Edexcel A-Level Economics - Government Intervention - 1.4.1-2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is an indirect tax?
A tax on expenditure
How does the imposition of indirect tax by the government prevent market failure?
- Imposing an indirect tax in the form of e.g. VAT, will disincentives the consumption and output/supply of a negative externality, as it will raise costs for consumers. This will result in the supply curve shifting left It is shown on the graph where MSB = MSC
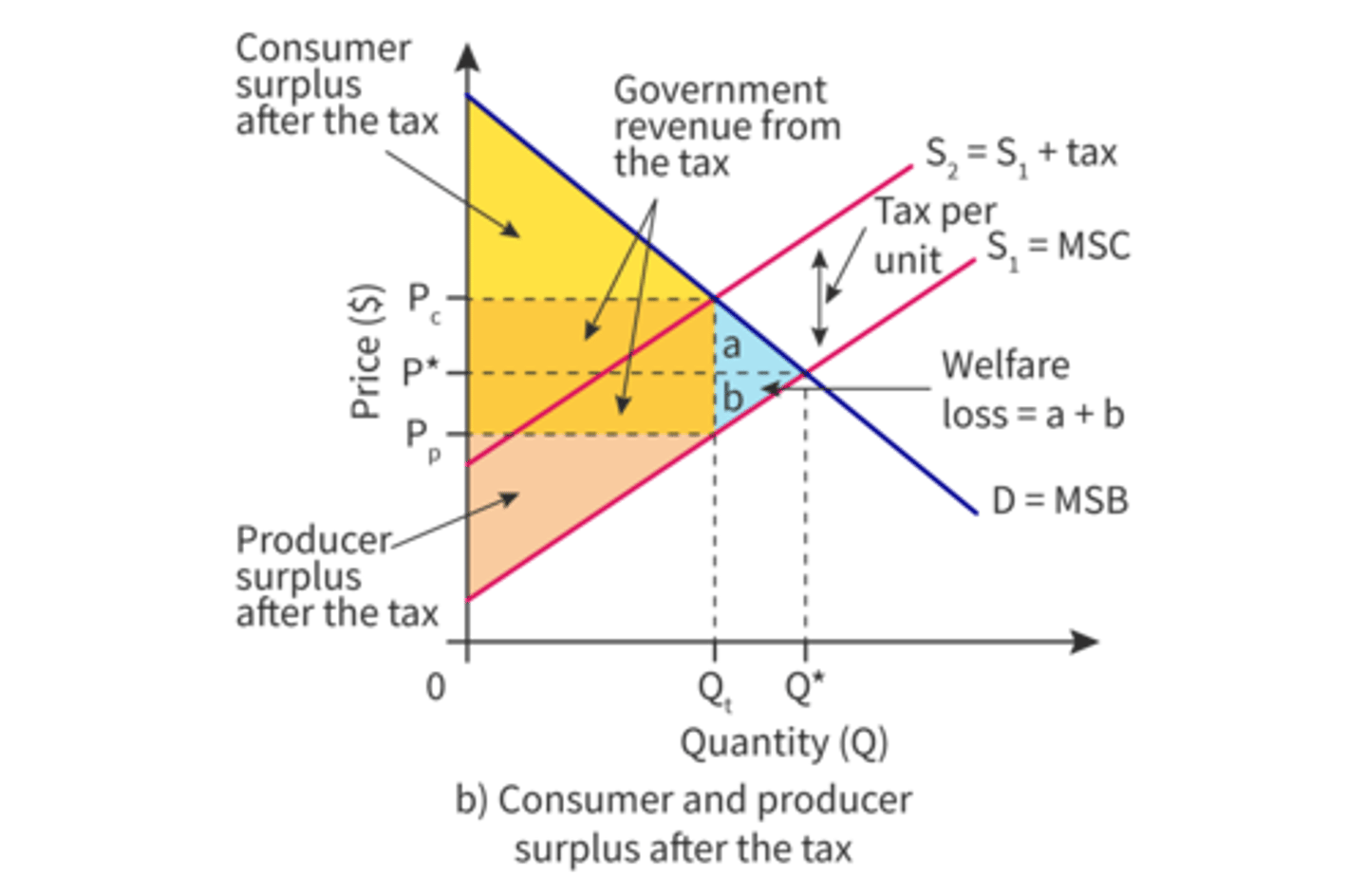
What are the advantages of the government imposing an indirect tax?
