Overview of the Modern Blood Bank Laboratories and Modern Trends
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
BLOOD BANK LABORATORY
A facility that is involved in the collection, storage, processing, and distribution, of human blood and blood products for transfusion.
Also function as a component of the heavily regulated health-care industry.
Non-profitable
All blood banks are (profitable / nonprofitable)
To save lives, not to earn money.
What is the main goal of blood banks?
American Association of Blood Banks (AABB)
Blood bank laboratory accrediting association
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Blood bank laboratory regulating agency
BLOOD COLLECTION
BLOOD STORAGE
DONOR SCREENING
BLOOD COMPONENT PREPARATION
BLOOD TYPING AND CROSS-MATCHING
ANTIBODY SCREENING AND IDENTIFICATION
APHERESIS
Examples of services that a blood bank provides
Size
Resources
Location
The capabilities of blood banks to offer services rely on their?
COMPONENT PREPARATION AND STORAGE
DONOR PROCESSING
PRODUCT LABELLING
MAIN LABORATORY
REFERENCE LABORATORY
Blood bank laboratory is divided into several distinct areas:
American Red Cross
Regional Blood Centers
In-house
Depending on the needs of a hospital, blood components may be acquired from external sources such as ___ or ____, or components may be processed ____
Blood bank has a collection facility
Blood bank does not have a collection facility
Component Preparation and Storage also depends on whether:
Blood bank with Collection Facilities
Blood banks that collect their own units of whole blood and use their blood resources more efficiently by separating them into a variety of components.
Blood Bank with no collection facility
These are blood banks that acquire blood components from external sources. They procure and store blood until needed.
Donor processing
What step is this?
The donated blood will be carefully screened and processed to ensure it meets safety and quality standards. These are screened for infectious diseases such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV, etc.
Product labelling
This is a mortal sin.
Packed RBCs (pRBCs)
Platelet concentration
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
Frozen Plasma collected within 24 hours (FP24)
Cryoprecipitate (Cryo)
Blood bank w collection facilities separates variety if components such as:
FOR WHOLE BLOOD
Room temperature (20-24C) as platelets deteriorate at higher temperatures.
Cooled to ref temperature (1-10C)
At what temperature is whole blood → platelets stored?
At what temperature is frozen plasma stored?
Within 8hrs of collection
Fresh Frozen Plasma must be processed within?
Fresh Frozen Plasma
This can be further processed to cryoprecipitate.
Cryoprecipitate
This is a concentrate of certain proteins used to treat bleeding disorders.
Prepared up to 24hr of collection if stored in room temp (20-24C)
How is Platelet Concentrate prepared?
Apheresis
It is a process where the whole blood is separated into different components.
Donor’s blood is removed
Anticoagulated
Transported directly to apheresis machine
Centrifugation
Desired component is removed
Remaining portion is returned to donor
Explain apheresis
Plateletpheresis
Plasmapheresis
Leukapheresis
RBC apheresis
Blood products obtained through apheresis:
Use a prominent vein for collection
Because the remaining portion is returned to the large vein
What is the requirement during blood collection?
Why?
PHILIPPINE RED CROSS
REGIONAL BLOOD CENTERS
External sources of blood bank if they dont have any collection facilities.
To ensure a safe and adequate supply of blood for patient’s need
Goal of blood bank
Plasma
Platelet
RBCs
Blood banks are responsible for preparing blood components such as ( __, __, __, ) from whole blood. They are stored under specific conditions until these products are needed for transfusion
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
HIV
The blood is screened for infectious diseases such as?
PRODUCT LABELLING
After blood components are prepared and tested, they are labelled with donor’s blood type, expiration date, and other special instructions. it is essential in blood bank.
MAIN LABORATORY
The heart of the laboratory; central area where various laboratory tests related to blood banking are performed, inclusive of compatibility testing.
REFERENCE LABORATORY
Some blood banks do not have this; they are laboratories that performed specialized testing and consultation services (rare blood type testing, unusual antibodies determination, infectious diseases such as HIV and hepatitis)
Anticoagulant
Density and size
This is where blood is placed after collection
Blood components are separated using centrifuge according to their…?
PROCESS OF PREPARATION:
Apheresis
Centrifugation, Apheresis, Leukoreduction Filtration
Centrifugation, Apheresis, In-line filtration
Frozen Plasma, Antihemophilic factor, Cryoprecipitate
Heavy Spin-Freezing (-18C)
What is the process of preparation?
