Anatomy and Physiology of the Cornea for Contact Lens Wearers
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What type of collagen is found in the cornea's basement membrane?
Type IV collagen.
What is the healing time for the cornea after epithelial debridement?
One week.
What are the primary functions of the corneal epithelium?
Provides an optically smooth surface, protects against microbial invasion and chemicals, serves as an adherent surface for tear film, acts as a barrier against water influx, and contains peripheral Langerhans cells.
What happens to the corneal epithelium in response to hypoxia?
It results in an edema response.
How long does it take for epithelial cells to differentiate and migrate to the corneal surface?
7 to 14 days.
What is Bowman's Layer and what is its role?
It is a layer of the cornea that does not regenerate after injury and maintains epithelial structure.
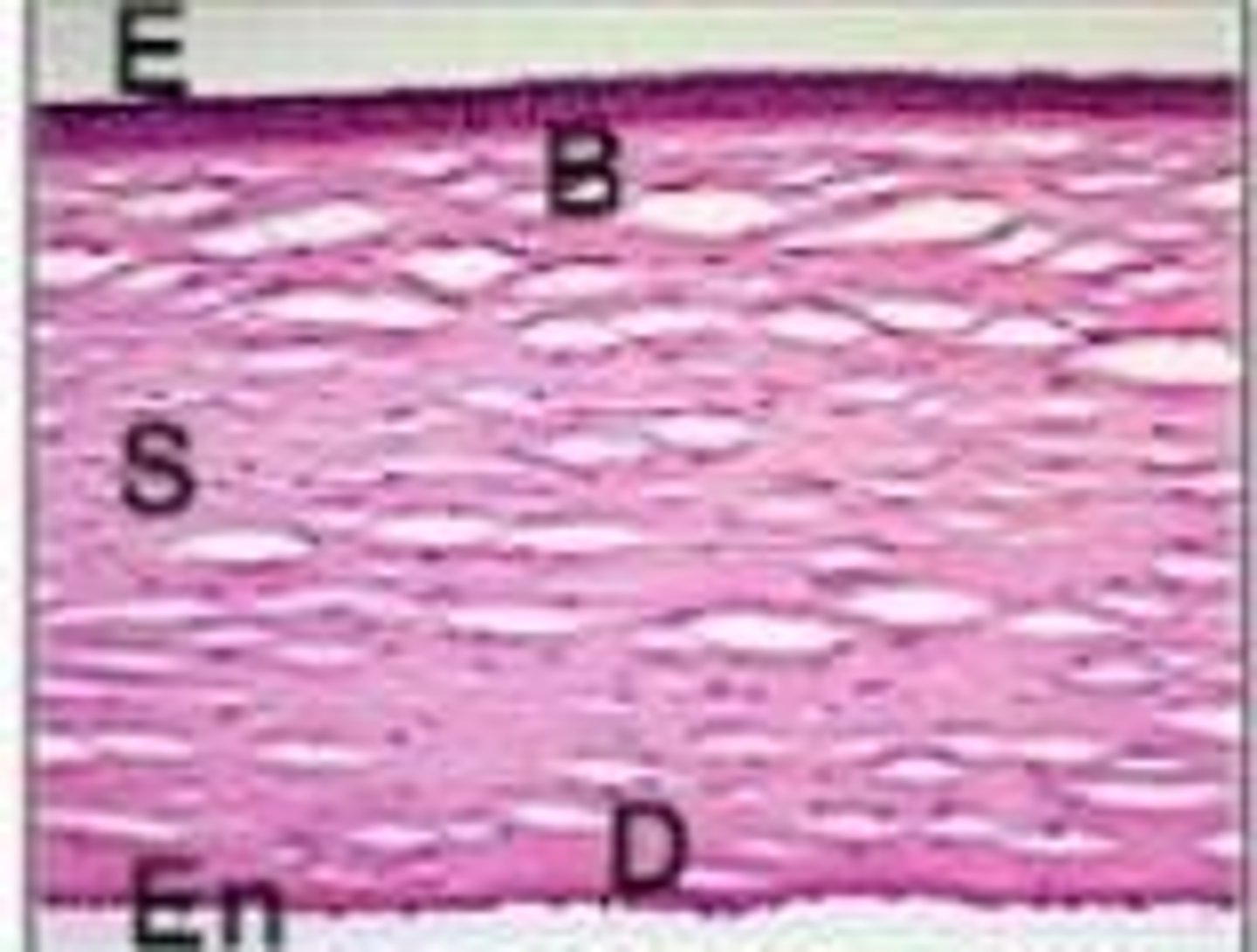
What is the central thickness of the corneal stroma?
0.51 mm.
What is the peripheral thickness of the corneal stroma?
0.66 mm.
What is the horizontal diameter of the cornea?
11 to 12 mm.
What is the vertical diameter of the cornea?
9 to 11 mm.
What is the primary composition of the corneal stroma?
90% of the cornea's thickness, composed of collagen fibers (type I) arranged in a regular pattern for clarity.
