Social Cognition and Mirror Neuron Theory Discussion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What functions are ascribed to the mirror neuron system (MNS) according to Rizzolatti and colleagues?
Action understanding, imitation, implicit understanding of action goals, social mimicry, understanding non-verbal social signals, facial expressions, mentalizing, and joint attention.
What critique does Hickok (2009) provide regarding the mirror neuron theory (MNT)?
Hickok argues that there is no evidence that mirror neurons support action understanding in monkeys, that action understanding can occur through non-mirror neuron mechanisms, and that the relationship between macaque and human mirror systems is unclear.
What are the eight problems for the mirror neuron theory of action understanding?
1) No evidence of mirror neurons supporting action understanding in monkeys. 2) Action understanding achievable via non-mirror mechanisms. 3) M1 contains mirror neurons. 4) Non-parallel relationship between macaque and human mirror systems. 5) Human action understanding dissociates from mirror system indices. 6) Action understanding and production dissociate. 7) Inferior frontal gyrus damage not correlated with understanding deficits. 8) Generalization of the mirror system to speech recognition fails empirically.
What do Grosbras et al. (2005) conclude about eye movements and gaze observation?
They found overlap between eye movements and gaze observation, suggesting a mirroring mechanism for gaze that includes the frontal eye fields (FEF) and indicates decoding of gaze in terms of attentional focus.
What is the significance of 'Point-Light Walkers' in understanding mirroring in the brain?
fMRI studies show that 'Point-Light Walkers' activate the MNS as well as the STS and occipital cortex, indicating a wider network involved in processing biological motion.
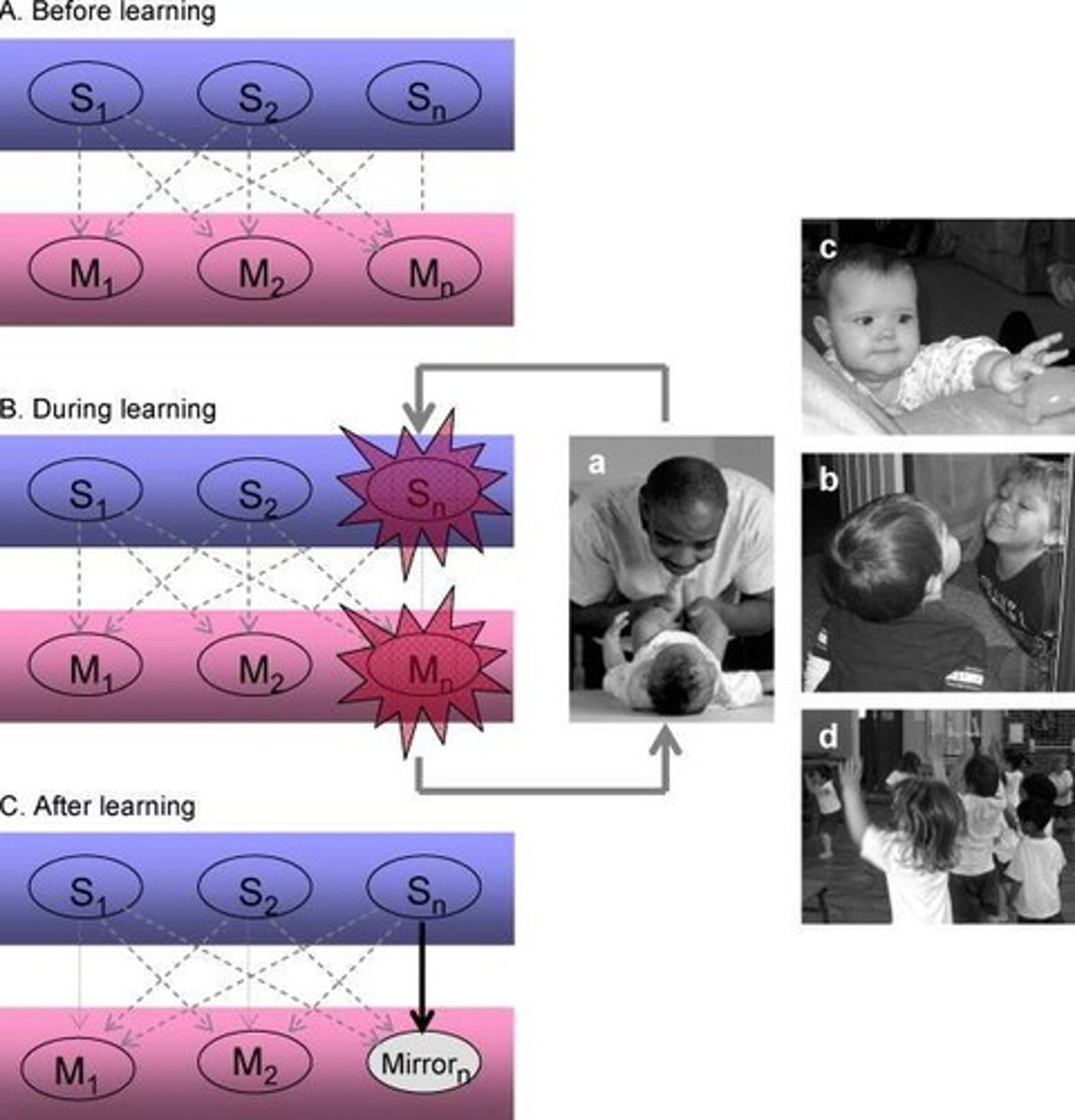
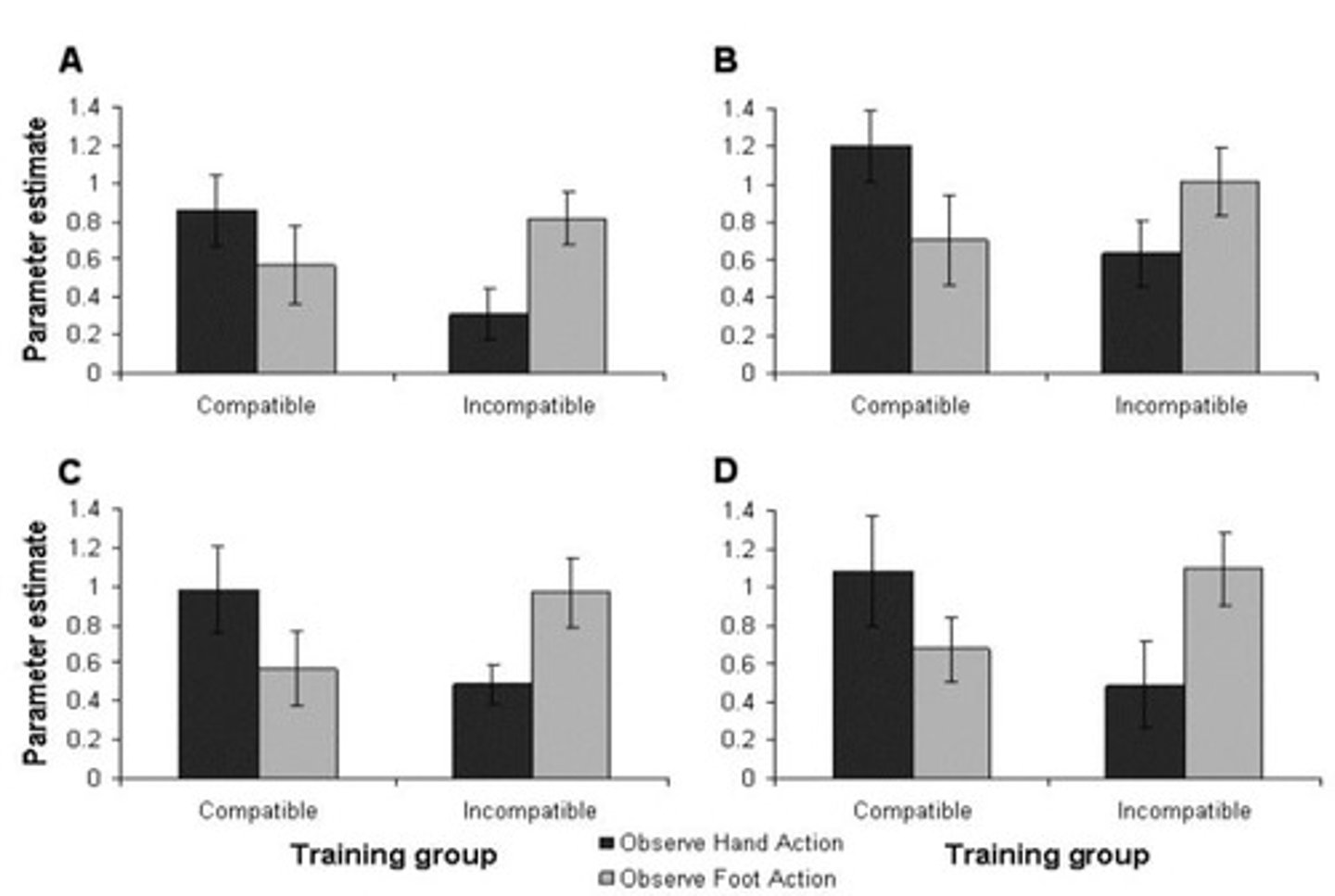
What does the research by Catmur et al. (2008) suggest about retraining the mirror neuron system?
Their study indicates that responses in the MNS can be altered through incompatible training, suggesting some aspects of mirroring can be retrained, but areas for hands and feet do not interchange.
What is the 'Broken Mirror Hypothesis of Autism'?
It posits that individuals with autism have deficits in the mirror neuron system, leading to difficulties in goal-directed imitation, understanding others' actions, and planning actions.
What evidence supports the 'Broken Mirror Hypothesis of Autism'?
Evidence includes EEG studies showing mu-rhythm suppression is absent in ASD and behavioral studies indicating a lack of goal-directed imitation and difficulties in understanding actions.
