CLS 272 UNIT 1/LAB PRACTICAL 1 STUDY GUIDE
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what does RACE stand for?
Rescue
Alarm
Confine
Extinguish or Evacuate
what are the four components needed for a fire to occur? what are their roles?
fuel → combustible material
heat → raises the temperature of the material until it ignites
oxygen → maintains the combustion
chemical reaction → produces the fire
what is a class A fire? what is needed to extinguish it?
fire that can occur due to ordinary combustible material like wood and paper
to extinguish, use water/water-based solutions
soda and acid fire extinguisher
what is a class B fire? what is needed to extinguish it?
fire can occur through flammable liquid and vapors like paint, oil, grease, and gasoline
to extinguish, block oxygen or smother the fire
foam, dry chemical, or CO2 fire extinguisher
what is a class C fire? what is needed to extinguish it?
fire that can occur through electrical equipment
to extinguish, use nonconducting agents
dry chemical, CO2, halon fire extinguisher
what is a class ABC fire extinguisher?
a fire extinguisher that can be used for class A, B, and C fires by using dry chemical agents to smother the fire
what is a class D fire? what is needed to extinguish it?
fire that can occur through combustible or reactive metals (Na, K, Mg, Li)
to extinguish, use dry powder or sand
what is a class K fire? what is needed to extinguish it?
fire that occurs through high-temp cooking oils , grease, or fats
to extinguish, use agents that prevent splashing, cool, and smother the fire
K-based alkaline liquid extinguisher
what does PASS mean?
Pull
Aim
Squeeze
Sweep
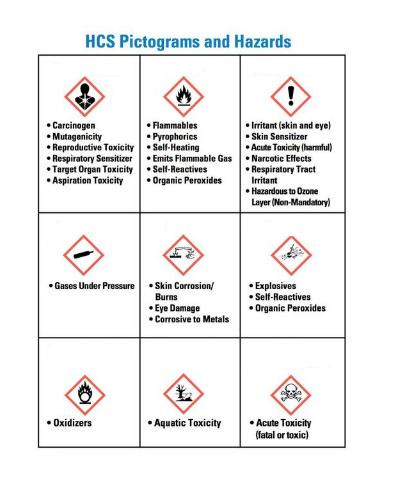
identify what the symbols are starting from the top left
health hazard
flame
exclamation mark
gas cylinder
corrosion
exploding bomb
flame over circle
environment (non-mandatory)
skull and crossbones

identify the meaning of this safety label from 1-8, explain them too
hazard statement = nature of the hazard
hazard class = class of the hazard
safety precautions = the necessary precautions to be safe when handling the product
NFPA hazard code = a way of communicating the dangers of the material to emergency responders
fire extinguisher type = fire extinguisher needed to extinguish
safety instructions
formula weight
lot number = to track the product’s history
what does the red mean on an NFPA label?
flammable and should be stored in an area away from flammable reagents
what does blue mean on an NFPA label?
health hazard, toxic if inhaled, ingested or absorbed through the skin and must be stored in a secure area
what does yellow mean on an NFPA label?
reactive and oxidizing reagents which may react violently with air, water, or substances and must be stored away from flammable and combustible materials
what does white mean on an NFPA label?
corrosive, may harm the skin, eyes, or mucous membrane and must be stored away from red, blue, yellow-coded reagents
what does gray mean on an NFPA label?
moderate hazard and can be stored in a general chemical storage
why is the fourth segment left blank on an NFPA label?
for special warnings like if it is radioactive
explain what the numbers mean for each color-coded segment in an NFPA label?
4 = extreme
3 = severe
2 = moderate
1 = slight
0 = no hazard
what is a flocked swab?
collection material resembles bristles of a brush
what is a mattress swab?
collection material wrapped around a flexible shaft and absorbs the specimen through the middle
what is important when collecting a sputum sample?
knowing the difference between saliva, sputum, and nasal secretions and the sputum can be contaminated with oropharyngeal flora
how would you pack an infectious substance?
needs triple packaging → primary leakproof receptacle with absorbent material incase the specimen leaks/breaks, leakproof secondary packaging, and a rigid outer packaging
name, address, and phone number of the shipper
infectious substance label
what do the different levels of specimen prioritization mean?
level 1 = life threatening/criticial/invasive
level 2 = possible degradation or contaminant overgrowth (refrigerate) and unpreserved
level 3 = possible inaccurate quanititation (preservative)
level 4 = holding or transport media preserve sample
what is nonselective media?