- It raises government revenue, which the government can use to solve the externality via education or compensate on those affected by the pollution
- Few administrative costs are involved
- Externality is internalised and social welfare is reached
- Incentive to reduce pollution
Evaluation of imposing indirect taxes?
- Difficult to gauge the size of the externality and is thus hard to target. The effect depends on where the tax is set and governments suffer from imperfect information when setting tax
- Could lead to creation of black market
- Ineffective in reducing pollution if demand is price inelastic, so might require a large tax to have any effect
- Indirect taxes are regressive, and could worsen inequality
- Any unintended consequences of setting the tax?
- How is the revenue from the tax used?
- What is the impact on businesses/competitiveness: capital investments, negatively affect trade?
What is a subsidy?
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.
How do subsidies prevent market failure?
A subsidy is used in the case positive externalities and information gaps. As a result of a subsidy, the product or service can be supplied at a lower price which results in supply shifting to the right. As a result production at a socially optimum level is encouraged at the level of . MSC = MSB
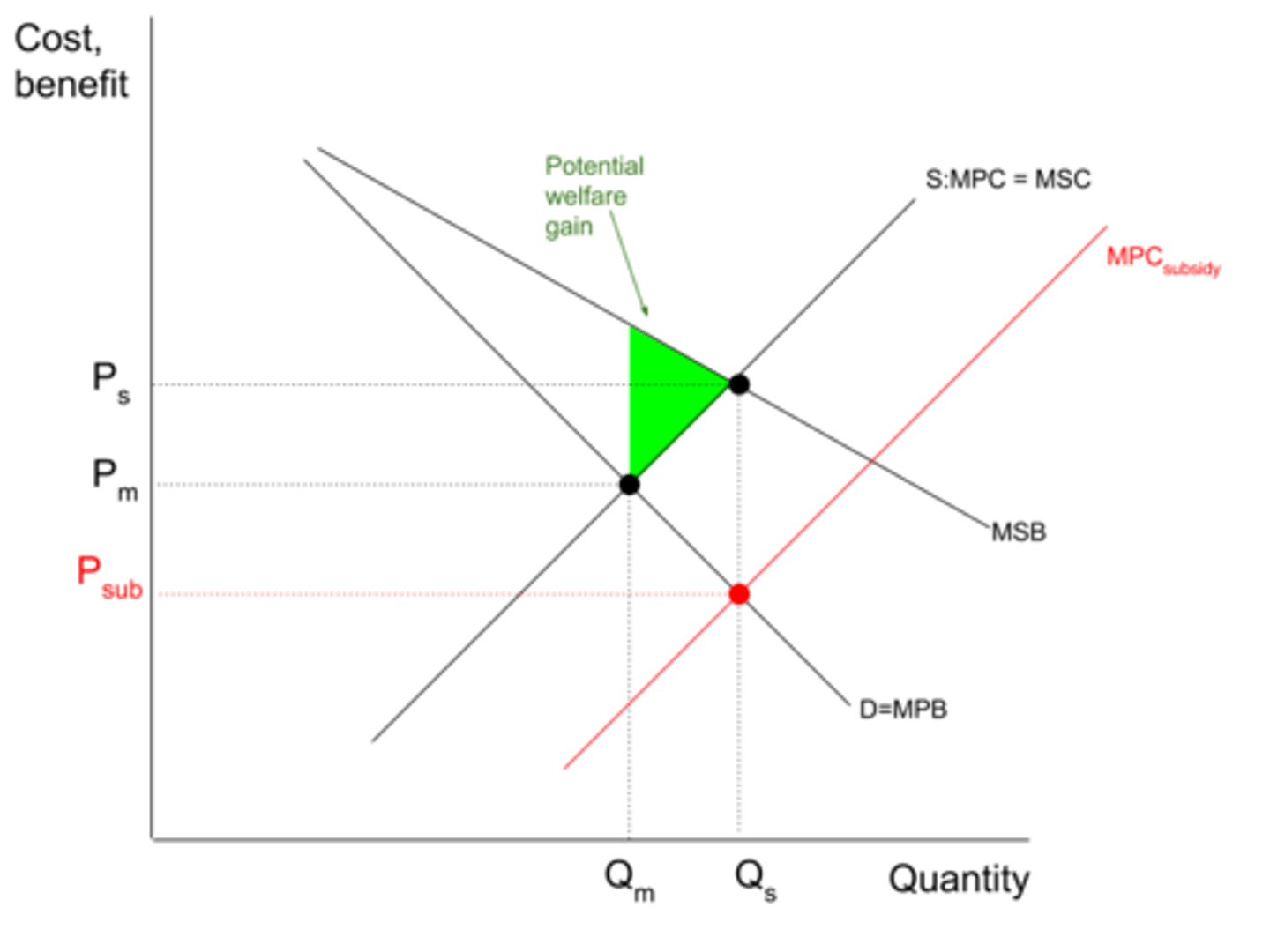
What the advantages of the government granting subsidies?
- Might help to reduce inequality
- Incentive for people to increase consumption
- reduction in cost of production enabling suppliers to reduce the price
- society reaches social optimum output and welfare is maximised
Evaluation of the government granting subsidies?
- Large opportunity cost involved, huge sum of money is involved
- Hard to quantify the externality, thus hard to set an appropriate sum
- Ineffective in increasing consumption if demand is inelastic
- Subsidy for investment and research can lead to positive externalities but Can cause producers to become inefficient and rely heavily on state support
What is a maximum price?
A legally imposed price for a good that the suppliers cannot charge above.
Why are maximum prices set?
