Pafology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
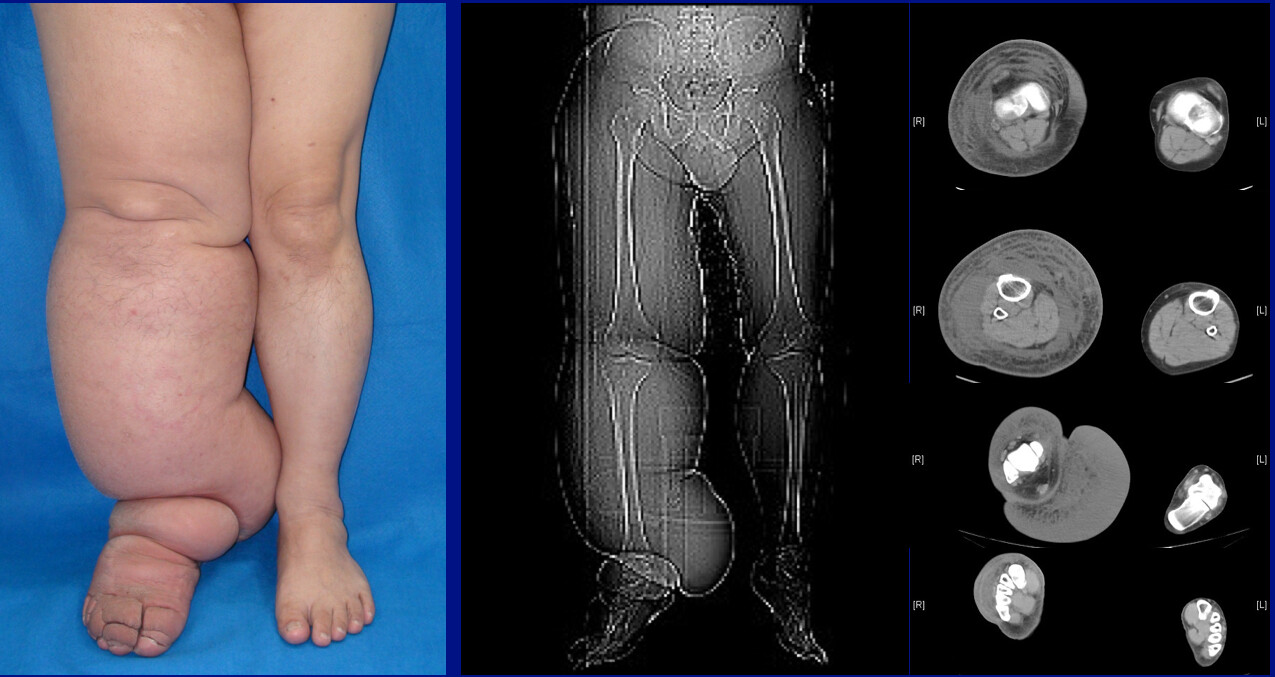
Elephantiasis - removal of lymph nodes, filaria parasites, Miliroy disease
Quincke Angioneurotic edema
Severe, generalised, sudden onset, allergy related. Larynx, lungs
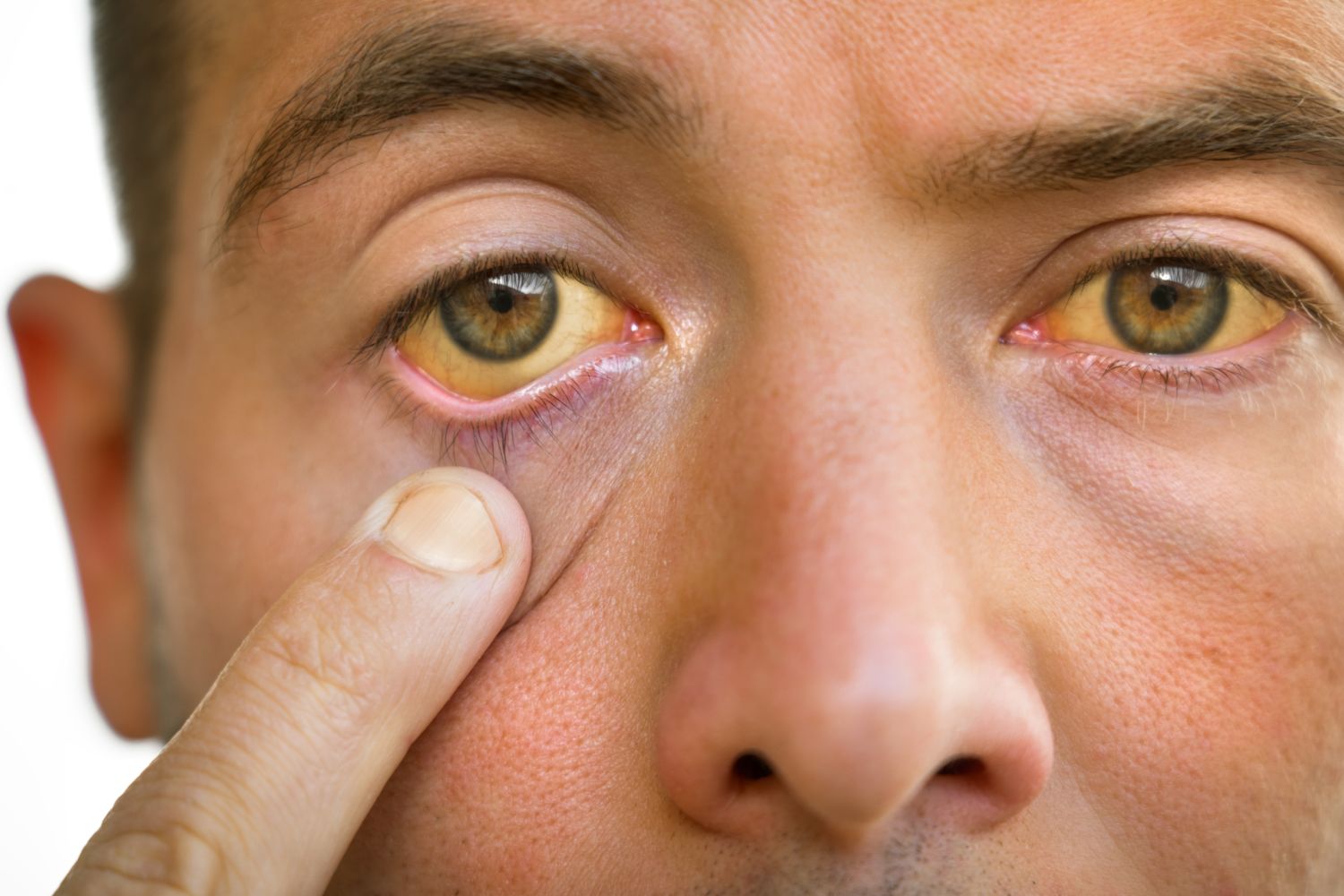
Gilbert-Meulengracht syndrome - reudction of glucoronil-transferase acitivity, fluctuating jaundice and tirendess
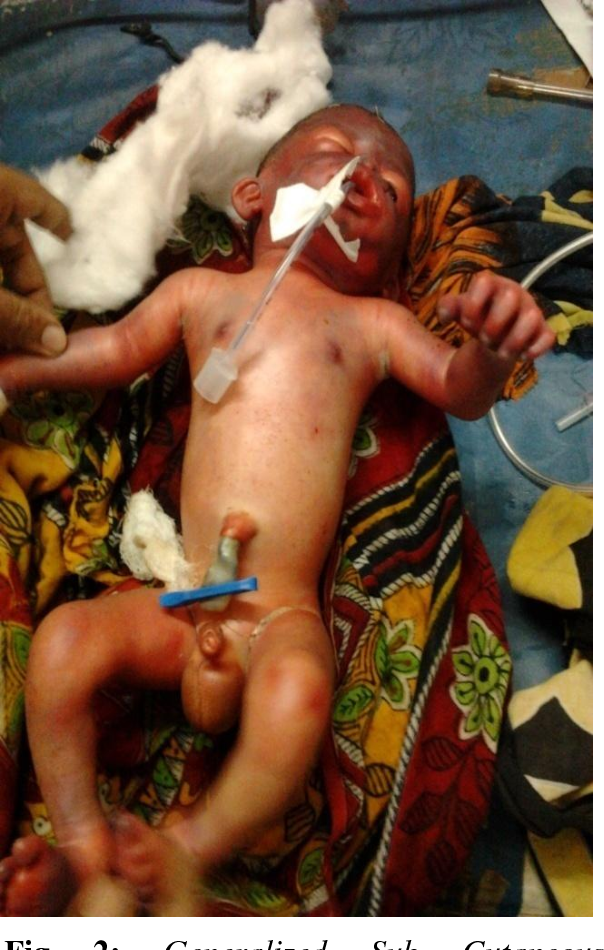
Crigler-Najjar syndrome - lack of glucornil transferase, death within first year of life

