[PHA6115 LEC] CHAPTER 3: ADRENERGICS
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
1
New cards
Drug that promotes sympathetic/parasympathetic activity
Mimetic Agent
2
New cards
Drug that promotes sympathetic activity
Sympathomimetic/Andromimetic
3
New cards
Drug that promotes parasympathetic activity
Parasympathomimetic/Cholinomimetic
4
New cards
Drug that inhibits sympathetic/parasympathetic activity
Blocking agent
5
New cards
Adrenergic blocking agent
Sympatholytic
6
New cards
Cholinergic blocking agent
Anti-muscarinic
7
New cards
Agents that act on adrenoreceptors (AR) and adrenergic \n neurotransmitter (NT)
Adrenergic agents
8
New cards
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
Neurotransmitters
9
New cards
NTs are stored in synaptic nerve endings and maintained by
Vesicular Monoamine Transporter
10
New cards
Uptake 1
Norepinephrine transporter (NET) and dopamine transporters (DT)
11
New cards
NTs are chemically derived from
Tyrosine
12
New cards
(---------------) adds -OH at 3’ position of tyrosine \n producing L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA)
tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)
13
New cards
tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) adds (---) at 3’ position of tyrosine \n producing L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA)
\-OH
14
New cards
tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) adds -OH at 3’ position of tyrosine \n producing (--------)
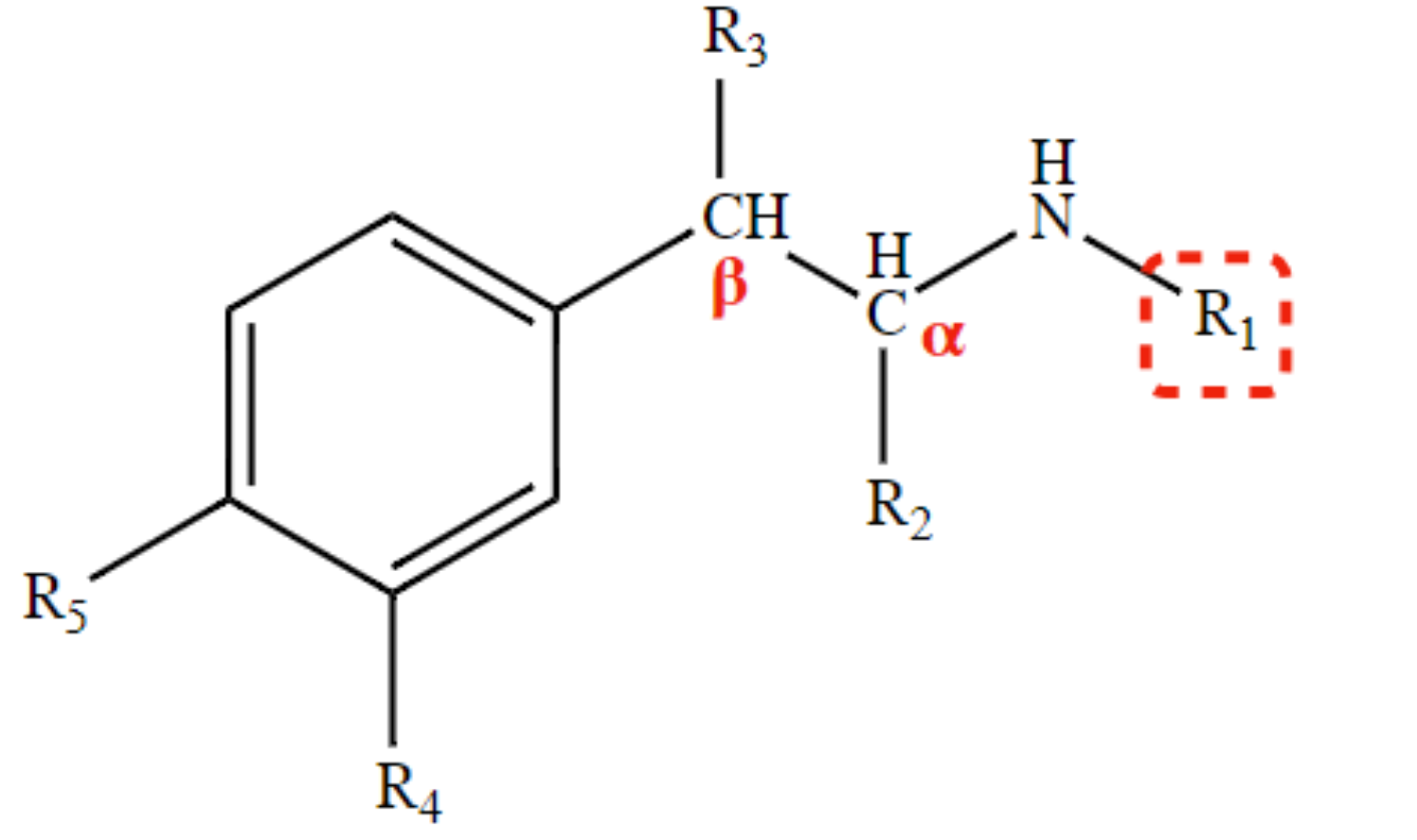
L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA)
15
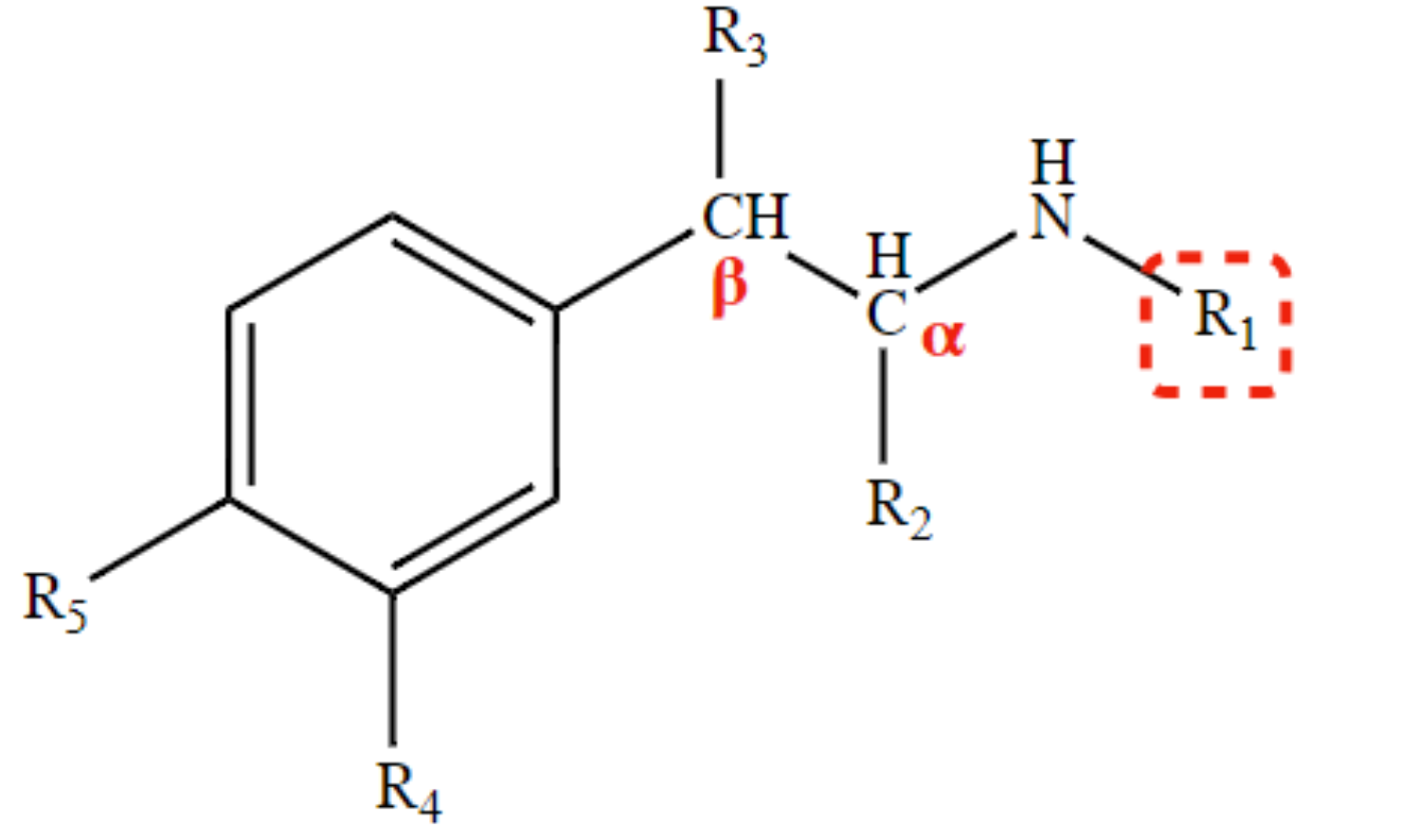
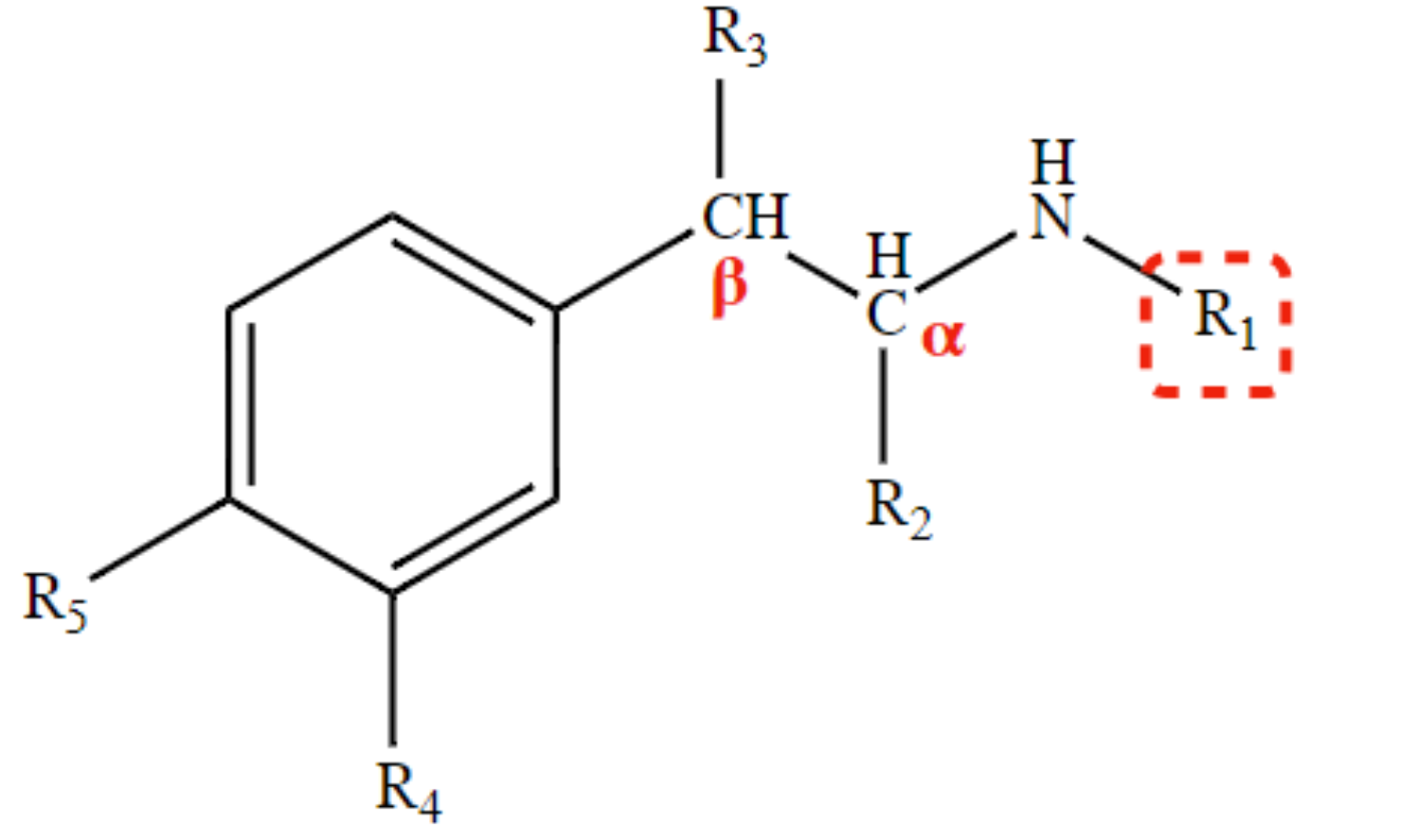
New cards
2\. (---------) of L-DOPA by L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
Decarboxylation
16
New cards
2\. Decarboxylation of (------) by L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
L-DOPA
17
New cards
2\. Decarboxylation of L-DOPA by (-----------------)
L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
18
New cards
3\. (-----------------) adds -OH to the side chain and form NE.
Dopamine-β-hydroxylase
19
New cards
3\. Dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH) adds (-----) to the side chain and form NE.
\-OH
20
New cards
3\. Dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH) adds -OH to the (-------) and form NE.
side chain
21
New cards
3\. Dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH) adds -OH to the side chain and form (----------)
NE
22
New cards
4\. (--------------) adds -CH3 to the amino group and forms Epinephrine.
Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT)
23
New cards
4\. Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) adds (------) to the amino group and forms Epinephrine.
\-CH3
24
New cards
4\. Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) adds -CH3 to the (------) and forms Epinephrine.
amino group
25
New cards
4\. Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PNMT) adds -CH3 to the amino group and forms (-------).
Epinephrine
26
New cards
The neurotransmitters are chemically described as
Catecholamines
27
New cards
Catecholamines are extensively metabolized by
catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
28
New cards
competes with TH, prevents the formation of L-DOPA
Metyrosine
29
New cards
competes with AADC and prevent L-DOPA metabolism, useful for Parkinsonism to ensure Dopa levels in the brain.
