Chapter 6- Bones and Skeletal Tissue
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Bones (osseous tissue)
organ made up of several different tissues (bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, adipoe, and nervous tissue) working together
skeletal system
framework of the bones and their cartilage
Functions of bones
-support
-protection
-movement
-mineral and growth factors storage
-blood cell formation/hematopoiesis
-fat storage
-hormone production: ostecalcin
Function of Bones: Support
vital organ support
Function of Bones: Protection
brain, spinal cord, vital organ protection
Function of Bones: Movement
levers for muscle action
Functions of Bones: Mineral and growth factor storage
Calcium and phosphorus and growth factors reservoir
Functions of Bones: blood cell formation/Hematopoiesis
occurs in red marrow cavities
Functions of Bones: fat storage
energy source stored in bone cavities
Function of bones: hormone production/osteocalcin
secreted by bones helps to regulate insulin secretion, glucose levels and metabolism
axial skeleton
along axis of body (skull, vertebral column, rib cage)
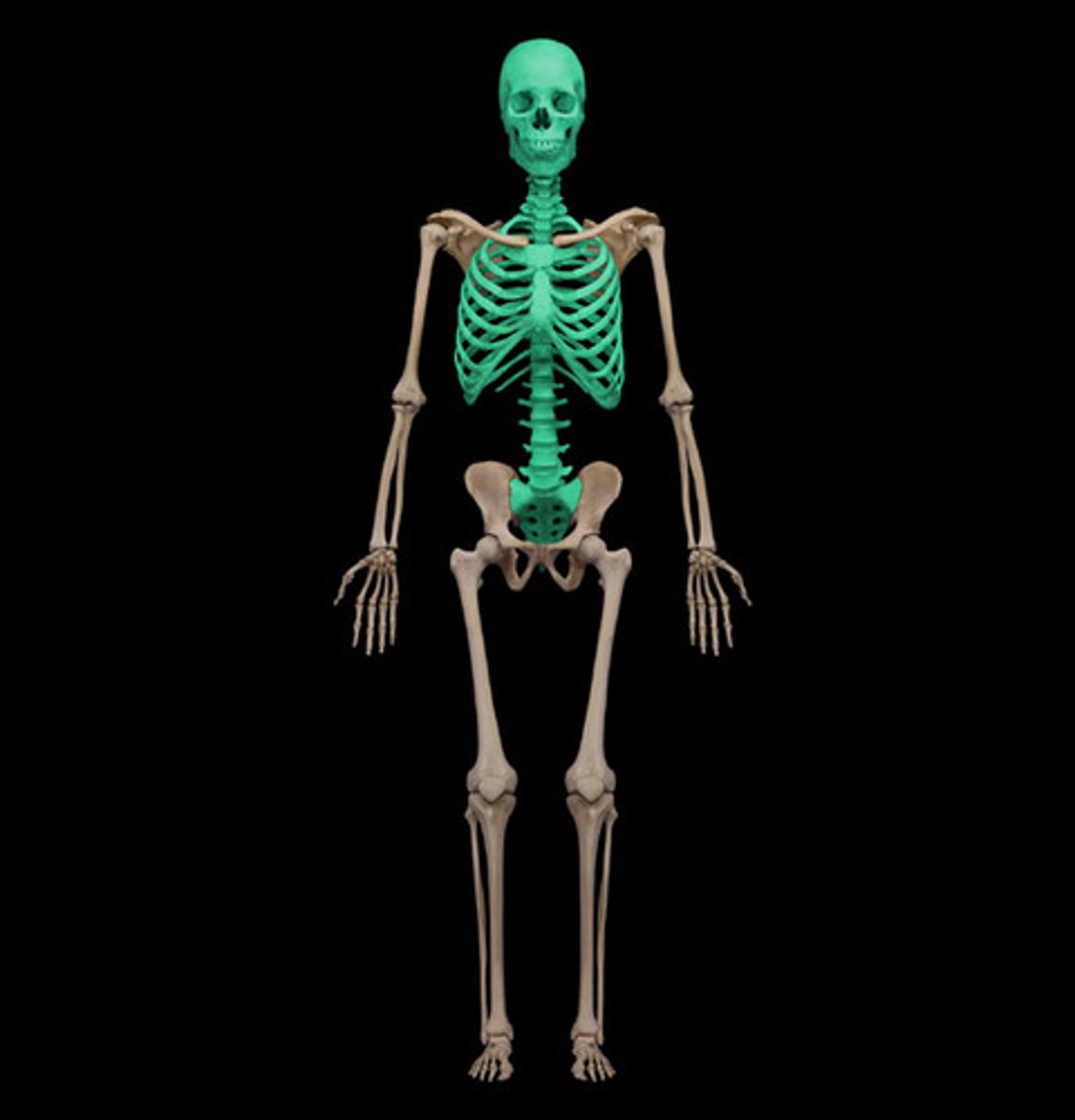
appendicular skeleton
Bones of upper and lower limbs
Girdles attaching limbs to axial skeleton
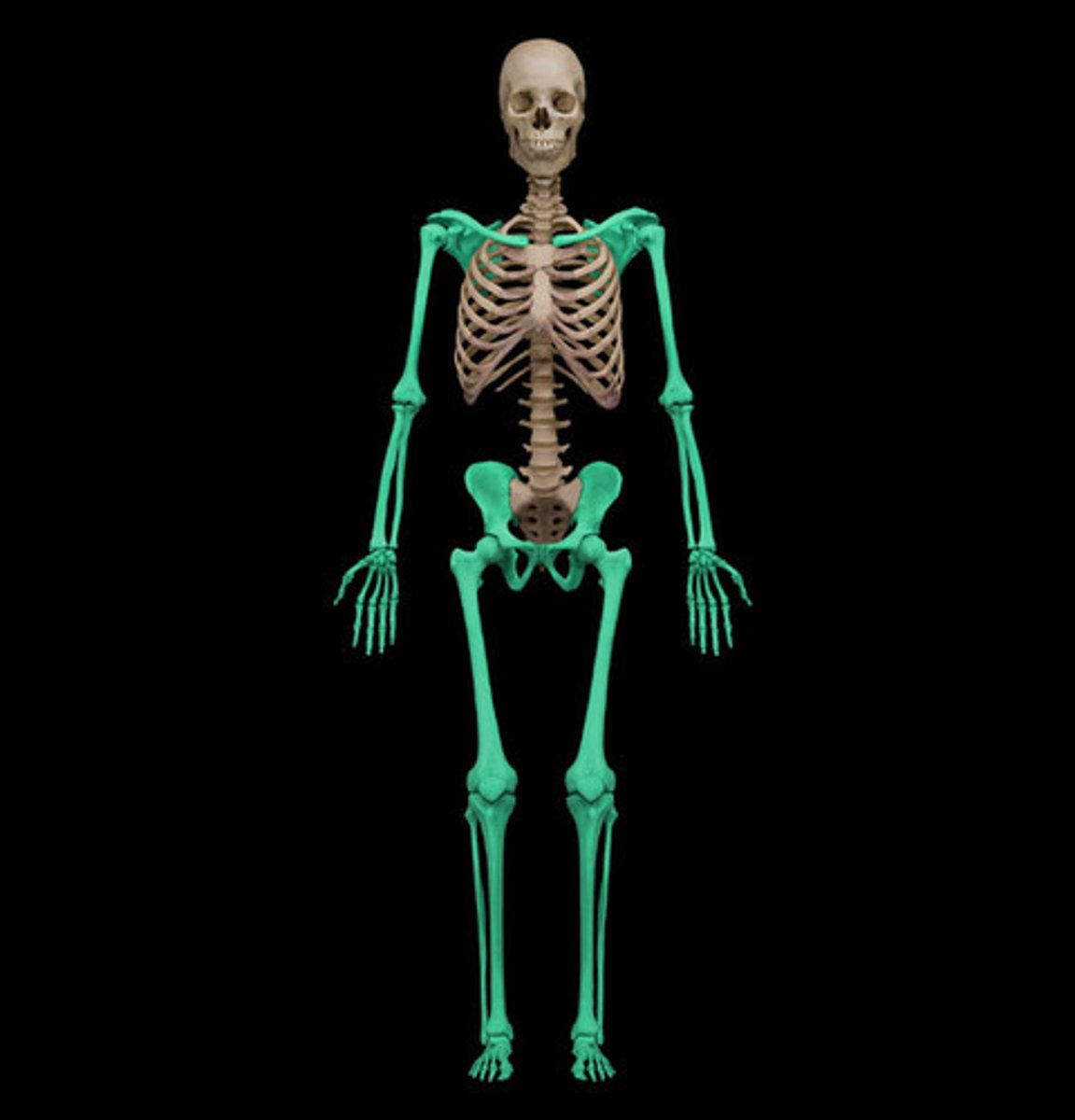
Division of skeletal system
axial and appendicular
Bone Classification
long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
long bones
longer than they are wide (ex. limbs)
short bones
Cube-shaped bones (ex. wrist and ankle)
Sesamoid bones within tendons (e.g., patella)
flat bones
thin and flattened, usually curved (ex. sternum, scapula, ribs, skull bones)
irregular bones
complicated shapes
(ex: vertebrae and hip bones)
3 levels of bone structure
1. Gross
2. Microscopic
3. Chemical
components of bones
1. Compact Bone
2. spongy bone
compact bone
-strongest, provides protection and support
-dense outer layer on every bone, appears smooth and solid
spongy bone
-lightweight and provides tissue support
-honeycomb stricture of small, needle-like pieces of bone called trabeculae
-open spaces between trabeculae are filled with red or yellow bone marrow
Gross Anatomy of short, irregular and flat bones
-thin plates of spongy bone (diploe) covered by compact bone
-periosteum: covers the outside of compact bone
-endosteum: covers the inside of compact bone
-bone marrow is scattered throughout spongy bone; no defined marrow cavity
-articular cartilage: hyaline cartilage covers movable joint surfaces
composition of long bones
1. shaft or diaphysis
2. bone ens or epiphyses
3. membranes (periosteum, endosteum)
Gross anatomy of a long bone
diaphysis, epiphysis, epiphyseal line
Diaphysis
compact bone surrounding a central cavity filled with yellow bone marrow
Epiphyses
compact bone (external) and spongy bone (internal) covered by articular cartilage
epiphyseal line
demarcation between diaphysis and epiphysis, is a remnant of childhood epiphyseal plate where bone growth occurs
Periosteum
-white, double-layered membrane that covers external surfaces except joints