Dublin-Johnson syndrome - decreasted biliribin exreation, chronic, fluctuating desiase, bilirubin and pigments in hepatocytes and heptomegaly
Rotor syndrome
Fluctuating jaundice, beningn outcome
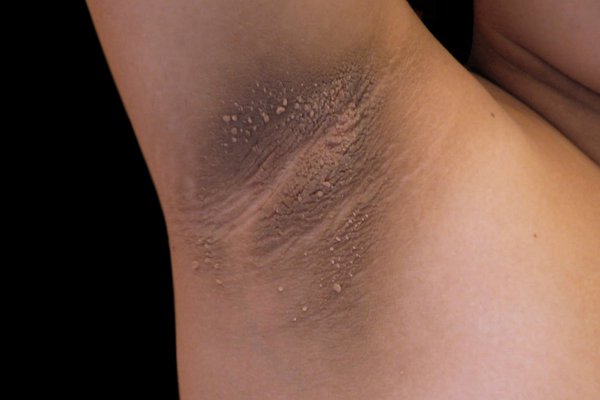
Acanthosis nigircans

Addisn’s disease
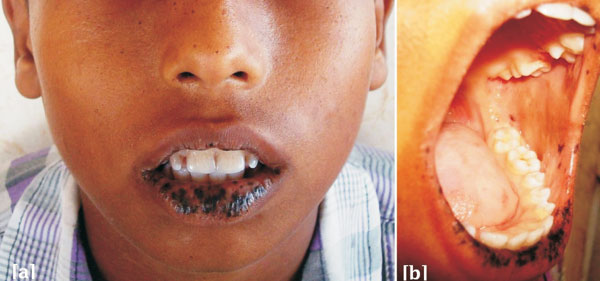
Peutz Jaghers sndrome
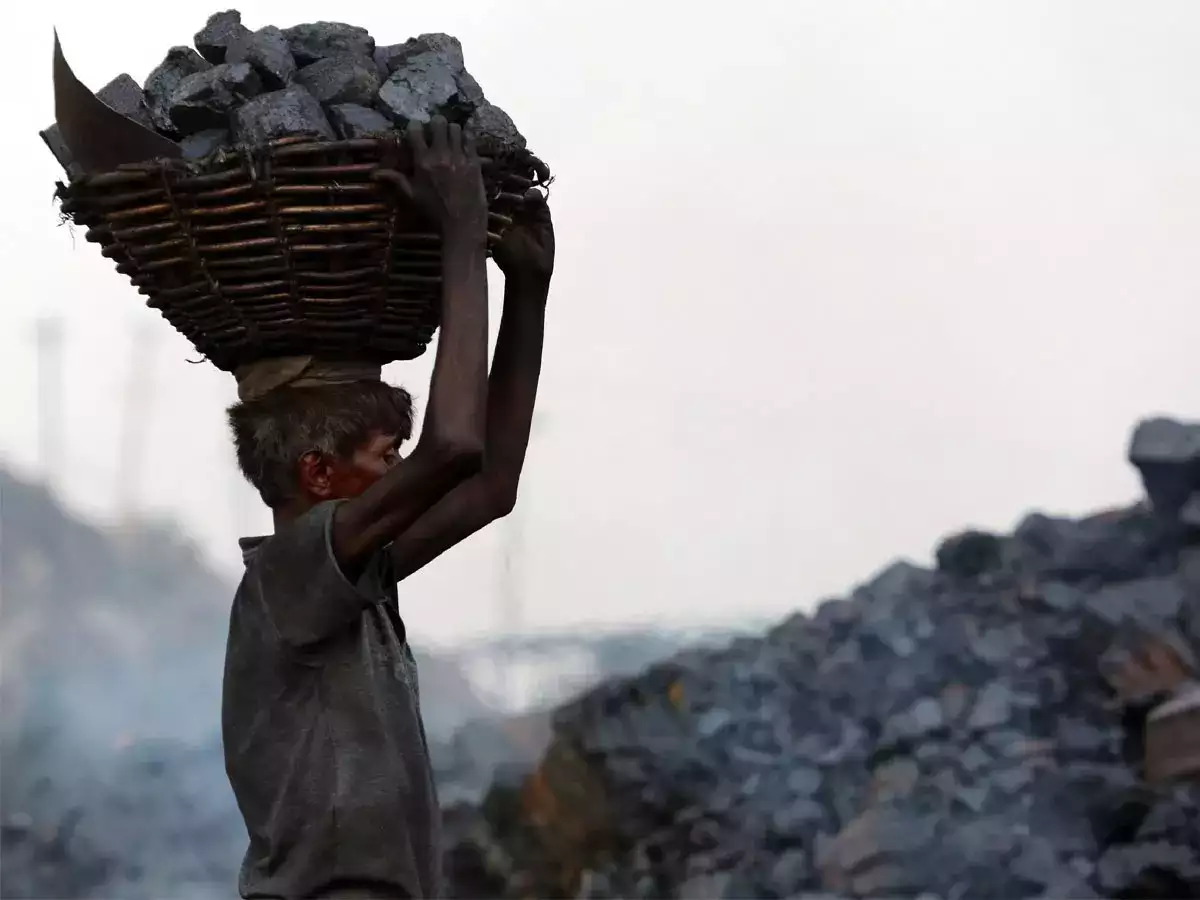

Anthrachosis/coal worker’s pneumconiosis - Carbon or coal dust
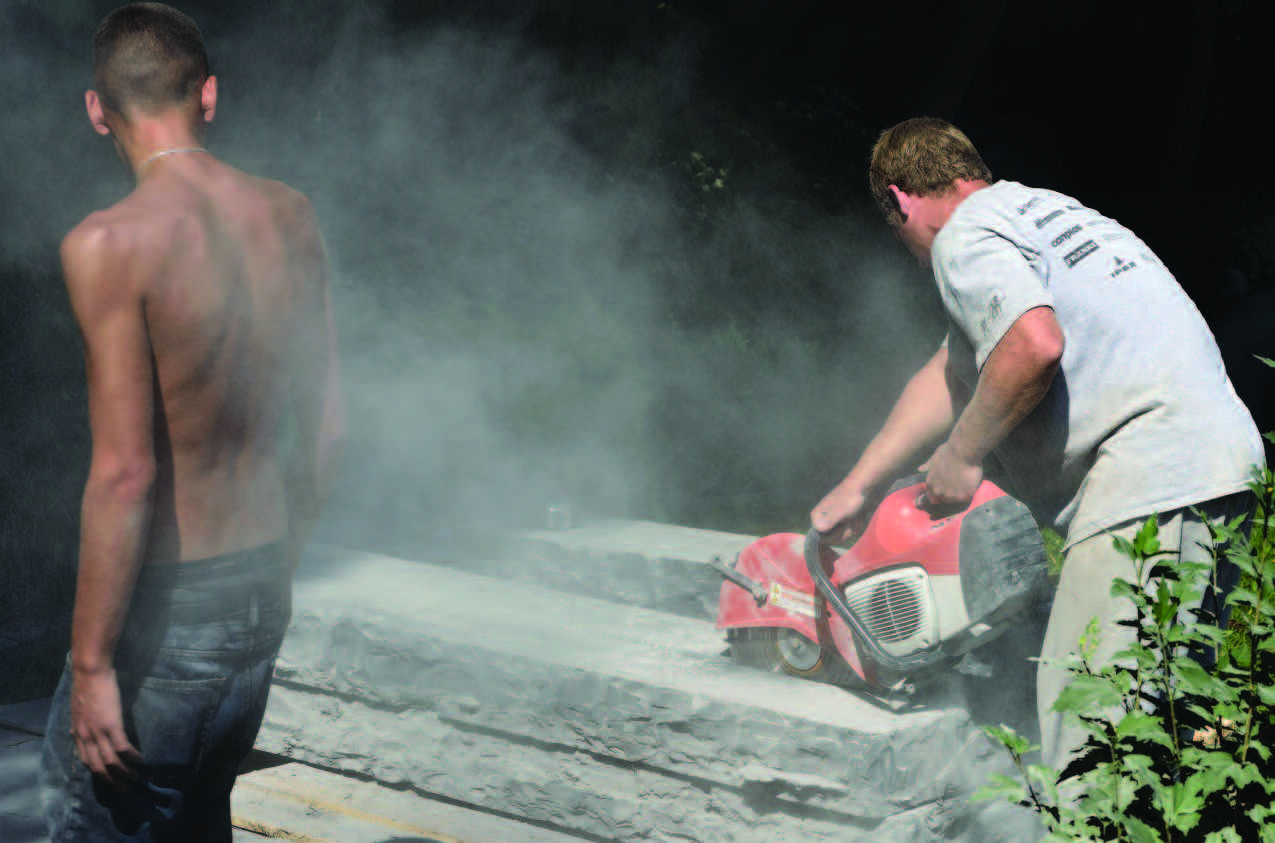

Silicosis - SiO2, in stone workers (silicia in rock, quartz, and sandstone) Forms garnulomas, fibrosis, and carcinomas
