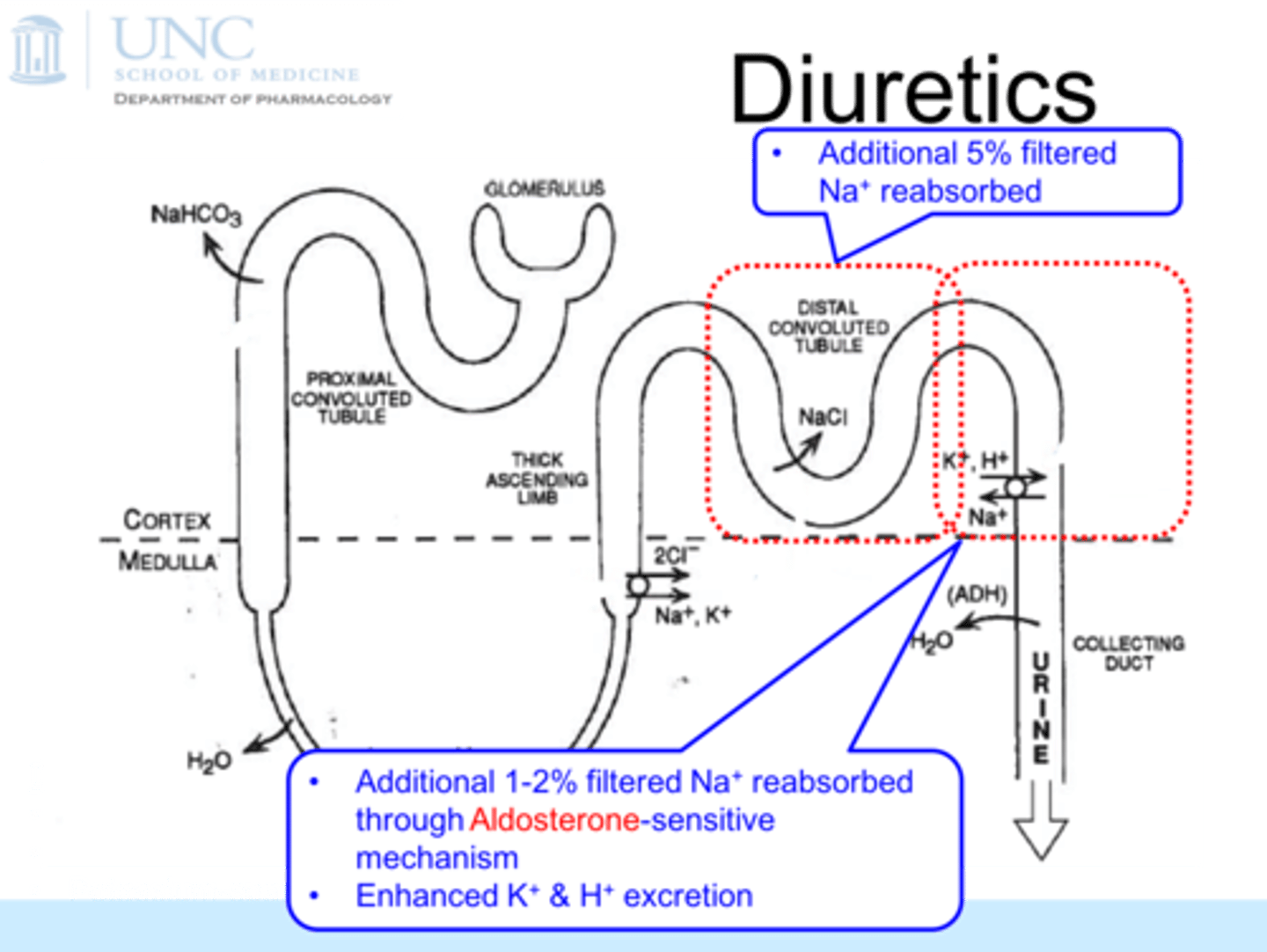
What regulates reabsorption
(both sodium and water )
bonus: what are the specific ___________, ____________________and __________
hormones
aldosterone, renin, Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
