AP Physics Unit13_3: Thin Lenses
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Compare converging and diverging lenses in terms of focal points and ray behavior.
Converging Lens (e.g., bi-convex):
Rays parallel to axis refract through the real focus (opposite side).
f is positive.
Diverging Lens (e.g., bi-concave):
Rays parallel to axis diverge from a virtual focus (same side).
f is negative.
Key Notes:
Converging lenses can form real or virtual images; diverging lenses only virtual.
Lens equation same as mirrors, but focal length sign differs.
What are the ray-tracing rules for converging and diverging lenses?
Converging Lens:
Parallel ray → refracts through far focus.
Ray through near focus → refracts parallel.
Ray through optical center (O) → undeflected.
Diverging Lens:
Parallel ray → refracts away from virtual focus.
Ray toward far focus → refracts parallel.
Ray through O → undeflected.
Key Notes:
Real images form on the opposite side; virtual images on the same side as the object.


An 11 cm object is placed 44 cm in front of a converging lens (f = 24cm). Find the image location, type, orientation, and height.
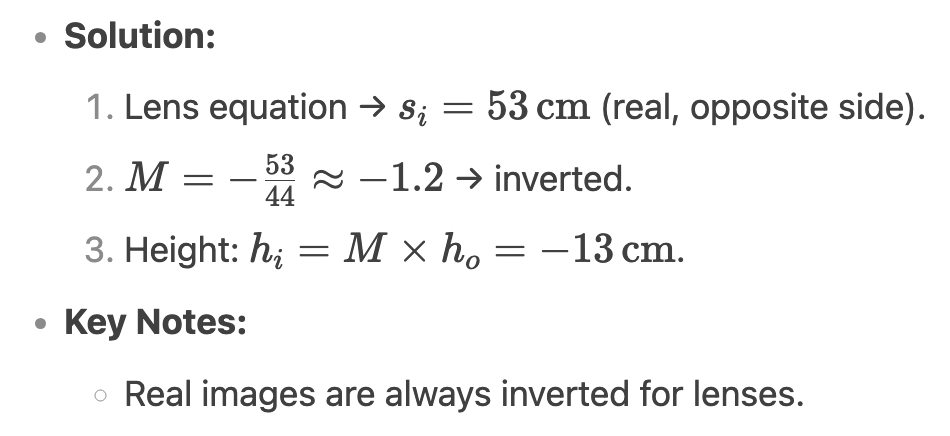
An 11 cm object is placed 48 cm in front of a diverging lens (f = −24.5 cm). Describe the image.