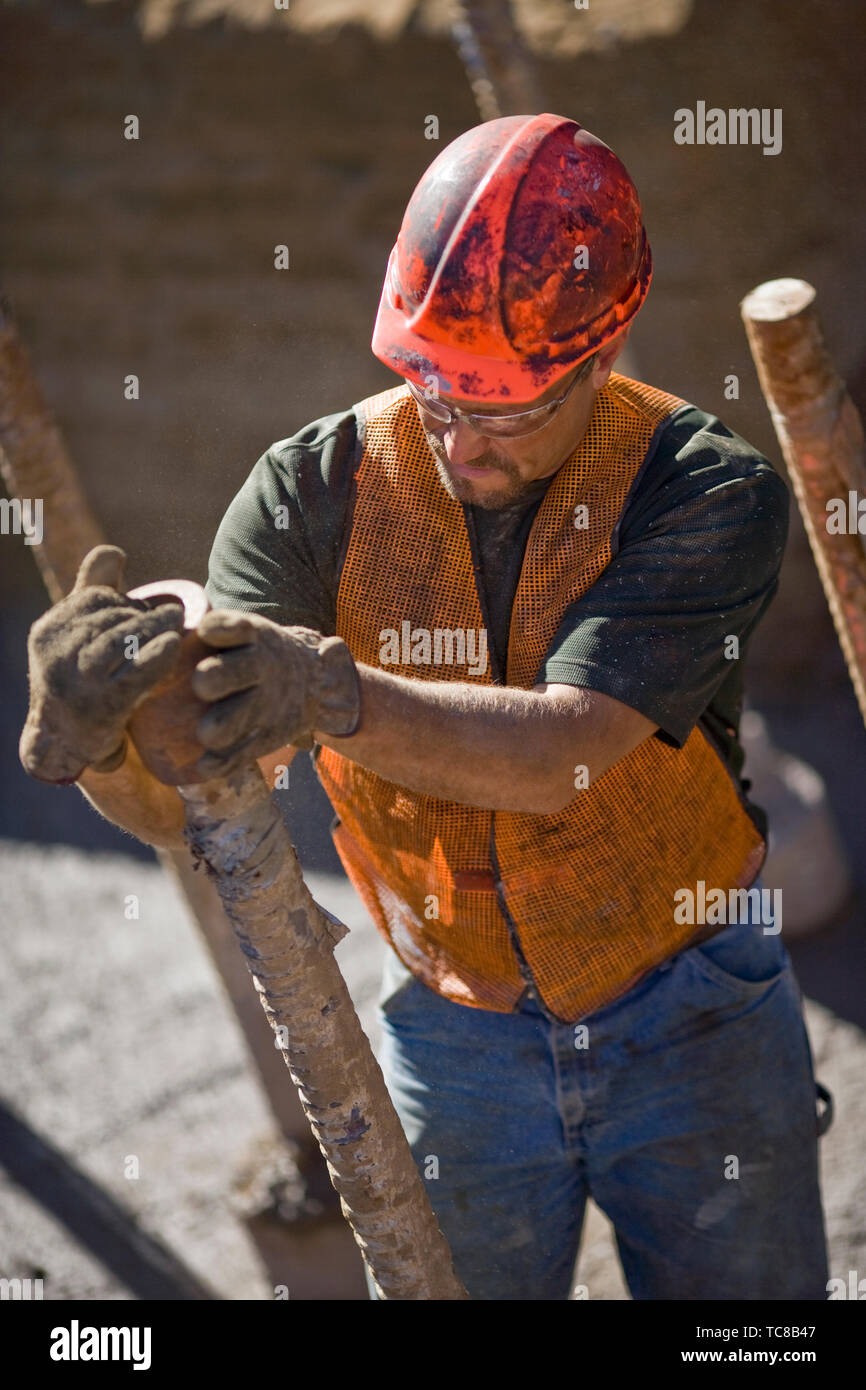

Asbestosis - Mig silicate from ship building, construction, demolitiion. Fibrosis and risk for mesothelioma

Siderosis - Fe, pyrite mines
Calcinosis and aluminosis…
Both risk factor for fibrosis

Bisinosis - cannavis sativa/ hemp

Bagasiosis - (bag of) sugar cane/saccharum officinale

Anthraquinone drugs - melanosis of the colon
Glycogen storage diseases causes HHCM
Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, cardiac failure, muscle cramps
