Bryophytes (bryophyta)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Bryophytes are a group of organisms at the transition between what groups?
Transitional between the Charophycean green algae and the vascular plants.
Are both Paraphylethic group’s (do not include all the descendants of a single common ancestor)
What characteristics are shared by bryophytes and vascular plants?
Multicellular sporanngia
Sporopollenin in spore walls
Tissues produced by an apical meristem
Antheridia and Archegonia with sterlie jacket layer
What are the Phyla of Bryophytes?
Liverwots-Heptophyta
Hornworts-Anthocerotophyta
Mosses-Bryophyta
What are the characteristics of bryophytes?
All are simple small plants
Sporophytes are permanently attached to gametophytes and nutritionally dependent
The archegonium contains a single egg
Each antheridium produces numerous sperm
Biflagellate sperm are free swimming
Lack conducting tissues called xylem and phloem lack lignin
How do liverworts differ from hornworts and mosses?
Lacking stomata
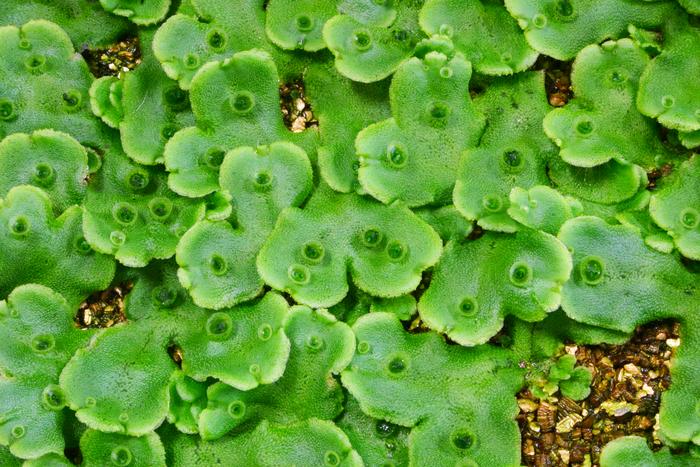

What do hornworts have that is unique?
Basal meristem and lack conducting tissue
What are the shared characteristics between bryophytes and vascular plants?
Shared characteristics include the presence of a male and female gametangia, called the antheridia and archegonia, which a protective layers called a starlike jacket layer.
Rentention of both the zygote and the developing multicellular embryo or young sporophyte (archegonia)
Presence of a multicellular diploid sporophyte, increases number of meiosis and amplification of the number of spores
4. Multicellular sporangia consisting of sterile jacket layer and internal spore-producing (sporogenous tissue)
Meiospores with walls containing spopopollenin, resists drying and decaying.
Tissues produced by an apical meristem
Gemma’s are multicellular structures involved in?
Asexually reproduction, they are multicellular bodies that gives rise to new gamtophytes.
Detach from parent plant and grow into identical individual
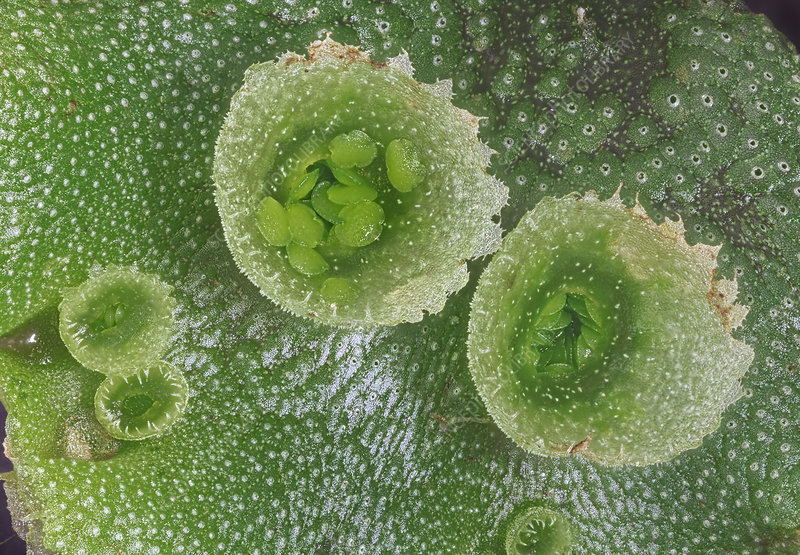

What is a flagellated cell in brophytes?
Sperm, swim through water for fertilization
Sexual Reproduction in bryophytes involves the production what..?