Carbidopa
30
New cards
comes from Rauwolfia serpentina, binds VMAT resulting \n to the metabolism of NE by MAO
Reserpine
31
New cards
binds storage vesicle and makes nerve impulse less responsive to signal triggers
Guanethidine and Guanadrel
32
New cards
𝜶1
* Blood Vessels / Skin
* Mucous membranes
* Uterus
* Mucous membranes
* Uterus
33
New cards
𝜶1A
Prostatic Gland Muscle
34
New cards
𝜶2
CNS
35
New cards
𝜷1 (minor 𝜷2 , 𝜷3 )
Heart
36
New cards
* 𝜶1 -smooth muscle contraction
* 𝜷2 - smooth muscle relaxation
* 𝜷2 - smooth muscle relaxation
Lungs
37
New cards
𝜷1
Kidney
38
New cards
𝜷3
Adipose tissue
39
New cards
binds to the receptors and activates responses like NE
Direct agonist
40
New cards
stimulate release of NE at presynaptic terminal
Indirect agonist 1
41
New cards
block uptake-1
Indirect agonist 2
42
New cards
inhibit NE metabolism
Indirect agonist 3
43
New cards
both direct and indirect agonist activity
Mixed
44
New cards
(----------------------) \n • β-phenylethylamine, catechol ring, (1R)-OH or (2S)-CH3 is required for maximal effect.
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist
45
New cards
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist \n • (--------------), catechol ring, (1R)-OH or (2S)-CH3 is required for maximal effect.
β-phenylethylamine
46
New cards
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist \n • β-phenylethylamine, (---------), (1R)-OH or (2S)-CH3 is required for maximal effect.
