Major Affective Disorders - Depression and Bipolar Async
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
A group of symptoms of worthlessness, guilt, low self esteem, lack of sleep, low energy, aimless, lethargic, loss of pleasure in life (anhedonia), introverted, poor social skills, suicidal thoughts, etc
depression
two types of depression
reactive depression and endogenous depression
causes/risk factors of depression
•Genetic – higher risk if parents have depression
•Biological – reduced levels of neurotransmitters, hormone imbalance
•Environmental - stress, lifestyle, health
•Psychological – childhood trauma, divorce, death of loved ones, financial problems, physical abuse, substance abuse, iatrogenic (medical like drug treatment) etc.
what could be a biological cause of depression?
reduced levels of neurotransmitters
•Debilitating condition that continues for weeks or longer and disrupts life.
•Symptoms include extreme sadness, hopelessness, lack of energy, irritability, trouble concentrating, changes in sleep or eating habits, feelings of guilt, physical pain, and thoughts of death or suicide.
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder
a mood disorder in which a person feels sad and hopeless for weeks or months
dysthymia
a form of depression that is not severe enough to be diagnosed as major depression
•also called persistent depressive disorder (PDD), involves fewer symptoms than MDD.
•A type of depression that causes a low mood over a long period of time; perhaps for a year or more.
dysthymia
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
depression that affects women during the second half of their menstrual cycles
PMDD vs PMS
- PMDD is more severe and disabling than
PMS
- Greater focus on mood disturbance than
physical symptoms
- PMS affects ~85% of women, while PMDD affects ~5%
characterized by feelings of extreme sadness, fatigue, loneliness, hopelessness, suicidal thoughts, fears about hurting the baby, and feelings of disconnect from the child
Postpartum Depression (PPD)
range of severity (PPD)
Baby blues --> PP depression --> PP psychosis
mental state characterized by delusions and hallucinations, not typically associated with depression
psychosis
People with _______________ may become catatonic (muscular rigidity and mental stupor), stop speaking and refrain from leaving their room.
psychotic depression
treatment psychotic depression
Both an antipsychotic and antidepressant might be used
A subtype of depression involving symptoms of
•Insomnia
•Loss of appetite
•Diminished ability to feel pleasure in positive things/events (anhedonia)
•Intense sadness -life has no meaning or purpose
•Mostly classified as a serious form of depression --> treatment resistant
Melancholic Depression
what disorder is melancholic depression associated with?
bipolar disorder
what form of depression is associated with bipolar disorder?
melancholic
this form of depression can be treated with light therapy and/or antidepressants
SAD
what are some challenges in diagnosing depression?
•Somatic complaints
•Social stigma
•Patient denial
•Associated with other diseases or side effects of other meds
•Absence of lab tests
name the neurotransmitter:
alertness, energy, anxiety, attention --> ?
anxiety, obsessions, compulsions --> ?
attention, motivation, pleasure, reward --> ?
alertness, energy, anxiety, attention --> NE
anxiety, obsessions, compulsions --> 5-HT
attention, motivation, pleasure, reward --> DA
Monoamine Theory
depression is due to decreased norepinephrine or serotonin in the limbic system
Neurotransmitter Dysregulation Theory
depression is due to a persistent impairment and failure to regulate neurotransmitters rather than a simple increase or decrease in neurotransmitter output
Neuroplasticity Theory
depression due to low levels of BDNF preventing growth and connection between neurons
BDNF
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes growth of immature neurons and promotes survival of adult neurons
what can affect BDNF levels?
stress
Neuroendocrine Theory
•Dysregulation of the HPA axis results in higher CRF released from the hypothalamus --> higher cortisol
•Dysregulation of HPT axis leads to thyroid hormone deficiency in treatment resistant depression
Neuroinflammation Theory
Dysregulation of the immune system (Cytokine 3) may be associated with the etiology and pathophysiology of depression
how has pharmacological treatment supported the monoamine theory of depression?