pH adjusted by either
• The reabsorption of the bicarbonate ions,
• The secretion of hydrogen ions
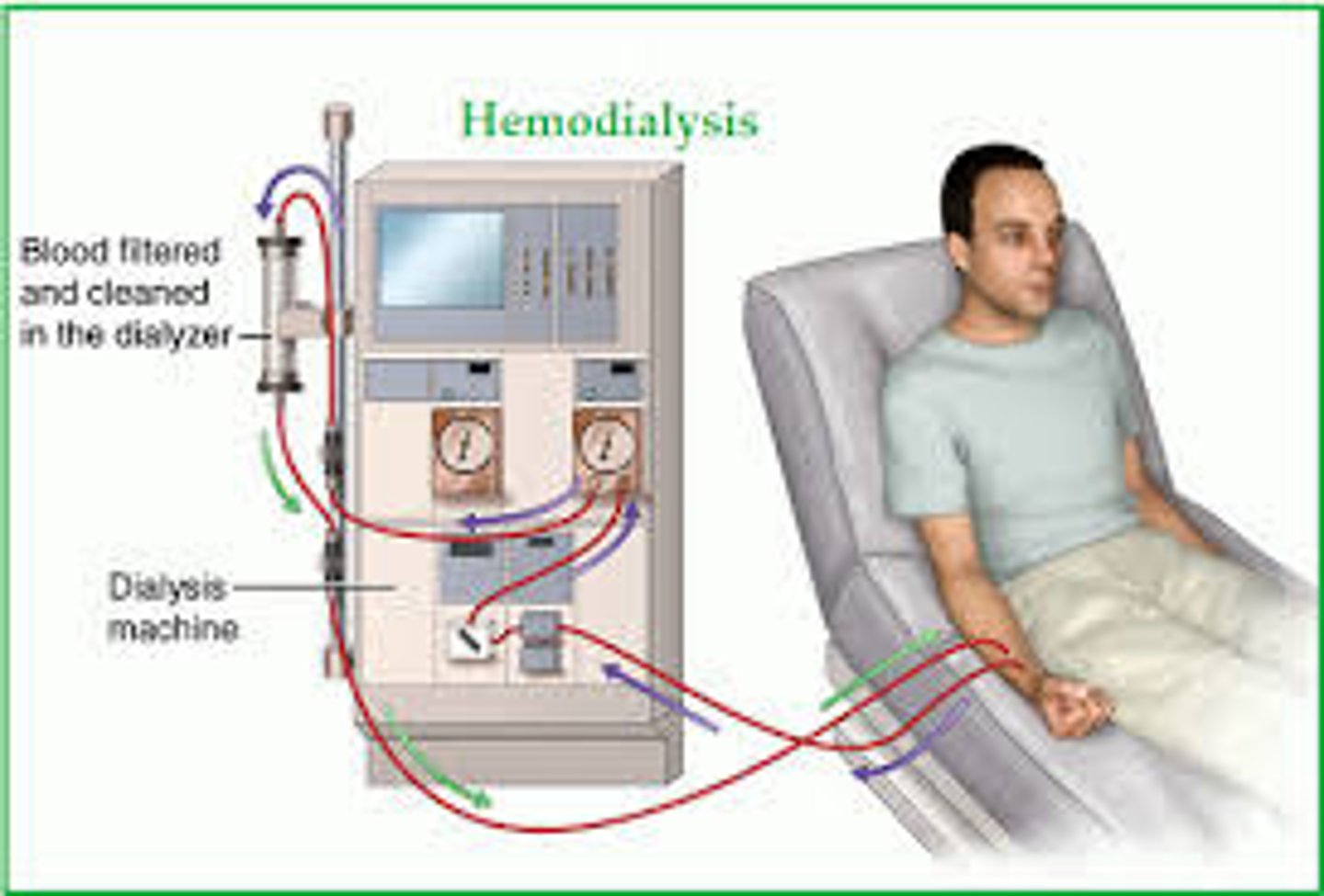
Hemodialysis
The clinical purification of blood by dialysis, as a substitute for the
normal function of the kidney.