catechol ring
47
New cards
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist \n • β-phenylethylamine, catechol ring, (------) or (2S)-CH3 is required for maximal effect.
(1R)-OH
48
New cards
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist \n • β-phenylethylamine, catechol ring, (1R)-OH or (2S)-CH3 is required for maximal effect.
(2S)-CH3
49
New cards
Phenylethylamine Adrenergic Agonist
* A (--------) is needed for receptor binding.
* A (--------) is needed for receptor binding.
Cationic amine
50
New cards
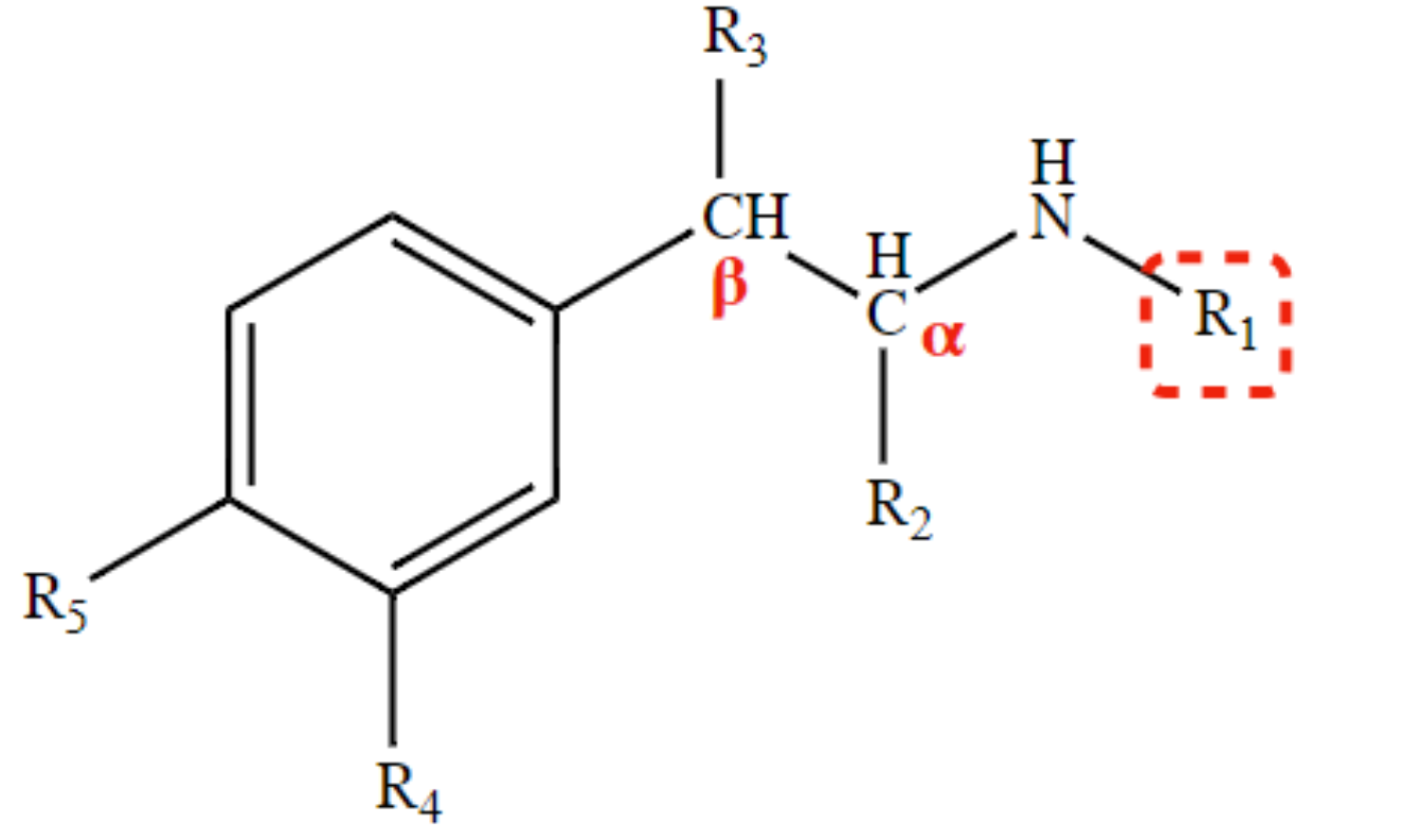
preferential α-agonist activity, some β1-agonist
H at R1
51
New cards
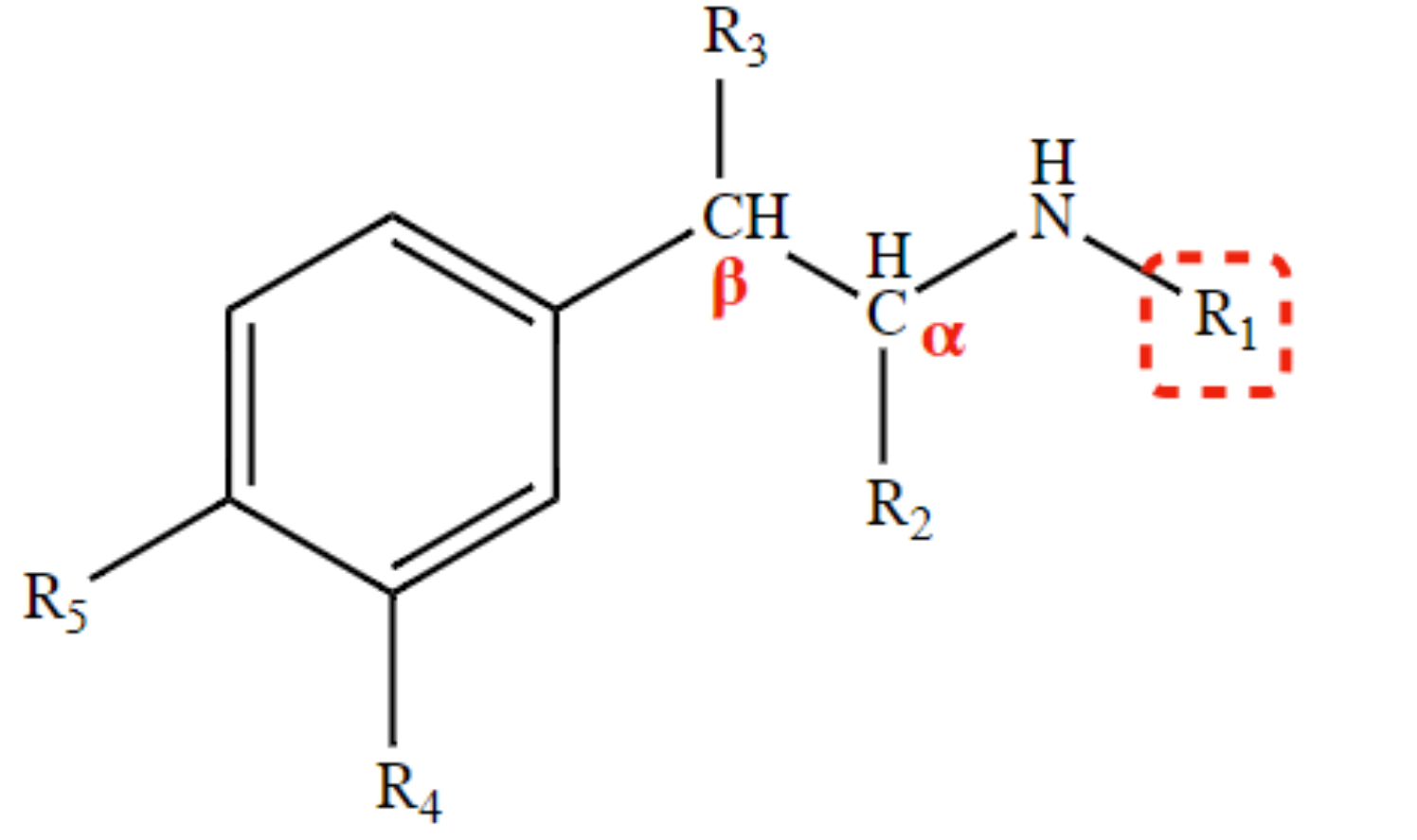
non-selective (𝛼 or β) activity
CH3 at R1
52
New cards
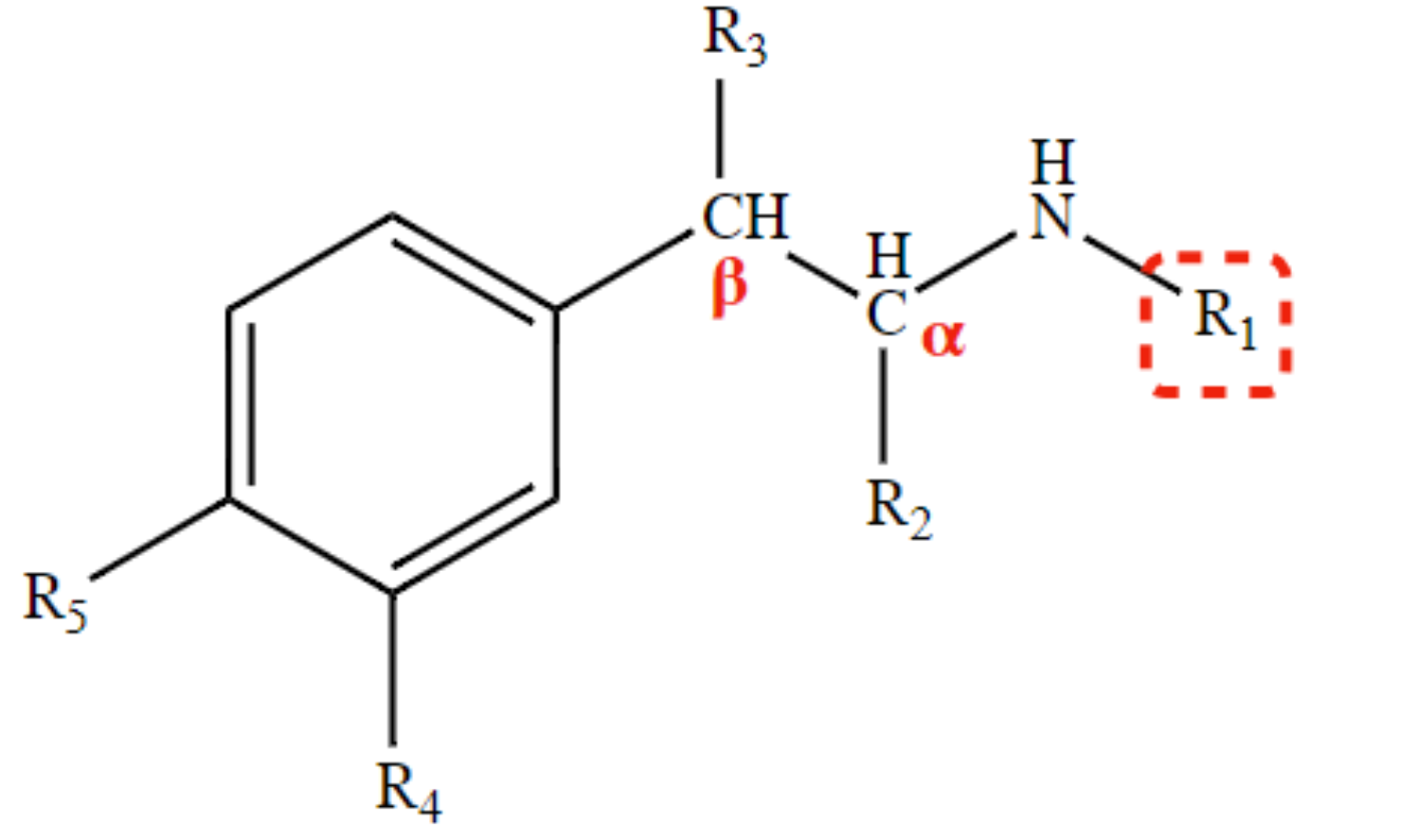
selective β-agonist
large substituents at R1
53
New cards
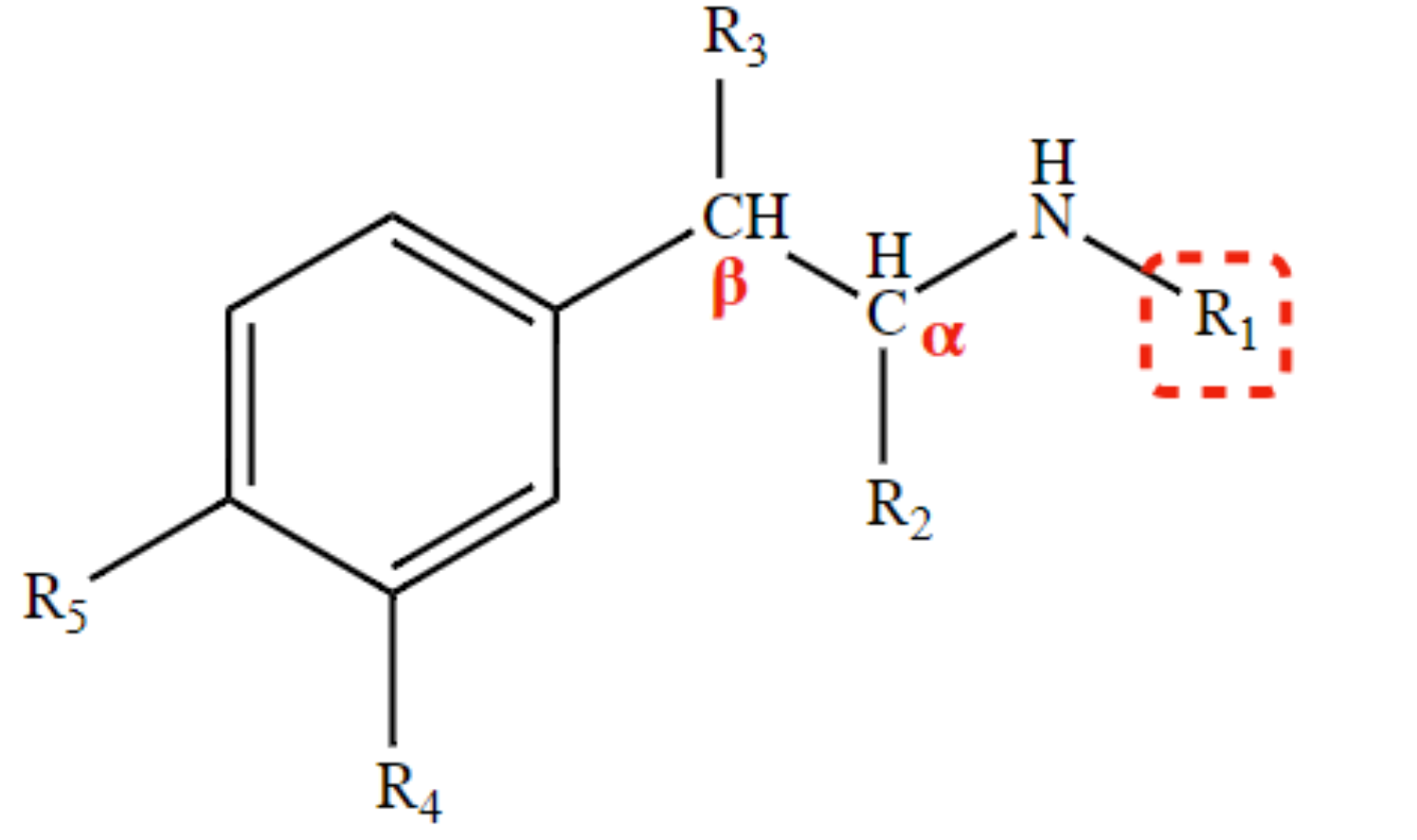
selective β1 and β2-agonist
isopropyl at R1
54
New cards
selective β2-agonist
tertbutyl at R1
55
New cards
slower MAO deamination
H at R2
56
New cards
R and S isomerism
CH3 at R2
57
New cards
decrease in 𝛼1 activity
R isomer with CH3 at R2
58
New cards
retains α2 and β-receptors activity
S isomer with CH3 at R2
59
New cards
β2-selective activity, even with α-preferential activity at the R1 position
C2H5 at R2
60
New cards
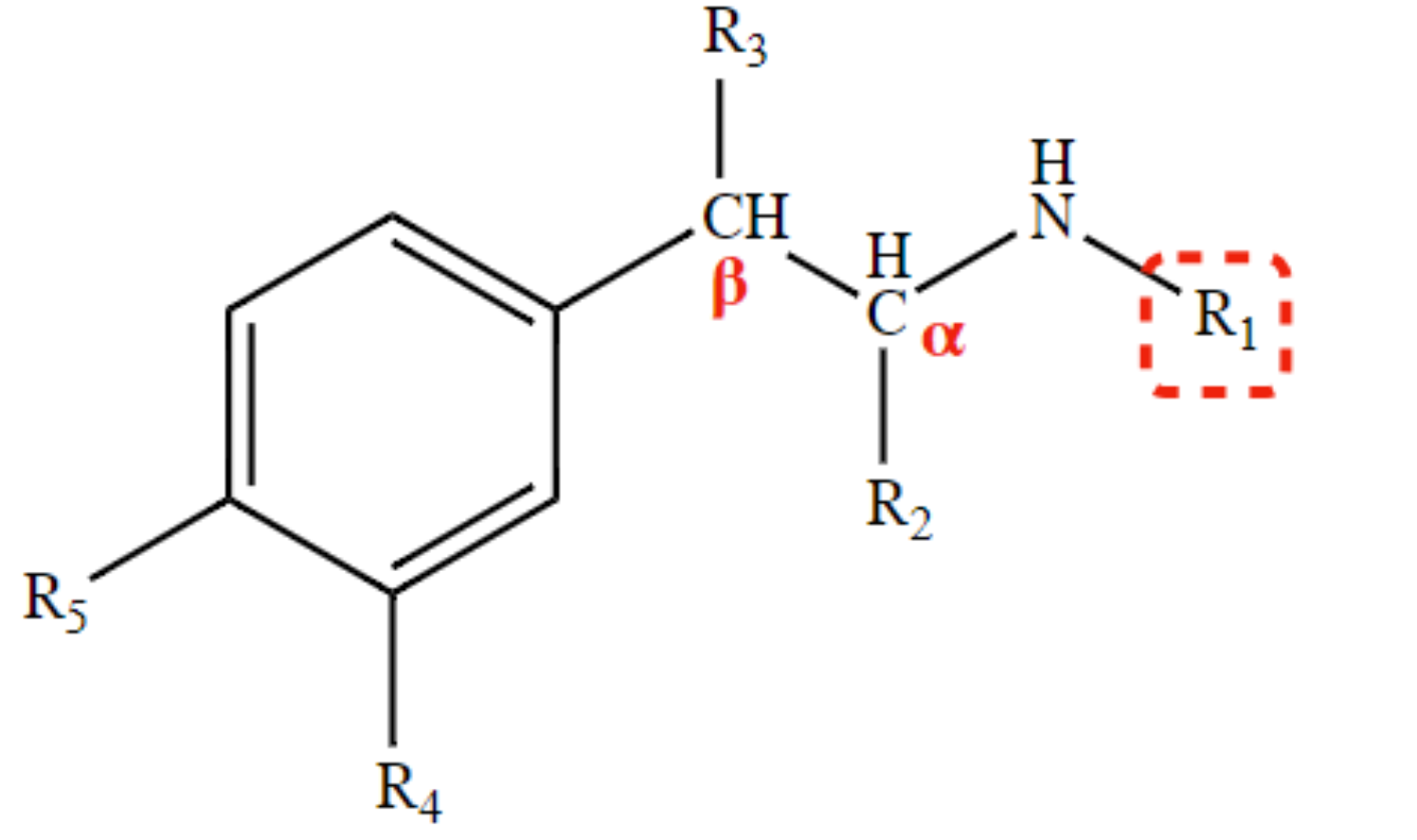
* decrease direct action (especially β receptors)