Pathologically low levels of monoamine causes depression [Abnormally high levels of monoamine causes mania]
Medications that increase monoamines improved depression [and worsened mania]
what do low levels of monoamine cause? and high?
low: depression
high: mania
what are the limitations of the monoamine theory?
1. L-dopa and tryptophan (direct precursors) do not affect mood
2. Cocaine and amphetamines which block reuptake do not improve mood
3. Lag time: Takes 2 -4 weeks to exert any benefits, even though a boost in monoamines occurs within hours
Imipramine, desipramine, nortriptyline, amitriptyline - examples of? MOA?
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
Block NE and 5-HT transporter sites on the presynaptic neuron which prevents their neuronal reuptake and increases their concentration and postsynaptic effect
Structurally related to the phenothiazine antipsychotics
Consist of 3 rings; 2 phenyl rings fused to a central 6 or 7 membered ring
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) - Imipramine, desipramine, nortriptyline, amitriptyline
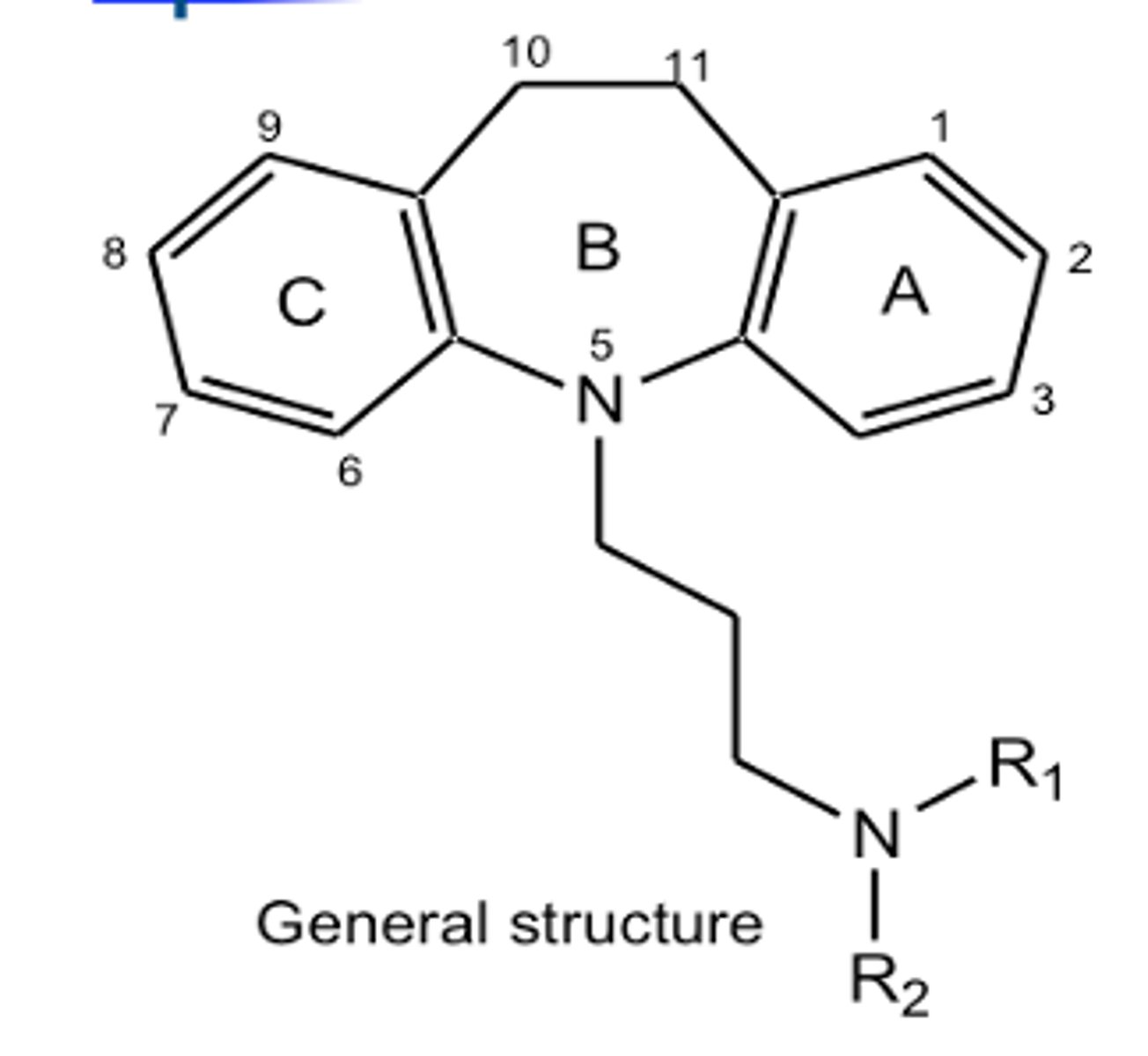
what would inactivate a tricyclic antidepressant?