-anchor for tendons and ligaments
-contains nerve and blood vessels that exit through nutrient foramens
1. fibrous layer
2. osteogenic layer
fibrous layer of periosteum
outer layer consisting of dense irregular connective tissue consisting of Sharpey's fibers that secure to bone matrix
osteogenic layer
inner layer of osteogenic stem cells
Endosteum
-thin membrane of connective tissue lining the bone cavity
-covers trabeculae of spongy bone
-lines canals that pass through compact bone
-contains osteogenic stem cells
-capillaries in endosteum supply nutrients
bone markings
projection, depression, opening
Bone Markings: Projections
outward bulge of bone
May be due to increased stress from muscle pull or is a modification for joints
Bone Markings: Depressions
groove can severe as passageways for vessels and nerves, or is a modification for joints
Bone Marking: Openings
hole or canal in bone that are passageways for blood vessels and nerves
Types of projections
where muscles and ligaments attach
-Crest
-Spine
-Tuberosity
-trochanter
-line
-tubercle
-epicondyle
-process
Crest
narrow ridge of bone, prominent
spine
sharp, slender, often pointed projection
Tuberosity
large round projection
Trochanter
large, blunt, irregularly shaped process (only found on femur)
Line
small, round process
Tubercle
small round process
Epicondyle
Raised area on or above a condyle
process
any bony prominence
surfaces that form joints
head, facet, condyle
head
bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
facet
smooth, nearly flat articular (joint) surface
Condyle
rounded articular projection with a corresponding depression (fossa)
openings and depressions
fissure, foramen, meatus, fossa, notch, sinus
fissure
Narrow, slitlike opening
Foramen
large round opening through bone
Meatus
canal-like passageway
Fossa
shallow, basin-like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
notch
indentation at the edge of a structure
sinus
Cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Cells of bone tissue
1. Osteogenic cells
2. Osteoblasts
3. Osteocytes
4. Bone-lining cells
5. Osteoclasts
osteogenic cells
-Also called osteoprogenitor cells
-Mitotically active stem cells in periosteum and endosteum
-When stimulated, they differentiate into osteoblasts or bone-lining cells
-Some remain as osteogenic stem cells
Osteoblasts
-Bone-forming cells that secrete unmineralized bone matrix called osteoid
-osteoid is made up of collagen and calcium-binding proteins
-collagen makes up 90% of bone protein
-osteoblasts are actively mitotic
Ostyocyte
-mature bone cell in lacunae that no longer divide
-maintain bone matrix and act as stress or strain sensors
-respond to mechanical stimuli such as increased force on bone or weightlessness
-involved in bone remodelling
bone lining cells
-flat cells on bone surfaces believed to also help maintain matrix (along with osteocytes)
Periosteal cells: line external bone surfaces
endosteal cells: lines internal surfaces
osteoclasts
-break down bone
-from the white blood lineage
-giant, multinucleate cells