What is the role of glycosaminoglycans in the corneal stroma?
They absorb and retain water.
What is the function of keratocytes in the cornea?
They produce collagen and glycosaminoglycans.
What does the endothelium of the cornea do?
It maintains corneal clarity by pumping fluid out of the stroma.
What is the significance of Descemet's Membrane?
It maintains the shape of the stroma during edema and does not regenerate after injury.
What is the Critical Oxygen Requirement (COR) for corneal health?
The minimum Dk/L value needed to avoid detectable corneal swelling.
What is the ideal Dk/L value for daily wear contact lenses?
23 x 10^-9 (cm x ml O2)/(sec x mL x mmHg).
What is the ideal Dk/L value for extended wear contact lenses?
87 x 10^-9 (cm x ml O2)/(sec x mL x mmHg).
What are the effects of hypoxia on the cornea?
Corneal swelling, premature desquamation, decreased healing rates, decreased corneal sensitivity, and vascularization.
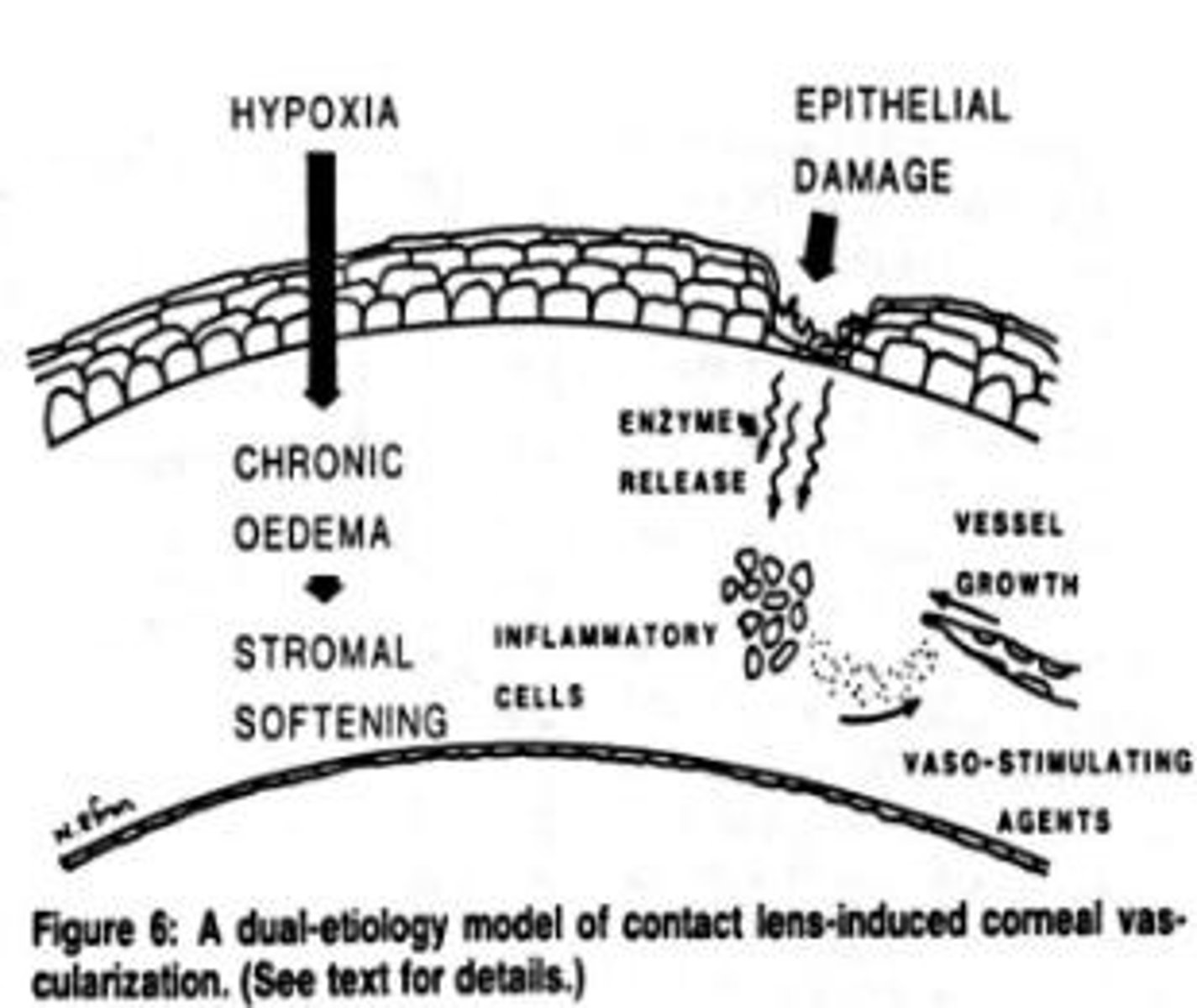
What is the consequence of wearing unsuitable contact lenses?
It restricts oxygen flow to the cornea, leading to corneal swelling and discomfort.