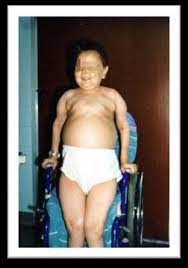
Gierke’s disease GSD 1 Glucose-5-phosphate DH - most frequent GSD, nanism, hypoglycemia, hyperlipedemia, hyperuicemia
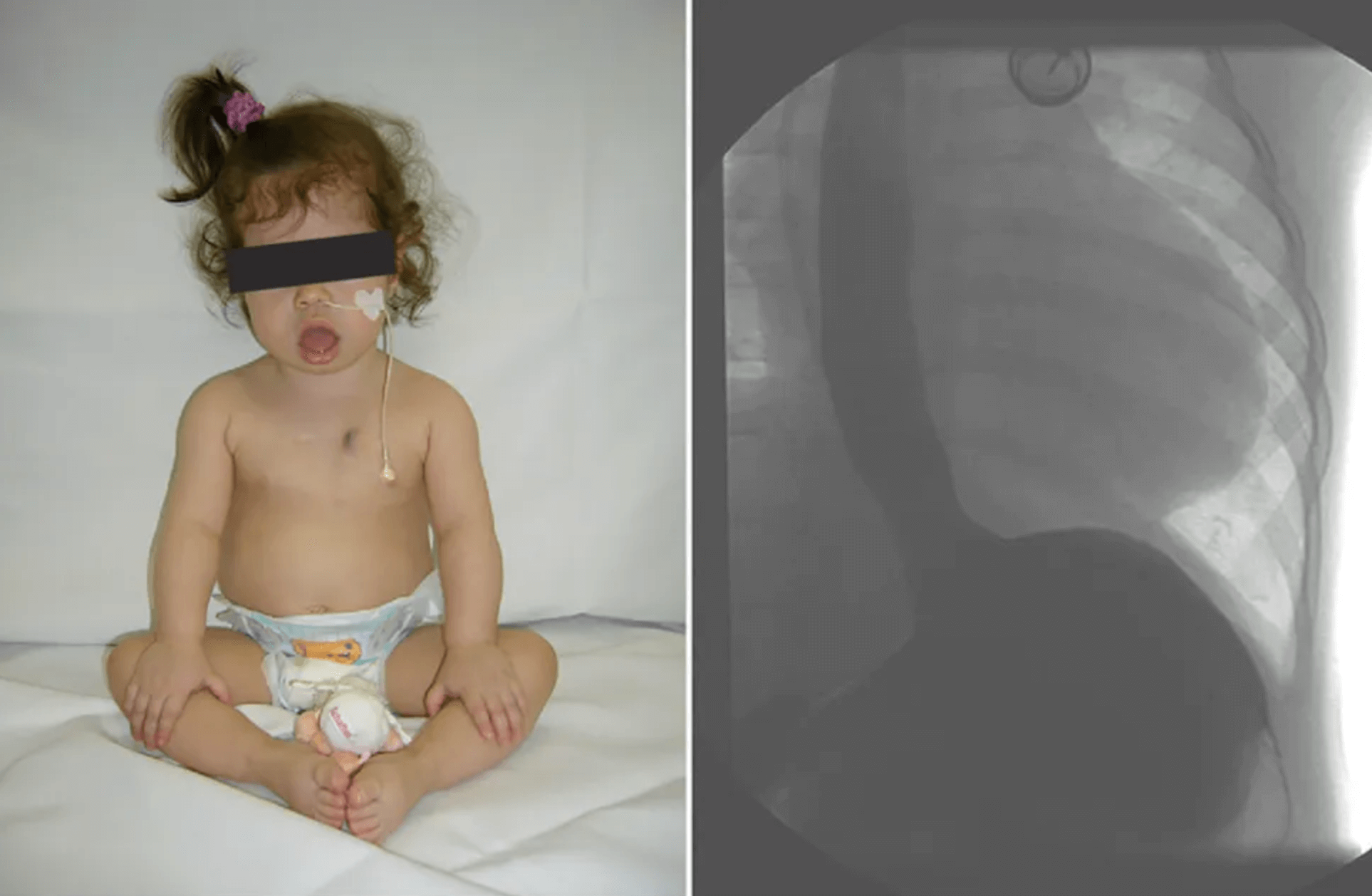
Pompe’s disease GSD2 Acid Maltase - most sever form of glycogenosis, death in first month of life
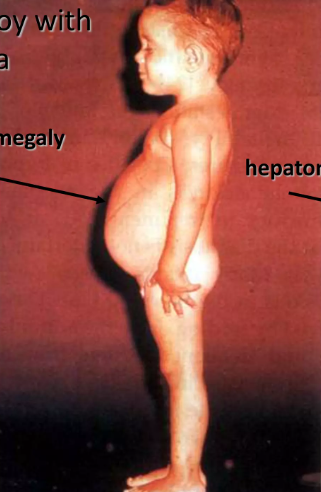
Forbe’s disease GSD3 Amylo 1-6 - hepatosplenomegalia
Galactosemia
Deficiency of galactose-1-phosphate-uridyl-transferase (GALT) - Galactose is transformed into galactitol, stored in liver, spleen, cristalin, kidney, cerebral cortex