removal of one of the benzene rings
Fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine, citalopram, escitalopram
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
what structurally makes SSRIs selective for 5-HT?
Halogen substituent on aromatic ring
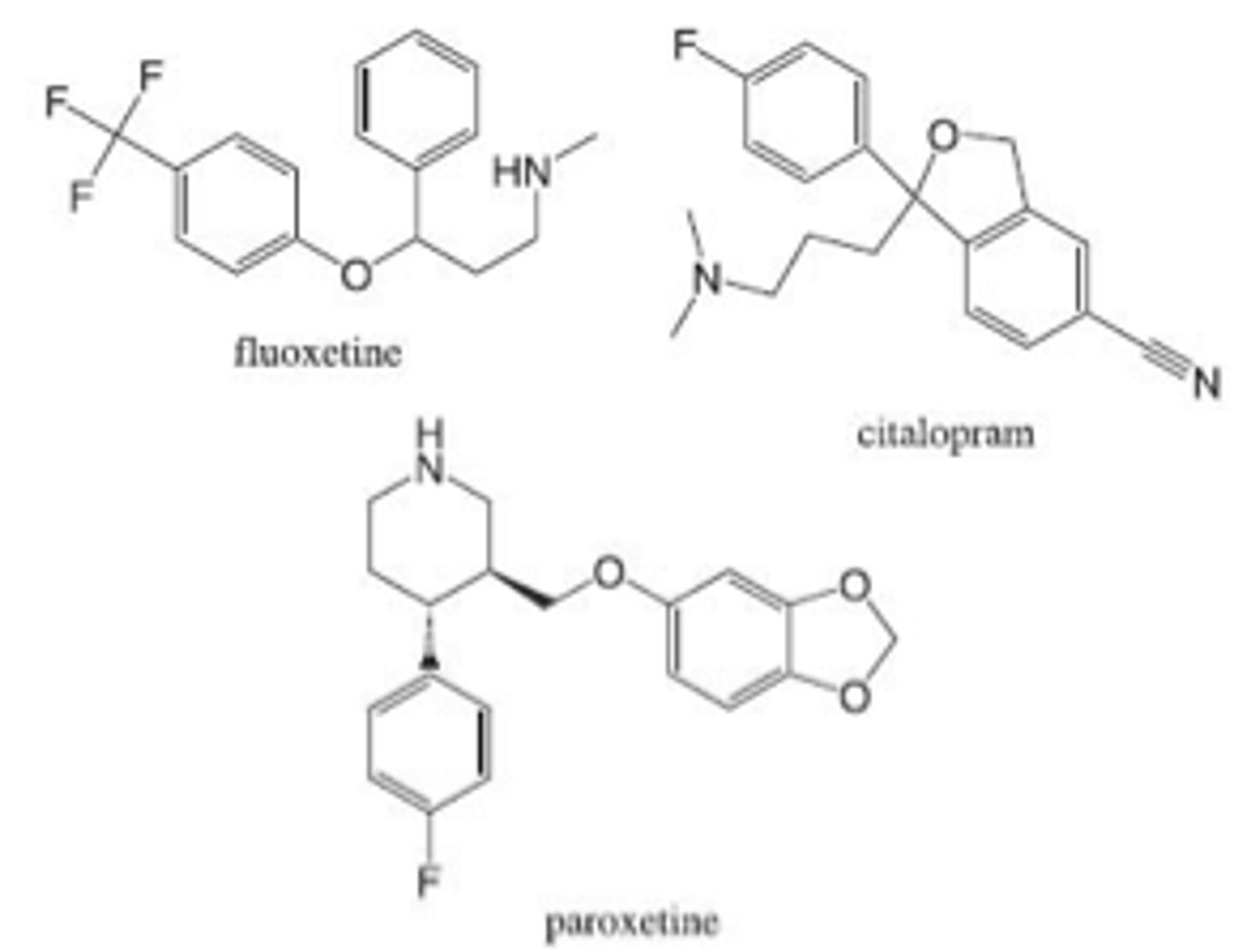
most prescribed antidepressant class
SSRIs - Fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine, citalopram, escitalopram
First FDA approved prototype SSRI (1987), least selective, most widely prescribed, sales exceed $1B/year
Fluoxetine
most selective SSRI for 5-HTT, half life of 35 h
Citalopram
Demethylated active metabolite of Fluoxetine, ______________ has half life of 4-16 days, resulting in considerable drug accumulation
Norfluoxetine
S(+) isomer of (±) Citalopram, high 5- HTT selectivity
Escitalopram
SSRI with highest affinity for 5-HTT, no active metabolites
Paroxetine
SSRI with high plasma protein binding
Sertraline
what happens to amitriptyline in the body and how?
Amitriptyline is metabolized by CYP2C19 to its active metabolite, nortriptyline
what NT does nortriptyline mostly prevent the reuptake of? what can it also block leading to side effects?
NE
Nortriptyline also inhibits Hist, 5-HT and ACh, leading to side effects
Amitriptyline mostly blocks reuptake of __________ while its active metabolite, nortriptyline blocks mostly _____________
5-HT; NE
what CYP metabolizes nortriptyline?
CYP2D6
Nortriptyline black box warning
suicide in adolescents, children, and young adults with MDD and other psychiatric disorders
