2. Bonding, Molecules, Intermolecular Forces
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Which electrons play a role in bonding?
Valence electrons (in the outermost shell)
Octet rule
G.N. Lewis; atoms will behave to gain a full octet/valence
Lewis Structure
Lone pairs count as 2 electrons; single bond counts as 2 electrons
Exceptions to Octet Rule - Incomplete Octets
Hydrogen, He are stable with 2 valence
Li stable with 3 valence
Be is stable with 4 valence
B is stable with 6 valence
Exceptions to Octet Rule - Expanded Octets
Atoms in the 3rd period and higher (P, Si, S, etc.) can have more than 8 valence because they aren’t limited to s and p subshells
When will octet rule not work?
When there is an odd # of valence in a molecule, radical is required on lewis structure
Ionic Bonding
Strongest; between cations/anions (nonmetal/metal); electrons are completely TRANSFERRED
Ionic Compound Properties
Highly ordered crystal lattice, high MP, brittle, “electrolytes”
Why are ionic compounds electrolytes?
When they dissociate, they conduct electricity
Covalent Bonding
Sharing of electron pairs; electrons are attracted by the nucleus of both atoms
Nonpolar Covalent
Between the same or very similar electronegative atoms (less than .5 difference)
Polar Covalent
Between a very electronegative and non-EN atom (.5-1.7 difference); more EN will gain partial positive charge (dipole)
More electronegative =
Uneven electron distribution due to dipole
Dipole moment
Electrons flow towards the more EN atom, conferring partial ± charges; calculated by adding up ALL dipoles
Isoelectronic Pair
Atom and ion with the same electron configuration (B- and C)
Can polar bonds exist in a nonpolar molecule?
Yes, since dipoles can cancel each other out
Coordinate Covalent Bond
Both shared electrons originate from the SAME atom (NH3 bonded to BF3, lone pair nitrogen is used)
Bond Order
Number of bonds between 2 atoms (Single - 1, Double - 2, Triple - 3)
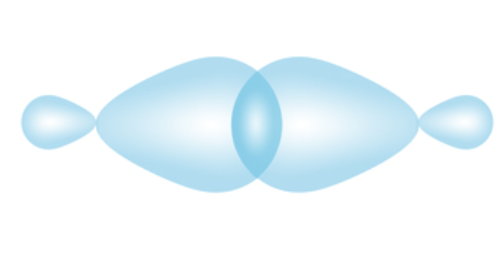
Sigma Bond
End-to-end overlap of atomic orbitals along axis
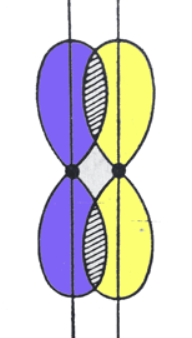
Pi Bond
Parallel atomic orbitals perpendicular to the internuclear axis
Are sigma or pi bonds stronger?
Sigma
How many pi bonds in a triple bond?
2 (always 1 sigma bond)
Can bond rotation occur in triple/double bonds?
No, the pi bond would break.
Bond energy and bond length:
Bond order increase → Bond energy increasing → Bond length decreasing
Metallic Bonding
Weakest bonding due to delocalization (electrons are attracted to multiple nuclei)
Intermolecular Forces
Forces that act between two or more molecules; not within a molecule (intra)
Are intermolecular forces stronger or weaker than intramolecular forces?
Inter are WEAKER than intra (easily disrupted by heat)
Four types of Intermolecular Forces (Decreasing Strength):
Ion-Dipole (Strongest)
Hydrogen Bonding
Dipole-Dipole
London-Dispersion (Weakest)
Van der Waals Forces are in these IMFs:
Hydrogen bonding
Dipole-dipole
LDF
London Dispersion Force (VDW)
Weakest IMF found in any pair of molecules; result in temporary dipoles that induces one in another molecule
LDF Strength increases as molecular size…
Increases; more likely to form temporary dipole
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Occur between polar molecules (- side of dipole of one is attracted to the + side of the other dipole)
Important Dipole-Dipole Interaction
Carbonyls; C=O bond (+C, -O) allows for many reactions
Hydrogen Bonding
Partial positive H attached to O, N, or F is attracted to O, N, or F of another molecule
Affect of IMFs Boiling Point/Melting Point
Stronger IMFs = Higher MP/BP
Ion-Dipole Force
Occurs between ions and molecules having a dipole
Lewis Structures
Valence electrons are shown by dots, covalent bonds shown by lines (add up valence for each atom in a molecule)
Resonance
Compounds that have more than one Lewis Structure due to differing distribution of electrons (Ex. NO2)
True Resonance Structure
Hybrid of all possible resonance that resembles the most stable one (partial double bonds)
Bond order of hybrid double bond due to resonance:
1.5
Why does resonance make a molecule more stable?
Distribution of electrons across multiple atoms
Formal Charge =
Valence Electrons - Number of Bonds - Lone Pair Electrons
Orbital Hybridization
When atoms combine to form a molecule, their orbitals overlap (sp, sp2, sp3 hybridized)
Number of hybrid orbitals =
Number of s and p superscripts (s1p2 = 3 sp2 orbitals)
How to determine hybridizatoin:
Count the number of groups around the central atom (include lone pair as 1 group)
VSEPR Theory
Use of Lewis structure and electronic relationships to predict shapes of molecules
Electronic vs. Molecular Geometry
Electron geometry considers lone pairs, molecular geometry does NOT (even if there are lone pairs in the molecule)
How to determine electron geometry:
Base on hybridization (sp = linear, sp2 = trigonal planar, sp3 = tetrahedral)
2 bonds, no lone pairs =
Linear, 180o
3 bonds, no lone pairs =
Trigonal planar, 120o
4 bonds, no lone pairs =
Tetrahedral, 180o
3 bonds, 1 lone pair =
Trigonal pyramidal, 107o
2 bonds, 2 lone pairs =
Bent, 104.5o
5 bonds, no lone pairs =
Trigonal bipyramidal; 90o, 120o, 180o
6 bonds, no lone pairs =
Octahedral; 90o, 180o
Why do bond angles decrease with lone pairs?
Lone pairs are stronger and push bonded atoms closer together