Gaucher’s disease
Lysosomal storage disease - Lack of glucocerebrosidase, storage of glucocerebroside, liver, spleenn, skeletal and brain involvement with Gaucher cells in the brain
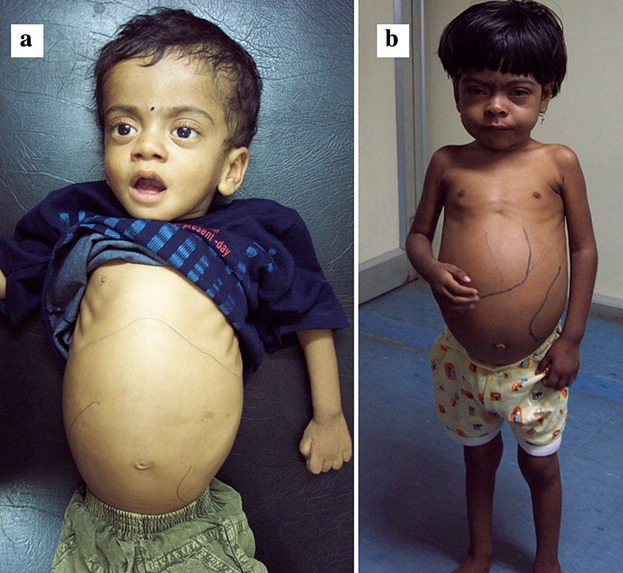
Niemann-Pick disease
Lack of sphingomyelinase, sotrage of sphingomyelin and cholesterol, mental retardation and visceral accumulation
Tay-Sachs disease
Lact of hexos A, storage GM2, neurns and retina affected, blind and death belowage of 3 years
Farber’s disease
Accumulation of ceramide
Fabry
