5. Population Distributions & Range
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Multiple individuals of the same species in a given area
Population
Important features of a population:
Genetic unit that defines the ___ ____
Has a defined ____ _____
Structure defined by characteristics of the _____, not individual
____ in time due to birth, death, and movement
gene pool
spatial boundary
collective
dynamic
A niche is much like a _____, where no two species will have the exact same niche
fingerprint
Range of abiotic conditions under which a species can persist (where is COULD be found)
Fundamental niche
Range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species persists (Where its ACTUALLY found)
Realized niche
If abiotic conditions are suitable, _______ can constrain the fundamental niche into the realized niche
competition
Even if suitable habitat is elsewhere, barriers to _______ can constrain the fundamental niche into a realized niche
dispersal
Outside of competition and barriers to dispersal, _____ can also constrain the fundamental niche into a realized niche
Predation
Modeling that is used to identify the fundamental niche of a species by analyzing the physical conditions of the species current realized niches
Ecological niche modeling
ENMs can be used to predict ______ ____ impacts
climate change
Surveys and abiotic data collection can be used to model how habitat is expected to change under future scenarios, termed ______ ____ models
habitat sustainability models
ENMs can be used to predict _____ ____ by seeing where they currently exist in their native habitat and what foreign areas align with those habitats
species invasions
In order to use an ENM to predict species invasion, you need to know something about their
fundamental and realized niche in their native range
What are the five characteristics of populations distributions?
Geographic range
Abundance
Density
Dispersion
Dispersal
Total area occupied by a population
Geographic range
Number of individuals living within a defined area
Abundance
Number of individuals per unit area or volume
Density
Spacing of individuals relative to one another
Dispersion
Movement of individuals from one area to another
Dispersal
A species that lives in a single, often isolated location
Endemic species
A species that has a very large range that can span multiple continents, may use portions of habitat seasonally
Cosmopolitan species
Are endemic or cosmopolitan species more susceptible to stochastic events/disasters?
Endemic
Dispersion type that is the “null hypothesis”, uncommon in nature
random
Dispersion type that results from limited dispersal, patchy resources, and social behaviors
Clumped/clustered
Dispersion type that is driven by competition
Uniform/even
Dispersion type can depend on
scale of observation
Dispersal type where individuals move from their birth site to a breeding site
Natal dispersal
Dispersal type where individuals move from one breeding site to another
Breeding dispersal
Migration is _____, dispersal is ______
temporary
permanent
In mammal species, dispersal of juvenile males prevents
inbreeding between relatives
Most individuals disperse a relatively short distance, but ___________ account for rapid colonization of new areas
super-dispersers
The exact distribution of individuals into patches (good patch/poor patch) can be predicted using the ____ _____ ______
ideal free distribution
The ideal free distrribution makes an assumption that there is a ______ _____ between habitat suitability and population density
negative relationship
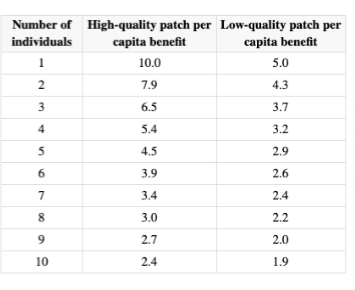
How many individuals must occupy the high-quality patch before the first individual should move to the low-quality patch?
4