Duloxetine, venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine
Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
___________was developed as a selective SNRI but later found to also work as SSRI
Venlafaxine
SNRIs indications
Effective in patients who do not respond to standard antidepressants
Also used for patients with chronic pain (e.g., neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, musculoskeletal pain)
Bupropion
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI)
what does Bupropion block? which does it block more?
blocks DA reuptake (more) and NE reuptake (less)
Off-label uses include anti-depressant-induced sexual dysfunction, ADHD, depression associated with bipolar disorder, and obesity.
Bupropion
how long does it take for Bupropion to start working?
2 weeks
Bupropion is metabolized in the liver by _____________ to hydroxy-bupropion (active metabolite)
CYP2B6
Bupropion black box warning
suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults
which antidepressant does not cause sexual dysfunction?
Bupropion
Most severe adverse effects of this antidepressant are lowered seizure threshold and the potential of worsening suicidal ideation
Bupropion
Selegiline
Irreversible, MAO B Inhibitor
Trazodone, nefazodone, vilazodone, vortioxetine
Mixed 5-HT modulators
what specific site on the 5-HT receptor sites can be targeted in SSRIs treatment resistant patients
5-HT2A R
5-HT1A R
Upregulation of which 5-HT presynaptic autoreceptor appears to be involved in the pathogenesis of major depression - what can treatment with an agonist of this receptor do over time?