Sotrage of glycolipids within endothelium
Mucopolysaccharides storage diorders, cause CRHMS
Deficiency of aLi, causes cardiac and respiratory disorders, hepatosplenomegay, mental deterioriation, and skeletal deformity
Recklinghausen disease
Extreme systemic iron accumulation. Liver cirrhosis, bronze skin pigmentation, bronze diabetes (pancreases fibrosis and diabetus), brown pigmentation of myocardium, brown pigementation and fibrosis of adrenal glands
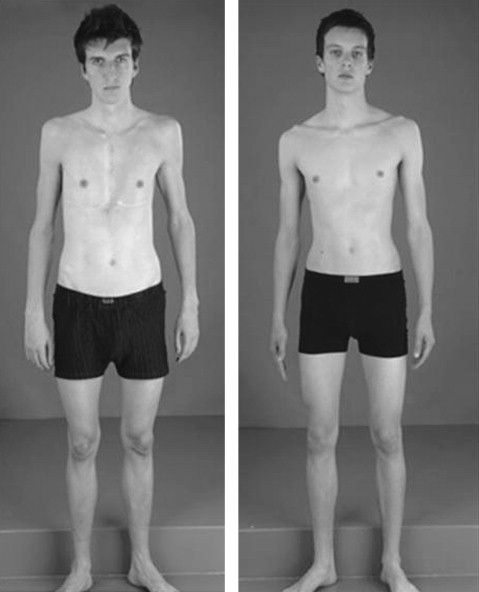
Marfan’s syndrome