* increases CNS penetration (if R1 & R2 is CH3
* increases CNS penetration (if R1 & R2 is CH3
H at R3
61
New cards
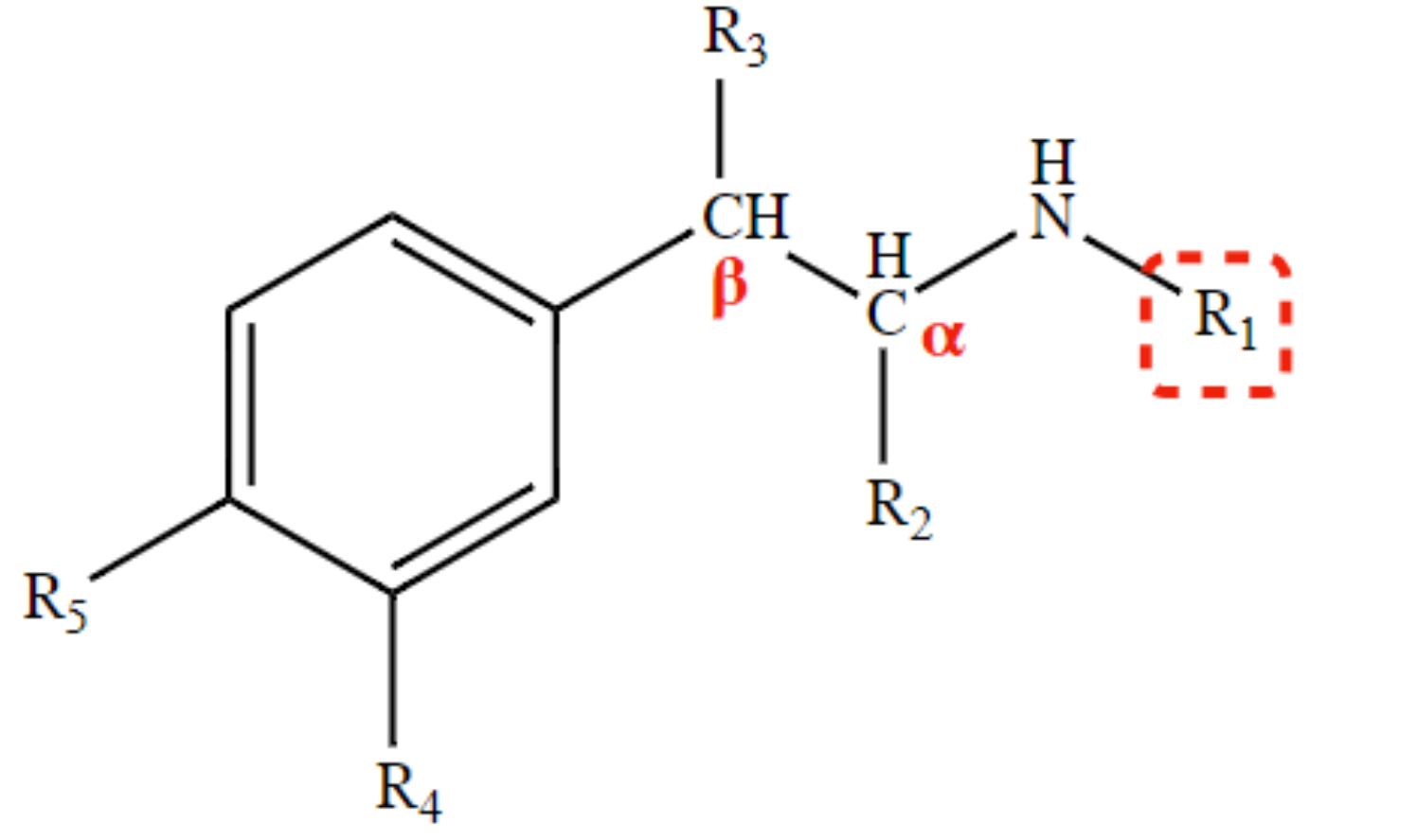
results to R & S isomerism (R3)
OH
62
New cards
optimal for direct action at receptors (OH at R3)
R isomer
63
New cards
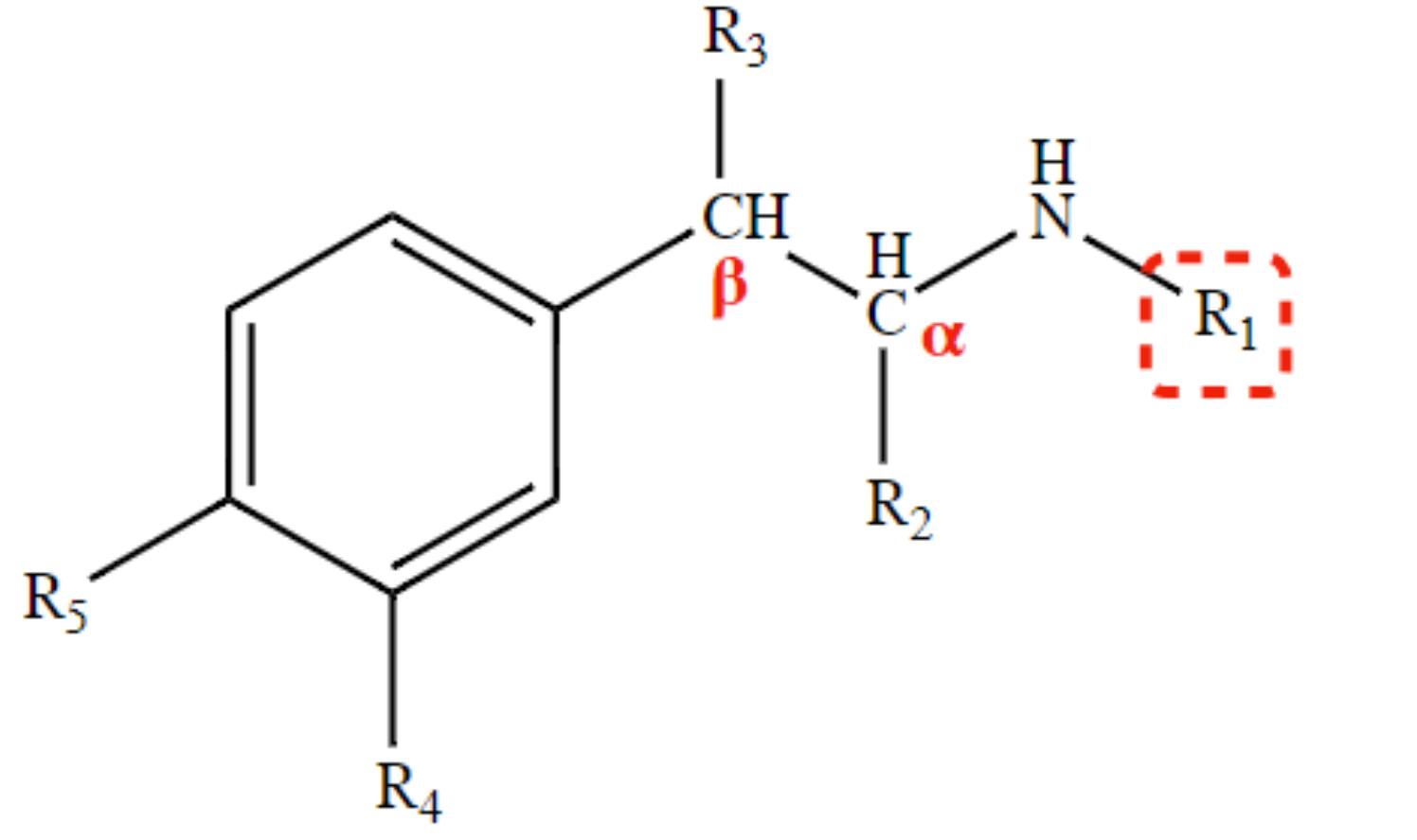
slow CNS penetration of drug agent
β-OH
64
New cards
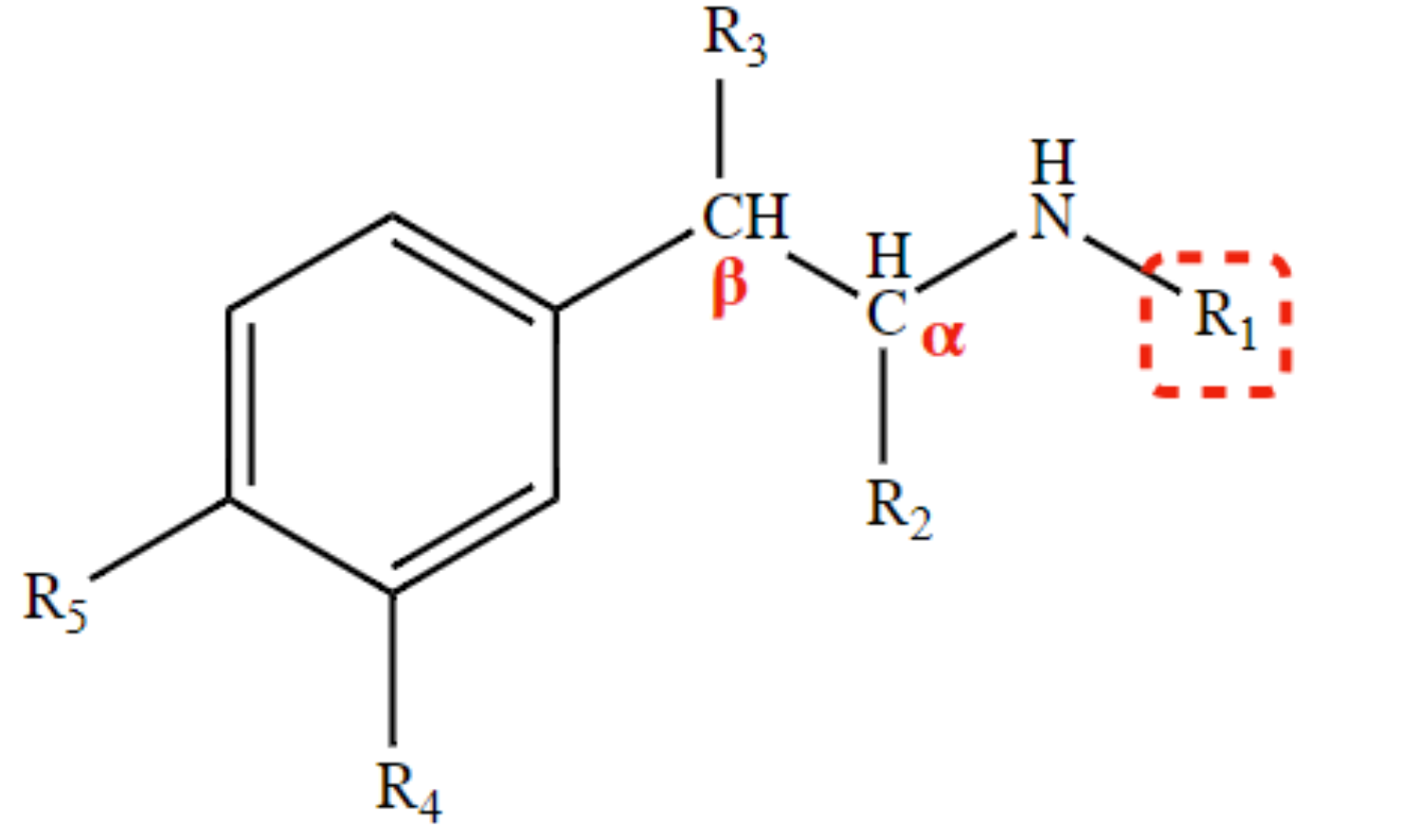
* decreases direct action (especially at β-receptors;
* renders indirect activity by blocking presynaptic uptake-1 \n Possible CNS stimulation (-H = promotes lipophilicity)
* renders indirect activity by blocking presynaptic uptake-1 \n Possible CNS stimulation (-H = promotes lipophilicity)
2H at R4 and R5
65
New cards
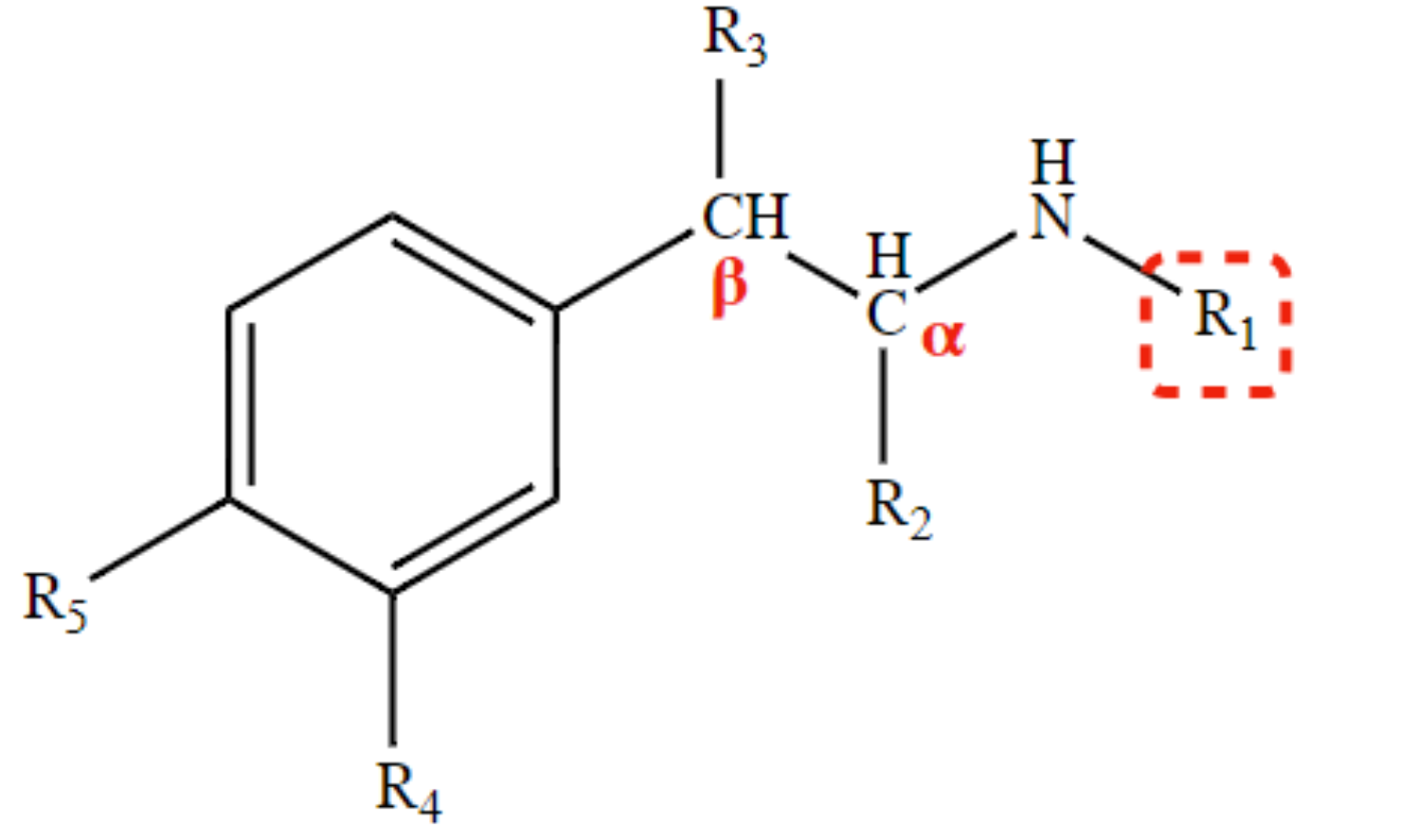
* Optimal direct action at all adrenoreceptors;
* Renders the structure a target for COMT attack;
* No CNS stimulation (-OH = increases hydrophilicity)
* Renders the structure a target for COMT attack;
* No CNS stimulation (-OH = increases hydrophilicity)
2OH at R4 and R5
66
New cards
* decreases direct action;
* provides β2-selective activity, even with α-preferential \n activity (R1 position)
* provides β2-selective activity, even with α-preferential \n activity (R1 position)
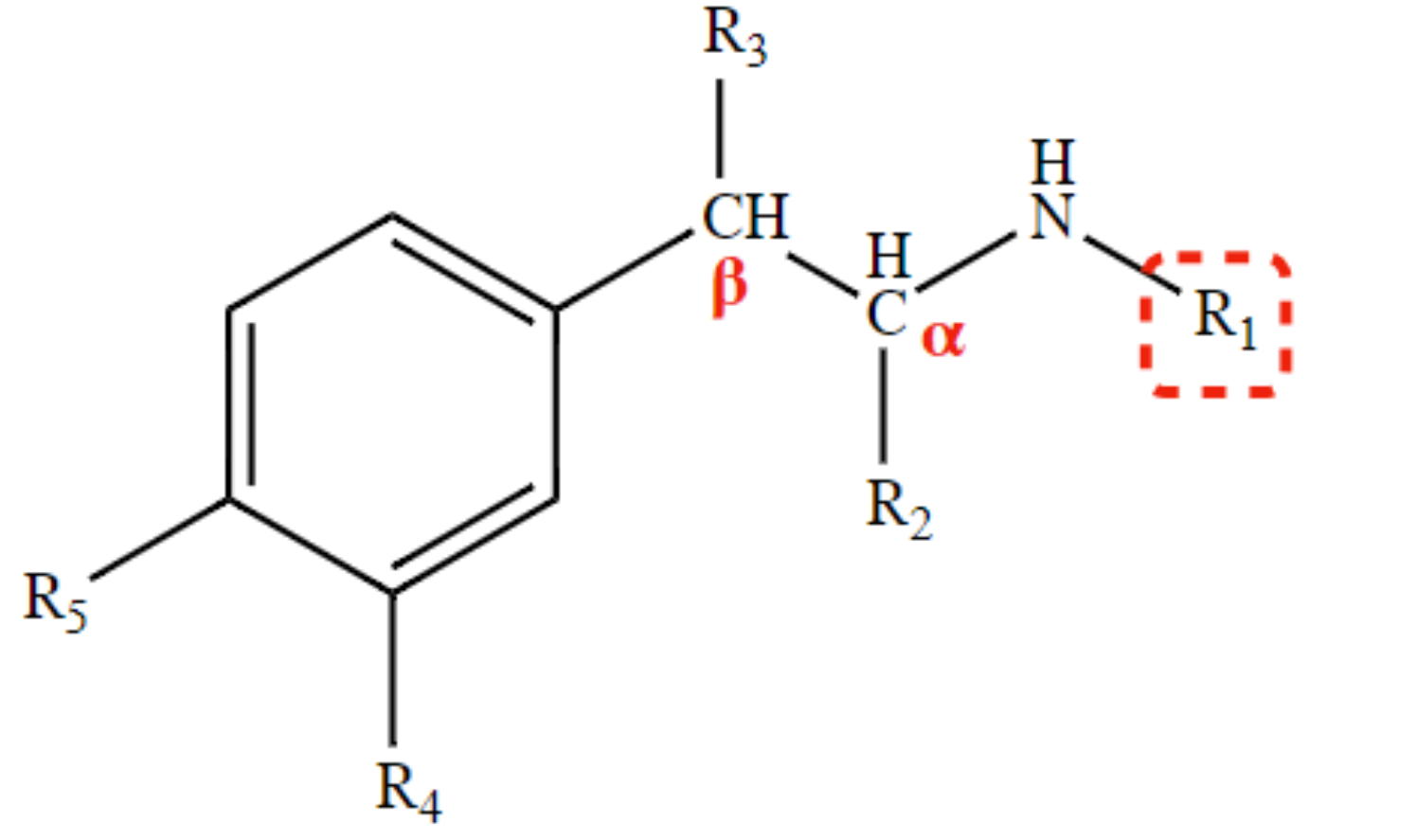
1OH at R4 or R5
67
New cards
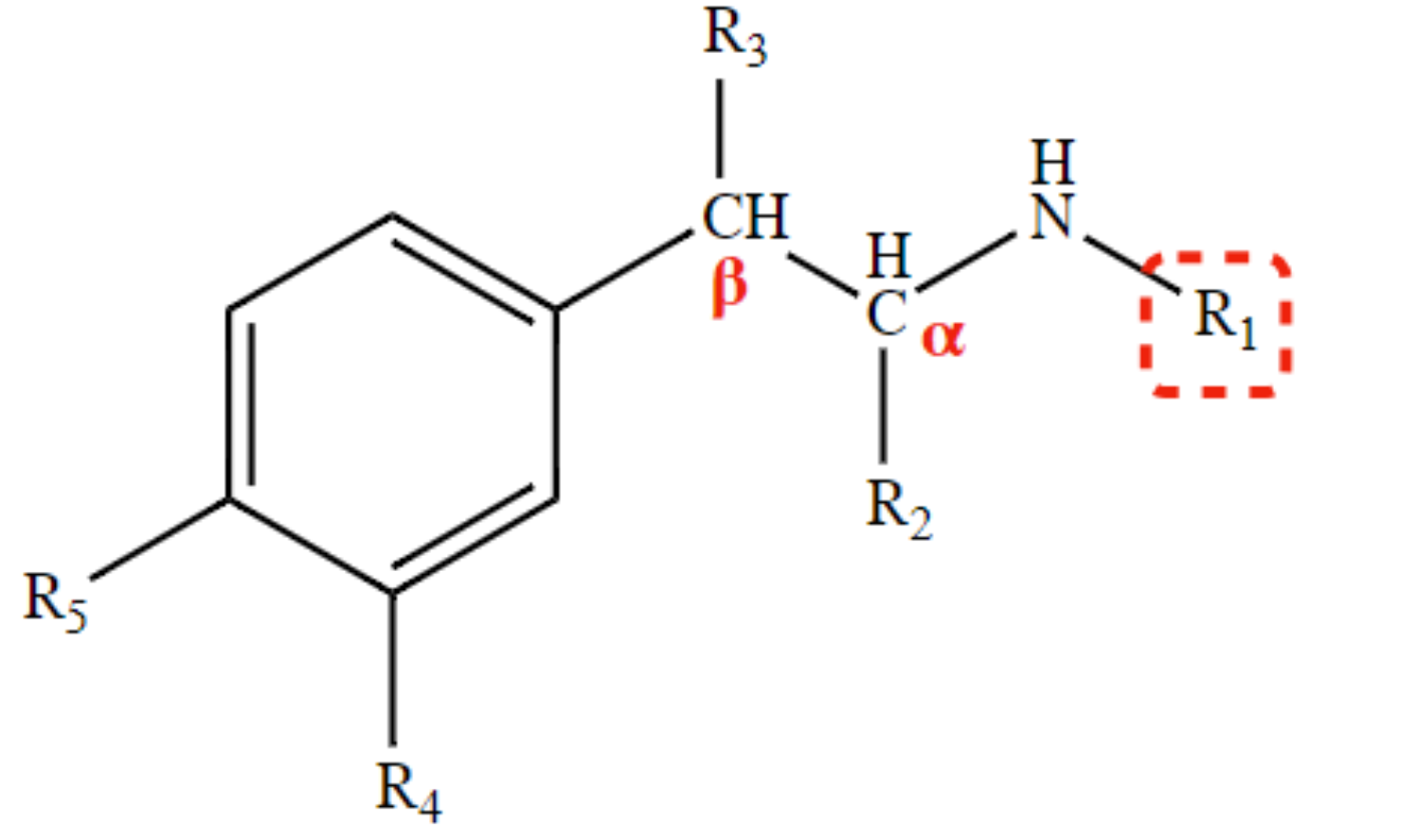
Determines receptor selectivity \n α1; α2 ; α and β; β 1 and β2; β2 .