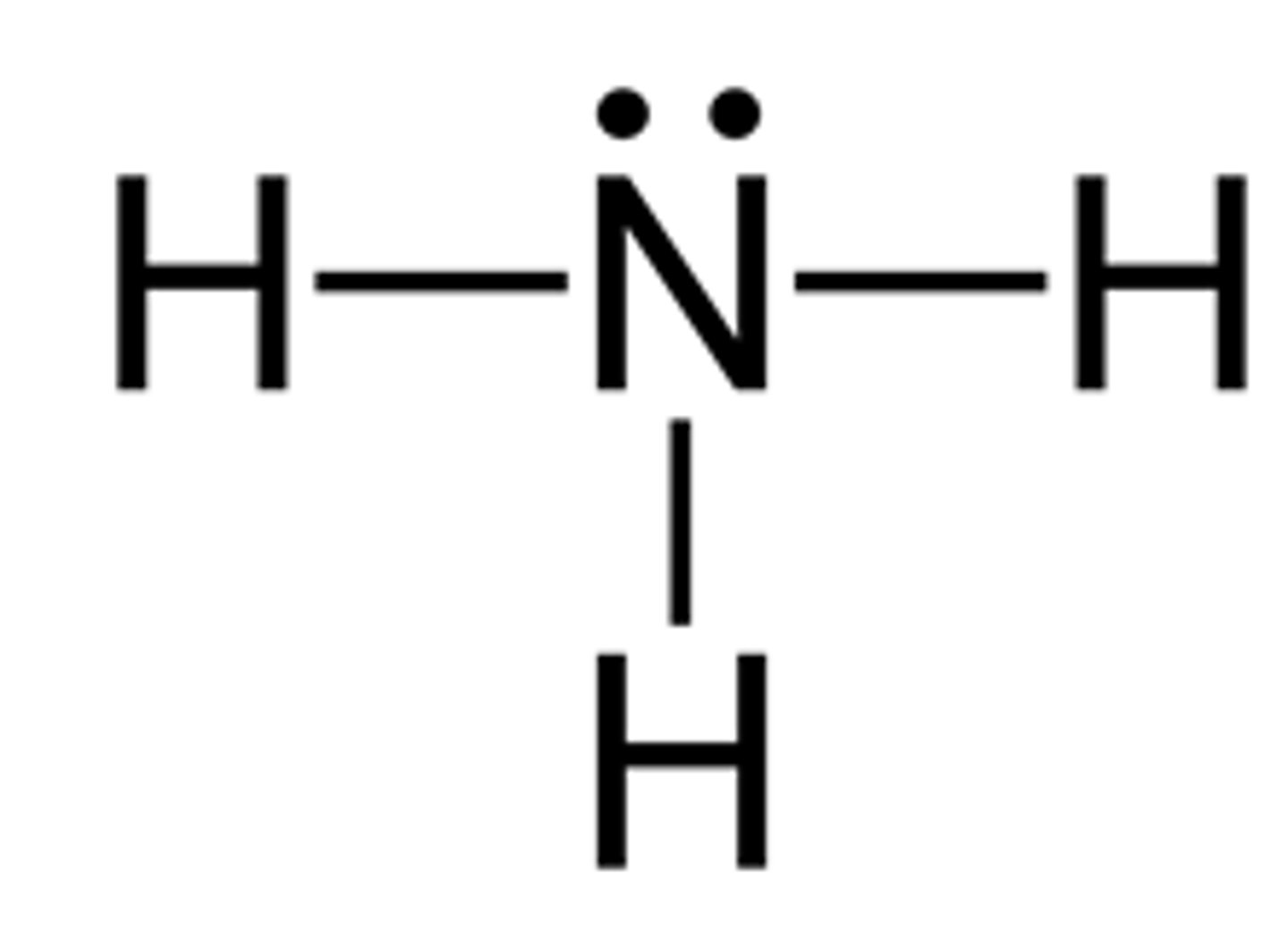
Catabolism of amino acids and nucleic acids results
In ammonia
• High solubility (of ammonia) permits it to be excreted directly by many __________________ ___________________
• ______________ _________________ must convert ammonia to urea or uric
acid
aquatic animals
terrestrial animals
_______________ causes loss of much water per unit of nitrogen
Urea
• Mammals and amphibians
• Must drink lots of water
___________ ___________ requires much less water per unit of nitrogen
excreted
Urea acid
• Reptiles, birds, and arthropods
• Allows invasion of drier habitats far from standing water
Nitrogenous Waste is created in aquatic animals
proteins
|
amino acids
|
NH2
|
most fishes and other aquatic animals
|
Ammonia