Antheridia and archegonia, distribution at meiosis of distinctive sex chromosomes, elongated antheridium is talked and consists of a sterile jacket layer, that surrounds numerous spermatogenous cells→ sperm cells
Archegonia are flanked shaped with along neck and a swollen basal portion, the venter, which encloses a single egg. The outer layer of cells of teh neck and venter form the sterile protective layers of the archegonium . The neck canal cells disintegrate when the egg is mature→ fluid filled tube sperm to the egg.
In bryophytes, fertilization takes place in the?
Archegonium, which contains that egg and neck canal cells so the flagellated sperm swim through to reach the egg.
Matrotophy refers to the what..?
The form of nutrition that the developing embryo (sporophyte) is nourished by sugars, amino acids provided by the maternal gametophyte
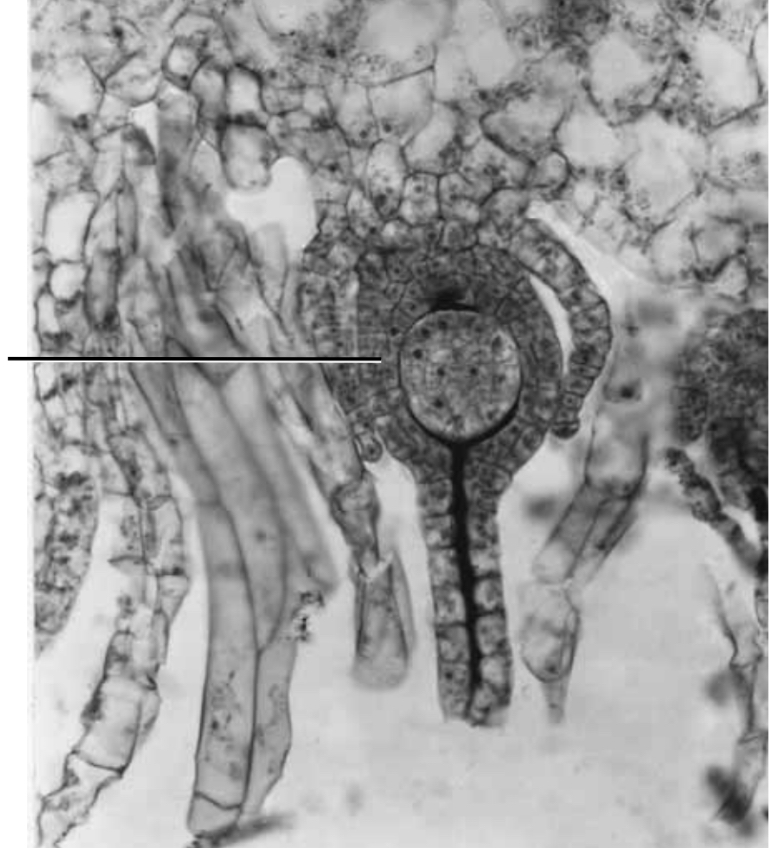
The base of the bryophyte archegonium, called the what_____. And contains ____.
At the base of the archegonium is the venter that encloses a single egg
What is the Calyptra?
As the bryophytes embryo develop, teh venter undergoes cell division, to keep pace the young sporophyte.
Enlarged Venter
At maturity, the sporophyte of most bryophytes consists of the?
Of a foot, which remains embedded in the archegonium, a seta or stalk and a capsule to sporangium. (The transfer cells constitute a placenta)
What do the Rhizoids do in byrophytes?
The primary functions of rhizoids as an anchor to plants, because the absorption occurs throughout the gametophyte
What are the characteristics of Embryophytes?
Occurrence of a multicellular, matrotrophic embryo in all group of plants from bryophytes through angiosperms (synonym for plants)
Embryo develops inside the female plant
What is the major difference between the spore walls of bryophytes and charophytes is that bryophytes spore walls contain?
Bryophytes spores contain a bio polymer, Sporopollenin (enables spores to survive dispersal through the air from one moist site to another.
At maturity, the sporophyte in most bryophytess consist of…?
Foot, Seta and Capsule
____. Is a liverwort that carries its gametangia on gametophyte
Marchantia, unisexual and distinguished by their gametophore and separated into antheridiopores and archegoniopohores.