R1
68
New cards
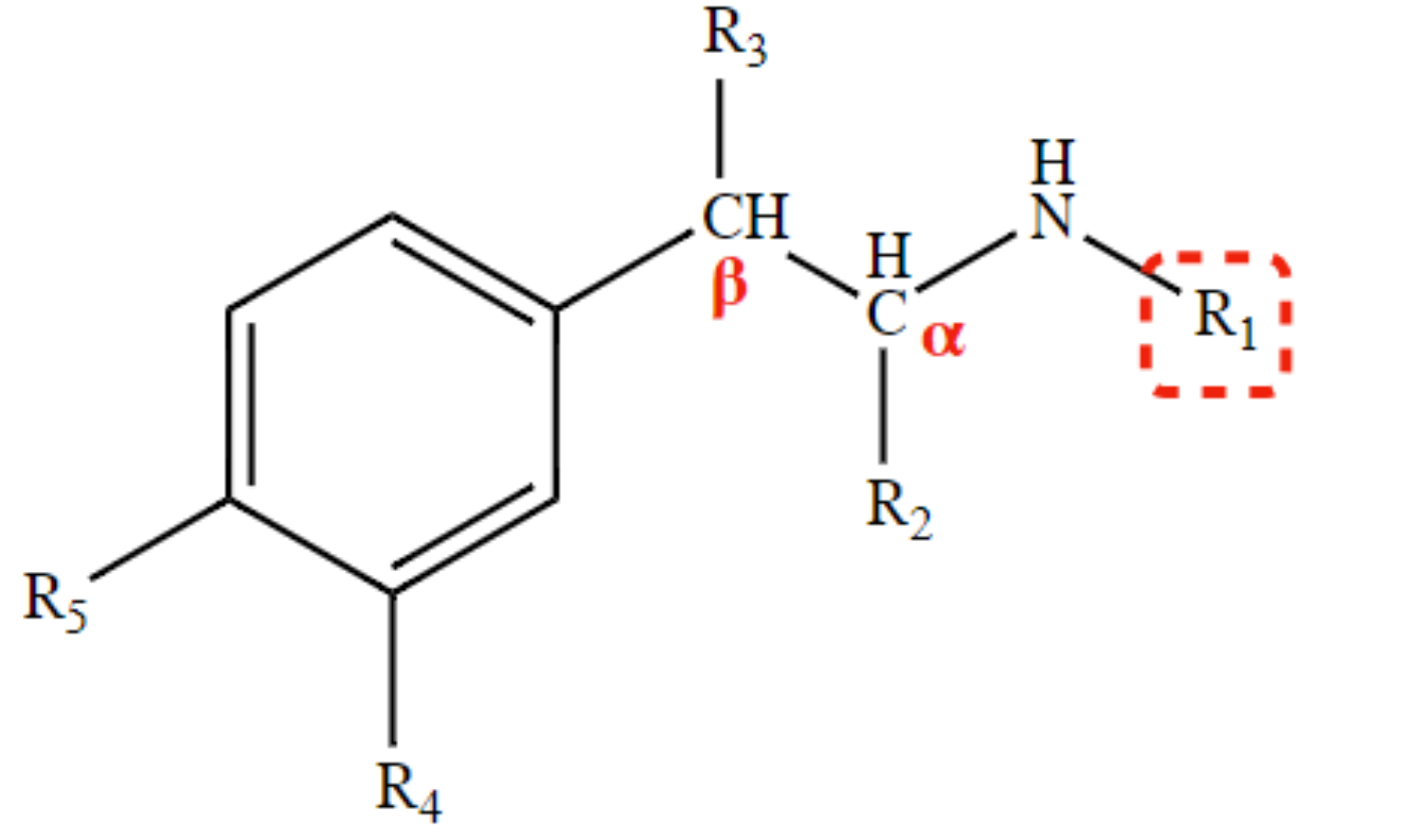
Protonation is required for receptor binding.
Basic amine
69
New cards
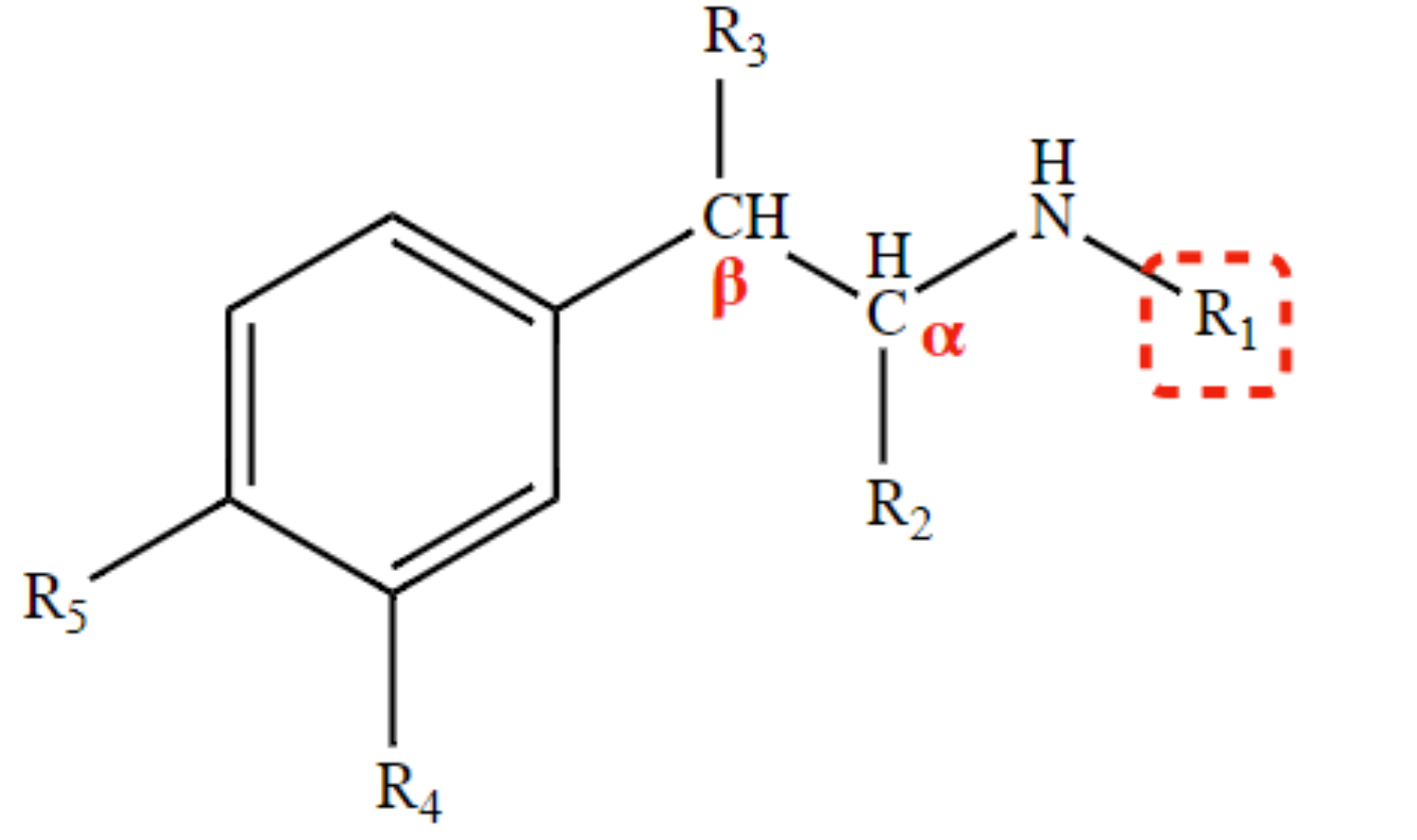
Determines vulnerability to MAO and extent of direct action.
R2
70
New cards
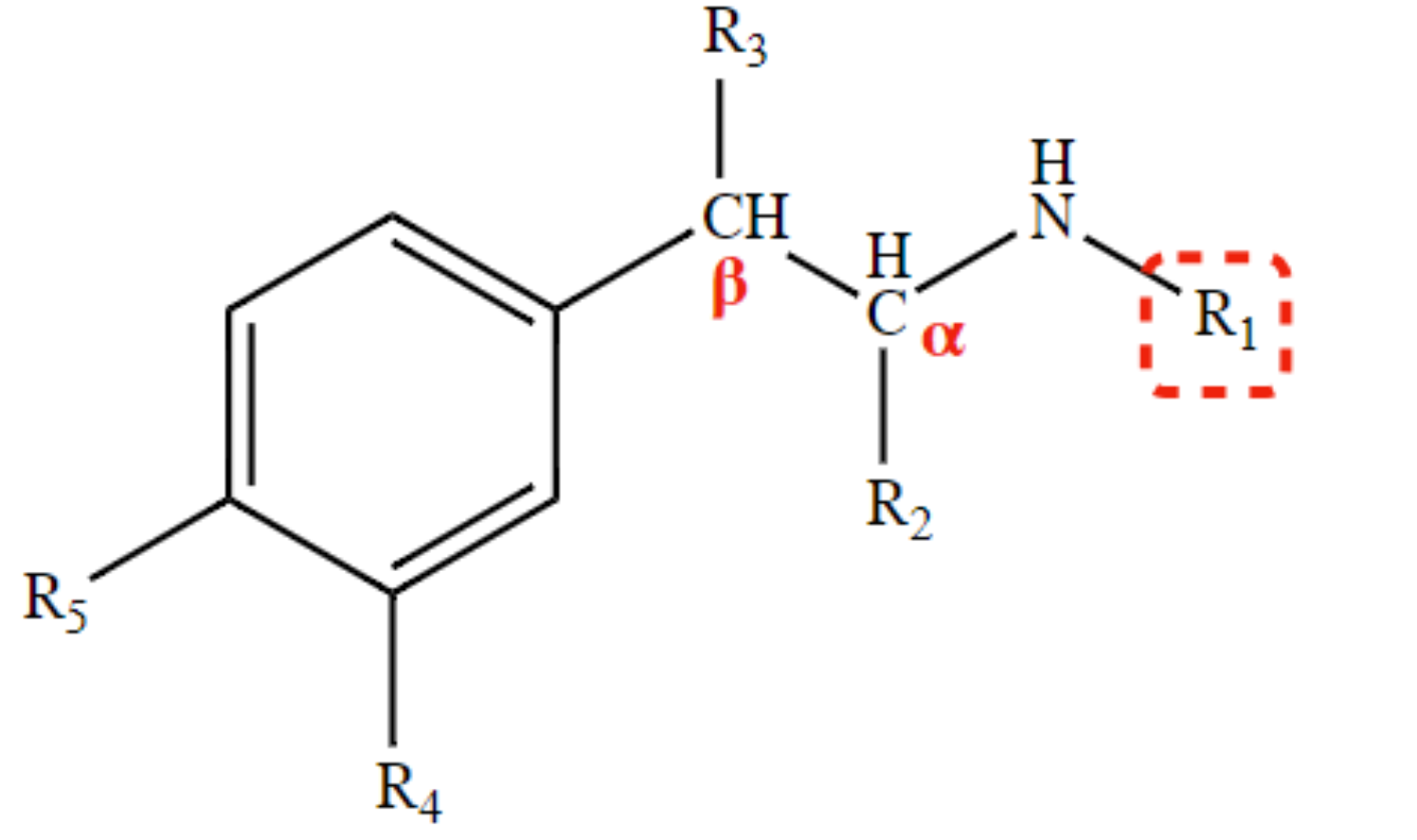
optimal distance between aromatic ring and amine
2-C
71
New cards
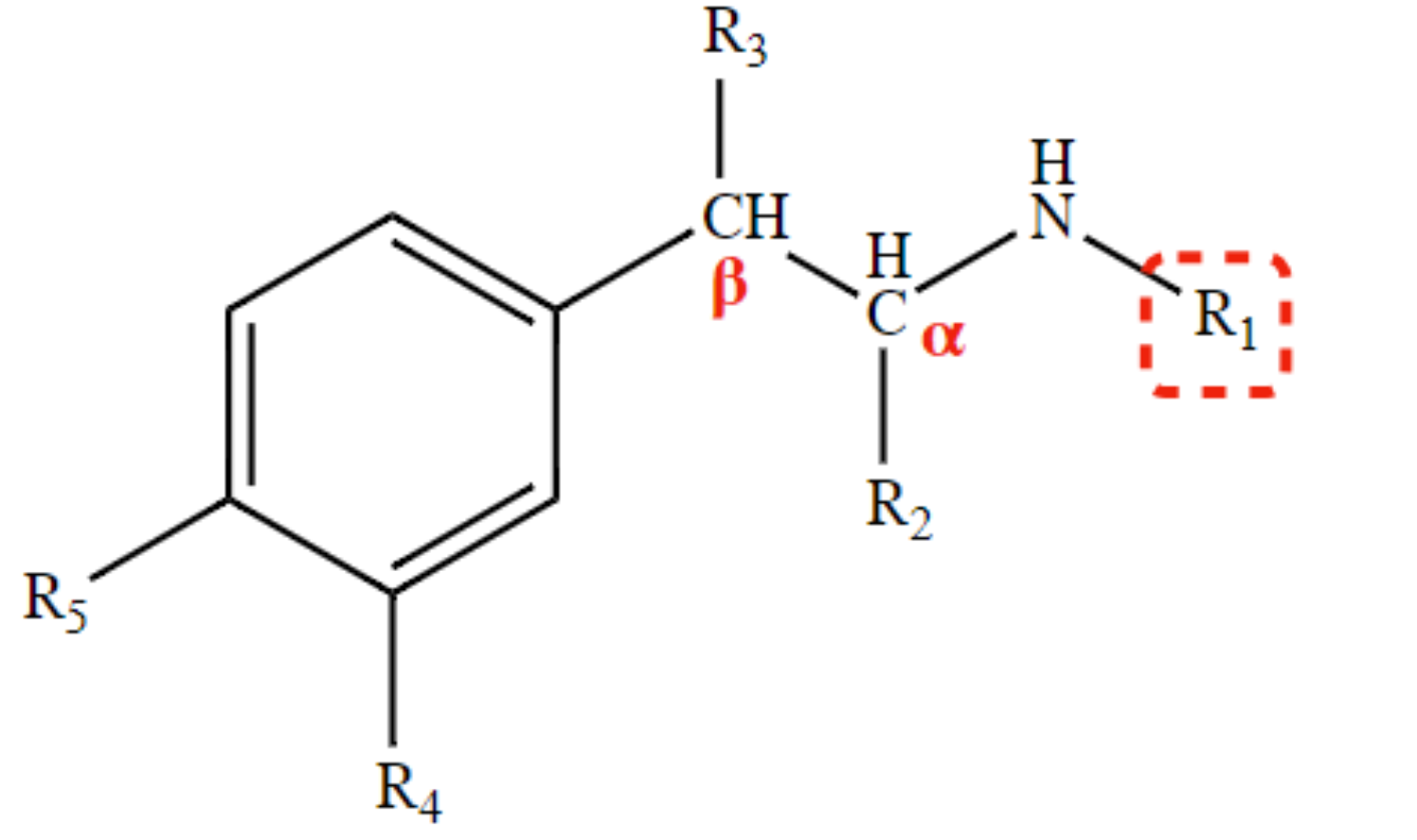
Determines extent of direct action and CNS activity.