5-HT1A
Long term treatment with a 5-HT1A agonist leads to desensitization of autoreceptors --> removes negative feedback and increases synthesis and release of 5-HT
overactivation of which 5-HT postsynaptic receptor contributes to etiology of depression and anxiety
5-HT2A
Trazodone MOA
5-HT modulator
First antidepressant with dual MOA, prolongs effect of 5-HT by blocking 5-HT receptors and reuptake:
1. SSRI
2. Blocks 5-HT2 (2A and 2C) receptors located on postsynaptic neuron
side effects of this 5-HT modulator include anticholinergic effects (dry mouth), orthostatic hypotension, and QTc prolongation
Trazodone
Vortioxetine MOA
Atypical antidepressant with dual effects to modulate 5-HT neurotransmission
MOA: SSRI and a 5HT1A agonist
-Blocks 5-HT reuptake (SSRI)
-Agonist at 5-HT1A autoreceptors
Mirtazapine MOA
5-HT and alpha 2 Antagonist
–By inhibiting a2 autoreceptors on NE neurons, it enhances NE synthesis and release of NE
–By concurrently blocking a2 heteroreceptors on 5-HT neurons, it facilitates the release of 5-HT
what are the 4 classes of reuptake (transporter) Inhibitors?
1. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) - first generation antidepressants
2. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
3. Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
4. Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRI)
what are the downsides to Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) ?
•Not selective
•Block other receptors (histamine, cholinergic, etc.)
•Results in many side effects
role of a2 autoreceptors & heteroreceptors in treatment of depression
The similarity between the synaptic mechanisms controlling 5-HT and NE transmission stimulated research into the role of presynaptic a2 autoreceptors in augmenting NE reuptake effects
Use of a2 R antagonist enhances therapeutic effect of NE reuptake blockers
By blocking a2 heteroreceptors located on 5-HT neurons, can also increase 5-HT release
MOAI MOA in depression treatment
MAOIs inhibit MAO enzyme, resulting in an increase in 5-HT, NE and DA in presynaptic neuron --> long lasting effects
1st MAOI antidepressant approved by FDA as a transdermal delivery system for MDD
Selegiline
adverse effects of this antidepressant include sudden sleep episodes, orthostatic hypotension, arrhythmias, mental status alteration, hallucinations, extrapyramidal symptoms, dyskinesia, and serotonin syndrome
Selegiline
Ketamine/Esketamine MOA
NMDA receptor antagonist
which antidepressant is available as a nasal spray?
Ketamine/Esketamine
what can Buproprion be formulated with for increased efficacy? what is that drug's MOA?
Dextromethorphan: Non-competitive antagonist at NMDA receptors
However, has other binding sites and other effects
what is Psilocybin?
Psilocybin is a 5-HT receptor agonist found naturally in some mushroom species (magic mushroom)
Prodrug with phosphate group. Dephosphorylation gives the drug.