What is anaerobic glycolysis and when does it occur?
It occurs when oxygen is lacking and produces only 2 ATP with lactic acid as a by-product.
What is the role of VEGF in the cornea?
It promotes new blood vessel growth into the cornea in response to chronic hypoxia.
What is the difference between daily wear and extended wear contact lenses?
Daily wear lenses are designed to be worn only while awake, while extended wear lenses can be worn continuously for several days.
What is the process of mitosis in corneal epithelial renewal?
Mitosis occurs approximately every 7 days under normal oxygen levels.
What happens to corneal sensitivity when oxygen levels drop below 8%?
Corneal sensitivity decreases, compromising protective reflexes.
What is the thickness of the endothelial layer of the cornea?
5 mm.
What is the typical cell count in the corneal endothelium of a young adult?
Approximately 300,000 cells.
What is the significance of oxygen transmissibility (Dk/t) in contact lenses?
It describes how much oxygen can actually pass through a contact lens to reach the cornea.
What are the potential long-term issues of hypoxia in the cornea?
Corneal swelling, discomfort, and long-term eye health issues.
What is the role of the peripheral conjunctiva in corneal oxygen supply?
It provides oxygen only to the outer edges of the cornea, insufficient for the entire cornea.
What are the effects of contact lens wear on corneal healing?
Hypoxia can impair healing and reduce nerve sensitivity.
What is the significance of the cornea being avascular?
It relies on the tear film and aqueous humor for oxygen supply.
What is the role of the endothelial pump?
It pumps water out of the stroma to maintain corneal deturgescence.
What does SAG represent in contact lens fitting?
SAG refers to the sagittal depth, which is the vertical distance from the tip of the lens to the flat plane across its edges, indicating how deep the lens sits.
How does a greater SAG affect the fit of a contact lens?
A greater SAG indicates a tighter fit of the lens on the cornea.
What is the relationship between back surface curvatures and SAG?
Steeper back surface curvatures and larger lens diameters result in greater SAG.
What is the significance of the base curve radius (BCr) in contact lenses?
BCr indicates the curvature of the lens, affecting how well it fits the cornea.
What is the conversion factor used to convert base curve radius (BCr) in millimeters to diopters?
The standard conversion factor is 337.5.
How does the lens diameter affect sagittal depth?
If the lens diameter increases, the sagittal depth also increases.
What happens to sagittal depth if the base curve radius (BCr) becomes steeper?
If the BC becomes steeper (smaller value), the sagittal depth increases.
What is the difference between flat, steep, and alignment fits in contact lenses?
Flat fit: less curved than the cornea; Steep fit: more curved than the cornea; Alignment fit: equally curved to the cornea.
What is the effect of using a higher index material on diopters for the same radius of curvature?
Using a higher index material increases the diopters for the same radius of curvature.
What is the relationship between radius in millimeters and curvature in contact lenses?
The smaller the radius in millimeters, the steeper the curvature.
What are the characteristics of RGP (Rigid Gas Permeable) lenses compared to soft contact lenses?
RGP lenses typically have smaller BC values (steeper curvature), while soft lenses have larger BC values (flatter curvature).
What is the impact of lens curvature on oxygen transmission in contact lenses?
RGP lenses allow oxygen permeability, making them healthier for long-term wear, while PMMA lenses do not allow gas to pass through.
What is the definition of diopters (D) in the context of contact lenses?
Diopters (D) measure the refractive power of a lens.
How does the curvature of a lens affect its fit on the cornea?
The curvature affects how well the lens conforms to the corneal shape, influencing fit, comfort, and oxygen transmission.
What is the significance of careful observation in contact lens fitting?
Careful observation is critical for accurately fitting lenses based on the individual patient's corneal shape.
What is the formula for calculating refractive power in diopters?
The formula is Diopter (D) = 337.5 / radius in mm.
What does a K-reading of 45.00 D correspond to in terms of radius of curvature?
A K-reading of 45.00 D corresponds to a radius of curvature of 7.50 mm.
What is the effect of lens fitting on individual eye anatomy?
Lens fitting is always relative to the individual eye anatomy, meaning what fits one patient may not fit another.
What are the implications of a flat fit in contact lenses?
A flat fit may cause the lens to sit on top of the cornea, leading to edge lift and poor centration.
What are the implications of a steep fit in contact lenses?
A steep fit may cause the lens edges to press against the peripheral cornea, creating a vault or pooling area beneath the center.
What is the definition of alignment fit in contact lenses?
An alignment fit occurs when the curvature of the lens closely matches the curvature of the cornea, resulting in even pressure distribution.
What is the relationship between lens diameter and fit in contact lenses?
Larger lens diameters require a flatter base curve for optimal fit.
How do changes in material and thickness affect diopters and radius in contact lenses?
Diopters are variable with changes in material and thickness, while radius is constant.
What is the role of the calibrated refractive index in keratometry?
The calibrated refractive index (n' = 1.3375) is used to calculate the sagittal depth and influence fitting.