Granulocytes/ WBC
RBC
Platelets
Cryoprecipitates
Fresh Frozen Plasma/FP24
Platelet Concentrates and Cryoprecipitate
These blood components may be received as individual units but are more easily administered if pooled before infusion
pRBCs
Individuals with IgA deficiency must not be transfused with?
AUTOMATED CELL WASHERS
These are used to prepare washed pRBCs
Sterile connecting devices (STCDs)
These devices produce sterile welds between two pieces of compatible tubing
this procedure permits sterile connection of a variety of containers and tube diameter
also called CLOSED SYSTEM
pRBCs, WBC
FFP/FP24, Cryopercipitate
Frozen RBC, Rare blood type [AB-], Rare autologous units
PC, Apheresis Platelet
PC, Apheresis Platelet
Determine which components are stored in the ff. temperatures:
Refrigerators maintained at 1-6C
Freezers maintained at -18C or Lower
Freezers maintained at -65C or Lower
Platelet rotators maintained at 20-24C
Platelet agitators maintained at 20-24C
TUBE SEALER
For sealing blood bag pilot tubing
For cutting blood bag pilot tubing
PLASMA EXPRESSOR
For packing RBCs, transferring plasma from one blood bag to another, and removing plasma
STERILE CONNECTING DEVICES
For creating sterile welds between two tubes
BLOOD BANK REFRIGERATED CENTRIFUGE
For preparing blood components
BLOOD IRRADIATOR
For preparing leukocyte-poor RBCs (to prevent Graft vs. Host Disease)
Rigorous testing
Before a unit of blood can be placed into the general inventory, ____ must be performed to determine its suitability for transfusion
Lavender top (EDTA)
Red top (Plain)
Collection tubes
used for retyping, hematocrit, and hemoglobin level determination
used for blood screening
ABO and Rh typing
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)
Anti-HCV
Antibodies to HIV (Anti-HIV-1)
Serologic test for syphilis (Syphilis Ag)
Malaria antibody and antigen
Tests important in blood screening (Philippine Setting)
PRODUCT LABELLING
Critical step in the transfusion process
no discrepancies in the ABO and Rh testing
Absence of detectable Ab in plasma-containing components
Nonreactive viral marker tests
non reactive syphilis test
Sustainability Requirements include:
Reconfirm
However, according to AABB Standards, the blood bank to which this blood is shipped is required to ____ the labeled ABO of each RBC-containing product received
Anti-A, Anti-B
Anti-A, Anti-B
Anti-A, Anti-B
Anti-A,B
Anti-A,B, Anti-D
Determine the tests performed.
A positive
B positive
AB positive
O positive
O negative
Patient care
The primary mission of the main laboratory
TYPE AND SCREEN
TESTS PERFORMED IN THE MAIN LABORATORY:
Determines the ABO and Rh type
Screens unexpected Ab in plasma
Helps identify compatibility issues before transfusion
TYPE AND CROSSMATCH
TESTS PERFORMED IN THE MAIN LABORATORY:
Crossmatches the donor’s blood with the patient’s blood
To avoid adverse transfusion reaction
PRENATAL EVALUATION
TESTS PERFORMED IN THE MAIN LABORATORY:
Performed to determine the blood type and Rh factor of the pregnant women; to identify any potential risks or HDFN
POSTNATAL EVALUATION
TESTS PERFORMED IN THE MAIN LABORATORY:
After childbirth (postpartum), the blood type and Rh of the mother is assessed (particularly if theres Rh sensitization); applicable for Rh negative mothers
CORD BLOOD STUDIES
TESTS PERFORMED IN THE MAIN LABORATOR:
Involved testing the blood collected from the umbilical cord of the newborns to determine the blood type and Rh factor
Proper patient identification
The single most important aspect of patient care in all health-care settings
2
A minimum of __ identifiers is required for patien samples
Px. Full name (First Name, Middle Name, Last Name)
Date of birth and/or Medical Record Number
What are the identifiers for patient samples?