Recent studies have assessed the therapeutic potential of psilocybin for anxiety, OCD, smoking and alcohol dependence, with promising preliminary results
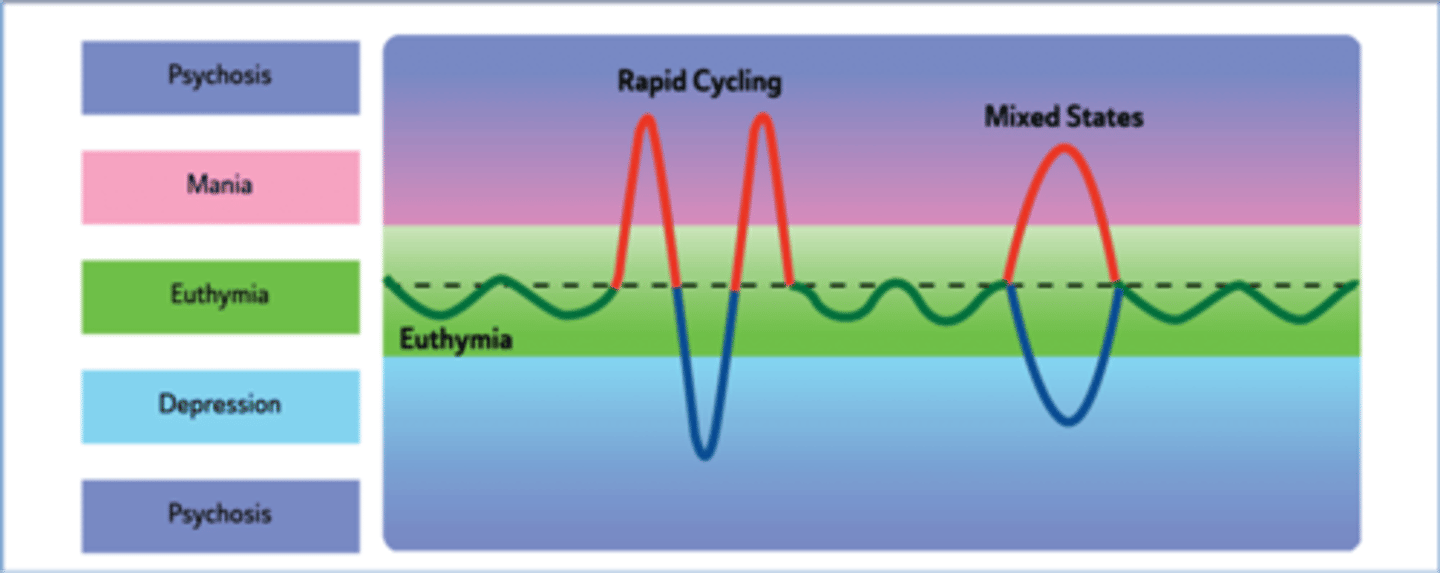
Episodes of mood swings from depressive lows to manic highs
BPD
what is a major challenge in the treatment of bipolar disorder?
the development of effective drugs with low toxicity for the patients
what is Bipolar I disorder?
has at least one manic episode in life
lasts for a few weeks to few months
what is Bipolar II disorder?
milder mania + depression
moods cycle between high and low
"up" moods do not reach full blown mania
hypomania
less severe manic phases
Cyclothymic disorder
frequent but brief periods of mood swings, hypomania and depression
can happen spontaneously even within the same day
Mixed mania
Symptoms of mania and depressive episodes are present at the same time
People who experience mixed states describe feeling activated and "revved up," but also feel anguish and despair.
Uncontrollable mood swings can occur over minutes
people with this condition describe feeling activated and "revved up," but also feel anguish and despair
mixed mania
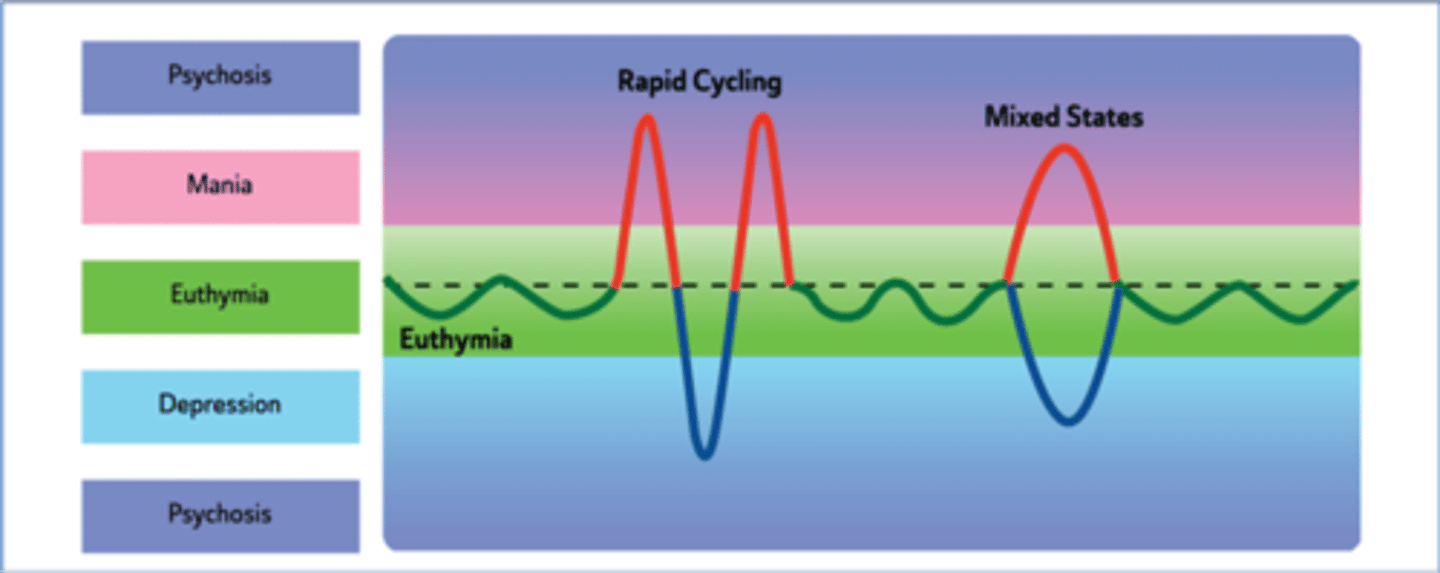
In ______________, a person can experience 4 or more episodes of mania or depression in one year.
rapid cycling
a pattern of frequent, distinct episodes
rapid cycling
what does Lithium treat? MOA?
acute bipolar mania
unknown MOA
Various hypotheses exist for lithium response --> regulating cell membrane properties, cell membrane transport, ion distribution, neurotransmitter regulation, and intracellular signaling
why do most BD patients not respond well to lithium monotherapy?
narrow therapeutic index, poor tolerability, especially at higher doses, and risk of "rebound mania" on withdrawal
common side effects include tremor, polydipsia, polyuria, and long-term treatment can lead to hypothyroidism
long term treatment with lithium can lead to?
hypothyroidism
what is the active species of Lithium salts? how might this affect its MOA?
Li+
-Resembles Na+, can occupy Na+ pump
•Cannot maintain membrane potentials, may prevent release of neurotransmitters (e.g. dopamine) that characterize manic state
activity of this molecule is linked to G proteins and second messenger Inositol triphosphate
Li+
are there animal models that can be used for BPD research?
there are no universally accepted animal models in bipolar disorder and no model can exhibit the characteristic mood swings
how do anticonvulsants act as mood stabilizers?
