Elbow Disorders
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
smoking, repetitive, forceful
Epicondylitis: Risk Factors
-_______
-Obesity
-Age 45-54
-__________ movement for at least two hours daily
-_________ activity (golf, tennis, construction)
extensors, lateral, carpi, brevis, supination, extension, epicondyle, extension, passive
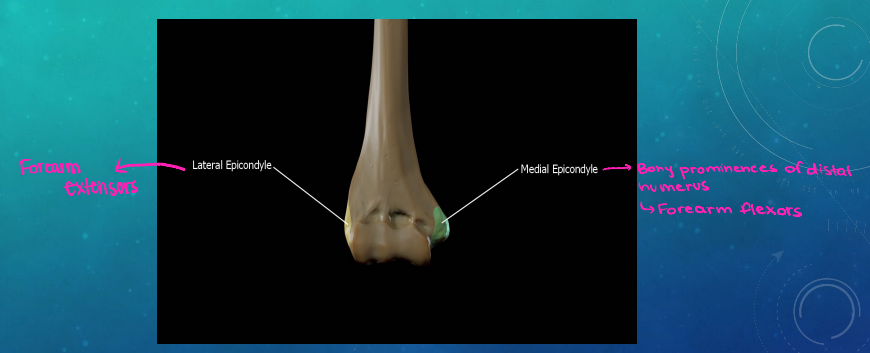
Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow): Background
-Inflammation of wrist __________ at lateral epicondyle
Extensor ____ radialis _____ muscle is affected
-Mechanism of Injury:
Overuse-repetitive ____________ and wrist _________
-S/S:
TTP over lateral ___________ and proximal wrist extensors
Pain with resisted wrist ___________
Pain with ________ wrist flexion
-Diagnosis:
Clinical
modification, brace, steroid, 6, 9-12
Lateral Epicondylitis: Treatment
-Activity ___________, ice, NSAIDs, counterforce ______, wrist splints, and PT are all first line options
-_______ injection, surgery is rarely indicated
-Indications for referral:
Severe pain or significant dysfunction for a minimum of _ months
Failure of conservative therapy for _-__ months
flexors, pronators, teres-flexor, pronation, epicondyle, flexion, passive
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow): Background
-Inflammation of wrist _______/___________ at medial epicondyle
Pronator _____-______ carpi radialis muscles
-Mechanism of Injury:
Overuse-repetitive wrist flexion and ___________
-S/S:
TTP over the medial ___________ and proximal wrist flexors
Pain with resisted wrist _______ and pronation
Pain with _________ wrist extension
clinical, activity, PT
Medial Epicondylitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis:
________
-Treatment:
_______ modification, rest, ice, NSAIDs, __
Steroid injection
bursa, olecranon, trauma, pressure, overuse, RA, swelling, cellulitis
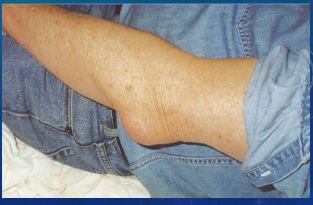
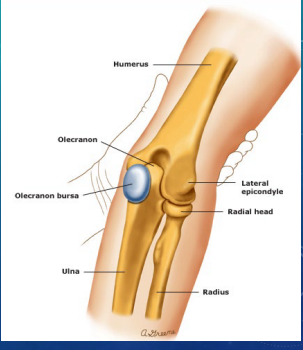
Olecranon Bursitis: Background
-Inflammation of the _____ that overlies the __________ process
-Mechanism of Injury:
_____
Prolonged _________ to area (think truck driver resting on elbow)
_________ or strenuous act
Crystal induced arthropathy
Inflammatory arthritis (__)
Septic bursitis
-S/S:
TTP and ___________ over the olecranon
Can be red and warm and appear like _____________
clinical, joint protection, aspiration, antibiotics
Olecranon Bursitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis:
_______
Aspiration, if concerned for infection or gout
-Treatment:
Ice, NSAIDs, _____ __________
___________ can sometimes be used for treatment if there is no improvement over 3-6 weeks
____________ if concerned for infection
ulnar, cubital, flexor carpi, flexion
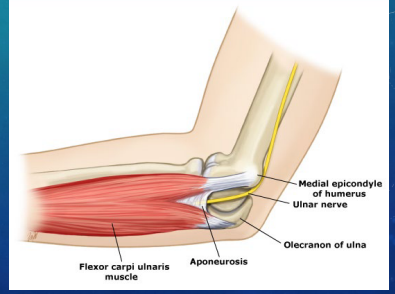
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Background
-______ nerve compression in the ______ tunnel along the medial elbow. The nerve is compressed by the _____ ______ ulnaris
-Caused by trauma, leaning on elbow, prolonged _________, and joint pathologies
4th, 5th, pain, flexion, Tinel, MRI, splinting, decompression
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment
-S/S:
Parathesias of the ___ and ___ digits
Medial elbow ____, aggravated by elbow _________
+ ____ sign possible
-Diagnosis:
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
___ and/or US
-Treatment:
Activity modification
________ elbow
Severe or refractory symptoms = ________________ surgery
FOOSH, pain, lateral, pronation, decreased
Radial Head and Neck Fractures: Background
-Mechanism of Injury:
Fall onto an outstretched arm (______)
Direct blow
-S/S:
____, TTP, and/or swelling over _______ elbow/radial head
Pain with _________/supination
____________ elbow ROM
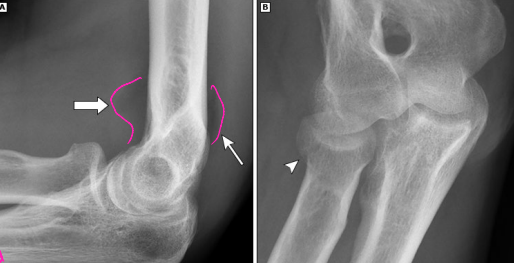
alignment, fat pads, occult, fragments
Radial Head/Neck Fracture: Diagnosis
-X-Ray
Fracture
Abnormal bony _________
Elevated ___ ____ (sail sign) → caused by blood distending joint capsule, may be the only sign of an ______ fracture
Small bone ___________ in joint
NSAIDs, sling, splint, ortho, displaced
Radial Head/Neck Fracture: Treatment
-Ice, _________
-Non-displaced → ____ vs posterior long arm ______ at 90 degrees (depending on severity)
-Refer to _____ for complex or __________ fractures → pt may need ORIF
Monteggia
What type of fracture is being described?
-Ulnar fracture with dislocation of the radial head
Galeazzi
What type of fracture is being described?
-Radius fracture with dislocation of the distal radiolunar joint