Type and Screen
Type and Crossmatch
Prenatal Evaluation
Postnatal Evaluation
Cold Blood studies
The tests in routine testing
Inspect the unit for any abnormal appearance (discoloration or hemolysis)
Verifies that all required transfusion forms and labels are complete and that they adequately identify the transfusion recipient
The individual in the blood bank who will issue the blood product must do the ff. critical checks
ABNORMAL APPEARANCE
INDICATES CONTAMINATION OR HEMOLYSIS
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Plasma of RBC unit is brown, red, murky, or purple
Indicates bacterial contamination
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Plasma of RBC unit is green
Not suitable for transfusion; RBCs are damaged
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Zone of hemolysis is above RBC mass
Contamination or Leakage
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Inadequate sealing of RBC segments in tubing
Pink to red plasma
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Hemolysis of RBC
Indicates metabolic disorders
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Grossly lipemic units
Bacterial contamination or presence of tissue
REASONS TO QUARANTINE BLOOD COMPONENTS BEFORE SHIPMENT OR TRANSFUSION:
Unusual cloudy or turbid appearance of platelet unit
REFERENCE LABORATORY
the problem-solving section of transfusion service
their goal is to ensure that any discrepancies detected in routine testing are resolved in an accurate and time-efficient manner
also serves as a vital source for ensuring the accuracy or reliability or efficiency of transfusion-related testing and services
