Test 1 biopolymers and biocompatibility
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What are the 4 free radical polymerization techniques
Bulk suspension Solution Emulsion
what polymerization technique has these advantages; Simple, no contaminants added
bulk
what polymerization technique has these disadvantages; Reaction exotherm difficult to control; high viscosity
bulk
what polymerization technique has these advantages; Heat readily dispersed; low viscosity; polymer obtained in granular form and may be used directly
suspension
what polymerization technique has these disadvantages; Washing and/or drying required; agglomeration may occur; contamination by stabilizer
suspension
what polymerization technique has these advantages; Heat readily dispersed; low viscosity; may be used directly as solution
solution
what polymerization technique has these disadvantages; Added cost of solvent; solvent difficult to remove; possible chain transfer with solvent; possible environmental pollution
solution
what polymerization technique has these advantages; heat readily dispersed; low viscosity; high molecular weight obtainable; may be used directly as emulsion; works on tacky polymers
emulsion
what polymerization technique has these disadvantages; contamination by emulsifier and other ingredients; chain transfer agents often needed to control DP; washing and drying necessary for bulk polymer
emulsion
what is required for bulk polymerization
Monomer + initiator
what is required for solvent polymerization
monomer + initiator + solvent
what is required for suspension polymerization
lots of water, monomer is an oil base
what is required for emulsion polymerization
initiator not inside droplets
how many ways are there to limit the MW in step-reaction polymerization
3
what is the first way to limit the MW in step-reaction polymerization
quench the polymerization reaction by rapid cooling when desired MW is obtained
what is the second way to limit the MW in step-reaction polymerization
Use an excess of one monomer when two difunctional monomers are polymerized
what is the third way to limit the MW in step-reaction polymerization
use small amounts of monofunctional reactant
what method of polymerization involves solutions of the two monomers in separate, immiscible solvent, one usually being water. when the two monomers are brought into contact, polymer is formed at the interface
interfacial polymerization
The ___ of any linear polymer having end groups that can be measured by ___ or ___ means can theoretically be determined if the method of measurement is sensitive enough
Mn chemical physical
End groups are present in ___ concentrations. presently avalible techniques allow a practical upper limit of molecular weight measurements of about ___
very low 50,000
Titration, using either indicators or potentiometric techniques
elemental analysis of element-specific end groups
measurement of activity of a radioactive-tagged end group
ultraviolet spectroscopic determination of an end group with a characterizable chromophore. Infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic techniques are of more limited use
End group determination
end group analysis ___ be applied to branched polymers unless the ___ is known with certainty thus it is practically limited to linear polymers
cannot number of branched
in a linear polymer there are ___ as many end groups as polymer molecules
twice
if the polymer contains different groups at each end of the chain and only one characterizable end group is being measure, the number of this type is equal to the ___
number of polymer molecules
Measurement of molecular weight by end group analysis is only meaningful when the ___ and ___ are well understood
mechanism of initiation termination
Define Amorphous
a physical state characterized by almost complete lack of order among the molecules
Define crystalline
the situation where polymer molecules are oriented in a regular array analogue to a degree to crystal lattice packing in a nonpolymeric solid
what are the following- dipole-dipole, induction forces, dispersion or london or van der waals forces between nonpolar molecules, ionic bonding and ion-dipole interaction between polymers containing ionic forces
intermolecular forces of polymers
what often forms dimers in vapor phase
Carboxylic acids
the temperature below which the physical properties of amorphous materials vary in a manner similar to those of a crystalline phase, and above which amorphous materials behave like liquids
glass transition temperature
what determines the glass transition temperature?
chemical structure, methods of measurements, molecular weight
when a polymer has a ___ structure with little or no chain branching, or when it contains ___ groups that give rise to very strong dipole-dipole interactions, it may exist in crystalline form
highly stereoregular highly polar
such crystallinity is unlike that of ___ compounds but exists instead in regions of the polymer matrix where polymer molecules order themselves in a ___ favorable alignment
low molecular weight thermodynamically
crystallinity is induced in any number of ways- cooling of molten polymer, ___ solution, or heating of a polymer under vacuum or in an ___ at a specific temperature, a process called annealing.
evaporation of polymer inert atmosphere
what is the process of Drawing
crystallization may be brought about by stretching a polymer sample at a temperature above its TG
crystalline structures are generally tougher, ___, more opaque, ___, and of higher density than their amorphous counterparts.
stiffer more resistant
the higher degree of crystallinity the more ___ the properties are
pronounced
The superior mechanical properties are a reflection of the greater ___ arising from more effective ___ forces among the closely packed molecules.
cohesive strength intermolecular forces
opaqueness arises from ___ by the crystallites
scattering of light
stereoregularity is ___ a prerequisite to crystallinity
not
what is the most severe mechanism for decreasing molecular freedom
chemical crosslinking
how does chemical crosslinking work
linking the polymer chains together through covalent or ionic bonds to form a network
what kinds of physical crosslinking exist
ionic crosslinks, crystalline polymers, block polymers
what are mechanical properties dependent upon
temperature and time
what is creep
measure of the change in strain when a polymer is subjected to a constant stress
what is stress relaxation
the decrease in stress when a sample is elongated rapidly to constant strain
What is thermal stability (TGA)
primarily a function of bond energy
when ___ increases to the point where ___ causes bond rupture, the polymer degrades
temperature vibrational energy
thermal stable polymers have high ___ or ___
Tg Tm
what is a biomaterial
nonviable material used in a medical device intended to interact with biological systems
how long is an implant intended to be used
30 or more days
what is regeneration
the renewal of a tissue or organ at the completion of healing
what is repair
the formation of scar at a site at the completion of healing
what is remodeling/maintenance/ turnover
process where ECM is replaced in a process of degradation followed by synthesis
what is an autotransplant
transplant to the same patient
what is an allotransplant
donor to another person
what is a heterotransplant/xenotransplant
donor to another species
what is the property of the materials to cause no biological effect on surrounding tissues and the whole organism and in its turn to resist their influence
biological inertness
what is the property of a material to perform a definite function in the organism during the time required with no harm to the latter
biological compatibility
what is the property of a material to have strong interactions with the cells and tissues, and positively affect the cells and tissues
bioactive
if only a few monomer units are joined the resulting low MW polymer is called what
oligomer
what is a homochain
only have carbon as the backbone
what is a heterochain
having more than carbon as the backbone
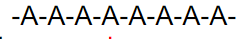
what kind of polymer is this
homopolymer
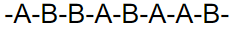
what kind of polymer is this
random copolymer
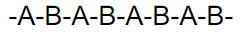
what kind of polymer is this
alternating copolymer
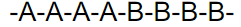
what kind of polymer is this
block copolymer
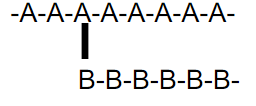
what kind of polymer is this
graft copolymer
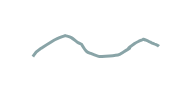
what polymer structure is this
linear