What evidence contradicts the 'Broken Mirror Hypothesis of Autism'?
Studies show that children with autism perform well in explicit tasks related to gesture recognition and grip imitation, suggesting that the hand-object related MNS may not be significantly impaired.
What neural activation differences are observed in children with autism during face perception?
Children with autism show abnormal activation and cortical thinning in the social brain, including parts of the MNS, during face perception tasks.
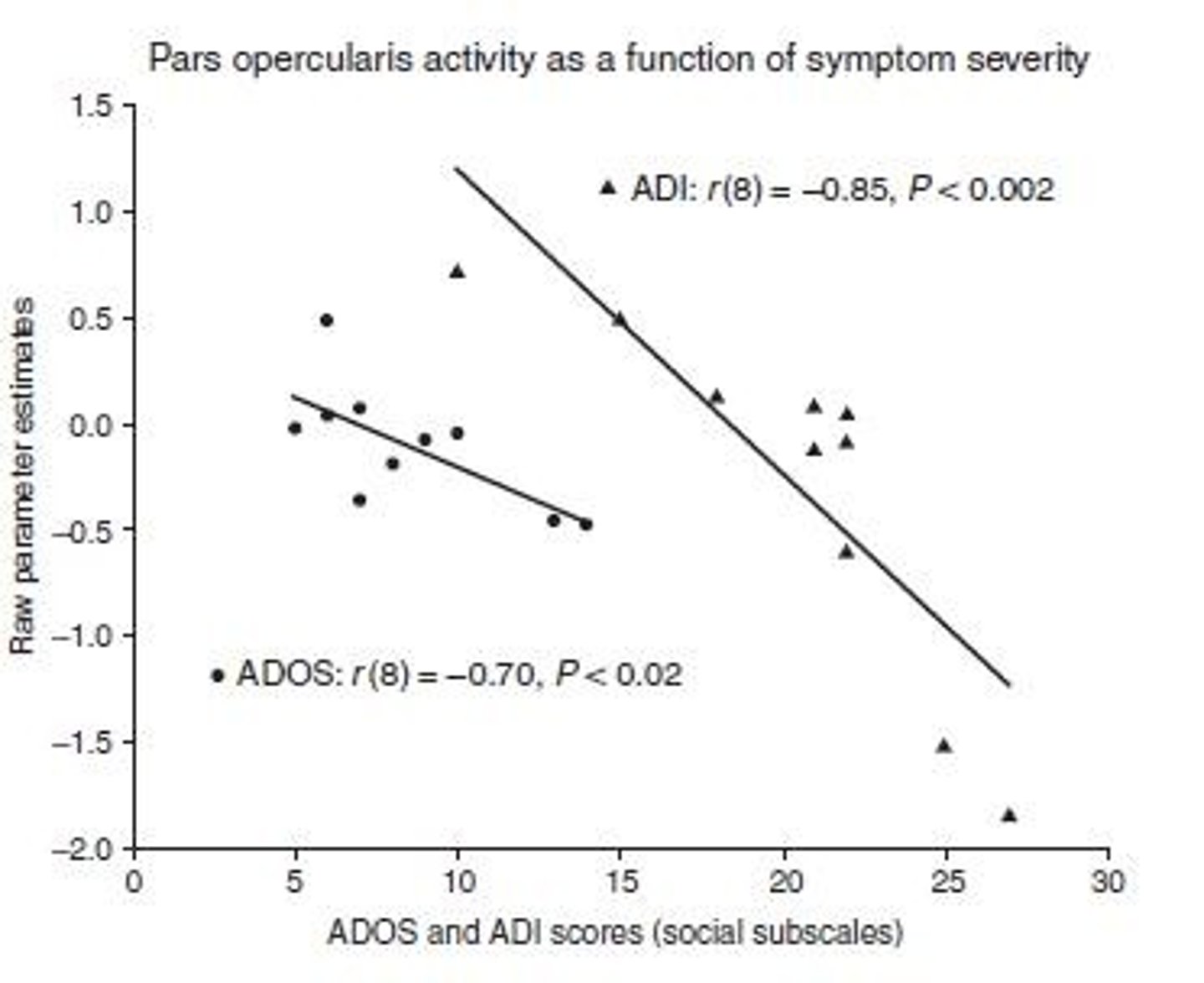
What is the role of the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) in autism according to Dapretto et al. (2006)?
Activity in the IFG correlates negatively with ASD symptom severity, indicating that stronger traits are associated with less activity in this area during imitation and observation.
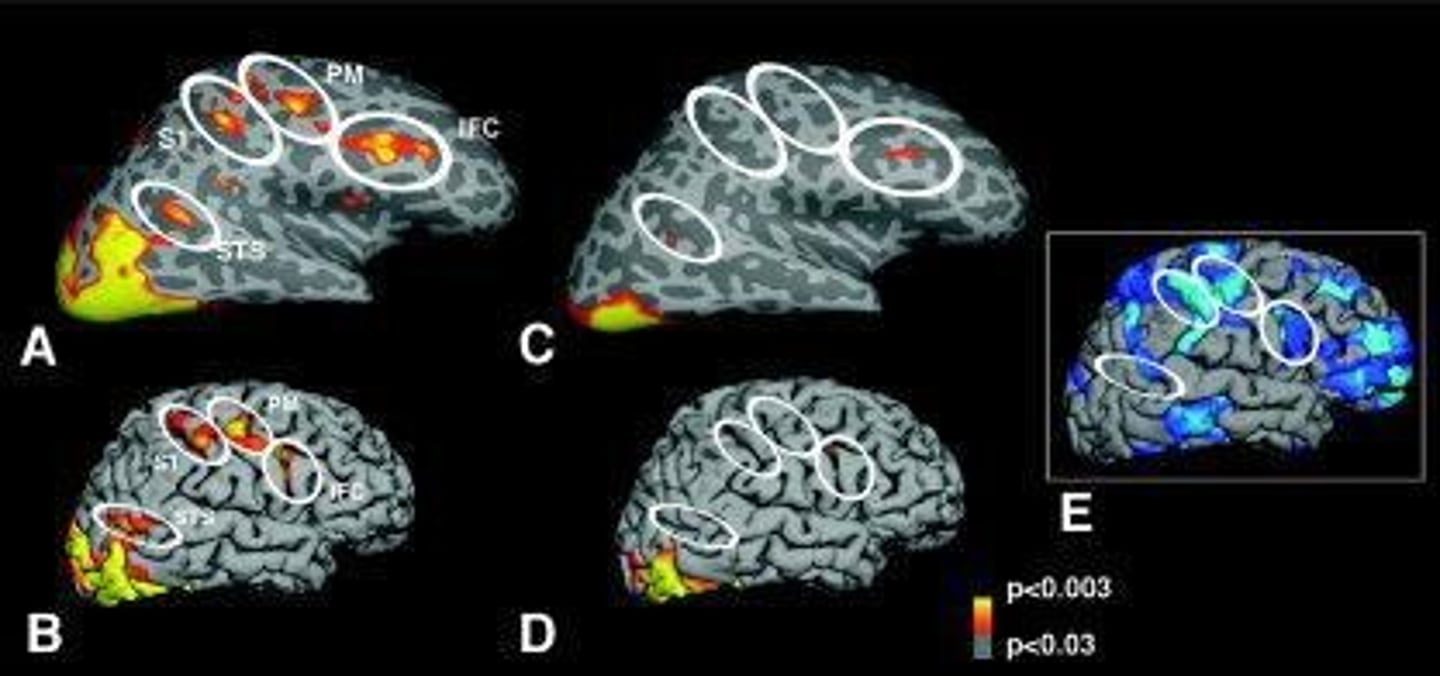
How does gaze perception differ in individuals with autism?
Individuals with autism do not distinguish implicitly between congruent and incongruent gaze, while controls show activation in the IPL and STS during gaze tasks.
What is the importance of considering a wider network beyond mirror neurons in understanding social cognition?