ABO discrepancies investigation
Rh discrepancies investigation
Unexpected Ab indentification
Transfusion reaction
Tasks of REFERENCE LABORATORY
RBC PRESERVATION
1-6 C
The goal of this is to provide viable and functional blood components for patients requiring blood transfusion
RBC units are stored at ___; storage time may vary depending on the preservative used
RBC VIABILITY
More than 75%
Less than 1%
A measure of in vivo RBC survival following transfusion
A critical aspect of blood preservation as it directly impacts the success of transfusion
The US FDA requires an average 24h post-transfusion RBC survival of ____?
This is assessed as free hemoglobin of ____ total of hemoglobin to meet viability standards
STORAGE LESION
Associated with loss of RBC viability; due to biochemical changes within the RBC
220-250 mg of iron
How many mg of iron is contained in one RBC unit
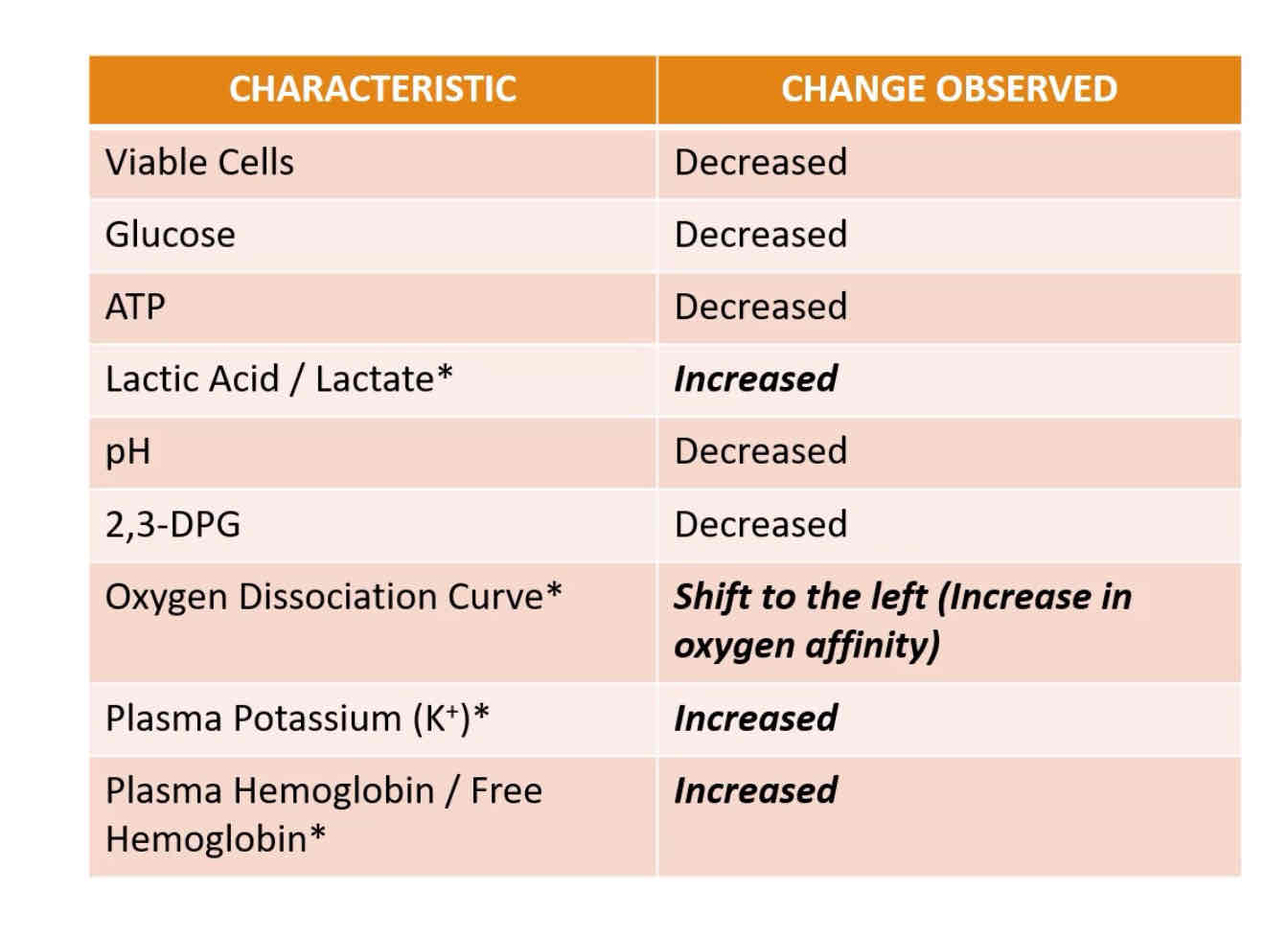
RBC STORAGE LESION
Acid citrate dextrose
Citrate phosphate dextrose
Citrate phosphate double dextrose
Citrate phosphate dextrose adenine
Enumerate the Anticoagulant Preservative Solutions.
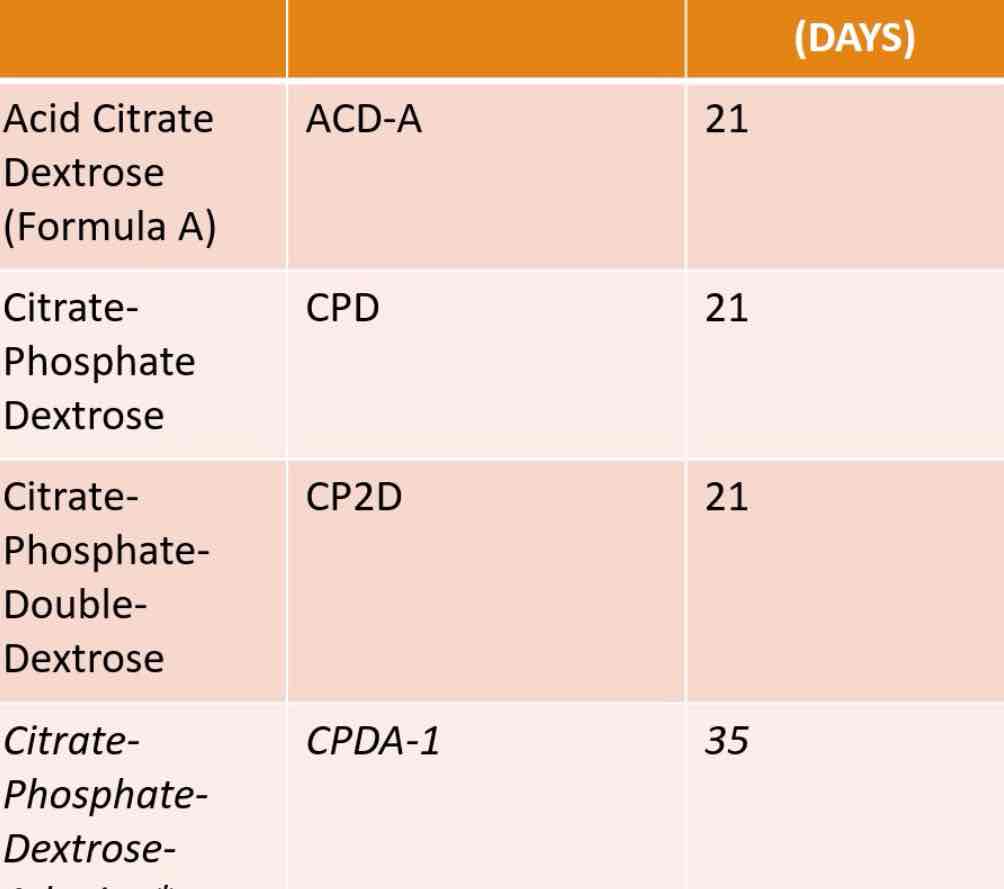
ANTICOAGULANT PRESERVATION SOLUTIONS
CITRATE (SODIUM CITRATE/CITRIC ACID)
MONOBASIC SODIUM PHOSPHATE
DEXTROSE
ADENINE
CONTENTS OF ANTICOAGULANT PRESERVATIVE SOLUTION:
Chelates calcium; prevents clotting
Maintains pH during storage; necessary for maintenance of adequate levels of 2,3-DPG
Substrate of ATP production (cellular energy)
Production of ATP (extends shelf-life from 21-35days)
Glucose
Adenine
Electrolytes (K, Na)
Additive solutions contains what essential nutrients?