They are set on positive externalities. They can prevent monopolies from exploiting customers
EX: Is set on rented accommodation, for pro athletes and for food items
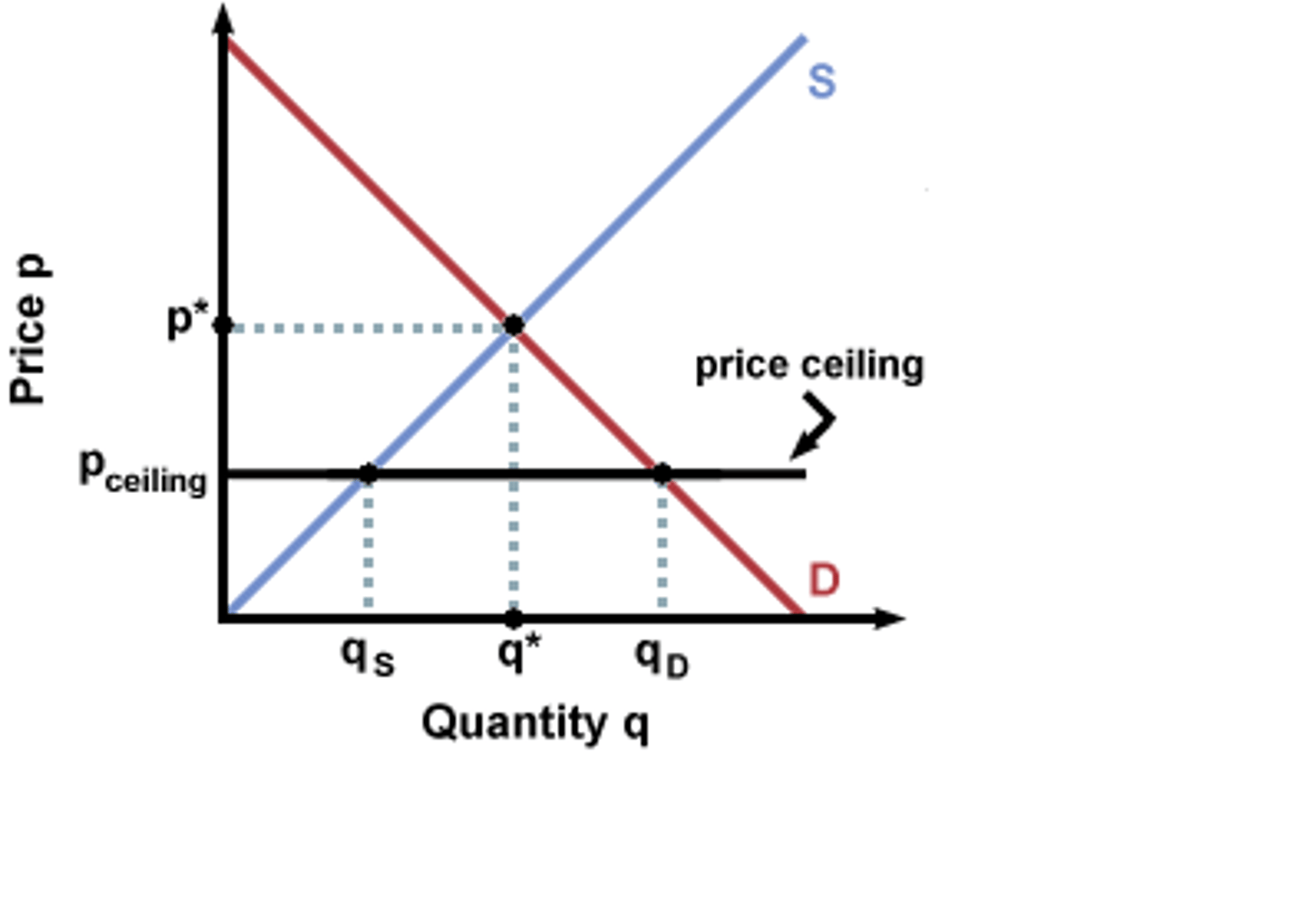
Advantages of setting a maximum price?
- Enable consumers on low incomes to be able to afford to buy a product.
- Prevent an increase on the rate of inflation
- Prevent exploitation of consumers by monopolies
Disadvantages of imposing a maximum price?
- Can lead to creation of black market as a response to shortages
- Difficulty in determining point to set price
- Distortion of price signals
- If subsidy is imposed to encourage them to maintain output, there will be a significant cost to the taxpayer
What is a minimum price?
A legal price floor below which the good cannot be sold in order to ensure producers receive a certain price for their product
Why are minimum prices set?
- Commodities: Set a minimum guaranteed price on a particular commodity. Producers know in advance that they will receive a certain amount per kilo. Designed to ensure greater certainty and therefore act as an incentive to producers to supply sufficient quantities