-cells have ruffled borders that serve to increase surface area for enzyme degradation of bones
Compact bones
hard outer shell of the bone
consists of
1. osteon
2.canals and canaliculi
3.interstitial and circumferential lamellae
Osteon
-structural unit of compact bone
-elongated cylinder that runs parallel to long axis of bone
-acts as tiny weigh-bearing pillars
-consist of several rings of bone matrix called lamellae
-lamellae contain collagen fibers that run in a different directions in adjacent rings
Canals
-central canal run through the core of osteon
-contains blood vessels and nerve fibers
-perforating canals: canals that lined with endosteum that occurs at right angles to central canal
-connect blood vessels and nerves of periosteum, medullary cavity and central canal
cavities and connections
lacunae & canaliculi
Lacunae (compact bone)
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
Canaliculi (compact bone)
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
-communication
-movement of nutrients and waste
chemical composition of bone
-extracellular matrix that surrounds distantly separated cells
-ECM
~15% water
~30% collagen
~55% crystallized mineral salts
-hydroxyapatite
Formation of bony skeleton
-up to about week 8, fibrous membranes and hyaline cartilage of fetal skeleton are replaced with bone tissue
-cartilage remains in areas requiring flexibility
-articular cartilage
-at the epiphyseal plate
Clacification
hardening of bone and cartilage due to calcium deposition, occurs during normal bone growth in youth
Bone Development
Human bones grow until about age 25
Ossification
formation of the bony skeleton
4 situations where bones form
1. During embryological and fetal development
2. When bones grow before adulthood
3. When bones remodel
4. When fractures heal
types of ossification
intramembranous and endochondral
endochondrial ossification
-replaces hyaline cartilage with bone in the developing embryo and fetus
-form most of skeleton except clavicles
-occurs in epiphyseal plates of long bones as they grow in length
ossification process
1. mesenchymal stem cells specialize into osteoblasts
2. osteoblasts secrete osteoid against the diaphysis creating a bone collar encasing cartilage
3. cartilage cells hypertrophy in the centre of the cartilage shaft
4. central cartilage in diaphysis calcifies
5. chondrocytes die due to a lack of nutrients, the matrix deteriorates and cavities form
6. cavities are invaded by the blood vessels, nerves, red marrow, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts from the periosteal bud
7. osteoclasts erode the calcified cartilage matrix
8. remaining clarified cartilage fragment form the earliest spongy bone
9. bones thicken thanks to the cooperative action of the osteblasts and osteoclasts
10. as osteoblasts deposit bone on the outer surface osteoclasts widen the medullary cavity by breaking down the newly-formed spongy bone from within
11. the cartilage along the shaft calcifies and is replaced by bone
12. secondary ossification centres appear in epyshises and the epiphyses ossify
intramembranous ossification