by making the nerve cells less excitable
Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, lamotrigine, valproic acid MOA (BPD)
Blockade of voltage-gated Na+ channels --> prolongs Na+ channel inactivation
Preventing Na+ influx leads to lowering of glutamate mediated excitation
Results in lowering neuronal excitability
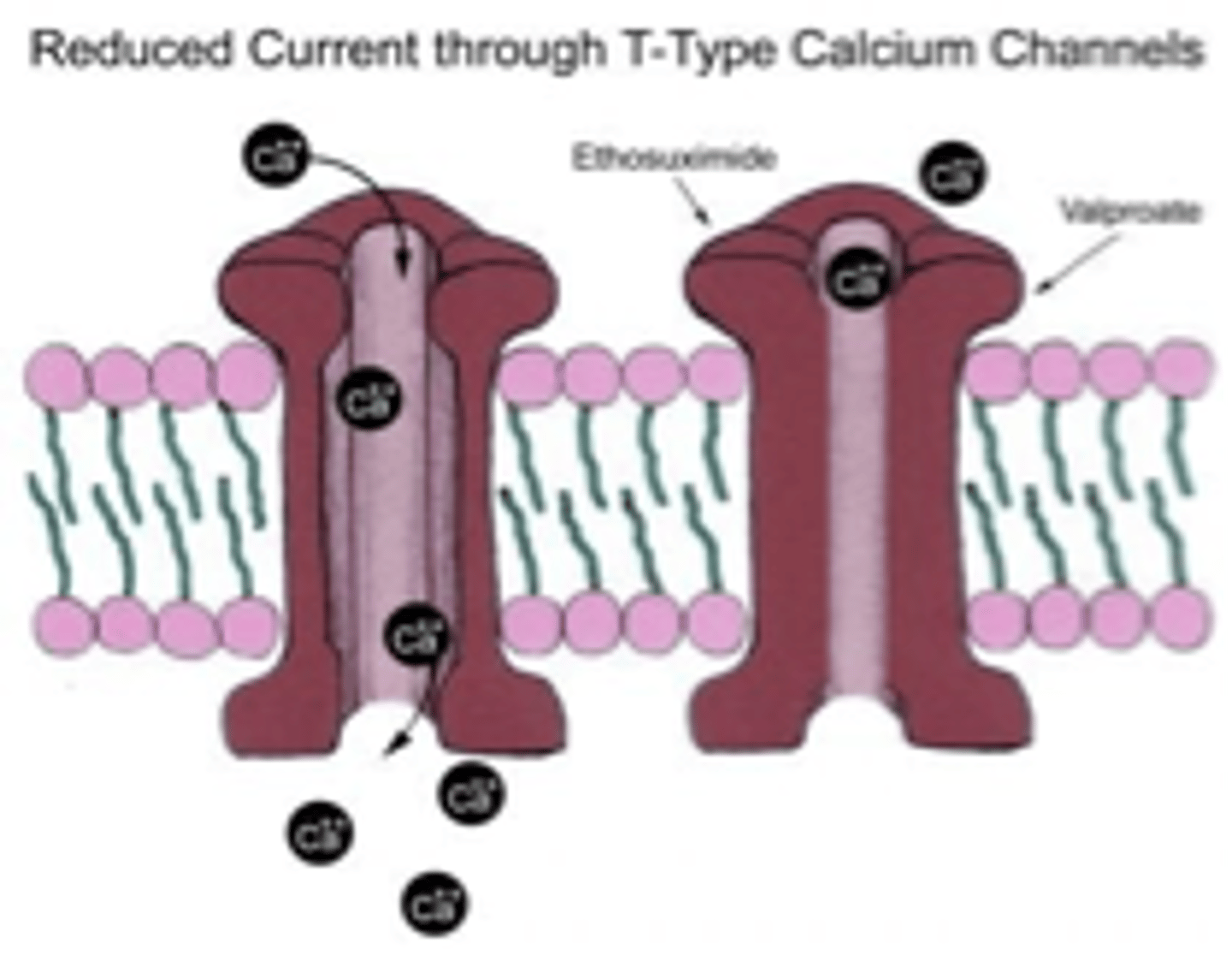
Multiple MOAs for Valproic acid
1. Blockade of voltage-gated Na+ channels --> prolongs Na+ channel inactivation
2. Reduces cell permeability to voltage-dependent Ca++ T-type channels
3. Increases brain levels of GABA by inhibiting GABA transaminase
atypical antipsychotics indications
as add-on treatment (with mood stabilizers and antidepressant drugs) and sometimes as monotherapy in treatment-resistant bipolar patients
for short or long-term treatment of bipolar disorder to control psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, or mania symptoms
pros and cons atypical antipsychotic medications
pros: less extrapyramidal symptoms (movement disorder) and less risk of tardive dyskinesia
cons: can cause weight gain (olanzapine and clozapine), sedation, and agranulocytosis (clozapine)
structural analog of clozapine with similar pharmacological properties
antagonist at 5-HT2A and DA2 Rs
Olanzapine