Defect in FBN1 gene for fibrillin controlling integrity of elastic fibers. Tall, arachnodactylly, long extremities, joint hypermobility, ectopia lentis, aortic and mitral valve incompetence, mitral valve prolpases, aortic dissection
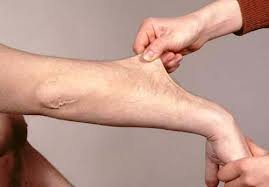
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Disorder in synthesis of collagen. Hypextensibility of skin, hypermobile joints, vessel wall lesions. Artery and colon rupture, aortic dissection, cornia rupture, retinal detachment, diapgragmatic hernia
Aging genes are on which chromosmoes and follow what transmission pattern
1, 4, and 6. AD
Coagulative (dry) necrosis occurs during…
Infarction (except brain)
Caseous necrosis occurs during
TB, syphilis, tumors
Liquefactive (colliquative) (wet) necorsis occurs during
Brain infarction
Fat necrosis (steatonecrosis) occurs during
Adipose tissue, pancreatitis
Gangrenous necrosis occurs during
Legs, ombiilucs. Dry gangrene occurs to tissues exposed to air, toes, legs, stump. Wet gangreme causes putrefaction, lung, bowl, gallbladder. Gas gangrene putrefecation and gas-producing anaerobic bacili, clostridium perfingens.