Saline
Adenine
Glucose
Additive solutions contains what basic contents?
ADDITIVE SOLUTIONS
preserving solutions that are added to the RBCs after removal of the plasma with or without platelets
it is intended to replace the nutrients in the plasma which were removed during packed RBC preparation
also helps to ease the flow of RBCs during transfusion
helps maintain the viability and functionality if RBCs during storage
improves RBC quality for transfusion
Extends the shelf-life of RBCs to 42 days by adding nutrients
Allows for the harvesting of more plasma and platelets from the unit
Produces a pRBC of lower viscosity that is easier to infuse
BENEFIT OF USING ADDITIVE SOLUTIONS:
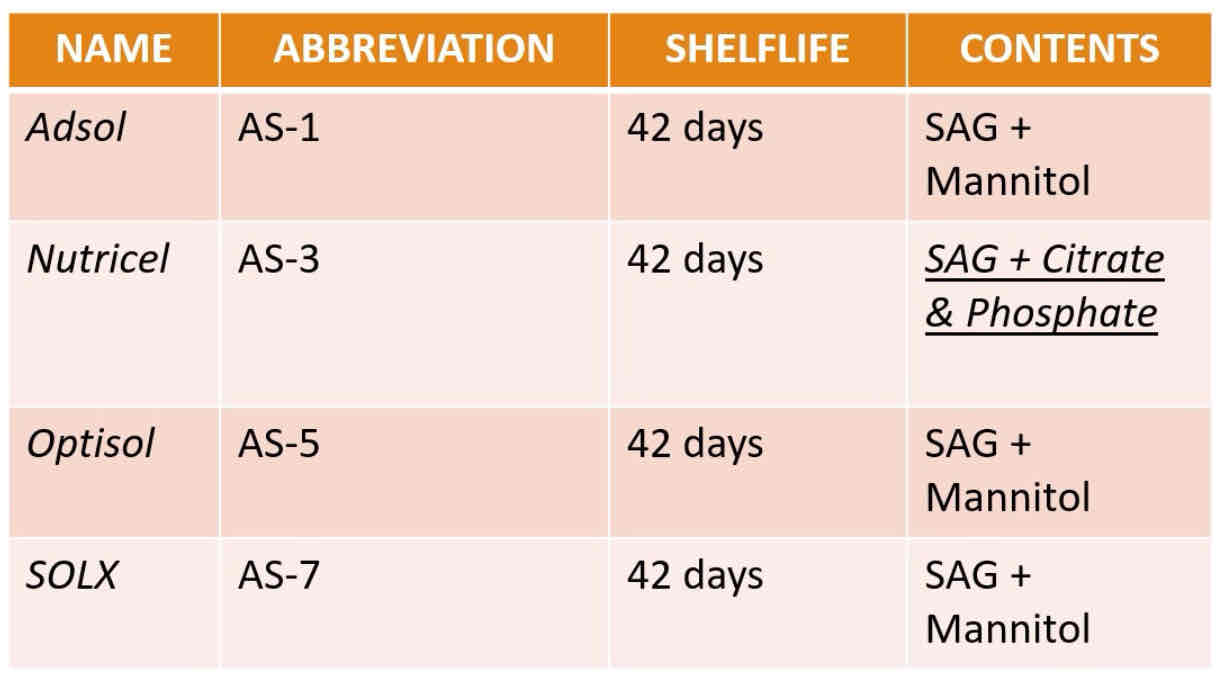
ADDITIVE SOLUTIONS CURRENTLY APPROVED BY THE FDA
Adsol
Nutricel
Optisol
SOLX
AS-1
AS-3
AS-5
AS-7
ASG + mannitol
ASG + citrate and phosphate
ASG + mannitol
ASG + mannitol
What are their contents?