process of bone development from fibrous membranes
intramembranous ossification process
-occurs in flat bones when a fibrous connective tissue membrane is replaced by bone
-bone formed by mesenchymal cells
-forms frontal, parietal , occipital, temporal and clavicle bones
4 steps of ossification
1. ossification centers are formed when mesenchymal cells cluster and become osteoblasts
2. osteoid is secreted, then calcified
3. woven bone is formed when osteoid is laid down around blood vessels, resulting in trabeculae that forms the periosteum
4. lamellar bone replaces woven bone, red marrow appears
post natal bone growth
-bones grow lengthwise via interstitial growth
-bones increase in width through appositional growth
increasing bone length
occurs along the epiphyseal plate
Five zones of epiphyseal plate
1. Zone of resting cartilage
2. Zone of proliferating cartilage
3. Zone of hypertrophic cartilage
4. Zone of calcified cartilage
5. Zone of ossification
resting zone of epiphyseal plate
Area of cartilage on epiphyseal side of epiphyseal plate that is relatively inactive
proliferation zone of epiphyseal plate
area of cartilage that is dividing rapidly
-new cells formed move upward pushing epiphysis away from the diaphysis causing lengthening
hypertrophic zone of epiphyseal plate
region with older chondrocytes closer to diaphysis
-cartilage lacunae hypertrophy and leave large interconnecting spaces
calcification zone of epiphyseal plate
area where the surrounding cartilage matrix calcifies causing the chondrocytes to die, matrix to deteriorate and blood vessels to invade
ossification zone of epiphyseal plate
new bone formation, cartilage is being broken down
-chondrocytes deterioration leaves calcified cartilage at epiphysis-diaphysis junction
-calcified cartilage is eroded by osteoblasts
-ultimately replaced with spongy bone
-medullary cavity enlarged as cartilage is eroded
epiphyseal plate
Growth plate, made of cartilage, gradually ossifies
epiphyseal plate closure
occurs when epiphysis and diaphysis fuse
appositional bone growth
formation of new bone matrix on surface of bone, increase in width of bone
Hormones that regulate bone growth
growth hormone, thyroid hormone, testosterone, estrogen
Growth Hormone (GH)
most important hormone in stimulating epiphyseal plate activity in infancy and childhood
Thyroid Hormone (TH)
modulates activity of growth hormone, ensuring proper proportions
testosterone and estrogen
promote adolescent growth spurts, end growth by inducing epiphyseal plate closure
bone deposition
the addition of minerals and collagen fibers to bone by osteoblasts
Osteiod seam
band of unmineralized bone matrix that marks area of new matrix
calcification front
abrupt transition zone between osteoid seam and older mineralized bone
bone resorption
the removal of minerals and collagen fibers from bone by osteoclasts
-break down bony matrix
-secrete lysosomes and enzymes and acid
control of bone remodeling
-controlled by negative feedback loop
1. maintaining homeostasis of calcium levels in the blood
2. response to mechanical stress