- Consumer goods: Set on goods with a negative externality like alcohol to reduce consumption
- Labour market: NMW to ensure workers receive a minimum of a certain amount per hour
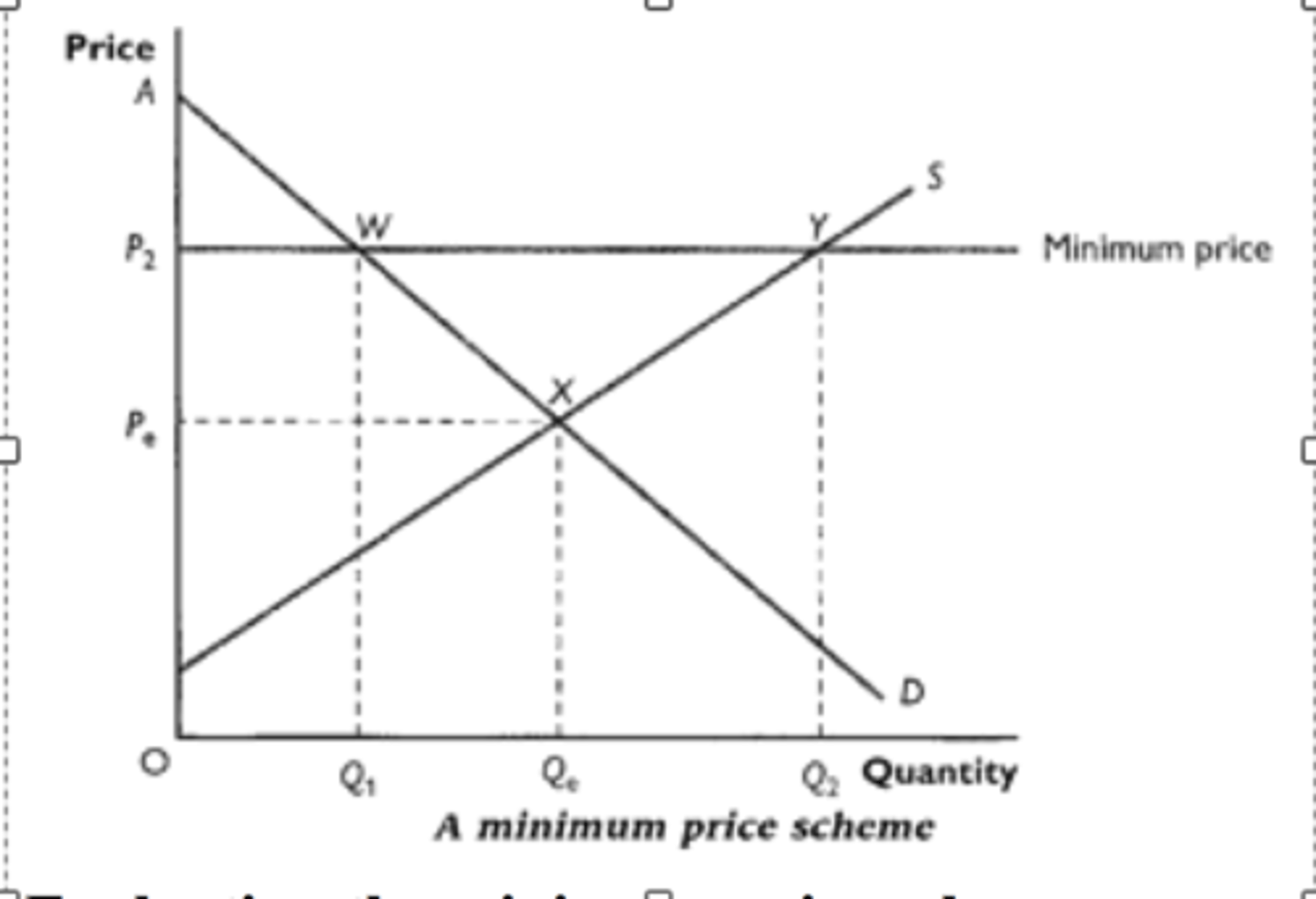
Advantages of setting a minimum price?
- Producers know in advance their profit
- Greater certainty allows producers to plan investment and output
- Can prevent exploitation of producers by wholesalers and retailers who have significant buying power
Disadvantages of setting a minimum price?
- If minimum price is set to high, there will be excess supply
- Encourage overproduction which might result in an inefficient allocation of resources
What is a trade pollution permit and why would the government issue it?
- A trade pollution permit are rights to sell and buy actual or potential pollution in artificially created markets
- permits are issued to firms to allow them to pollute up to a certain limit. Any pollution above this limit is subject to fines.
How do trade pollution permits work?