Adsol
Nutricel
Optisol
SOLX
PLATELET PRESERVATION
PLATELET STORAGE LESION
Platelets are routinely stored at room temp (20-24C) for 5days with constant agitation
loss of platelet quality during storage
Agitation has been shown to facilitate oxygen transfer into the platelet bag and oxygen consumption by the platelets
Agitation also maintains constant pH inside the platelet bag
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF AGITATION?
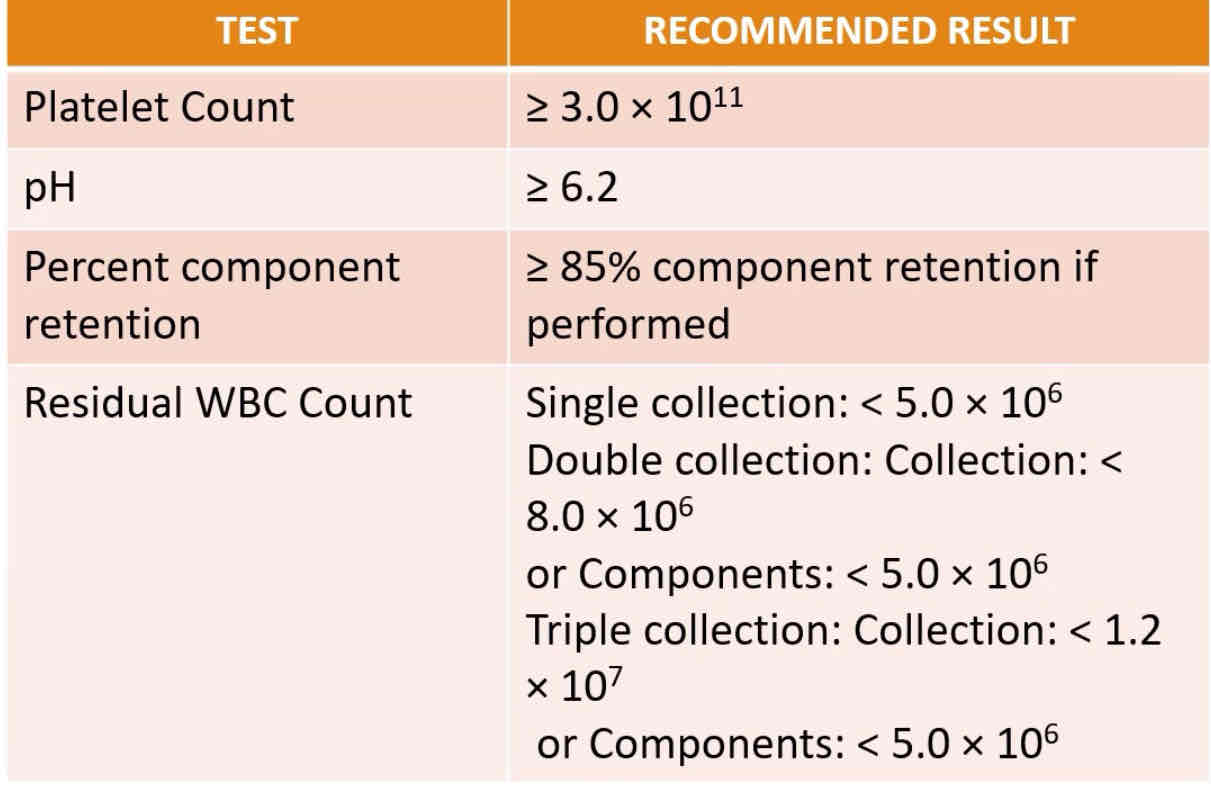
PERFORMANCE CRITERIA FOR PLATELET CONCENTRATE COLLECTIONS
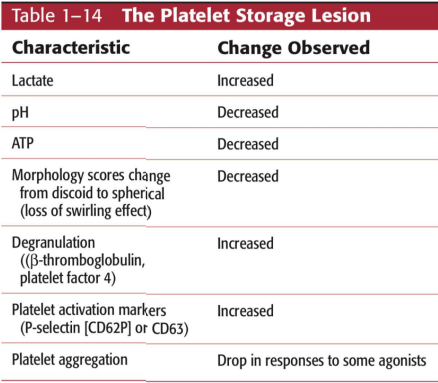
PLATELET STORAGE LESION
JASMYN DANIELLY PATUBO MANUEL
MY FAVORITE HUMAN