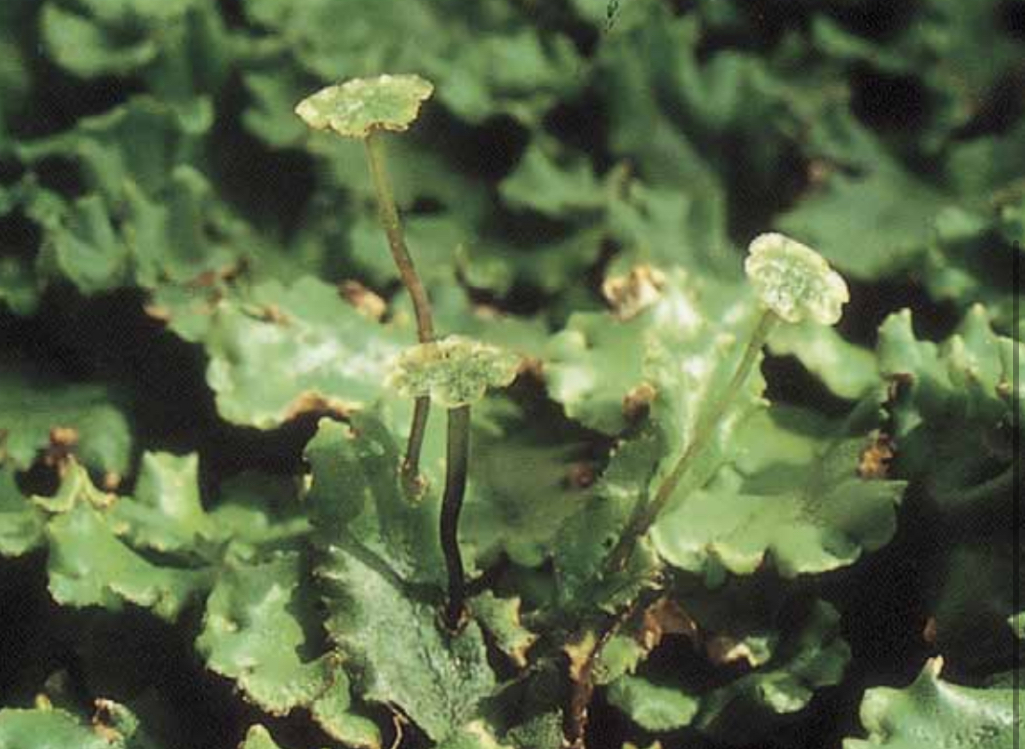

In Marchantia, the mature capsule contains what?
Spores and Elaters- Elators are elongated cells that as moisture absorbing wall thickening. Helps disperses spores.
Characteristics of Hornworts (phylum Anthocerotophyta)
Single Large Chloroplast with a pyrenoid
A meristem is developed between the foot and the sporanguim
Having the sporophyte with several layers of photosynthetic cells and dehiscence longitudinally.
That is covered with a cuticle and a stomata
Anthoceros is an example of what?
Hornwort, most familia of 11 genera- resemble those of thalloid liverworts.
What are the 3 classes of mosses that we talked about?
Sphagnidae (Peat Mosses)
Andreaeidae(granite mosses)
Bryidae(True Mosses)
Peat Mosses belong to the phylum___, class_____.?
Bryophyta, and Sphagindae
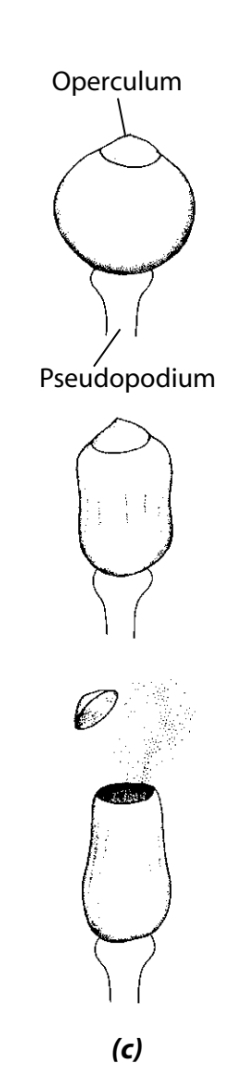
What is the characteristic of the sporophyte of Sphagnum?
The red to blackish-brown capsules that raised on a stalk called the pseudo podium, and the top of the capsule is a lid like operculum
The protonema of Sphagnum consists of ___ of cells?
A plate of cells, one layer thick that grows by a marginal meristem and the erect gametophytes arises from the bud like structure that grows from the cells.
Consists of large dead cells (hyaline cells)
A narrow green living cells containing chlolorplasts
The granite mosses belong to the phylum____, class____.