supports growth of most nonfastidious organisms (sheep blood)
what is selective media? give an example of two medias
supports growth of one type of organism but not another (gram negative and gram positive)
ex. macconkey = gram negative
ex. phenylethyl alcohol (PEA) = gram positive
what is differential media? give examples of two medias
allows grouping of microbes based on demonstrated characteristics on the media
ex. sheep blood agar = non selective differentiates hemolysis
ex. macconkey agar = differentiates lactose fermenters
what is enriched media? give an example
contains growth factors added to nonselective media to allow fastidious organisms to grow
ex. chocolate agar
what is enrichment broth?
liquid medium designed to encourage small numbers of organisms to grow and suppress other flora present
what is broth media?
supplement to agar to detect small number of aerobes, anaerobes, and microaerophiles
in what order would aerobes, anaerobes, and microaerophiles be seen in a thioglycolate broth?
aerobes = top
anaerobes = bottom
microaerophiles = in the middle
how do you do a four quadrant isolation streak?
place loop with specimen into broth, roll swab, or place drop of liquid specimen at the TOP of the plate
from the TOP, spread the specimen in a tight zigzag horizontally for first quadrant
for the second quadrant = sterilize the loop, rotate the plate, then go into the first quadrant to grab the microorganisms and go into another tight zigzag
applies for the third and fourth quadrant
what are the incubation conditions?
most cultures will grow between 35 C and 37 C
most will be incubated for 48 to 72 hrs
some cultures will be held for 5 to 7 days
place petri plates upside down to prevent condensation which may ruin your plate
what is capnophilic?
higher CO2
what is microaerophilic?
reduced O2 and increased CO2
how should plates be labeled?
label with initials, date (mm/dd/yy), time (military), organism name or code #
NEVER label plate in the middle, should be around the side of the plate
may use computer generated labels
what is the goal of streak plate isolation?
reduce the number of bacteria in each subsequent quadrant
what are colonies?
masses of offspring from an individual cell
what is aseptic technique the process of?
ultimately prevents contamination of a culture from the environment and yourself
what is sterilization?
destruction of ALL forms of life, including spores
what is disinfection?
elimination of a defined scope of microorganisms
what are the 10 factors that influence the degree of killing>
types of organisms
number of organisms
concentration of disinfecting agent
presence of organic material
nature (composition) of surface to be disinfected
contact time
temperature
pH
biofilms
compatibility of disinfections and sterilants
name the 7 microorganisms that are the most resistant to killing to least resistant
prions
bacterial spores
mycobacteria
nonlipid viruses
fungi
bacteria
lipid viruses
how do you sterilize with heat?
using an autoclave which uses steam pressure for moist heat or heat
1 atm at 121 C for 15 min destroys endospores
dry heat sterilizes glassware but requires longer contact time
how are cultures initially observed?
colony morphology is initially observed 18 to 24 hrs post culture then is incubated for another 24 hrs after plate reading
plate reading determines the growth of the M/O and the colony morphology
when using a macconkey plate, what would lactose fermenters and nonlactose fermenters look like? give examples
lactose fermenters = pink
ex. E. coli/Citrobacter
nonlactose fermenters = colorness
how do you see hemolysis on a blood agar?
observe the media immediately surrounding or underneath the colony by using transillumination
what is important regarding hemolysis on a blood agar?
important to determine whether true hemolysis is present or it is discoloration due to organism growth
what is alpha (α) hemolysis?
partial clearing of blood that results in a green discoloration of the medium; can see through the plate “a” little
what is beta (β) hemolysis?
complete clearing of blood cells (lysed) around the colonies; can look through the plate “mo beta”
what is gamma (γ) hemolysis?
nonhemolytic; can’t see through the plate at all
regarding size of colonies, what is larger? gram positive or gram negative?
gram negative (gram positive is less than gram-negative)
what are the four forms of colonies? explain them
smooth
filamentous = looks like thread or has connected cells that are forming a thread
rough or rhizoid = still looks somewhat like a circle with rough edges
irregular = doesn’t look like a circle at all
what is swarming?
hazy blanket of growth on surface
how would you determine elevation of a colony?
tilt the culture plate and look at the side
what are the five types of elevation? describe them
raised = raised flat top
convex = dome-shaped
flat = not raised
umbilicate = convex with a depressed center/pitting
umbonate = convex with a protuding nipple
what are the three types of density?
transparent
translucent
opaque
what are the four colors to describe colonies?
white
gray
yellow
buff (pale yellow-brown)
what are the five consistencies that describe colonies?
brittle (splinters)
creamy
dry
waxy
sticky = entire colony comes off the plate
what are pigments?
inherent characteristics of a specific organisms confined generally to a colony
how would you determine the odor of a colony?
when the lid comes off (NEVER inhale directly from the plate)
what is the “streamer” description for organisms in liquid media?
vinelike growth in media, puff ball-like, scumlike growth