Research suggests that a wider network involving perception, attention, motor planning, and action control is necessary for understanding social cognition and imitation.
What are the implications of the findings on the relationship between mirror neurons and social signals?
Findings suggest that while mirror neurons may play a role in processing social signals, a broader network is involved, particularly for complex social interactions.
What does the research by Hadjikhani et al. (2006) indicate about cortical thinning in autism?
It indicates that areas of the brain associated with social cognition, including parts of the MNS, show more widespread thinning in individuals with autism.
What is the significance of joint attention in relation to the mirror neuron system?
Joint attention may be facilitated by mechanisms that align gaze and attention, indicating a role of the MNS in understanding social cues and intentions.
What are the potential limitations of the mirror neuron theory in explaining autism?
The theory may not fully account for the complexities of social cognition deficits in autism, as evidence suggests involvement of a wider network beyond just mirror neurons.
What is the relationship between associative learning and mirror neurons according to Cecilia Heyes?
Heyes suggests that mirror neurons may be influenced by associative learning, which can explain how individuals learn to imitate actions they can see.
How does the concept of 're-wiring' the mirror neuron system challenge traditional views?
It suggests that the MNS is not entirely hard-wired and can be modified through training, indicating a level of plasticity in neural mechanisms related to imitation.
What is the significance of the study by Hamilton et al. (2007) regarding the broken mirror hypothesis?
It questions the validity of the broken mirror hypothesis by showing that children with autism may not have significant impairments in tasks related to goal-directed imitation.
What are the implications of findings on emotional facial expressions in autism?
Research indicates that individuals with autism show lower imitation and observation activity for emotional facial expressions, suggesting a potential deficit in processing these signals.
What does the term 'saccades' refer to in the context of gaze perception?
Saccades refer to rapid eye movements that shift attention and may play a role in how gaze is perceived and understood in social contexts.
What are the broader implications of understanding the mirror neuron system for social cognition research?
Understanding the MNS and its limitations can inform interventions for social cognition deficits, particularly in conditions like autism, and highlight the need for a comprehensive approach.