1. Government sets pollution cap - max amount firms can release in a year - at the socially optimum level
2. Government then issue permits to firms across the economy to match the cap - A market for permits has been created
3. If firms are producing above the permitted level they now have a choice to make, either they invest in new green tech to reduce emissions or they stock up on spare permits. (They decide on which is either cheaper for them)
4. Either way the firm is internalizing the externality as they are paying to either invest or to buy more permits
5. Pollution will decrease to a socially optimum level and allocative efficiency will be met
6. LR incentive is to invest in green tech as permit prices will increase in the future
Advantages of issuing a tradable pollution permit
- Government can raise revenue by selling permits and by fining firms
- Encourages companies to use more green technology
- Scheme is cheap to impose and works through the market mechanism
- Government caps amount of permits made, it is gauranteed pollution will fall
Evaluation of issuing a tradable pollution permit
- Can be expensive to monitor and police, can only work if monitored well.
- Need to be internationally enforced to be effective, as pollution is a global market failure. many developing countries are scared to burden their firms who undergoing industrialisation
- In developing countries enforcement might be expensive
- Is technology accurate enough to measure emissions
- Imperfect info. so govt. doesn't really know the socially optimum level at which they can set the cap, so cap is likely to be set to tight
- Unintended consequences such as firms moving operations to another country, cost push inflation.
Advantages of the government providing the state with public goods
- Corrects market failure which would otherwise not be provided under a free market system
- Can help to bring equality
- By providing healthcare the government ensures that the workforce is healthy and so can improve economic growth
Disadvantages of the government providing the state with public goods?
- Expensive and has high opportunity cost
- Since the market is not involved, the government may produce the wrong combination of goods as consumers can not indicate their preference
- The government may be inefficient at production since they have no incentive to cut costs
- Corruption
How can the government provide information
- Encourage parents to have their children vaccinated against measles
- Inform people about health risks associated with smoking or eating junk food
- Inform people about opportunities for apprenticeships and courses available in higher education
Disadvantages of the government providing information?
- can be expensive for the government to do, incurring an opportunity cost
- Government might also suffer from imperfect information
- Consumers may not listen due to irrational behaviour
How do legal regulations prevent market failure?
- complete ban on the production of a good or provision of a service
- Regulations on the the production process
- Ensure firms provide full information
Advantages of imposing legal regulations
- Can limit amount of pollution
- Prevent exploitation
- Can keep consumers fully informed
- It can limit external costs without an impact on price
Disadvantages of imposing legal regulations
- Laws may be expensive for the government to monitor. O/C
- gov. can suffer from regulatory capture
- Limits consumer soveriegnity
- Pass on costs to consumers
- Excessive regulation can reduce comp. in the market.
What causes government failure?
- Distortion of price signal
- Unintended consequences
- Excessive administrative costs
- Information gaps
What is government failure?
Arises as a result of government intervention in a market in an attempt to correct a market failure that causes output and consumption to move further away from the socially efficient point
explain distortion of price signals as a cause of government failure
- Maximum and minimum prices lead to excess demand/supply and make it difficult to allocate resource.
- The price mechanism aims to allocate resources to their best use and where consumers want and value them the most. By interveining, the government distorts the mechanism and so resources may allocated inefficiently.
Explain unintended consequences as a cause of government failure?
- policy can have effect that was no expected
- EX: Very high taxes on cigarettes in the UK have resulted in a significant increase in cigarette smuggling from which the government gains no tax
Explain excessive administrative costs as a cause of government failure?
Although government intervention might seem desirable, the costs may be considerable. The social costs may be higher than the social benefits, once administration costs are taken into account
EX: A lot of money to the NHS is actually spent on organisational administration rather than putting the money into medical care
Explain information gaps as a cause of government failure
When a government intervenes in a market it is unlikely to have all the information required. Governments can make a wrong investment resulting in a welfare loss
Explain examples of government failure in different markets
1) Indirect taxes: very high indirect taxes might result in smuggling as a means of avoiding the tax. Also movement away from socially optimum level of output
2) Agricultural stabilisation schemes: EX: minimum guaranteed price. Schemes could result in massive surplus, which involves huge storage costs
3) housing polices: State provision of housing at low rent is desirable for those on low incomes. However, housing subsidies prevent the market from working efficiently.
4) Environmental polices: Subsidies have been given for the establishment of wind farms but many argue that the energy produced from them is relatively expensive and they can an environmental eyesore