Bryophyta, and class Andreaeidae, (Consists of small blackish-green or dark reddish-brown tufted mosses
Often on granite rocks- protonema with two rows of cells
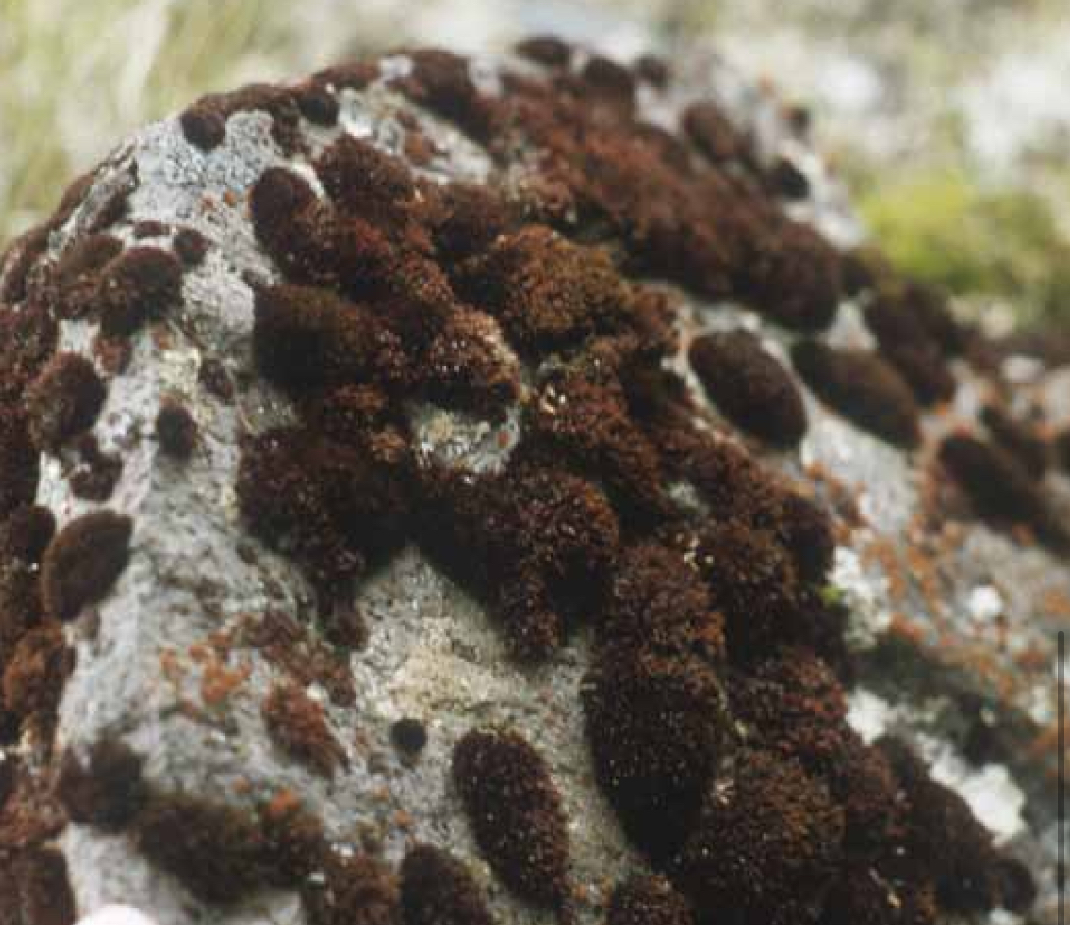

The true mosses belong to the phylum____, and class_____?
Bryophyta, and the class Byridae- which are the branching filaments of the protonema tea are composed of a single row of cells
What is a Hadron?
A water conducting tissue that contains eater conducting cells known as Hydroids
What is the function of a hydroids?
Conduct water, since they are elevated cells that have inclined end walls that are thin and permeable to water,
these resemble the water conducting elements of vascular plants
Some can have login containing wall thickenings, known as Leptoids

A peristome is a capsular structure characteristic of members of the phylum____, class____.?
Bryophyta and class Bryidae.