Nitrogenous Waste is created in mammals
proteins
|
amino acids
|
NH2
|
adult amphibians,
sharks, and mammals
|
Urea
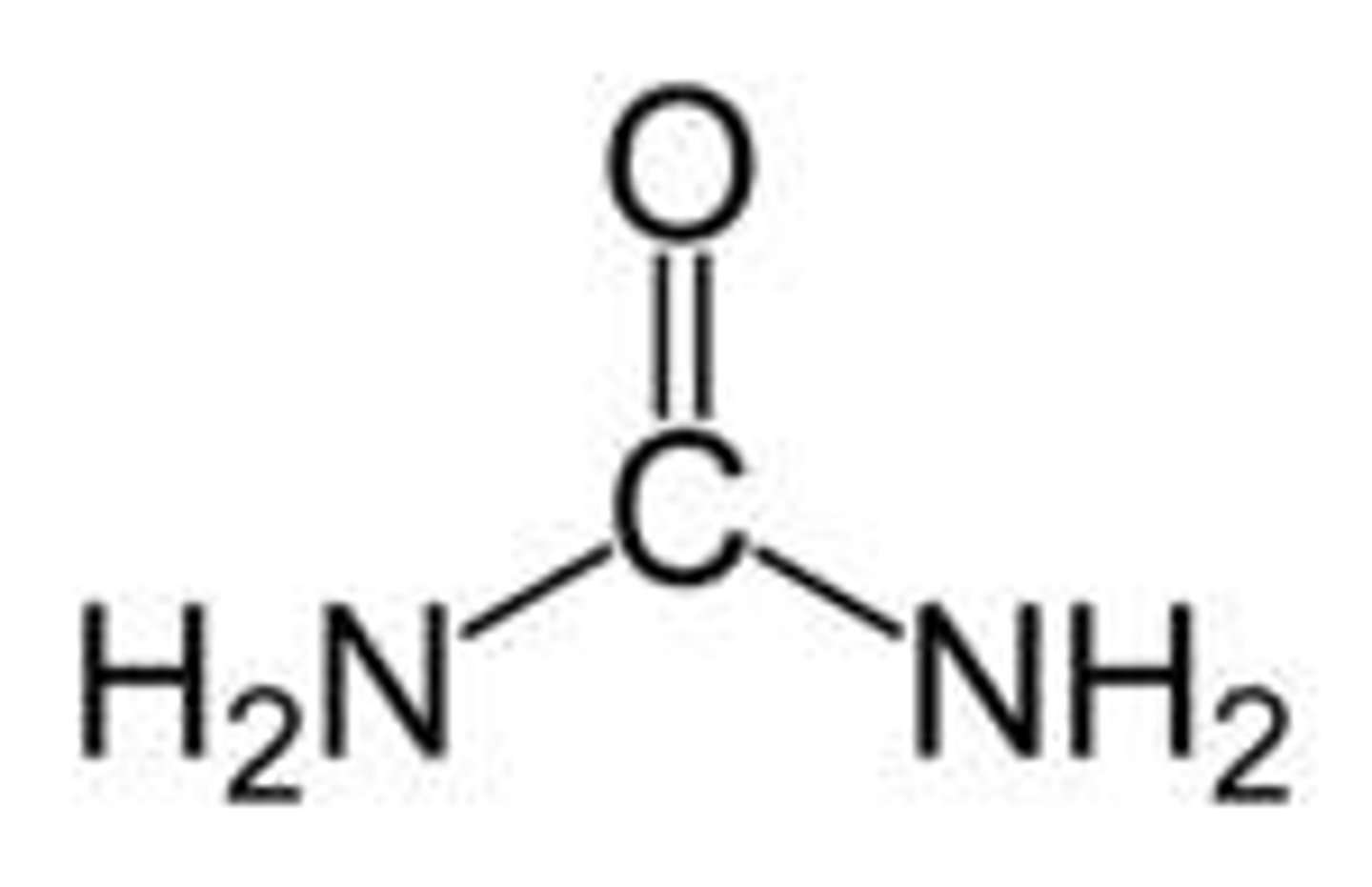
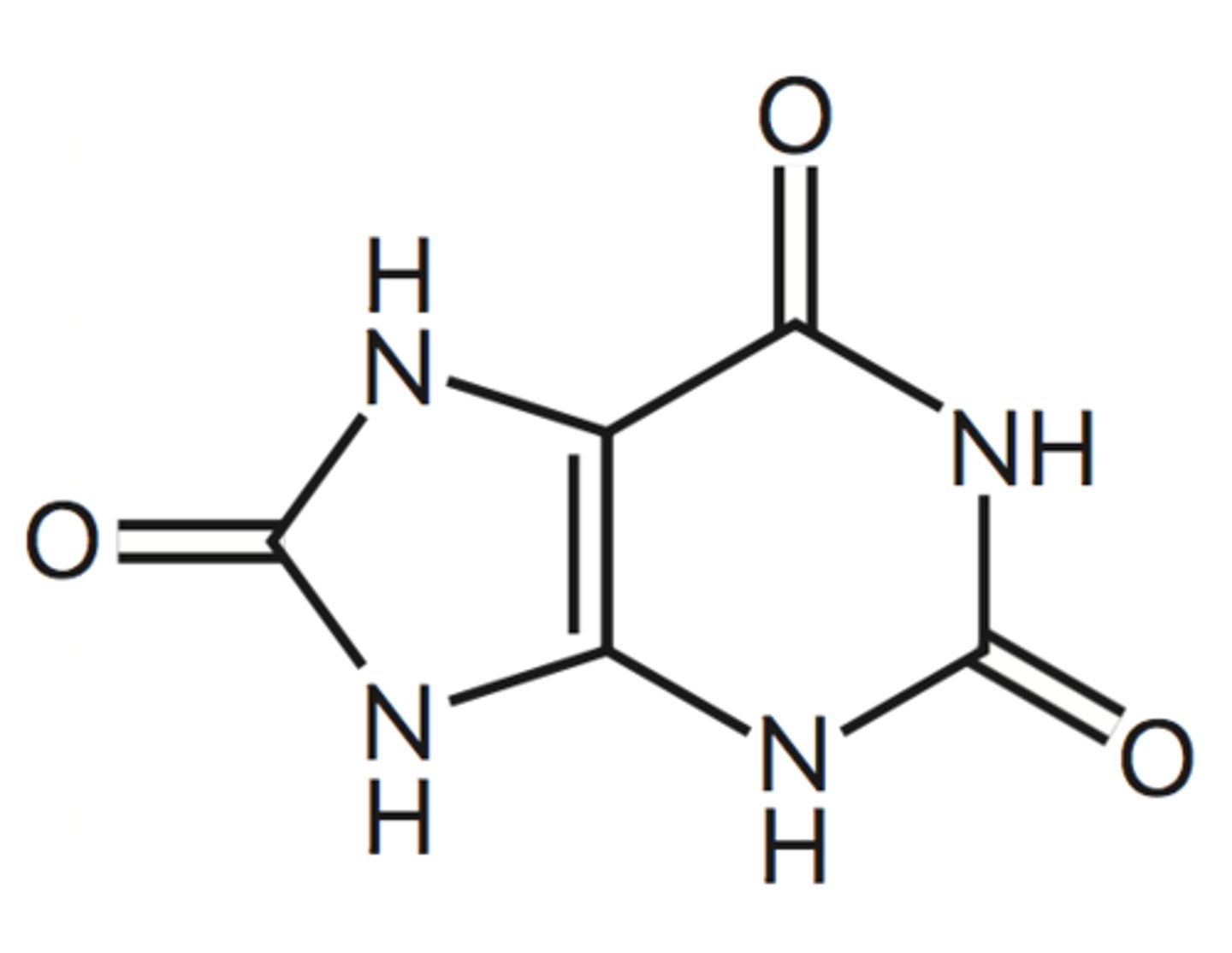
Nitrogenous Waste is created in birds
proteins
|
amino acids
|
NH2
|
Insects, birds, and
reptiles
|
Uric Acid
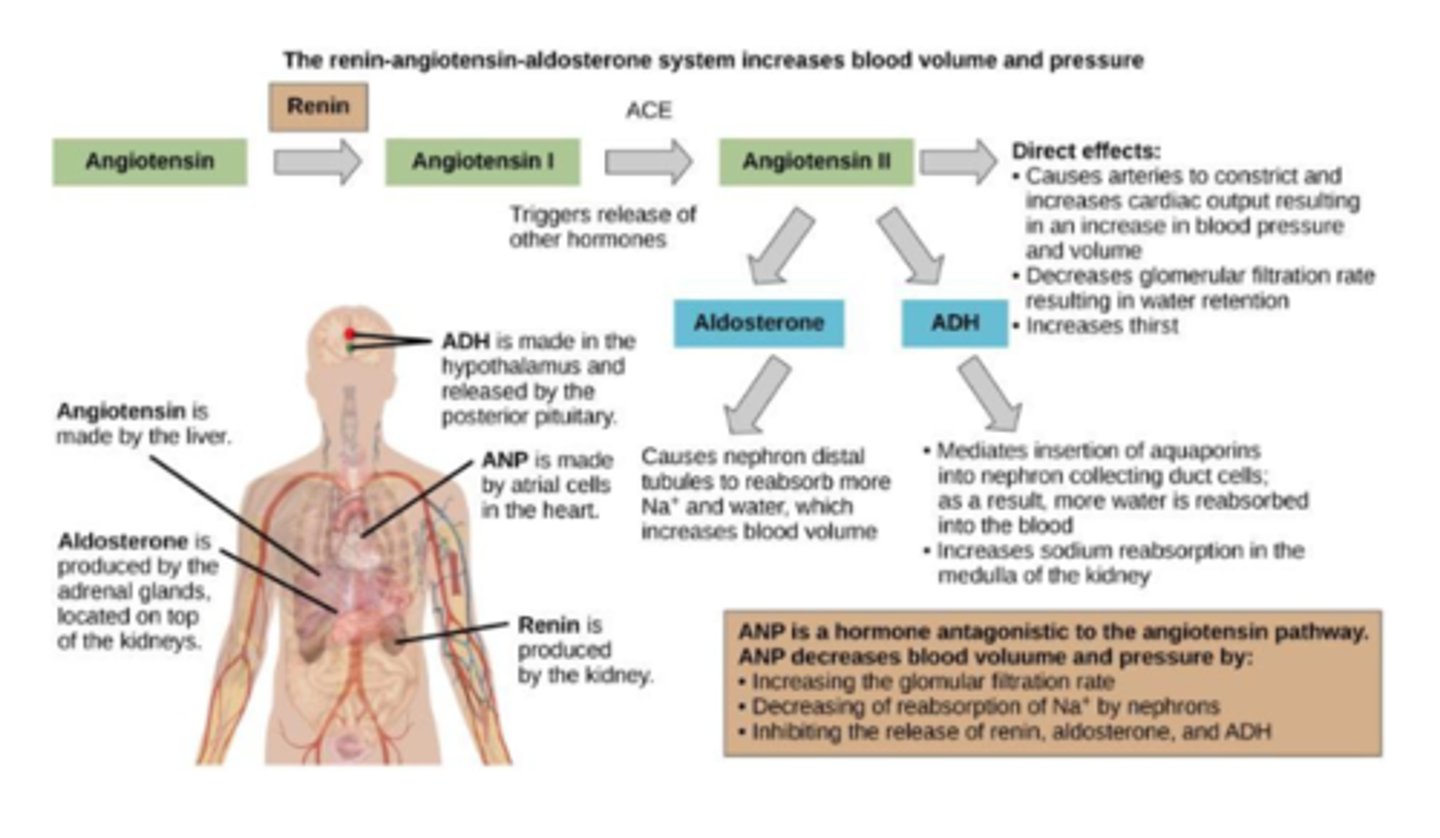
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are produced where
adrenal medulla
epinephrine and norepinephrine function
Can decrease kidney function temporarily by vasoconstriction
Renin produce where
kidney nephrons
Renin function
Increases blood pressure by acting on angiotensinogen
Angiotensin produced where
Liver
Angiotensin function
Angiotensin II affects multiple processes and increases blood
pressure