R3
72
New cards
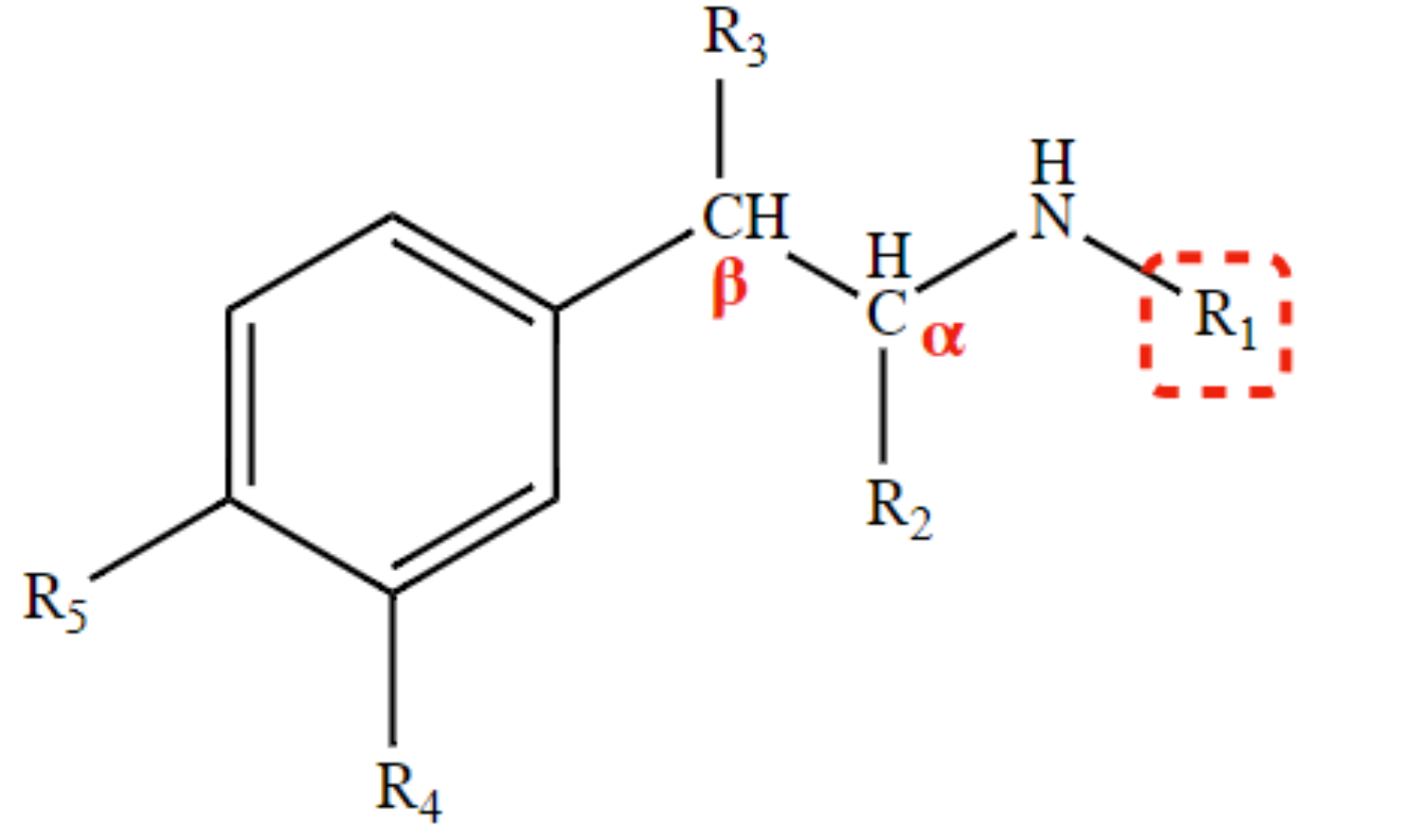
Determines extent of direct action, selectivity, vulnerability to COMT, and ability to cross BBB.
R4 and R5
73
New cards
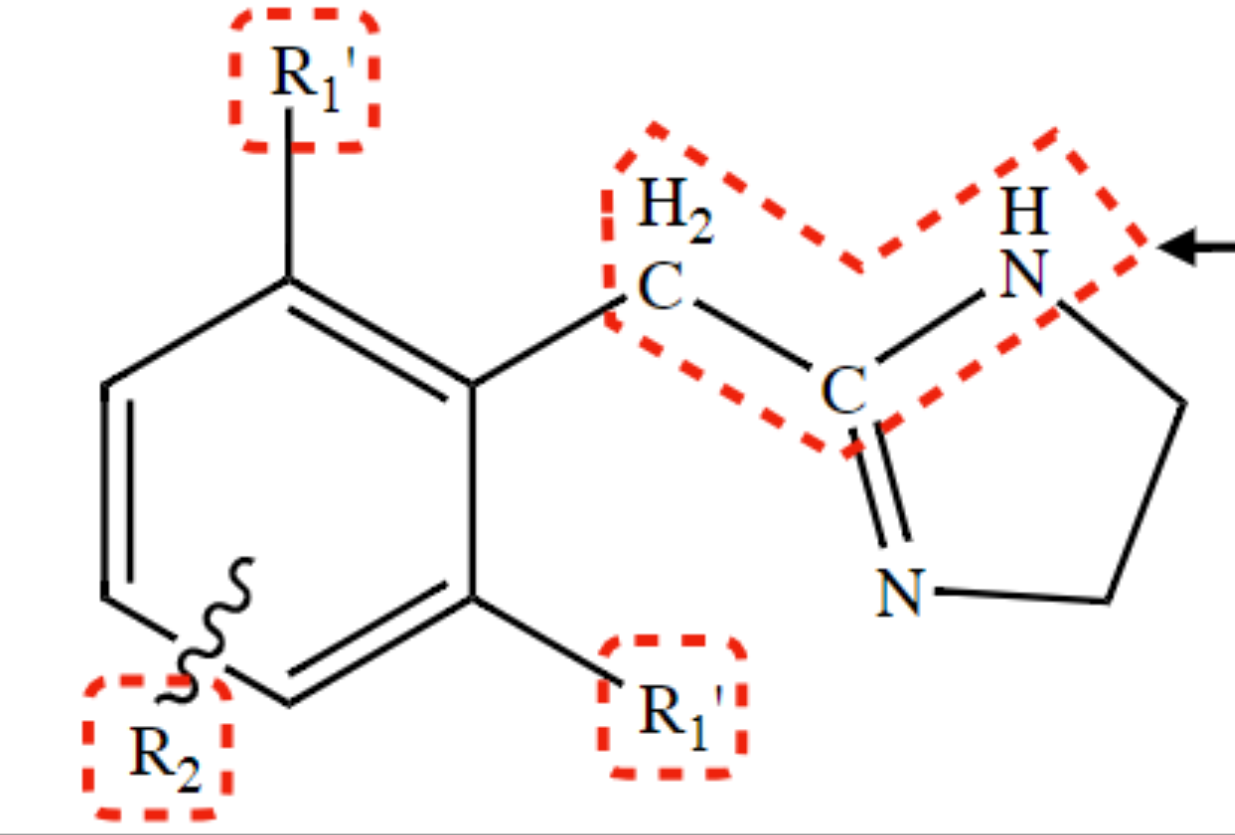
Pharmacophore of Arylimidazoline Adrenergic Agonist
Phenylethylamine within an imidazoline ring.
74
New cards
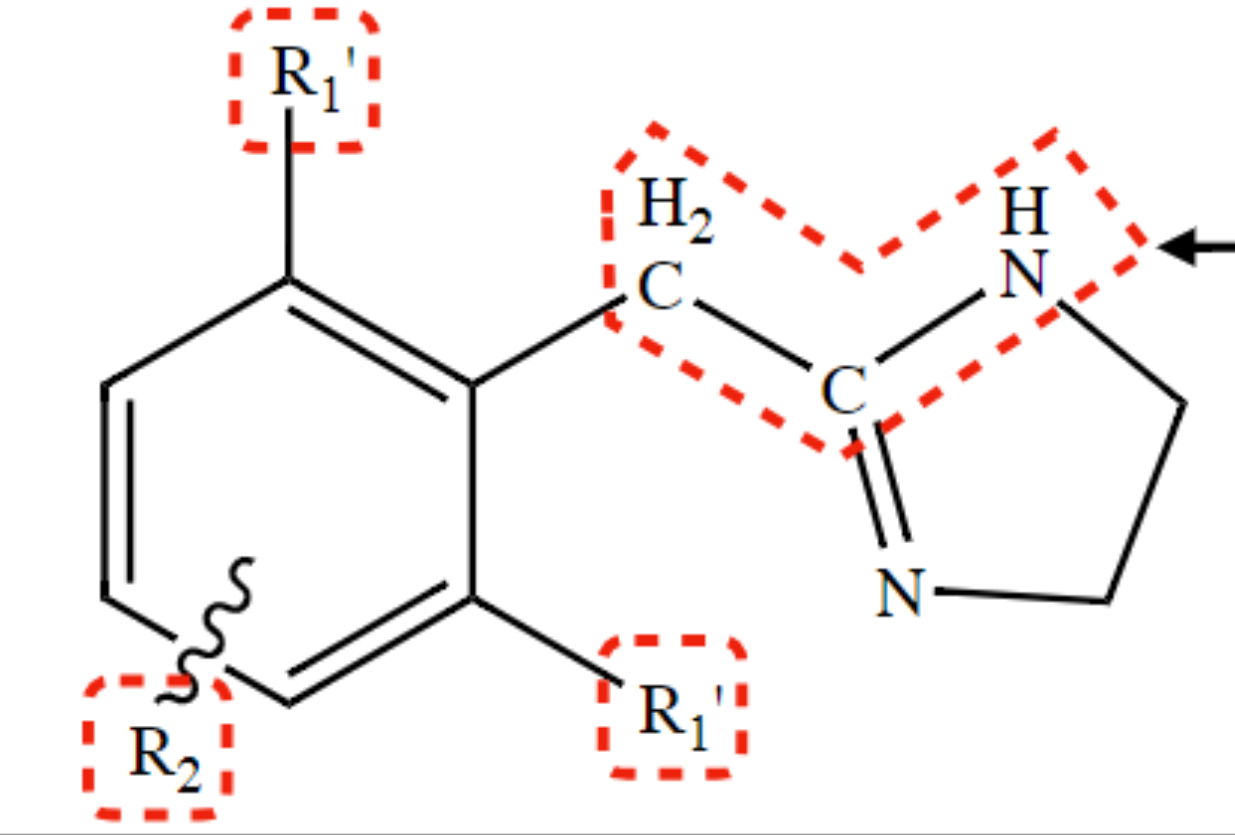
1 substitution R1
required for potent α-agonist action
75
New cards
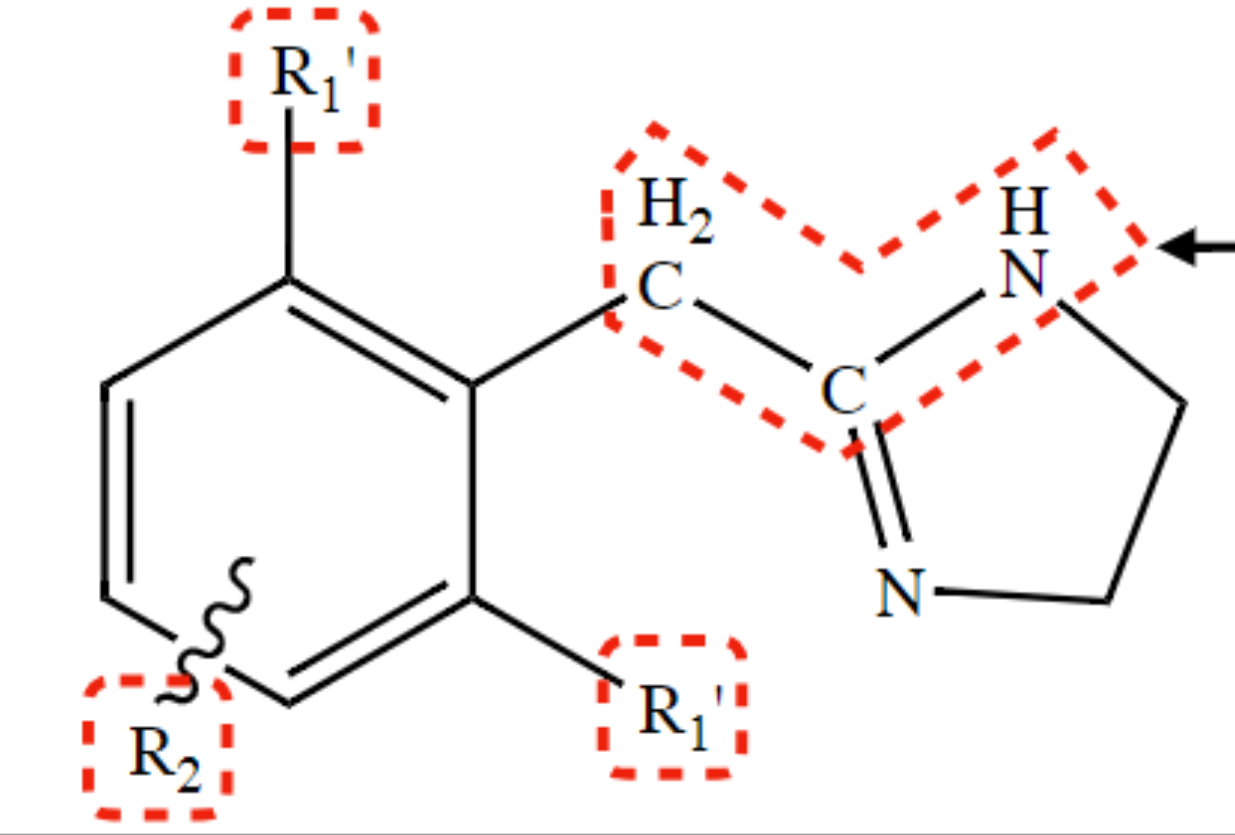
2 substitution R1
facilitate central distribution (increase lipophilicity)
76
New cards
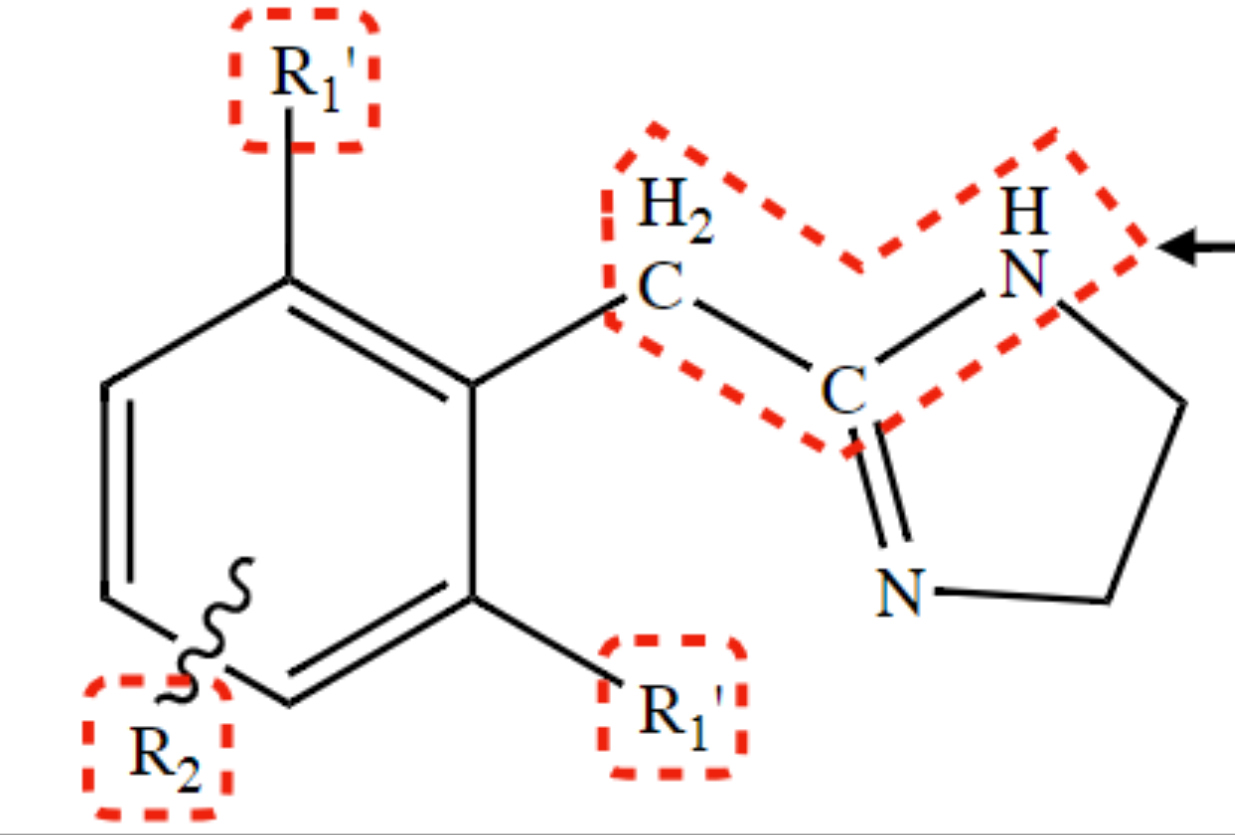
promotes α1-receptor selective activity
substitution at R2
77
New cards
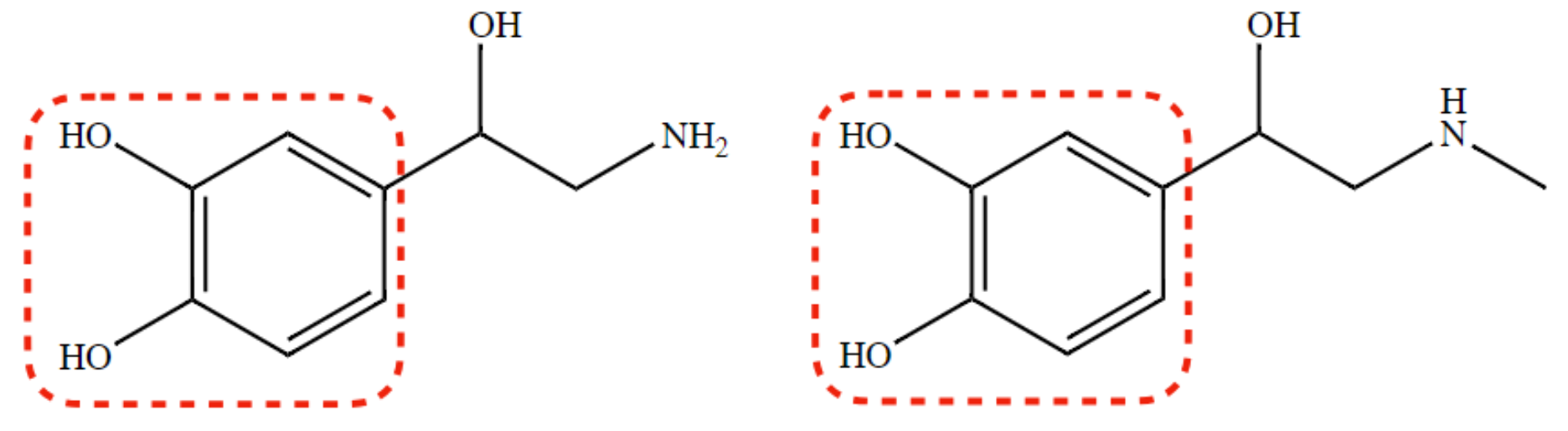
catecholic agents
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine
78
New cards
Metabolism of epinephrine and norepinephrine
COMT and MAO (orally inactive, short DOA)
79
New cards
Use of epinephrine and norepinephrine
life-threatening hypotension, hemorrhagic situations, stimulates \n heart (β1), and dilates bronchi (β 2)
