Cytogenetics - Lesson 9
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pedigree Analysis and Genetic Counseling
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Sheldon Reed in 1947
Person who coined Genetic Counseling
Sheldon Reed
Geneticist who advises physician on how to explain heredity to patients with single-gene diseases
1971
When the first batch of trained genetic counselors were trained
Family history of cancer
Family history of multifactorial disease
Family history of abnormal chromosomes
Elevated risk of single-gene disease
Reasons for patient to see a Genetic Counselor
Family history assessment
Pedigree construction and identifying family members who are at risk
Genetic testing (including karyotyping) and discussion of results and treatments
Involvements of Genetic Counseling
Karyotype
Genetic testing technique that tests for abnormalities of chromosomes
Aminocentesis
Genetic testing technique that samples amniotic fluid to screen for abnormalities in a fetus
Pedigree Analysis
Genetic testing technique that determines disease family history
X
In Pedigree Analysis, Genetic Counselor deduce dominance and distinguish autosomal from _-linked inheritance
If a trait is dominant or recessive
Autosomal or sex chromosome a trait is linked to
Genotypes of family members
Probabilities of phenotypes in future generations
Analyzing pedigrees can reveal
Males
Squares
Females
Circles
Presence of a trait
Shaded squares or circles
Roman numerals
Rows are generations labeled with ____
Unknown Sex
Triangles
Carrier Female
Circle with Dot
Autosomal Dominant
One mutated allele causes the disease
Autosomal Dominant
Appears in every generation of an affected family (vertical)
Autosomal Dominant
Each affected person usually has one affected parent
Autosomal Dominant
Marfan Syndrome
Autosomal Dominant
Achondroplasia
Autosomal Dominant
Huntington Disease
Autosomal Dominant
Myotonic Dystrophy
Autosomal Recessive
Two mutated alleles cause disease
Autosomal Recessive
Parents are usually unaffected heterozygotes
Autosomal Recessive
Not typically seen in every generation (horizontal)
Autosomal Recessive
Beta Thalassemia
Autosomal Recessive
Cystic Fibrosis
Autosomal Recessive
Homocystinuria
X-Linked Dominant
Females are more frequently affected than males
X-Linked Dominant
No male-to-male transmission
X-Linked Dominant
Rett Syndrome
X-Linked Dominant
Hypophosphatemia
X-Linked Recessive
Males are more frequently affected than females
X-Linked Recessive
Both parents of an affected daughter must be carriers
X-Linked Recessive
Father cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons
X-Linked Recessive
Hemophilia
X-Linked Recessive
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Mitochondrial
Only females can pass on conditions (maternal inheritance)
Mitochondrial
Both males and females can be affected
Mitochondrial
Can appear in every generation of a family
Mitochondrial
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
Autosomal Dominant
Approximately half of everybody
Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Recessive
Rare
Autosomal Recessive
Consanguinity
X-Linked Dominant
Males get it from affected mothers and give it to their daughters
X-Linked Recessive
Males generally get it from unaffected mothers
Y-Linked
All males, all the time, all generations
Mitochondrial
Every child of affected mother is affected
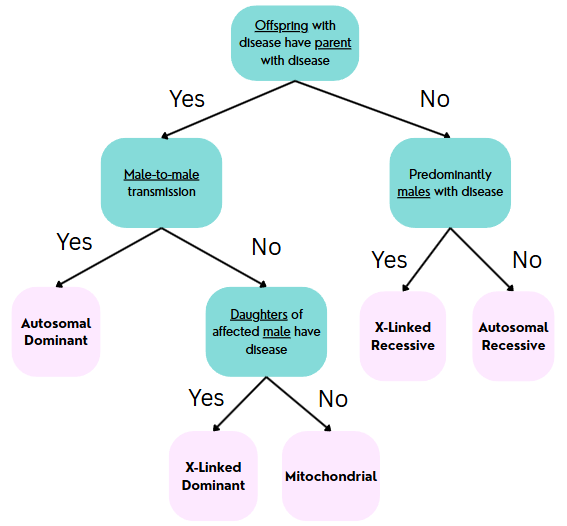
Algorithm
Autosomal Recessive
Tay-Sachs Disease
Autosomal Recessive
Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Metabolic disease caused by a mutation in a gene encoding phenylalanine which leads to mental retardation
Autosomal Recessive
Autosomal Dominant
Freckles
Autosomal Dominant
Polydactylism
50 to 60 years
Life expectancy of Huntington Disease
Huntington Disease
Affects central nervous system
X-Linked Recessive
Affected father do not pass disease to their sons
X-Linked Recessive
Defects in enzymatic genes
X-Linked Recessive and Dominant
Presents usually after puberty
Manifesting Heterozygotes
Affected with just one defective copy if normal X chromosome is inactivated to Barr body
X-Linked Recessive
Red-Green Color Blindness
X-Linked Recessive
X-Linked Ichthyosis
X-Linked Dominant
Affected fathers pass to all of daughters but not their sons
X-Linked Dominant
Incontinentia Pigmenti (skin lesions)
X-Linked Dominant
X-Linked Rickets (bones soften or deform)
Holandric Inheritance
Also known as Y-Linked Inheritance
Mitochondrial
Defects in electron transport or oxidative phosphorylation process
Mitochondrial
Presents as neuropathies or myopathies
Mitochondrial
Variable expression due to heteroplasmy