Aldosterone produce where
Adrenal cortex
Aldosterone function
Prevents loss of sodium and water
Anti-diuretic hormone (vasopressin) is produced where
Hypothalamus
(stored in the
posterior pituitary)
Anti-diuretic hormone (vasopressin) function
Prevent water loss
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is produced where
Heart atrium
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) function
Decreases blood pressure by acting as a vasodilator and
increasing glomerular filtration rate; decreases sodium reabsorption in kidneys
how hormones work (pathway)
angiotensin--- renin---angiotensin 1---ACE--- angiotensin 2---aldosterone and ADH
How many ways can species reproduce?
asexual
sexual

Hydras reproduce by
asexual
as an outgrowth
(bud) of the parent
flatworms reproduce by
asexual
by splitting in half
Sponges, annelids, and echinoderms reproduce by:
Both asexual and sexual
can have the ability to
regenerate from fragments
Parthenogenesis
mostly seen in Asexual reproducers
a form of asexual reproduction where growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization
Sexual reproduction is
Egg of one parent fertilized by
sperm of another
Can sexual reproduction be performed external
true
1 multiple choice option
In sexual reproduction
Animals usually produce ___________
In specialized organs called ___________
gametes, gonads
Testes produce ________ , whereas ovaries produce ________
sperm , eggs
Copulation
sexual union to
facilitate reception of sperm
Most animals are _______________ = separate sexes
dioecious