80
New cards
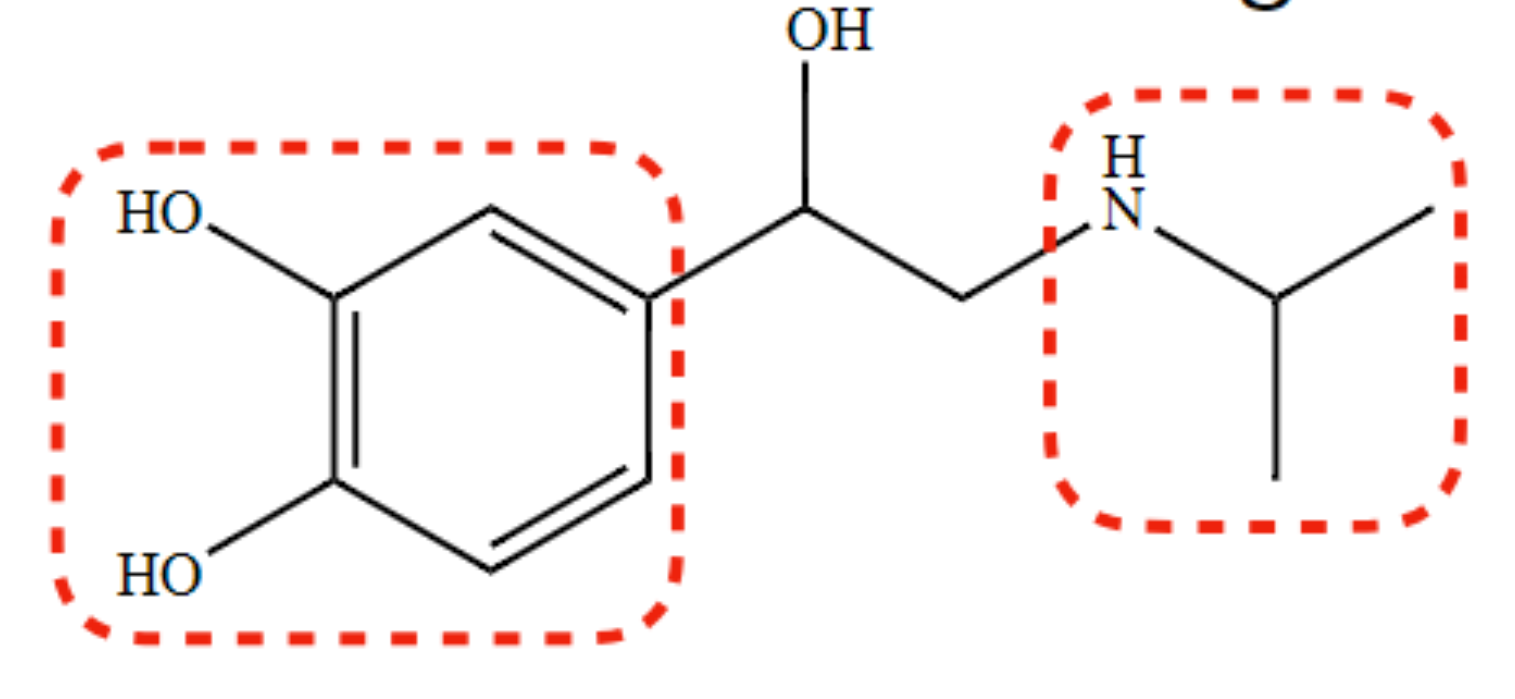
non-selective β-agonist with a catechol ring
Isoproterenol
81
New cards
causes non-selective β-receptor activity in isoproterenol
isopropyl moiety
82
New cards
Metabolism of isoproterenol
COMT, sulfation, and glucuronidation
83
New cards
Use of isoproterenol
↑cardiac output, bronchodilation
84
New cards
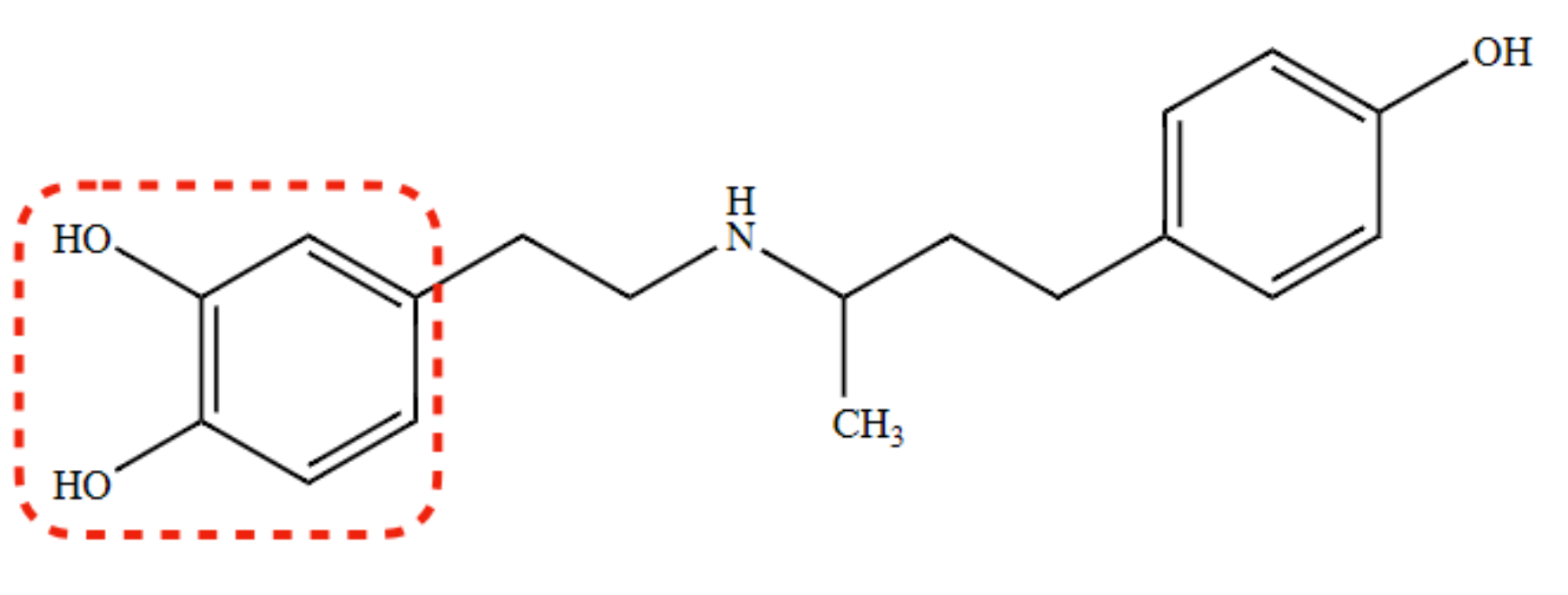
dual α- and β- agonist/antagonist
Dobutamine
85
New cards
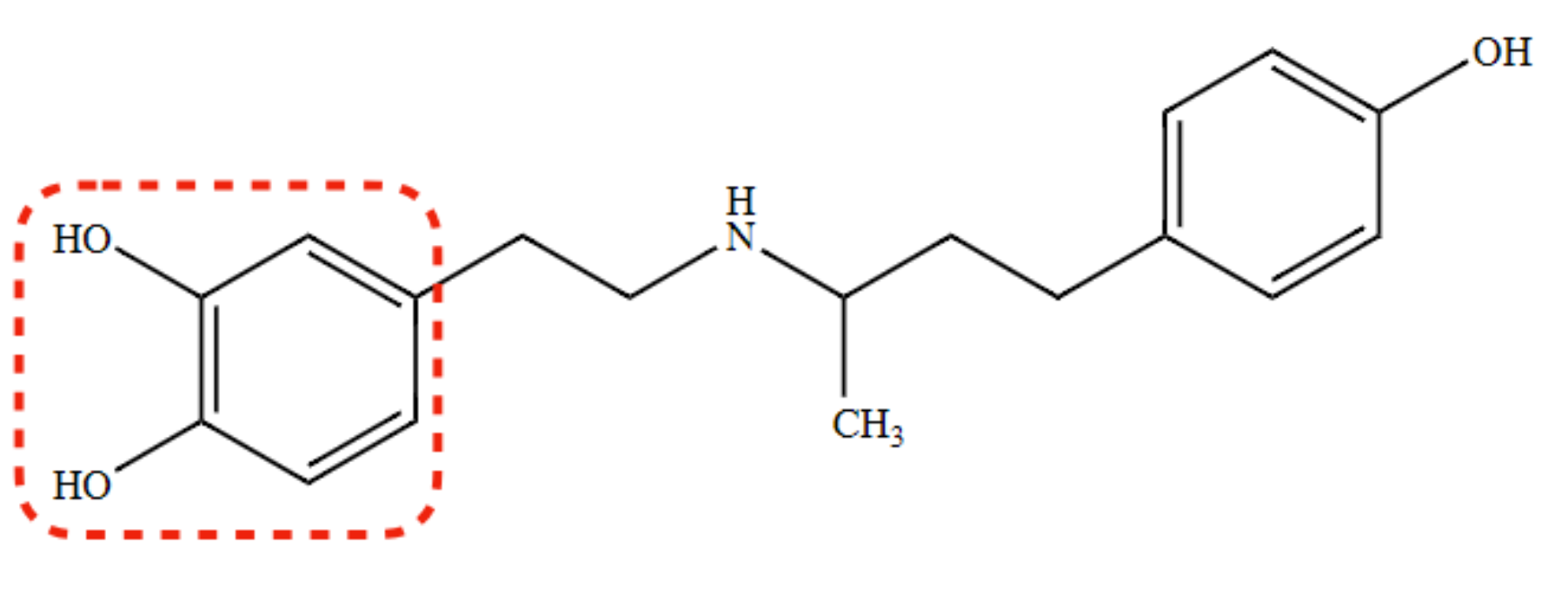
(S) isomer of Dobutamine
α1 -agonist, β 1-agonist
86
New cards
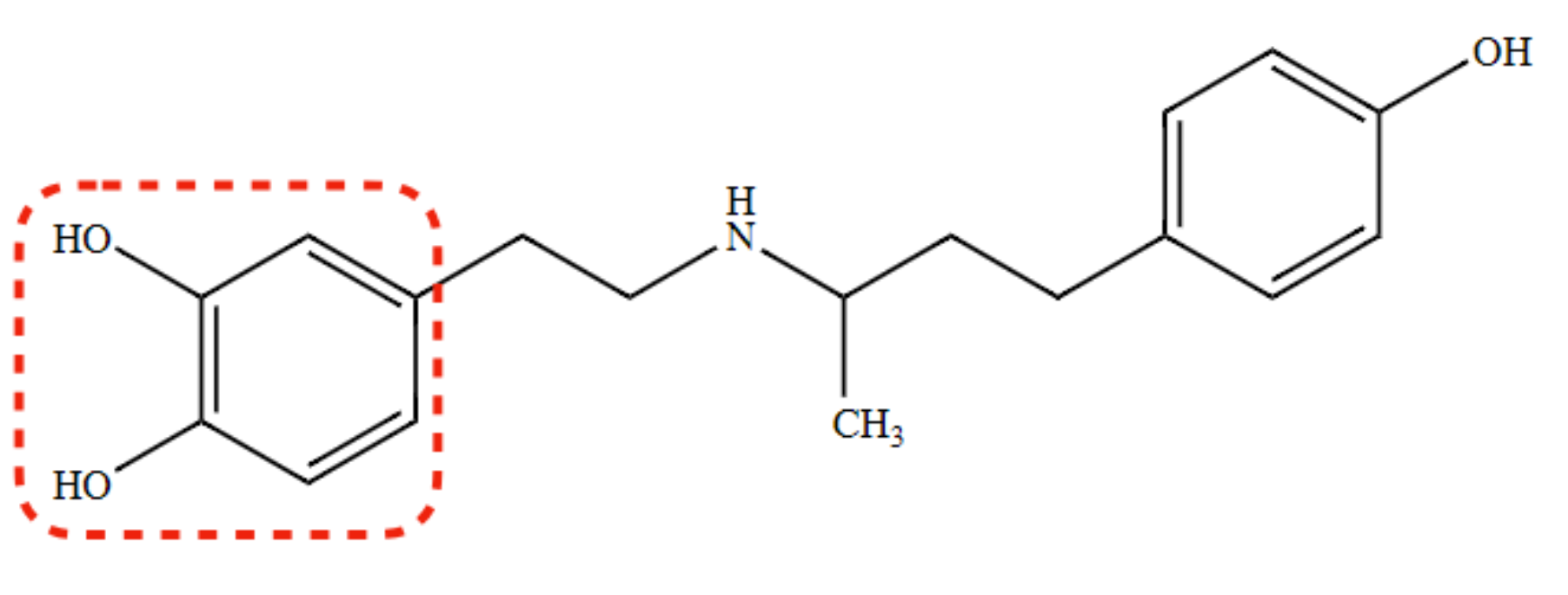
(R) isomer of Dobutamine
α1 -antagonist, potent β1-agonist
87
New cards
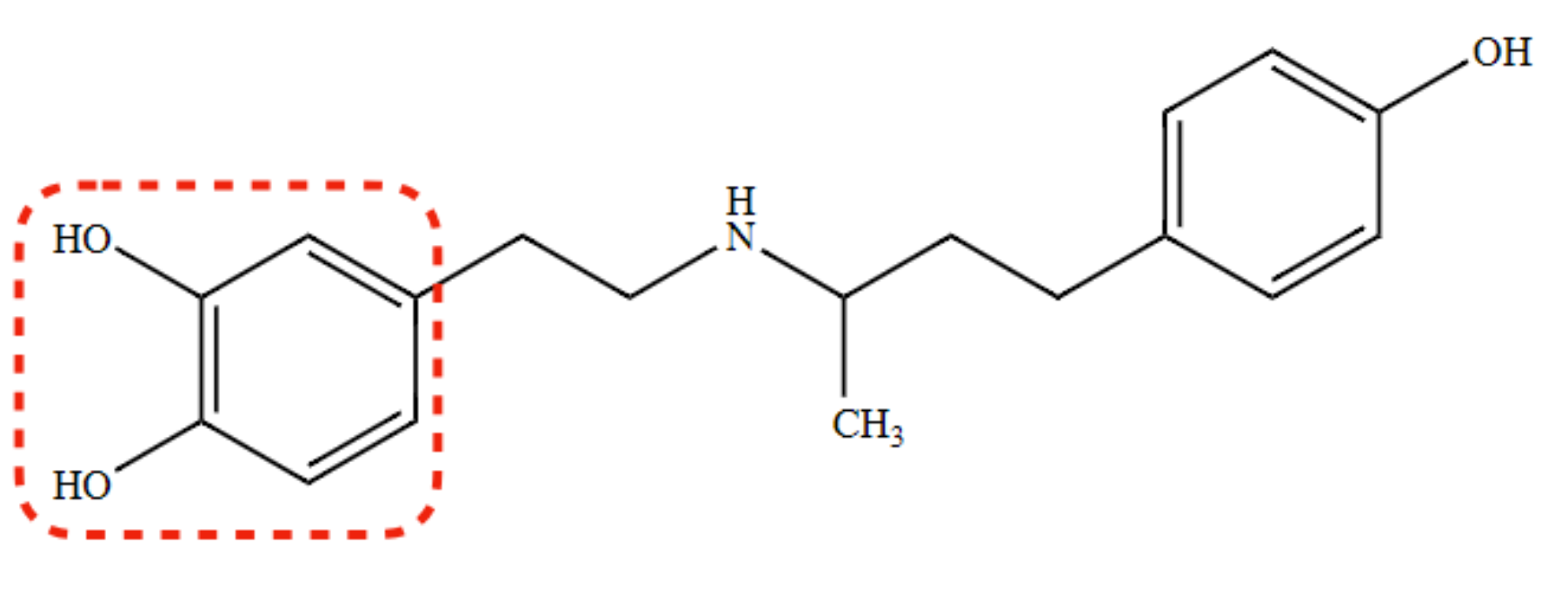
Metabolism of Dobutamine
COMT, sulfation, and glucuronidation
88
New cards
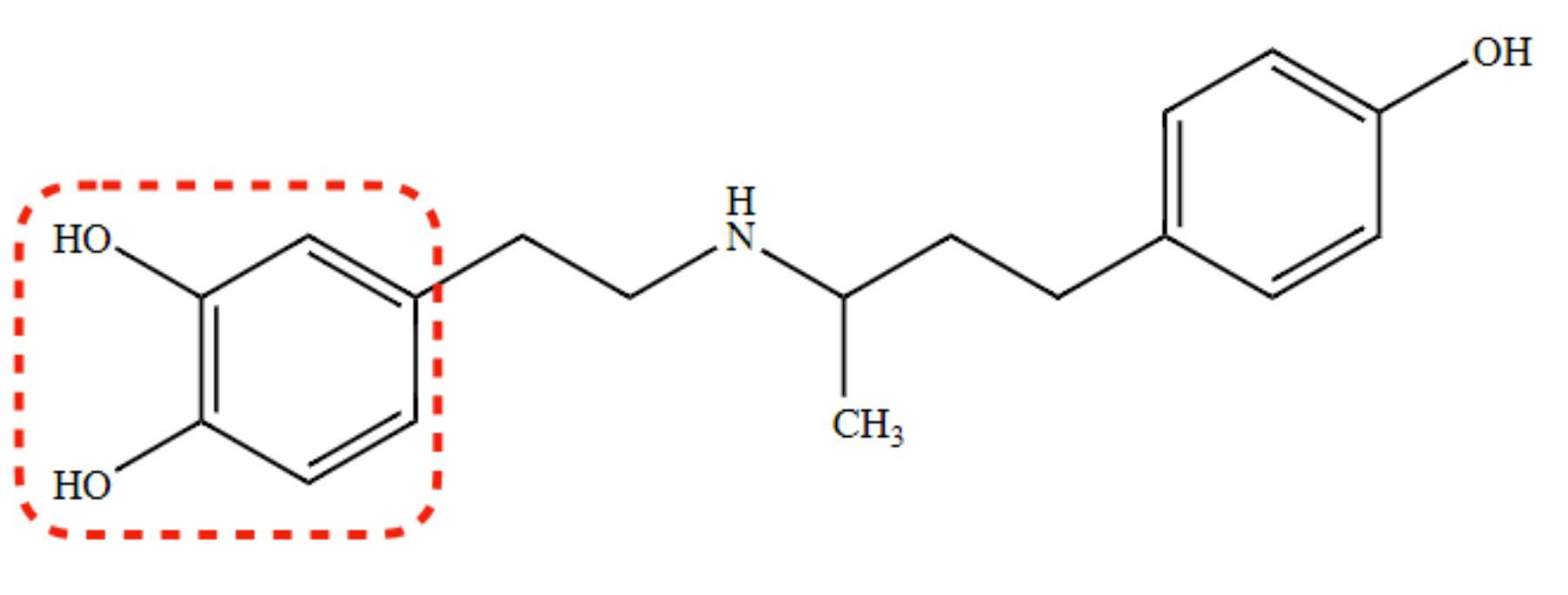
Use of Dobutamine
(+) inotropic effect for CHF (primarily due to β 1-agonist activity)
89
New cards
direct-acting α1-agonist
Phenylephrine
90
New cards
SAR that provides provides α1-selectivity to phenylephrine
m-OH