what polymer structure is this
branched

what polymer structure is this
network
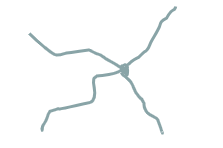
what polymer structure is this
star
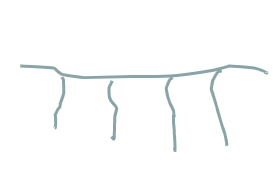
what polymer structure is this
comb
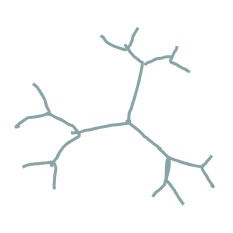
what polymer structure is this
dendrimer ladder
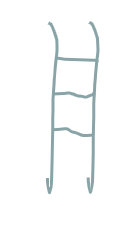
what polymer structure is this
ladder
what polymer structure is this
what is this process? MW increases by the successively linking of monomer molecules to the end of a growing chain
chain growth polymerization
What is this process? polymer chains are built up in a stepwise fashion by the random union of monomers to form dimers, trimers, and higher species throughout the monomer matrix
step growth polymerization
what are the two kinetic steps for chain reaction polymerization
initiation propagation
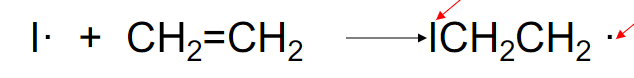
what is this step
initiation
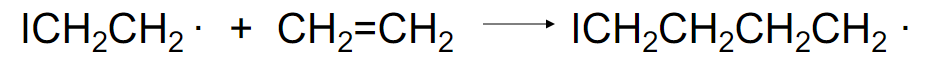
what is this step
propagation

what is this step
termination
most step reaction polymerizations are what
condensation precesses
most chain reaction polymerizations are what
addition processes
is this a step or chain reaction? growth occurs throughout matrix by reaction between monomers, oligomers, and polymers
step
is this a step or chain reaction? DP* low to moderate
step
is this a step or chain reaction? monomer consumed rapidly while MW increases slowly
step
is this a step or chain reaction? no initiator needed; same reaction mechanism throughout
step
is this a step or chain reaction? no termination step end groups still reactive
step
is this a step or chain reaction? polymerization rate decreases steadily as functional groups consumed
step
is this a step or chain reaction? growth occurs by successive addition of monomer units to limited number of growing chains
chain
is this a step or chain reaction? DP* can be very high
chain
is this a step or chain reaction? monomer consumed relatively slowly, but MW weight increases rapidly
chain
is this a step or chain reaction? initiation and propagation mechanisms different
chain
is this a step or chain reaction? usually chain-terminating step involved
chain
is this a step or chain reaction? polymerization rate increases initially as initiator units generated; remains relatively constant until monomer depleted
chain
what polymerization classification is this? The same as step reaction polymerization with concurrent formation of low MW byproducts (pet synthesis)
polycondensation
what polymerization classification is this? the same as step reaction polymerization without byproduct formation
polyaddition
what polymerization classification is this? the same as chain reaction polymerization without formation of byproducts (PE)
chain polymerization
what polymerization classification is this? the same as chain reaction polymerization with the formation of low MM byproducts
condensative chain polymerization