Rivers
1/129
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
discharge
the amount of water in a river at a particular point
tributary
a smaller river which joins a larger river
mouth
where the river flows into the sea/lake
watershed
the boundary dividing one drainage basin from another; a ridge of high land
confluence
the point at which two rivers join
source
the upland area where the river begins
catchment area/drainage basin
the area from which water from a river and its tributaries is drained
drainage density
total length of all the streams in the basin divided by the total area of the basin
flood plain
the land that floods when the river overflows
what cycle is the drainage basin system a part of
hydrological (water) system
is the hydrological cycle a closed or open system
closed system
are drainage basins closed systems or open systems
open systems
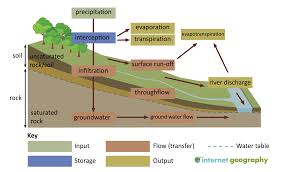
inputs of the drainage basin
precipitation
stores of the drainage basin
interception
groundwater storage
outputs of the drainage basin
river runoff
evaporation
transpiration
flows (transfers) of the drainage basin
infiltration
groundwater
throughflow
surface runoff
percolation
groundwater flow
outputs of the drainage basin
river runoff
evaporation
transpiration
which direction do all rivers flow
downwards towards sea level, even if they don’t reach the sea
from where does a river get wider
gets wider as it goes from source to mouth
transpiration
water vapour released through stomata in leaves
interception
water is stored on leaves and branches of vegetation
throughflow
water flows horizontally through soil into river
percolation
water flows vertically through soil rocks
infiltration
water seeps into the ground
groundwater flow
water flows horizontally through rock into river
evaporation
water turns from droplets into vapour
surface runoff
water flows horizontally over land into river
the three processes of rivers
erosion- wearing away
transportation- carrying
deposition- dropping
courses of a river
upper course
middle course
lower course
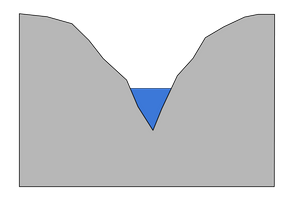
features of the upper course
erosion dominates
lots of energy
fast flowing
steep
narrow
steep sided, V shaped valley
narrow, not deep channel
mainly vertical erosion as its steep
lot of traction occurs as theres enough energy to roll heavy boulders
waterfalls
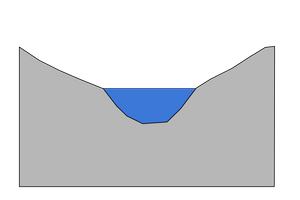
features of the middle course
less energy
slower flow
erosion and deposition- neither dominant
gentle-sloping valley
wider and deeper than the upper course
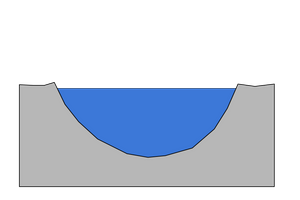
features of the lower course
little energy
slow flowing
wide
deposition dominates
wide and flat valley
wide and deep channel
mainly lateral erosion as its flat
river course
the path the river takes from its source
what does the long profile of a river show
shows how the steepness of a river changes over the course
how does the gradient of the river change as the river moves from upper to the lower course
the gradient decreases and the slope becomes gentler
erosion
the wearing down and removal of rock; shapes our landscape
where does erosion mostly occur
upper course
methods of erosion
hydraulic action
attrition
abrasion/corrasion
solution/corrosion
how does hydraulic action work
force of river against the bed and banks can cause air to be trapped in cracks and crevices; pressure weakens banks and gradually wears it away
when is hydraulic action most effective
when water moving fast and there’s a lot of it (upper course)
how does attrition work
rocks being carried by the river smash together and break into smaller, smoother, rounder particles
how does abrasion work
river load rubs against bed and banks of river; this action causes some of the material to break off, by a sandpapering action, and causes the banks to collapse
how does solution work
soluble particles are dissolved into the water
which directions does a river erode in
both downwards and sideways: vertical and lateral erosion
which part of the course does vertical erosion take place
upper, where the gradient is steep and the river flows quickly
what happens during vertical erosion
causes the channel to deepen to form a deep sided V-shaped valley
which course does lateral erosion take place in
lower course, where the gradient is gentler and the volume of water is higher
how does lateral erosion work
the speed of flow is slow and causes the river to erode horizontally, causing the river channel to widen and forms a broad and flat valley
methods of transportation
traction
saltation
suspension
solution
traction
large boulders and pebbles are rolled along the river
where does traction mainly occur and why
upper course as it has the energy needed to push heavy boulders and goes downhill so gravity helps to move them
saltation
small stones, pebbles and silt bounces along the river bed
which course does saltation mainly occur in
middle and lower course, as there’s less energy
suspension
fine material, such as clay and sediment, is carried by the river
which course does suspension mainly occur in
every course
solution
dissolved minerals are carried by the river
what course does solution mainly occur in
any course, as minerals are always present in water
when does deposition occur
when the river loses energy as it cannot carry the material anymore, such as:
a river enters an area of shallow water
gradient drops
volume of water decreases
where does deposition mainly take place
the end of a rivers journey at the mouth, as it has less energy here and can no longer carry the load/sediment
where is the source of the river Tees
high up in the mountains, can be natural spring/rainwater/snow
what happens in the upper course of the river Tees
water rushes downhill
flows over roads, boulders and down deep slopes
erosion
valleys
canyons
what happens in the middle course of the river Tees
slows down at flatter land, causing meandering
tributaries, rivers and streams join together
larger and wider
what happens in the lower course of the river Tees
widens into estuaries and deltas where sediment slows water down
provides rich soil
mouth- river flows out to sea
where is the Tees located
northeast England, starts in the moorlands, near the border to county Durham
how long is the river Tees
100km long
what is annual rainfall at the source of the river Tees
1200mm, means the bogs never dry out
where does the Tees flow
through v shaped valley, moorland and then a resevoir
name of waterfall on the river Tees
high force waterfall
what course do waterfalls form
upper course
how do waterfalls begin to form
when the river meets a hard/resistant rock
what allows a waterfall to erode rapidly
the river gains a great deal of energy where it falls over the lip of the waterfall
stages of the formation of a waterfall
river meets a band of softer, less resistant rock
underlying, softer rock is eroded away more quickly
rock causes abrasion of the river bed
hydraulic action also helps to create a deep plunge pool
processes of erosion such as abrasion causes undercutting
more resistant rock is left unsupported and overhangs
eventually the more resistant rock collapses onto the riverbed
process is repeated and the waterfall retreats upstream
a steep-sided river valley is created, called a gorge

what is a meander
a bend in the river
what course are meanders found in
the middle course
how is a meander formed
a large bend in the river formed by lateral erosion
water on the outside of the bend travels fastest and erodes away from a river cliff
water on the inside of the bend travels slowest and deposits material to form a river beach or slip off slope
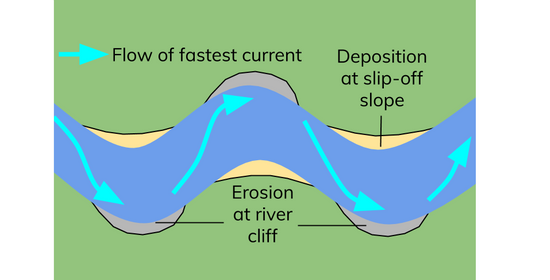
what methods of erosion are most common in the formation of a meander
mainly hydraulic action and abrasion
what occurs at the outer bend
river cliffs
deeper
erosion
more energy
faster flow
what occurs at the inner bend
slip-off slopes
shallower
deposition
less energy
slower flow
slip-off slope
current is weakest where water shallowest
sediment deposited here
leaves a not-steep gradient
river cliff
erosion is highest as current is strongest here
creates a steep gradient
how is an oxbow lake formed
outside of the meander has the quickest flow and are eroded
outside of the meanders move closer together narrowing the neck in between
eventually (usually during floods) the river cuts straight across the neck following the quickest route
after this the river slows down by the old bend and deposits material cuttinf off an oxbow lake
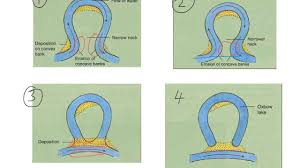
what are the main methods of erosion to form an oxbow lake
hydraulic action and abrasion
features of the lower course
floodplains
levee
floodplain
the area of land surrounding a river thats likely to flood when a river overflows
to create a floodplain what form of erosion occurs
lateral erosion
stages of a floodplain formation
river erodes laterally
the river valley is widened creating a large flat area
when the river overflows (floods) material is deposited as the water loses energy
over time sediment builds up in layers creating a floodplain
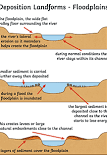
levee
a raised riverbank
how is a levee formed
lateral erosion occurs, creating a wide flat valley
river floods onto a floodplain
river drops the heavier sediment first, right by the river, and smaller sediment later, further away
sediment builds up in layers forming natural embankments, which are levees
delta
low-lying bits of land where rivers meet the ocean/lake
why do deltas form
rivers lose momentum in the flatter lower course as they reach the ocean, causing them to deposit their sediment load
river channel can be blocked by this build-up of material
this splits the river into lots of tiny rivers named distributaries
if this material builds up enough, a piece of land called a delta is created
what does a flood hydrograph show
how a river responds to a rainfall event
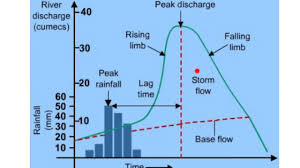
discharge
the amount of water in a river at a particular point
peak rainfall
the max rainfall (mm)
peak discharge
the max discharge (cumecs, cubic metres per second)
lag time
the time taken between peak rainfall and peak discharge
rising limb
shows the increase in discharge on a hydrograph
falling limb
shows the return of discharge to normal/base flow on a hydrograph
what does a long lag time show about a river
respond slowly to rain and are therefore less likely to flood
physical factors effecting hydrographs
impermeable soil
impermeable rocks
cold weather
steep slopes
drainage basin shape
antecedent conditions
vegetation
human factors effecting hydrographs
deforestation
impermeable building materials