91
New cards
produces COMT resistance and longer DOA to phenylephrine
absence of p-OH
92
New cards
Metabolism of phenylephrine
MAO, sulfation, and glucuronidation (3’-O-glucuronide)
93
New cards
Uses of phenylephrine
open-angle glaucoma, ↑ effects of spinal anesthesia
94
New cards
direct-acting α1-agonist with an arylimidazoline ring
Naphazoline, Tetrahydrozoline, Xylometazoline, and Oxymetazoline
95
New cards
causes α-selectivity in Naphazoline, Tetrahydrozoline, Xylometazoline, and Oxymetazoline
o-lipophilic at Phenyl
96
New cards
causes α1-selectivity in Naphazoline, Tetrahydrozoline, Xylometazoline, and Oxymetazoline
m-/p- bulky lipophilic at Phenyl
97
New cards
Use of Naphazoline, Tetrahydrozoline, Xylometazoline, and Oxymetazoline
topical nasal/ocular decongestants
98
New cards
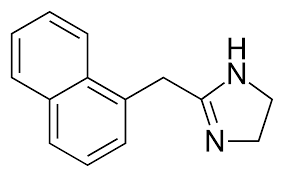
naphthalene and imidazoline ring
Naphazoline
99
New cards
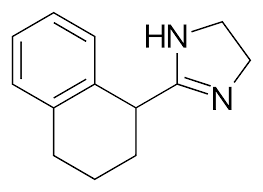
Tetrahydrozoline
100
New cards
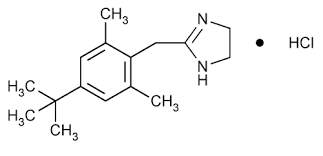
with bulky lipophilic group
Xylometazoline