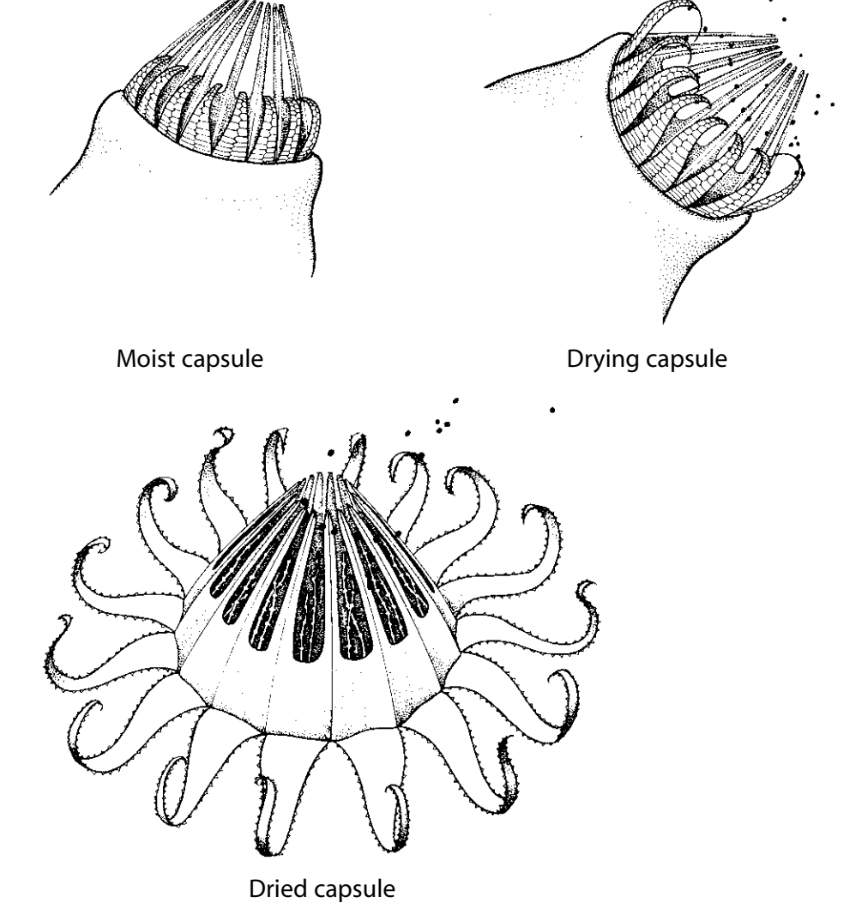
What is a peristome?
When the protective calyptra falls off and the capsule bursts off, reveals a ring of teeth that surround the opening.
Movements of the teeth expose the spores which are gradually released. (Haploid)
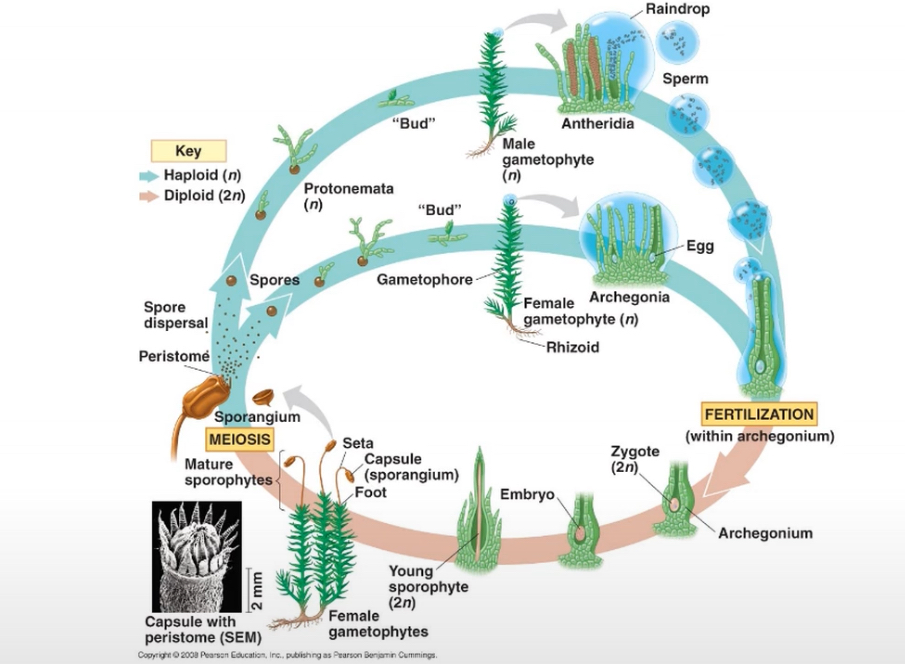
What is the Life Cycle of moss (phylum Bryophyta)
Fertilization occurs in the archegonium that is diploid (2n0 that hold the zygote→ which becomes the embryo and the sporophyte (spore made by the plant) is formed by mitosis and the sporophyte generation grows out of the archegonium. The spores are produced by sporangium that undergo meiosis
After meiosis some of the spores will develop into a archegonium and the antheridium gametophyte (1n) and the
antheridium will develop sperm by mitosis and the archegonium will produce egg by mitosis
Water needed to reproduce since they are flagellated in order to swim up and down to the archegonium.